Spatial Navigation in the Hippocampal Formation
Understanding spatial reasoning
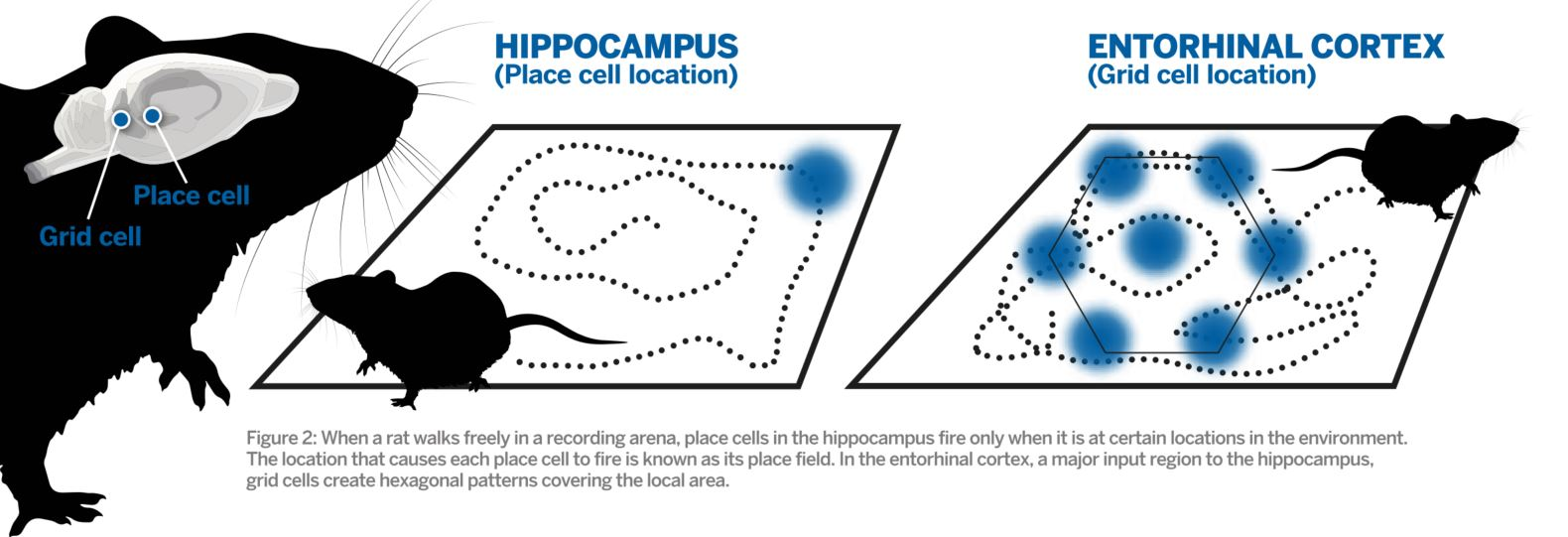
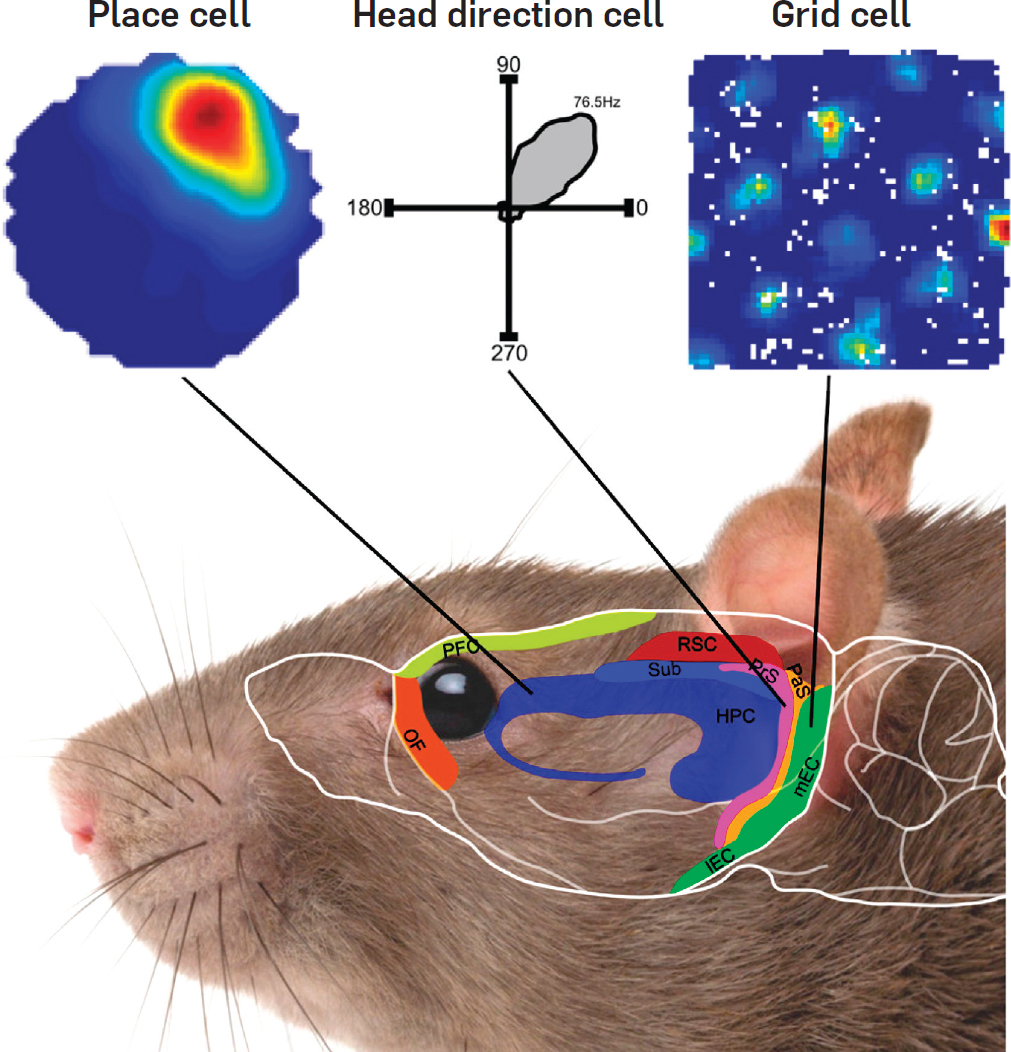
