Place Cells
Understanding spatial reasoning
What is a place cell?
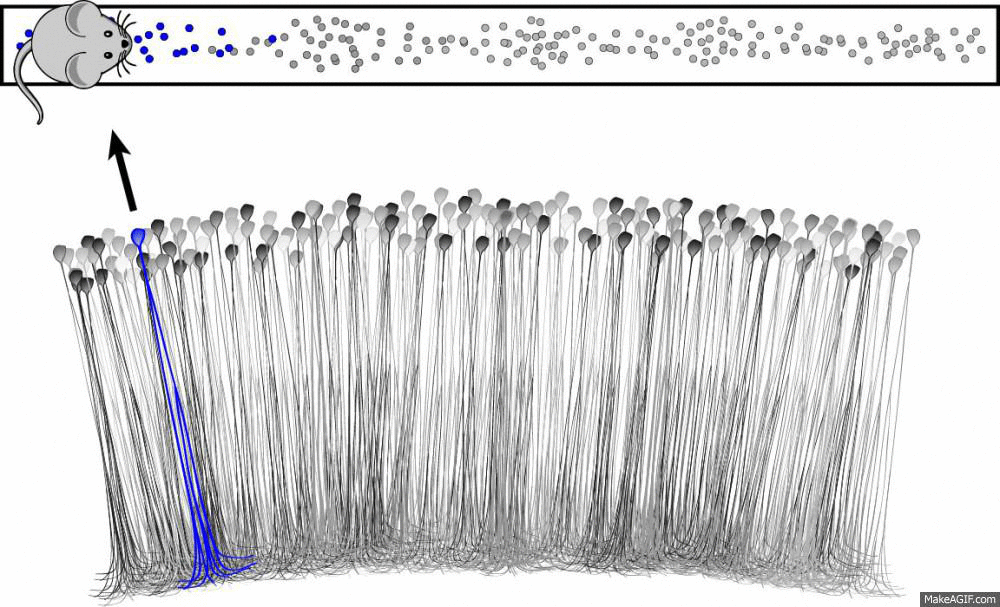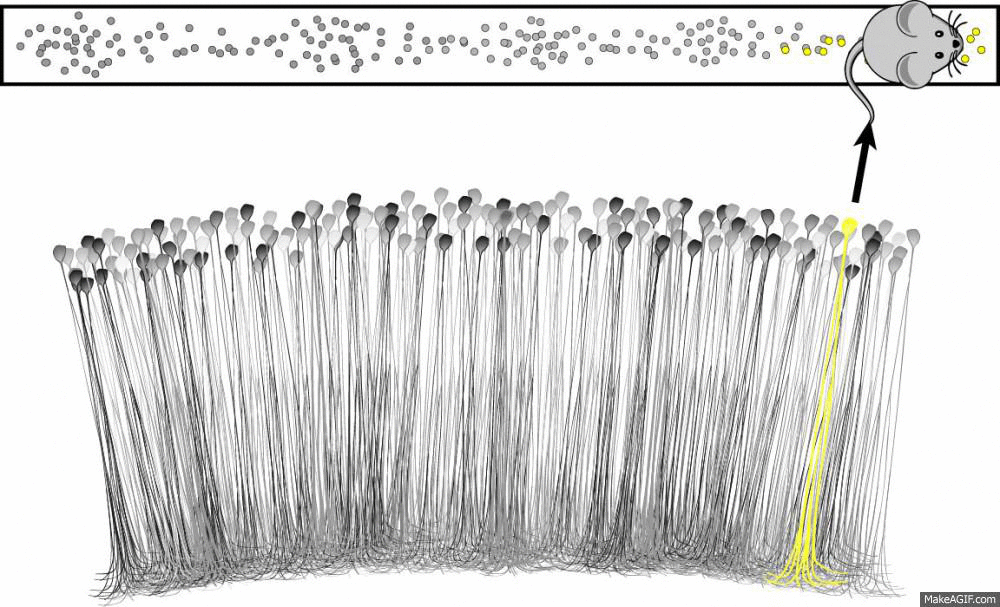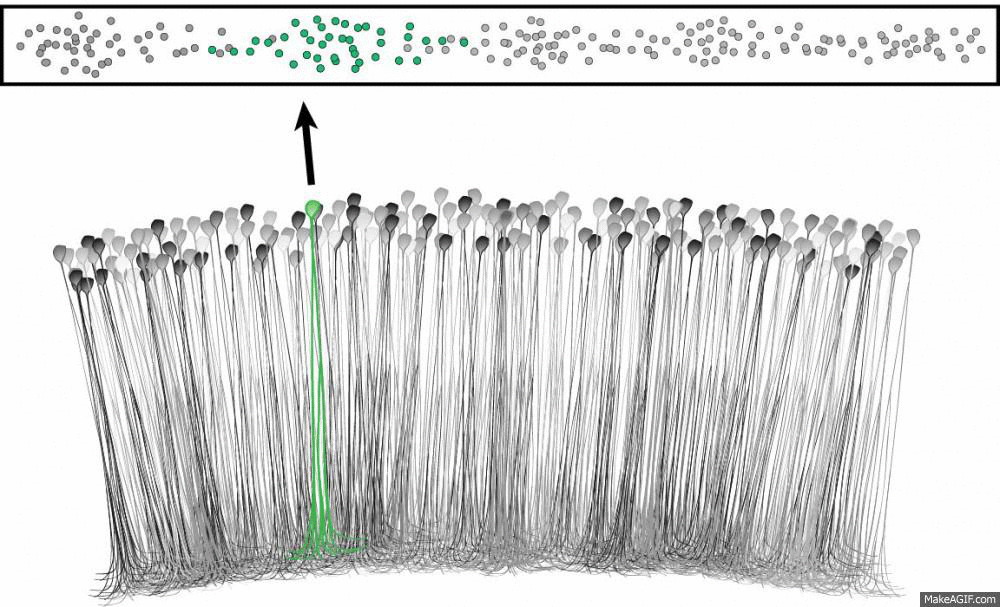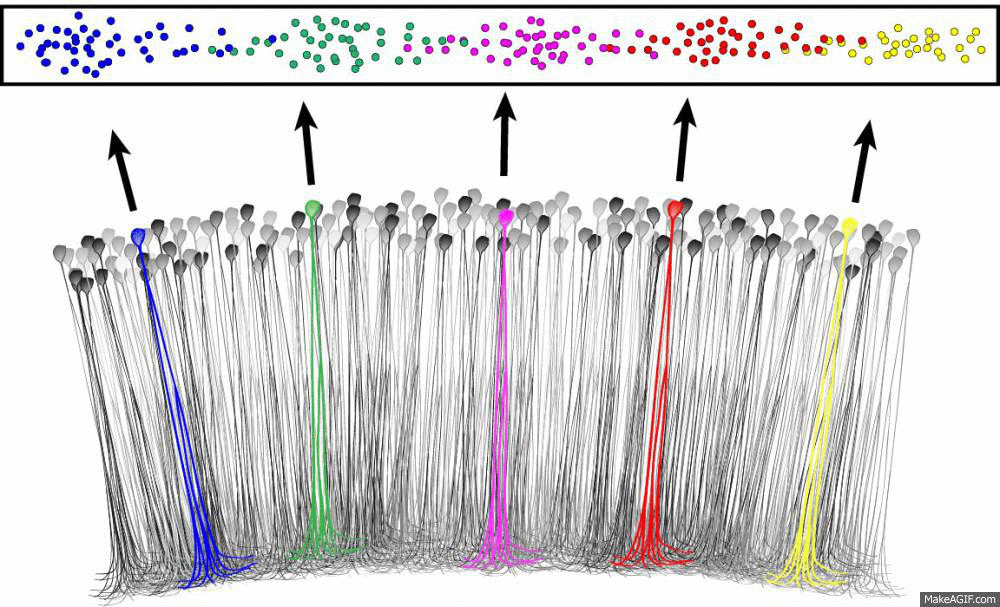
Source: Ryan Jones
- Pyramidal neuron typically located in CA1 or CA3

- Attenuate firing with changes in spatial location
- Circuitry to be discussed
- Role in spatial learning, decision making and memory encoding

Sharp Wave Ripples (SWRs)
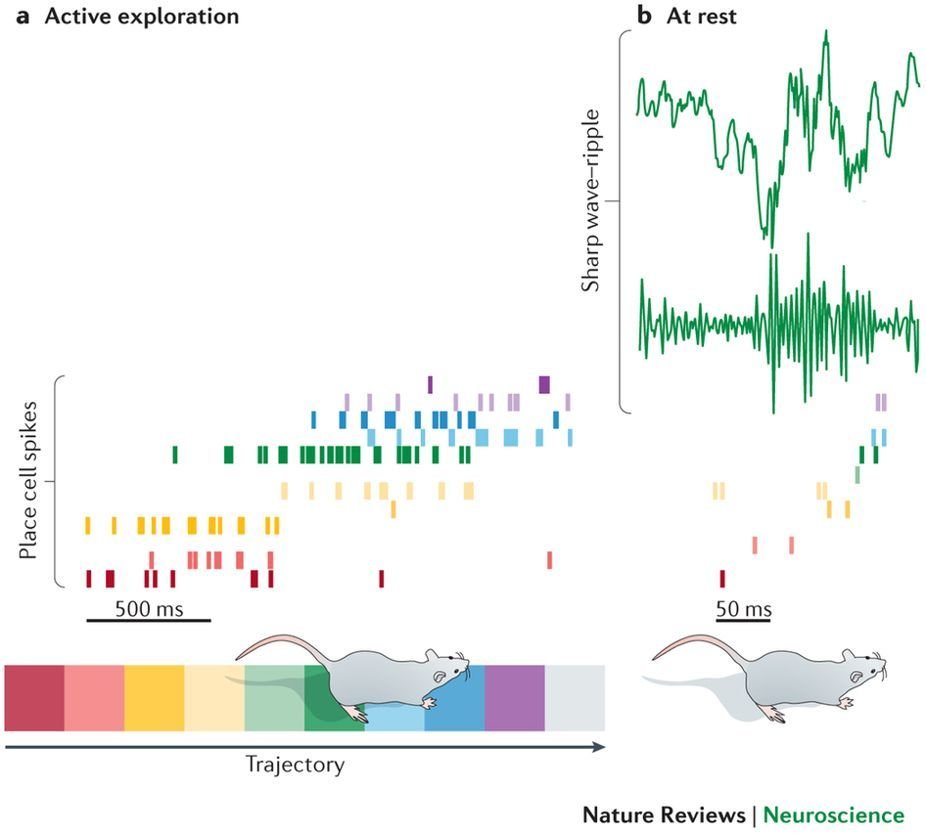
raw LFP
ripple band filtered
SWR
CA1 propagates to CA3, to produce SWRs

Adapted from Laura Colgin
