
HyperText Markup Language is a simple, elegant way to structure content.
What is HTML?
In 1980, physicist Tim Berners-Lee, a contractor at CERN, proposed and prototyped ENQUIRE, a system for CERN researchers to use and share documents.
In 1989, Berners-Lee wrote a memo proposing an Internet-based hypertext system.
Berners-Lee specified HTML and wrote the browser and server software in late 1990.
The first publicly available description of HTML was a document called "HTML Tags", first mentioned on the Internet by Tim Berners-Lee in late 1991.
It describes 18 elements comprising the initial, relatively simple design of HTML.
Except for the hyperlink tag, these were strongly influenced by SGMLguid, an in-house Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML)-based documentation format at CERN.
HTML Structure
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>Elements
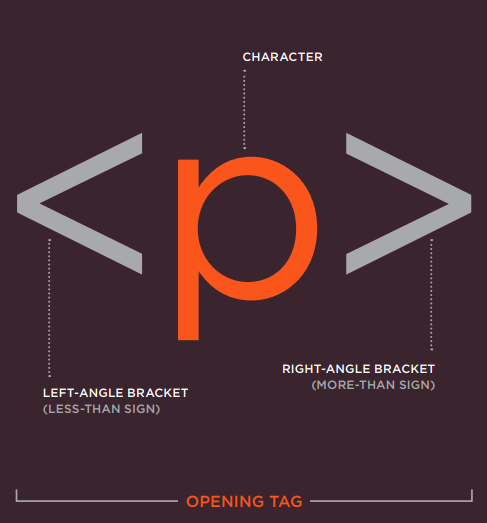
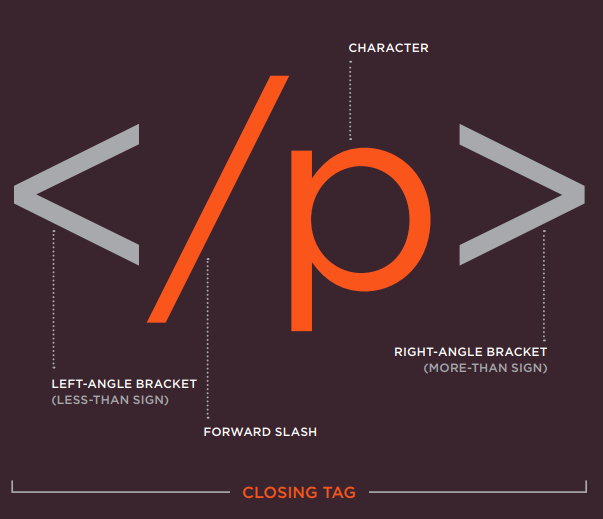
- The HTML code is made up of characters that live inside angled brackets — these are called HTML elements.
- Elements are usually made up of two tags:
- an opening tag
- closing tag. (The closing tag has an extra forward slash in it.)
- Each HTML element tells the browser something about the information that sits between its opening and closing tags.
<b> Hellow </b>Tags
Attributes
Attributes provide additional information about the contents of an element. They appear on the opening tag of the element and are made up of two parts: a name and a value, separated by an equals sign.
<a href='https://www.google.com'> Google </a>Attribute Name
Attribute Value
Semantic HTML
In programming, Semantics refers to the meaning of a piece of code — for example "what effect does running that line of JavaScript have?", or "what purpose or role does that HTML element have" (rather than "what does it look like?".)
- Semantic HTML or semantic markup is HTML that introduces meaning to the web page rather than just presentation.
- For example, a <p> tag indicates that the enclosed text is a paragraph.
- This is both semantic and presentational, because people know what paragraphs are and browsers know how to display them.
Why You Should Care About Semantics
- The benefit of writing semantic HTML stems from what should be the driving goal of any web page— the desire to communicate.
- Specifically, semantic tags make it clear to the browser what the meaning of a page and its content is.
- That clarity is also communicated with search engines, ensuring that the right pages are delivered for the right queries.