The Hippocampal Structures

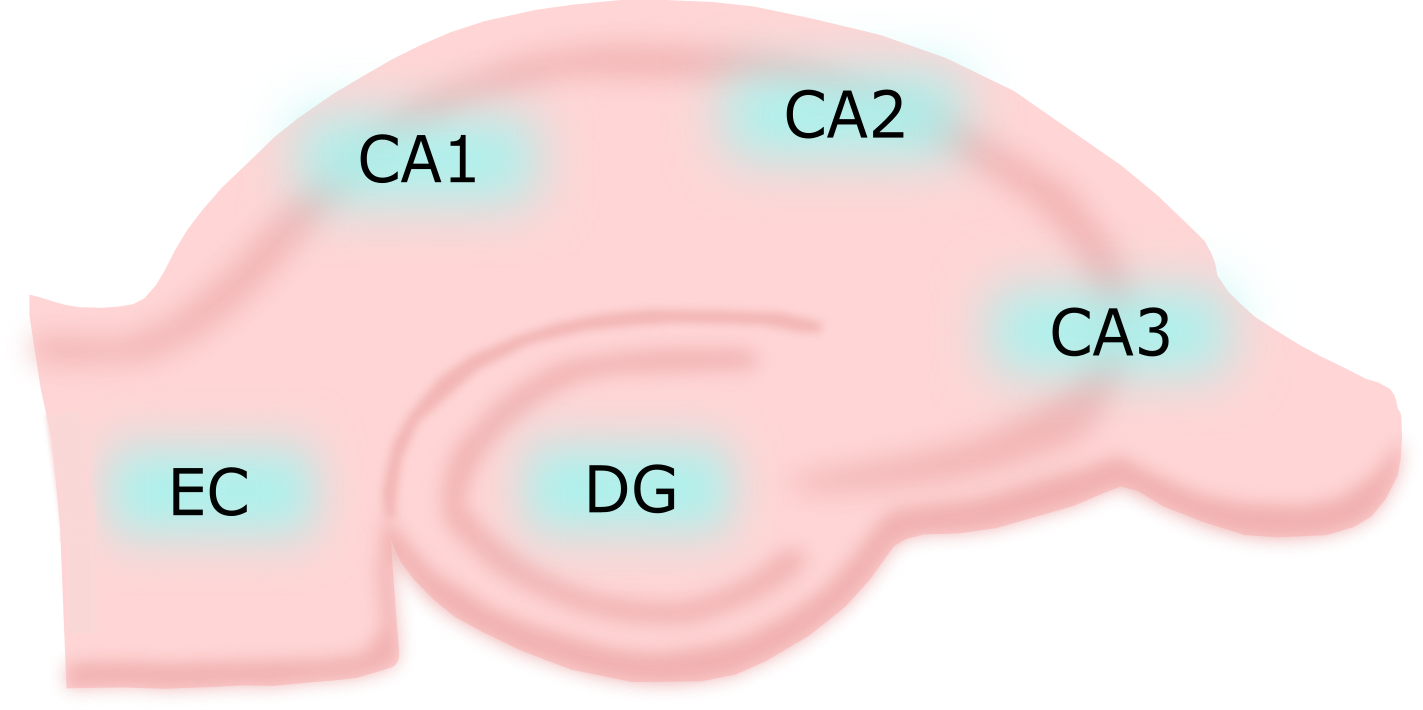
The Hippocampal Neurons

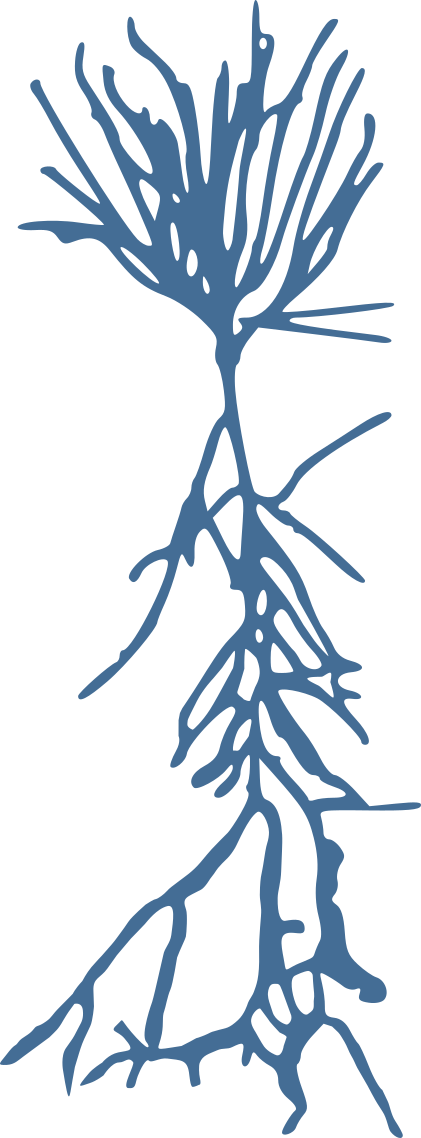