def sosfiltfilt(timeseries, *, fl=None, fh=None, fs=None, inplace=False, bandstop=False,
gpass=None, gstop=None, ftype=None, buffer_len=None, overlap_len=None,
parallel=True,
**kwargs):
# make sure that fs is specified, unless AnalogSignalArray is passed in
if isinstance(timeseries, (np.ndarray, list)):
if fs is None:
raise ValueError("Sampling frequency, fs, must be specified!")
elif isinstance(timeseries, core.RegularlySampledAnalogSignalArray):
if fs is None:
fs = timeseries.fs
else:
raise TypeError('Unsupported input type!')
try:
assert fh < fs, "fh must be less than sampling rate!"
except TypeError:
pass
try:
assert fl < fh, "fl must be less than fh!"
except TypeError:
pass
if inplace:
out = timeseries
else:
out = deepcopy(timeseries)
if overlap_len is None:
overlap_len = int(fs*2)
if buffer_len is None:
buffer_len = 4194304
if gpass is None:
gpass = 0.1 # max loss in passband, dB
if gstop is None:
gstop = 30 # min attenuation in stopband (dB)
if ftype is None:
ftype = 'cheby2'
try:
if np.isinf(fh):
fh = None
except TypeError:
pass
if fl == 0:
fl = None
# Handle cutoff frequencies
fso2 = fs/2.0
if (fl is None) and (fh is None):
raise ValueError('Nonsensical all-pass filter requested...')