- Text that is enclosed in the <code> tag is immediately recognized by the browser as some type of coding language.
Use Semantic Tags Correctly
Some of the most commonly misused semantic tags include:
- blockquote - Some people use the <blockquote> tag for indenting text that is not a quotation.
- p - Some web editors use <p> </p> (a non-breaking space contained in a paragraoph) to add extra space between page elements, rather than defining actual paragraphs for the text of that page.
- ul - Like blockquote, enclosing text inside a <ul> tag indents that text in most browsers.
- h1–h6 - The heading tags can be used to make fonts bigger and bolder, but if the text is not a heading, it should not be inside a heading tag.
What's the difference between <b> and <strong>, <i> and <em>?
- "Bold" is a style - when you say "bold a word", people basically know that it means to add more, let's say "ink", around the letters until they stand out more amongst the rest of the letters.
- <strong> however is an indication of how something should be understood.
Some of the benefits from writing semantic markup are as follows:
- Search engines will consider its contents as important keywords to influence the page's search rankings (see SEO)
- Screen readers can use it as a signpost to help visually impaired users navigate a page
- Finding blocks of meaningful code is significantly easier than searching though endless divs with or without semantic or namespaced classes
- Suggests to the developer the type of data that will be populated
- Semantic naming mirrors proper custom element/component naming
Ask Yourself
- "What element(s) best describe/represent the data that I'm going to populate?"
- For example, is it a list of data?; ordered, unordered?;
- is it an article with sections and an aside of related information?;
- does it list out definitions?;
- is it a figure or image that needs a caption?;
- should it have a header and a footer in addition to the global site-wide header and footer?; etc.
When approaching which markup to use, ask yourself,
<Body>
You met the element in the first example we created. Everything inside this element is shown inside the main browser window
<body>
<!-- All the content that is viewable in browser goes here -->
</body><Head>
- Before the <body> element you will often see a <head> element.
- This contains information about the page (rather than information that is shown within the main part of the browser window).
- You will usually find a <title> element inside the <head> element.
<head>
<title> Hellow World </title>
...
</head>The HTML <head> element provides general information (metadata) about the document, including its title and links to its scripts and style sheets.
Elements that can be used inside a <head> element:
- <title>
- <base>
- <link>
- <style>
- <meta>
- <script>
- <noscript>
- <template>
The HTML Title element (<title>) defines the document's title that is shown in a browser's title bar or a page's tab. It only contains text and tags within the element are ignored.
<title>Awesome page title</title>The HTML <base> element specifies the base URL to use for all relative URLs contained within a document.
There can be only one <base> element in a document.
- href
- The base URL to be used throughout the document for relative URL addresses.
- If this attribute is specified, this element must come before any other elements with attributes whose values are URLs.
- Absolute and relative URLs are allowed.
- The HTML External Resource Link element (<link>) specifies relationships between the current document and an external resource.
- This element is most commonly used to link to stylesheets, but is also used to establish site icons (both "favicon" style icons and mobile home screen/app icons) among other things.
<link href="main.css" rel="stylesheet">Text
<link href="default.css" rel="stylesheet" title="Default Style">
<link href="fancy.css" rel="alternate stylesheet" title="Fancy">
<link href="basic.css" rel="alternate stylesheet" title="Basic">The HTML <style> element contains style information for a document, or part of a document. It contains CSS, which is applied to the contents of the document containing the <style> element.
The HTML <meta> element represents metadata that cannot be represented by other HTML meta-related elements, like <base>, <link>, <script>, <style> or <title>.
-
charset
- This attribute declares the page's character encoding. It must contain a standard IANA MIME name for character encodings. Although the standard doesn't request a specific encoding, it suggests:
- Authors are encouraged to use UTF-8.