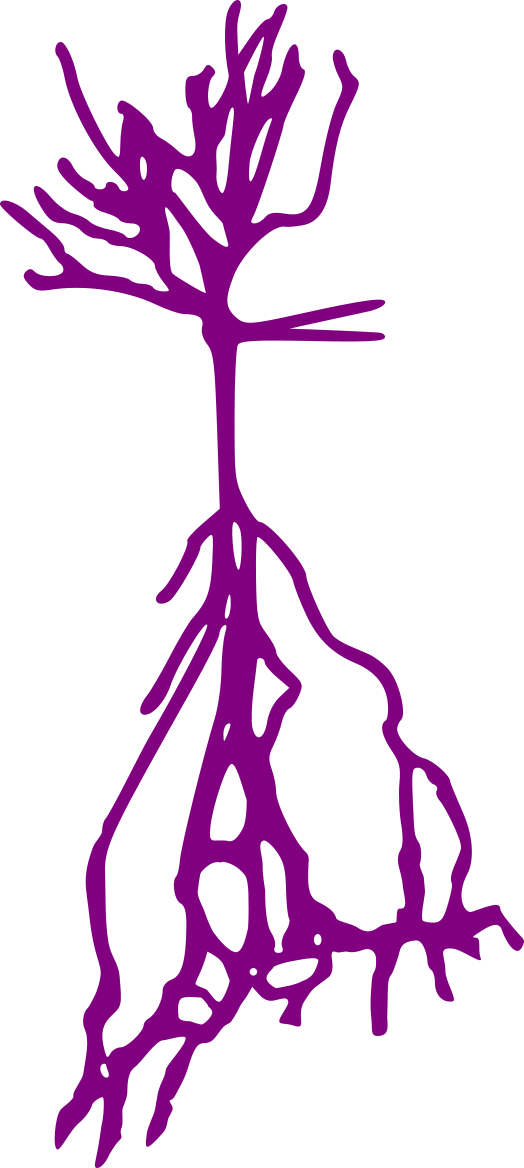
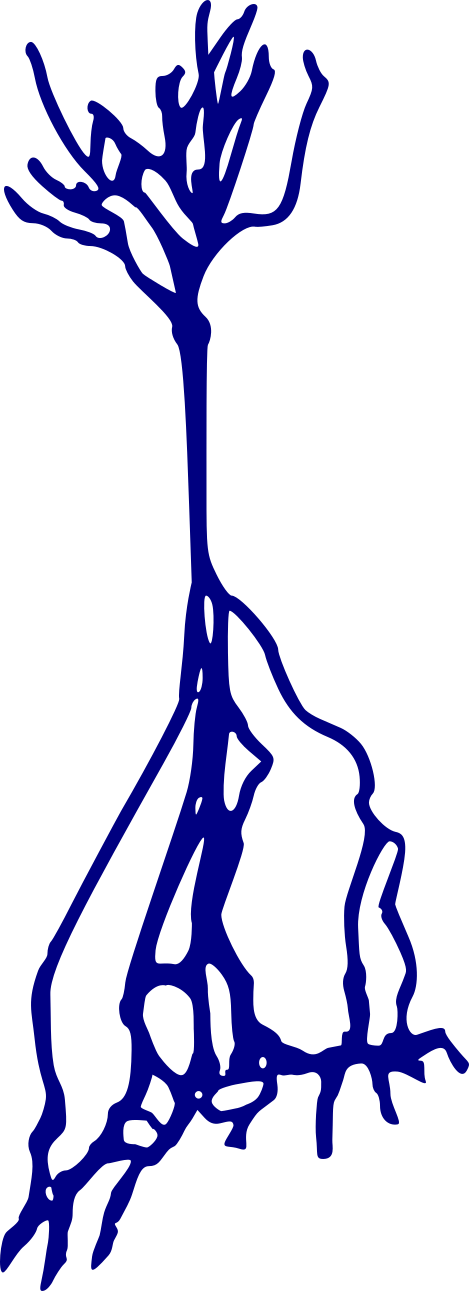

Stellate neurons
Pyramidal neurons

Granule neurons
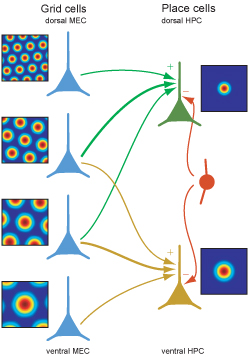