elif fl is None: # lowpass
wp = fh/fso2
ws = 1.4*fh/fso2
elif fh is None: # highpass
wp = fl/fso2
ws = 0.8*fl/fso2
else: # bandpass
wp = [fl/fso2, fh/fso2]
ws = [0.8*fl/fso2,1.4*fh/fso2]
if bandstop: # notch / bandstop filter
wp, ws = ws, wp
sos = sig.iirdesign(wp, ws, gpass=gpass, gstop=gstop, ftype=ftype, output='sos', **kwargs)
# Prepare input and output data structures
# Output array lives in shared memory and will reduce overhead from pickling/de-pickling
# data if we're doing parallelized filtering
if isinstance(timeseries, (np.ndarray, list)):
temp_array = np.array(timeseries)
dims = temp_array.shape
if len(temp_array.shape) > 2:
raise NotImplementedError('Filtering for >2D ndarray or list is not implemented')
shared_array_base = Array(ctypes.c_double, temp_array.size, lock=False)
shared_array_out = np.ctypeslib.as_array(shared_array_base)
# Force input and output arrays to be 2D (N x T) where N is number of signals
# and T is number of time points
if len(temp_array.squeeze().shape) == 1:
shared_array_out = np.ctypeslib.as_array(shared_array_base).reshape((1, temp_array.size))
input_asarray = temp_array.reshape((1, temp_array.size))
else:
shared_array_out = np.ctypeslib.as_array(shared_array_base).reshape(dims)
input_asarray = temp_array
elif isinstance(timeseries, core.RegularlySampledAnalogSignalArray):
dims = timeseries._data.shape
shared_array_base = Array(ctypes.c_double, timeseries._data_rowsig.size, lock=False)
shared_array_out = np.ctypeslib.as_array(shared_array_base).reshape(dims)
input_asarray = timeseries._data
# Embedded function to avoid pickling data but need global to make this function
# module-visible (required by multiprocessing). I know, a bit of a hack
global filter_chunk
def filter_chunk(it):
"""The function that performs the chunked filtering"""
try:
start, stop, buffer_len, overlap_len, buff_st_idx = it
buff_nd_idx = int(min(stop, buff_st_idx + buffer_len))
chk_st_idx = int(max(start, buff_st_idx - overlap_len))
chk_nd_idx = int(min(stop, buff_nd_idx + overlap_len))
rel_st_idx = int(buff_st_idx - chk_st_idx)
rel_nd_idx = int(buff_nd_idx - chk_st_idx)
this_y_chk = sig.sosfiltfilt(sos, input_asarray[:, chk_st_idx:chk_nd_idx], axis=1)
shared_array_out[:,buff_st_idx:buff_nd_idx] = this_y_chk[:, rel_st_idx:rel_nd_idx]
except:
raise ValueError(("Some epochs were too short to filter. Try dropping those first,"
" filtering, and then inserting them back in"))
# Do the actual parallellized filtering
if (sys.platform.startswith('linux') or sys.platform.startswith('darwin')) and parallel:
pool = Pool(processes=cpu_count())
if isinstance(timeseries, (np.ndarray, list)):
# ignore epochs (information not contained in list or array) so filter directly
start, stop = 0, input_asarray.shape[1]
pool.map(filter_chunk, zip(repeat(start), repeat(stop), repeat(buffer_len),
repeat(overlap_len), range(start, stop, buffer_len)),
chunksize=1)
elif isinstance(timeseries, core.RegularlySampledAnalogSignalArray):
fei = np.insert(np.cumsum(timeseries.lengths), 0, 0) # filter epoch indices, fei
for ii in range(len(fei)-1): # filter within epochs
start, stop = fei[ii], fei[ii+1]
pool.map(filter_chunk, zip(repeat(start), repeat(stop), repeat(buffer_len),
repeat(overlap_len), range(start, stop, buffer_len)),
chunksize=1)
pool.close()
pool.join()
# No easy parallelized filtering for other OSes
else:
if isinstance(timeseries, (np.ndarray, list)):
# ignore epochs (information not contained in list or array) so filter directly
start, stop = 0, input_asarray.shape[1]
iterator = zip(repeat(start), repeat(stop), repeat(buffer_len),
repeat(overlap_len), range(start, stop, buffer_len))
for item in iterator:
filter_chunk(item)
elif isinstance(timeseries, core.RegularlySampledAnalogSignalArray):
fei = np.insert(np.cumsum(timeseries.lengths), 0, 0) # filter epoch indices, fei
for ii in range(len(fei)-1): # filter within epochs
start, stop = fei[ii], fei[ii+1]
iterator = zip(repeat(start), repeat(stop), repeat(buffer_len),
repeat(overlap_len), range(start, stop, buffer_len))
for item in iterator:
filter_chunk(item)
if isinstance(timeseries, np.ndarray):
out[:] = np.reshape(shared_array_out, dims)
elif isinstance(timeseries, list):
out[:] = np.reshape(shared_array_out, dims).tolist()
elif isinstance(timeseries, core.RegularlySampledAnalogSignalArray):
out._data[:] = shared_array_out
return outNelpy Filtering