Text

Headings
<h1>This is a Main Heading</h1>
<h2>This is a Level 2 Heading</h2>
<h3>This is a Level 3 Heading</h3>
<h4>This is a Level 4 Heading</h4>
<h5>This is a Level 5 Heading</h5>
<h6>This is a Level 6 Heading</h6>
Code
Result
HTML has six "levels" of headings:
Paragraphs
<p>A paragraph consists of one or more sentences
that form a self-contained unit of discourse. The
start of a paragraph is indicated by a new
line.</p>
<p>Text is easier to understand when it is split up
into units of text. For example, a book may have
chapters. Chapters can have subheadings. Under
each heading there will be one or more
paragraphs.</p>
To create a paragraph, surround the words that make up the paragraph with an opening tag and closing tag.
By default, a browser will show each paragraph on a new line with some space between it and any subsequent paragraphs.
Bold & Italic
By enclosing words in the tags we can make characters appear bold.
The element also represents a section of text that would be presented in a visually different way (for example key words in a paragraph) although the use of the element does not imply any additional meaning.
<b>By enclosing words in the tags we can make characters appear italic.
The element also represents a section of text that would be said in a different way from surrounding content — such as technical terms, names of ships, foreign words, thoughts, or other terms that would usually be italicized.
<i>Superscript & Subscript
<sup><sub>The element is used to contain characters that should be superscript such as the suffixes of dates or mathematical concepts like raising a number to a power such as 2^2 .
The element is used to contain characters that should be subscript. It is commonly used with foot notes or chemical formulas
<p>On the 4<sup>th</sup> of September you will learn
about E=MC<sup>2</sup>.</p>
<p>The amount of CO<sub>2</sub> in the atmosphere
grew by 2ppm in 2009<sub>1</sub>.</p>
Other Tags
<blockquote><br /><q><hr /><strong><abbr><em><cite><dfn><address><ins><del><s>Lists

Types of Lists
- Ordered lists are lists where each item in the list is numbered. For example, the list might be a set of steps for a recipe that must be performed in order, or a legal contract where each point needs to be identified by a section number.
- Unordered lists are lists that begin with a bullet point (rather than characters that indicate order).
- Definition lists are made up of a set of terms along with the definitions for each of those terms.
Ordered List
<ol>The ordered list is created with the <ol> element.
<li>Each item in the list is placed between an opening tag and a closing tag. (The li stands for list item.)
<ol>
<li> Item 1 </li>
<li> Item 2 </li>
<li> Item 3 </li>
<li> Item 4 </li>
</ol>
Unordered List
<ul>The unordered list is created with the <ul> element.
<li>Each item in the list is placed between an opening tag and a closing tag. (The li stands for list item.)
<ul>
<li> Item 1 </li>
<li> Item 2 </li>
<li> Item 3 </li>
<li> Item 4 </li>
</ul>

Definition List
<dl>The definition list is created with the <dl> element and usually consists of a series of terms and their definitions.
<dt>This is used to contain the term being defined (the definition term).
<dl>
<dt>Hellow</dt>
<dd>This message just says
hello to the reader.</dd>
<dt>Scale</dt>
<dd>Something used to measure</dd>
<dd>A technique by which the scales
are removed
from the skin of a fish</dd>
<dt>Scamorze</dt>
<dt>Scamorzo</dt>
<dd>An Italian cheese usually made from whole
cow's milk (although it was traditionally made
from buffalo milk)</dd>
</dl><dd>This is used to contain the definition.

Links

What are Links?
Links are the defining feature of the web because they allow you to move from one web page to another enabling the very idea of browsing or surfing.
You will commonly come across the following types of links:
- Links from one website to another.
- Links from one page to another on the same website.
- Links from one part of a web page to another part of the same page.
- Links that open in a new browser window.
- Links that start up your email program and address a new email to someone
Writing Links
- Links are created using the element.
- Users can click on anything between the opening tag and the closing tag.
- You specify which page you want to link to using the href attribute.