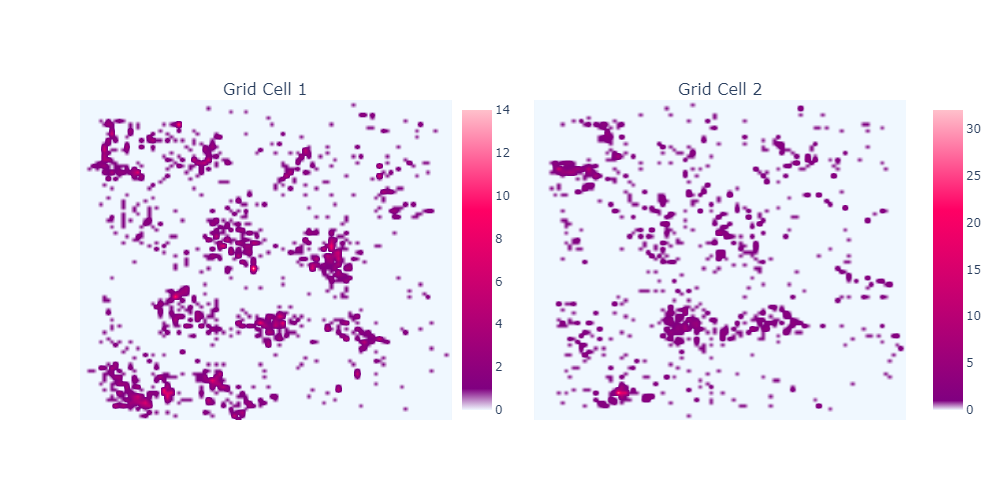
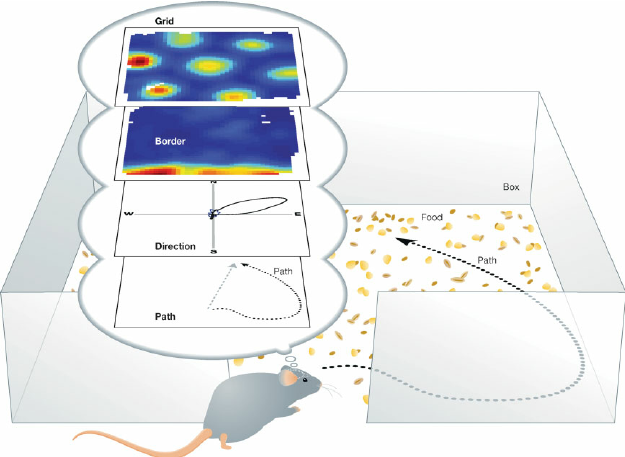
What is a grid cell?
- Mostly stellate neurons in EC between pyramidal neurons
- Modulate firing within a 2D space, regardless of landmarks
dorsal
ventral
- Spacing/size of fields increase moving to ventral mEC
What is a place cell?
