Optical Character Recognition

About Us
- Archana Iyer & Soham Chatterjee
- Undergraduate students at SRM University
- Deep Learning Intern at Saama
- B. Tech. Electrical and Electronics
- Next Tech Lab
- Saama Blog
- Soham's Blog

What is OCR?

OCR is the conversion of typed or handwritten text into machine-encoded text. It is one of the hardest problems to solve in computer vision and is still an active area of research with no one standard model.

Why OCR?


OCR has wide-ranging implications in many industries.
Anywhere there is a need to convert handwritten text into machine-encoded text, OCR can be used to reduce errors and increase speed.
Most Interesting Recent Use Cases
- Let us first see how Coca-Cola is applying OCR in their everyday products
- OCR is used widely by shipping agencies and post offices to read the addresses written by senders.


Where should I begin?
- After seeing such interesting use cases the first thing that pops into our heads is where shall we also start learning how to do the same-If not, we hope our use case might help you get started
- OpenCV- It is a image manipulation library
- MNIST/EMNIST
- IAM Dataset-Industry standard for OCR


OCR For Patient Form Text
- There is no good way predict handwritten text yet.
- CNN-RNN architectures have far lower levels of accuracy
- In the medical/Pharma-written text is far greater prevalent
- Doctor written prescriptions are the next level to explore
- We have tried to explore fixed form to understand handwritten text

Process for Solving Our Problem


Choosing a Deep Learning Model
- CNN Based Computer Vision Works Best

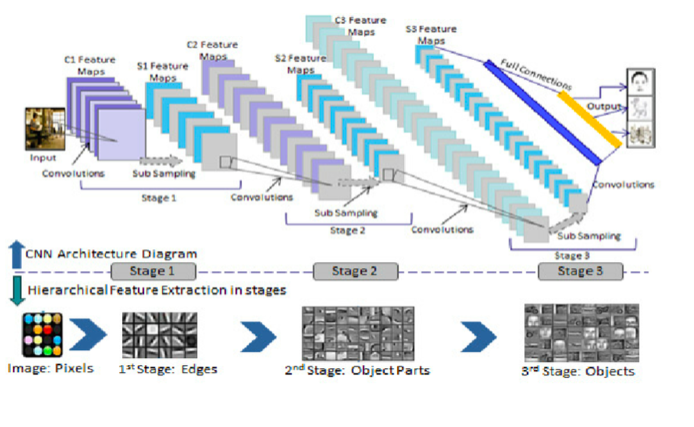
CNN Recap

Approach 1: Simplify the Problem
- Detect Individual Letters
- Use a windowing technique to identify all the letters

Process
- Get Data - MNIST
- Clean and Pre-process - Done!
- Model - Done!
- Test - Demo
- Improve?

2nd Approach: Brute Force
- Train on all words of the English Language
- Assume a max word length of 10
- Total Labels - 10^26

Process
- Model - CNN
- Clean and Pre-process
- Get Data

3rd Approach – Read Papers

Instead of
“MOVE”
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0


Learning Attributes Instead of Words – Unigram Approach
Consider the case of a training set of size 1,000. The word “SLEEP” may appear only twice, but attributes such as “does the word contain the unigram ‘S’ in the first half of the word could occur multiple times – which is great for CNN's.
Similar words may confuse the network - Consider the words “KIDS” and “BIDS”. A “KIDS” word image is a negative sample for the “BIDS” category, although a large part of their appearance is shared. This similarity between some categories makes a category based classifier harder to learn, whereas an attributes based classifier uses this to its advantage.

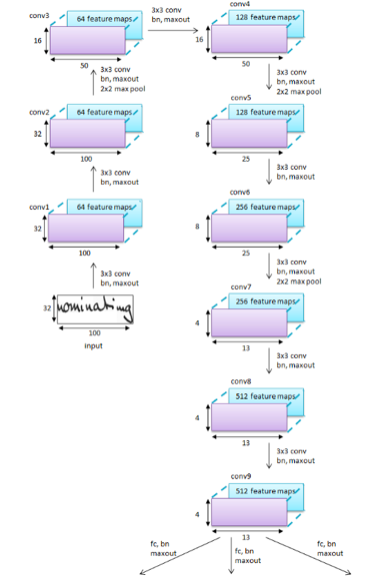
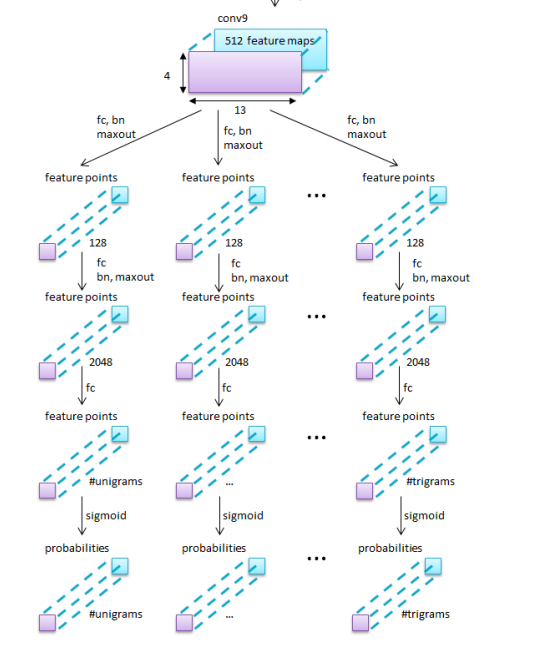

STEP 1: Getting and Cleaning Data
- IAM Dataset
-
657 writers contributed samples of their handwriting
1'539 pages of scanned text
5'685 isolated and labeled sentences
13'353 isolated and labeled text lines
115'320 isolated and labeled words



Step 2 -Training and Preprocessing
- Normalization – Convert to grayscale – Divide each pixel by 255.
- Label Encoding – One hot vector.
- Image augmentation


Step 3-Training
- Monitor Validation Loss
- Reduce Learning Rate
- A word on accuracy


Step 4-Testing and Improving
- What if the results are not that good?
- Monitor loss function
- Why is accuracy so high
- Should we consider accuracy or some other score?
- Does not generalize well even though the training and validation accuracy is good.
- Overfitting
- After training and testing accuracy is improved, how do we generalize to other areas?
- Pre-processing of form data
- What to do with the line
- How to filter blue values
- Pre-processing issue, still not working/generalizing well outside of IAM database

DEMO

Contact us

- Feedback- A link to give us a feedback-https://tinyurl.com/dnamethyltalk
- We would love to hear from you and your responses will be Anonymous!
- Contact us:
- Archana Iyer:
- varchanaiyer139@gmail.com
- Soham Chatterjee:
- 96soham96@gmail.com
- csoham.wordpress.com