<a href="https://pesto.tech">PESTO</a>THIS IS THE PAGE THE
LINK TAKES YOU TO
THIS IS THE TEXT THE
USER CLICKS ON
Relative URL's
- Relative URLs can be used when linking to pages within your own website.
- They provide a shorthand way of telling the browser where to find your files.
<a href="../../htmlcode.html">PESTO</a>This means go two directories
up and look for index.html
URL's
<a href="#applications">PESTO</a>This means scroll the page to someid in the page.
Email Links
<a href="mailto:ab@gmail.com">Mail</a>Opens default mail app, and creates
a new mail with the receiver's email
as the one mentioned here
javscript:void(0)
<a href="javascript:void(0)">Mail</a>This tells the browser to go NOWHERE, but instead execute the valid JavaScript:void(0); function first in the HREF tag
Images

Adding Images
<img src = "images/koala.jpg" alt = "Koala Image" title = "An koala image" />
Aligning Images
<p><img src="https://upload...climbing_tree.jpg" alt="Bird" width="100"
height="100" align="right" />There are around
10,000 living species of birds that inhabit
different ecosystems from the Arctic to the
Antarctic. Many species undertake long distance
annual migrations, and many more perform shorter
irregular journeys.</p>
// Horizontal align = "left/right"
// Vertical align = "top/middle/bottom"
HTML5 FIGURE AND FIGURE CAPTION
<figure>Images often come with captions. HTML5 has introduced a new <figure> element to contain images and their caption so that the two are associated.
<figcaption>The <figcaption> element has been added to HTML5 in order to allow web page authors to add a caption to an image.
<figure>
<img src="img_pulpit.jpg" alt="The Pulpit Rock" width="304" height="228">
<figcaption>Fig.1 - A view of the pulpit rock in Norway.</figcaption>
</figure>Tables
Main Elements
- <table>
- <caption>
- <colgroup>
- <col>
- <tr>
- <th>
- <tr>
- <td>
- <thead>
- <tbody>
- <tfoot>
Important Attributes
| colspan | th, td | extends a cell to be as wide as 2 or more cells |
| rowspan | th, td | extends a cell to be as tall as 2 or more cells |
| span | col | Makes the column apply to more to 2 or more columns |
| headers | td | space-separated string corresponding to ID’s of the <th> elements relevant to the data |
| scope | th | axis of the header |
- align
- valign
- char
- charoff
- bgcolor
- abbr
- axis
- border
- cellpadding
- cellspacing
- frame
- rules
- summary
- width
Deprecated attributes
Basic Table Structure
<table>
<tr>
<th>Firstname</th>
<th>Lastname</th>
<th>Age</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Jill</td>
<td>Smith</td>
<td>50</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Eve</td>
<td>Jackson</td>
<td>94</td>
</tr>
</table>
Long Tables
<table>
<thead>
...
</thead>
<tbody>
...
</tbody>
<tfoot>
...
</tfoot>
</table>Forms
Forms
HTML forms give you a set of elements to collect data from your users. In this chapter you will learn:
- How to create a form on your website
- The different tools for collecting data
- New HTML5 form controls
<input>
The <input> element is used to create interactive controls for web-based forms in order to accept data from the user.
Important attributes
- disabled
- form - Associates the control with a form element
- name - Name of the form control. Submitted with the form as part of a name/value pair.
- type
- value
<form>
The <form> element represents a document section containing interactive controls for submitting information.