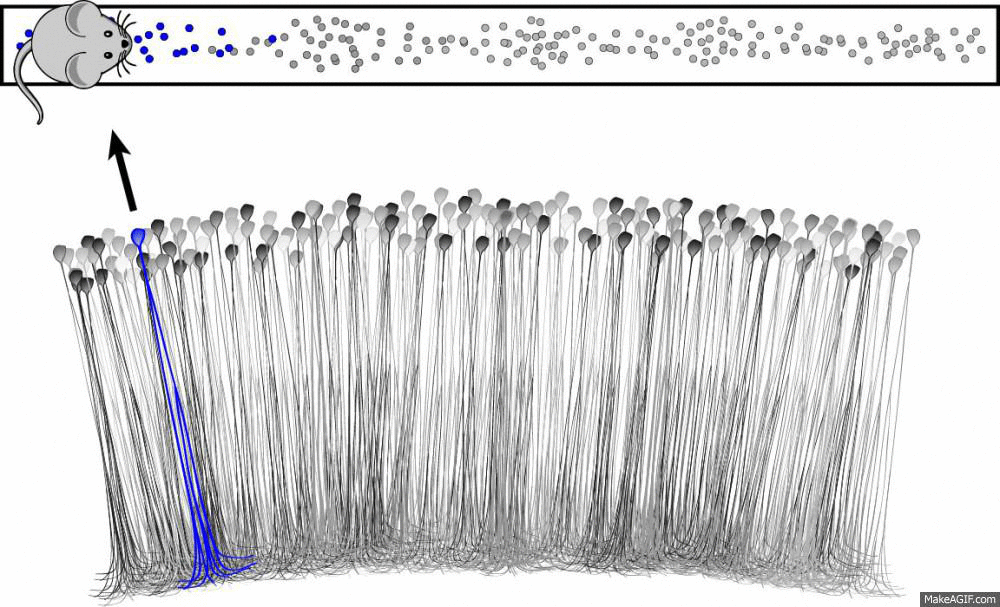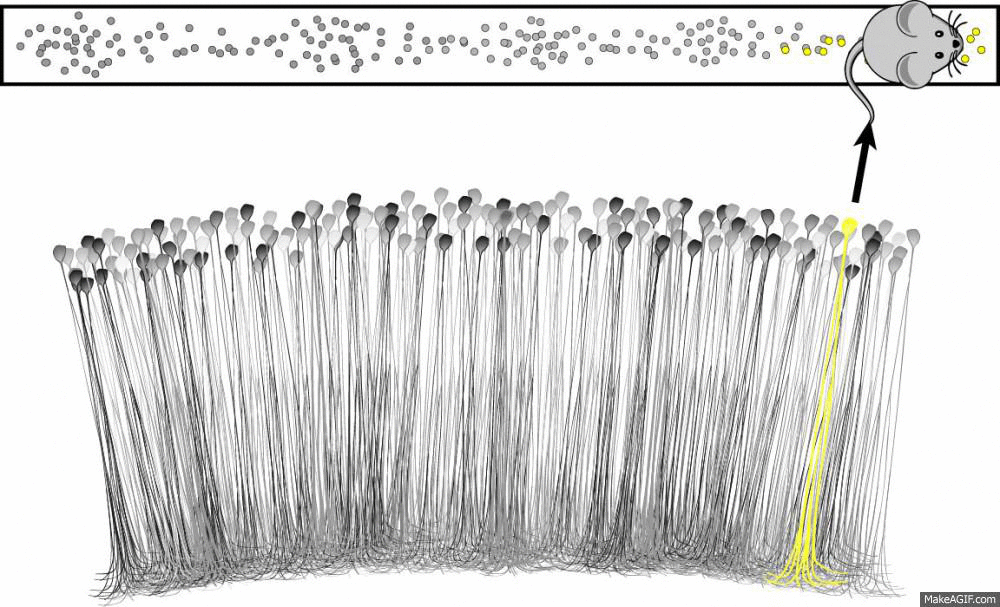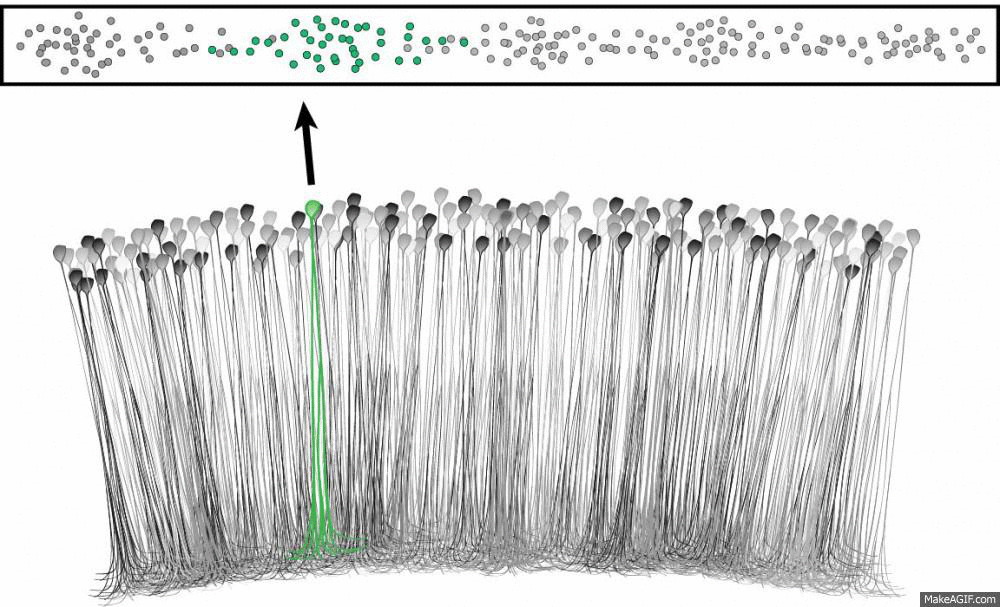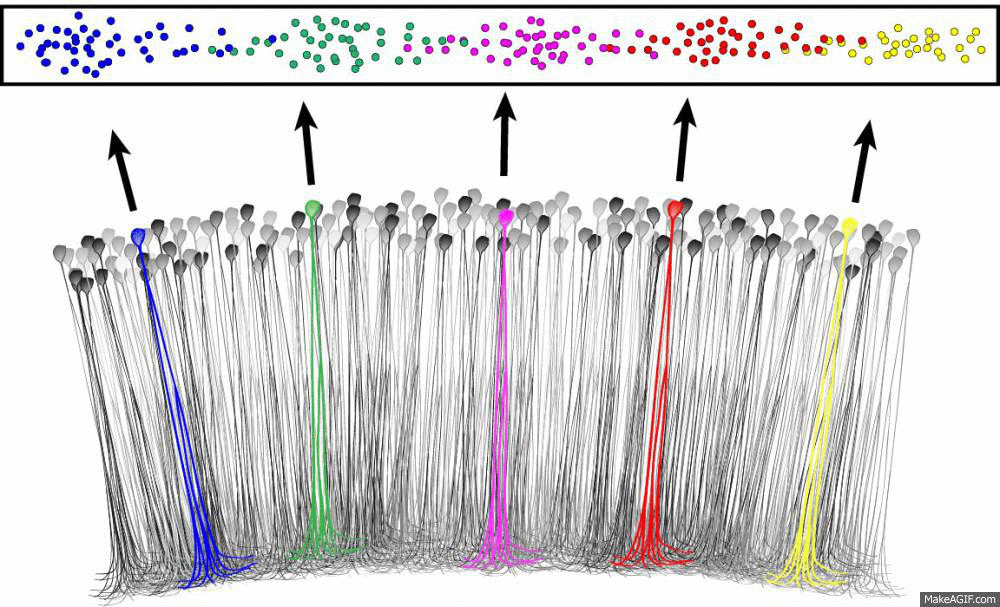
Source: Ryan Jones
- Pyramidal neuron typically located in CA1 or CA3
- Attenuate firing with changes in spatial location (one location)
- Role in spatial learning, decision making and memory encoding
What's the difference?