Important attributes
name
action
enctype
method
novalidate
Form Controls Adding Text
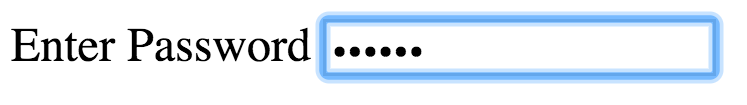
Text Input
Password
Text Area


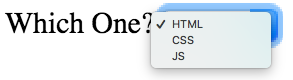
Form Controls Making Choices
Radio Button
Checkbox
Dropdown
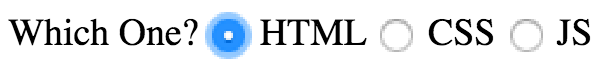

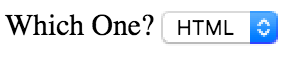
Form Controls Submitting Forms
Submit Button
Uploading Files


Other Form Tags
<legend><label><fieldset>
Other Form Tags
Other input types
- color (value="#e66465")
- date
- datetime-local
- image
- hidden
- range
- tel
- time
- url
Some other tags
- meter
- progress
- output
<meter id="fuel"
min="0" max="100"
low="33" high="66" optimum="80"
value="50">
at 50/100
</meter><form oninput="result.value=a.valueAsNumber + b.valueAsNumber">
<input type="range" id="b" name="b" value="50" /> +
<input type="number" id="a" name="a" value="10" /> =
<output name="result" for="a b">60</output>
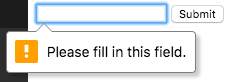
</form>HTML5 Form Validation
<form>
<input type="text" required />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>1. Required
HTML5 Form Validation
<form>
<input type="email" required />
<input type="url" required />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>2. Email Input
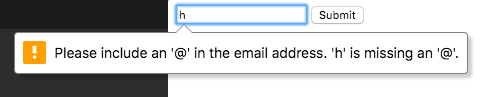
3. URL Input
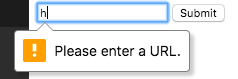
HTML5 Date
<form>
<input type="date" required />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
How Forms Work?
- A user fills in a form and then presses a button to submit the information to the server.
- The name of each form control is sent to the server along with the value the user enters or selects
- The server processes the information using a programming language such as Javascript, Ruby , Python etc. It may also store the information in a database.
- The server creates a new page to send back to the browser based on the information received.
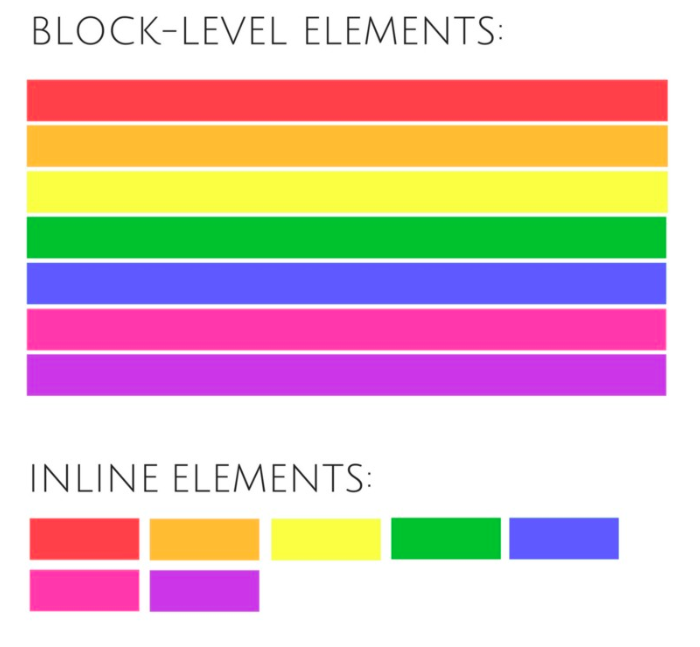
Block Level vs Inline elements
1. <div>
- The <div> tag defines a division or a section in an HTML document.
- The <div> element is often used as a container for other HTML elements to style them with CSS or to perform certain tasks with JavaScript.

2. <datalist>
<form method="get">
<input list="browsers" name="browser">
<datalist id="browsers">
<option value="Internet Explorer">
<option value="Firefox">
<option value="Chrome">
<option value="Opera">
<option value="Safari">
</datalist>
<input type="submit">
</form>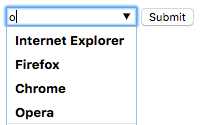
3. <video>
<video width="320" height="240" controls>
<source src="movie.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="movie.ogg" type="video/ogg">
Your browser does not support the video tag.
</video>The <source> element allows you to specify alternative video files which the browser may choose from. The browser will use the first recognized format.
4. <audio>
<audio controls>
<source src="horse.ogg" type="audio/ogg">
<source src="horse.mp3" type="audio/mpeg">
Your browser does not support the audio element.
</audio>5. <map>
<img src="planets.gif" width="145" height="126" alt="Planets" usemap="#planetmap">
<map name="planetmap">
<area shape="rect" coords="0,0,82,126" alt="Sun" href="sun.htm">
<area shape="circle" coords="90,58,3" alt="Mercury" href="mercur.htm">
<area shape="circle" coords="124,58,8" alt="Venus" href="venus.htm">
</map>6. <progress>
Downloading progress:
<progress value="22" max="100">
</progress>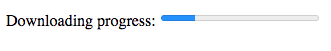
7. <svg>
<svg width="100" height="100">
<circle cx="50" cy="50" r="40" stroke="green" stroke-width="4" fill="yellow" />
</svg>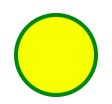
8. <noscript>
<noscript>Your browser does not support JavaScript!</noscript>
9. <base>
<head>
<base href="https://pesto.tech/images/" target="_blank">
</head>
<body>
<img src="logo.gif" width="24" height="39" alt="Stickman">
<a href="https://pesto.tech">W3Schools</a>
</body>10. <bdo>
<bdo dir="rtl">
This text will go right-to-left.
</bdo>bdo stands for Bi-Directional Override.
The <bdo> tag is used to override the current text direction.
10. <canvas>
The HTML <canvas> element is used to draw graphics on a web page.
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="200" height="100"></canvas>var c = document.getElementById("myCanvas");
var ctx = c.getContext("2d");
ctx.moveTo(0, 0);
ctx.lineTo(200, 100);
ctx.stroke();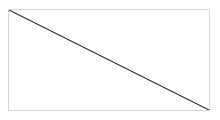
11. <input type="range">
<input type="range">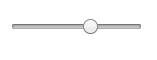
<input type="range" list="tickmarks">
<datalist id="tickmarks">
<option value="0">
<option value="10">
<option value="20">
<option value="30">
<option value="40">
<option value="50">
<option value="60">
<option value="70">
<option value="80">
<option value="90">
<option value="100">
</datalist>
12. <nav>
<nav>
<a href="/html/">HTML</a> |
<a href="/css/">CSS</a> |
<a href="/js/">JavaScript</a> |
<a href="/jquery/">jQuery</a>
</nav>- The <nav> tag defines a set of navigation links.
- Notice that NOT all links of a document should be inside a <nav> element. The <nav> element is intended only for major block of navigation links.
- Browsers, such as screen readers for disabled users, can use this element to determine whether to omit the initial rendering of this content.
1. data-* Attributes
<ul>
<li data-animal-type="bird">Owl</li>
<li data-test="fish">Salmon</li>
<li data-check="spider">Tarantula</li>
</ul>2. draggable
The draggable attribute specifies whether an element is draggable or not.
Tip: Links and images are draggable by default.
Tip: The draggable attribute is often used in drag and drop operations.
3. contenteditable, spellcheck
<p contenteditable="true" spellcheck="true">
This is a praggagraph. It is editable.
Try to change the text.
</p>
4. translate
<p translate="no">Don't translate this!</p>
<p>This can be translated to any language.</p>Quirks Mode
<!DOCTYPE html><!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">In computing, quirks mode refers to a technique used by some web browsers for the sake of maintaining backward compatibility with web pages designed for Internet Explorer 5 and earlier, instead of strictly complying with W3C and IETF standards in standards mode.
Share via Whatsapp
<a href="https://web.whatsapp.com/send?text=The text to share!">
WhatsApp
</a><a href="whatsapp://send?text=The text to share!">
WhatsApp
</a>Desktop
Mobile