Head direction, border & speed cells
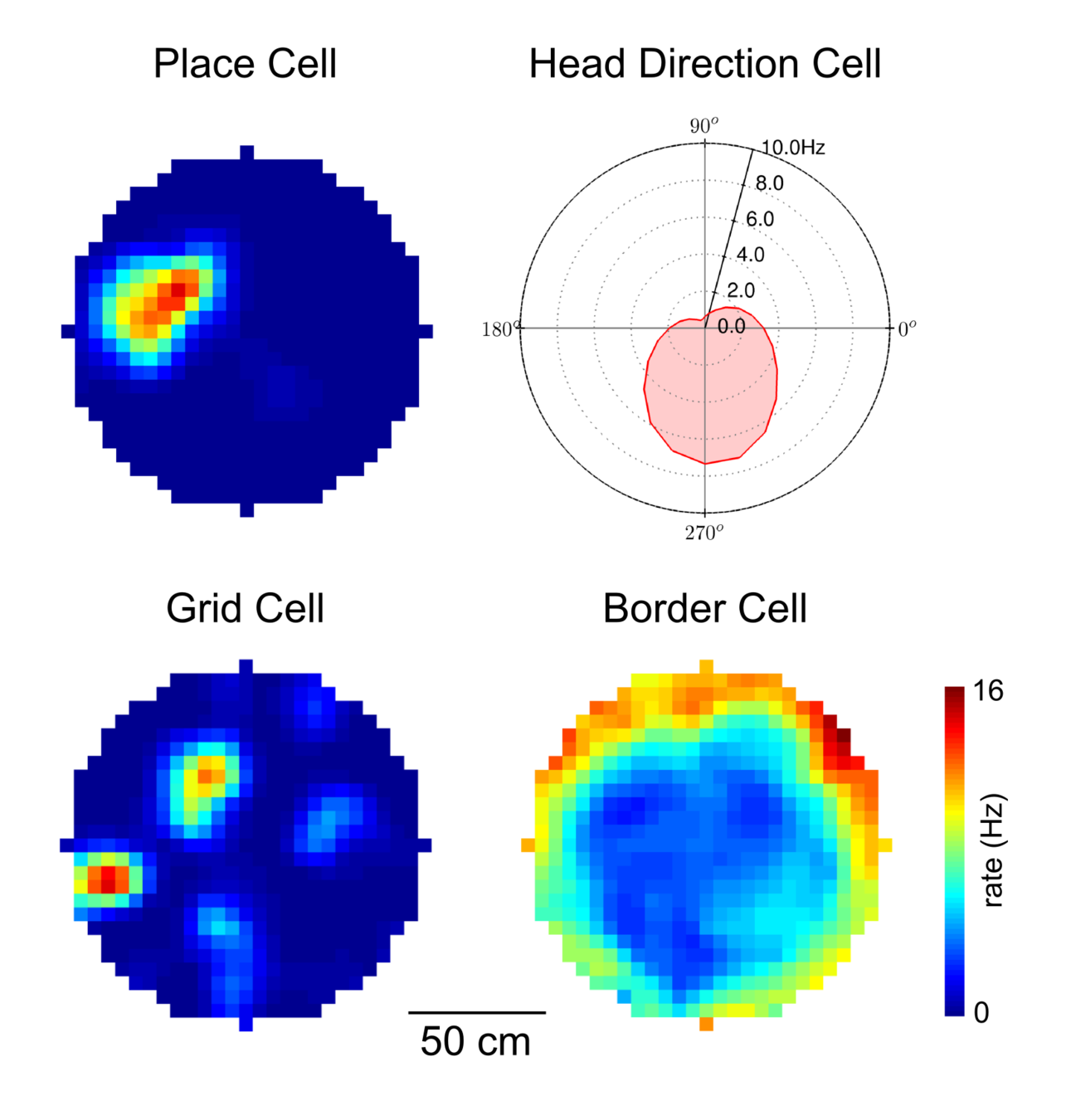
Head Direction
- Subiculum & EC
Border
- Entorhinal Cortex
- Responds to changes in where the animal is looking
- Attenuates firing as nears a barrier

Speed
- Entorhinal Cortex
- Increase firing with speed
How do these work together?
- Head direction and speed cells inform grid cells
- These three, with border cells, inform place cells
- Project back to EC/subiculum from place cells
- Indicate some level of feedback?
- Hebbian learning of place cells
Rhythms of the hippocampal network
Theta
Sharp-wave ripples (SWRs)
Gamma
- ~4-12 Hz
- ~150-250 Hz
- Slow ~22-55 Hz
- Fast ~60-100 Hz
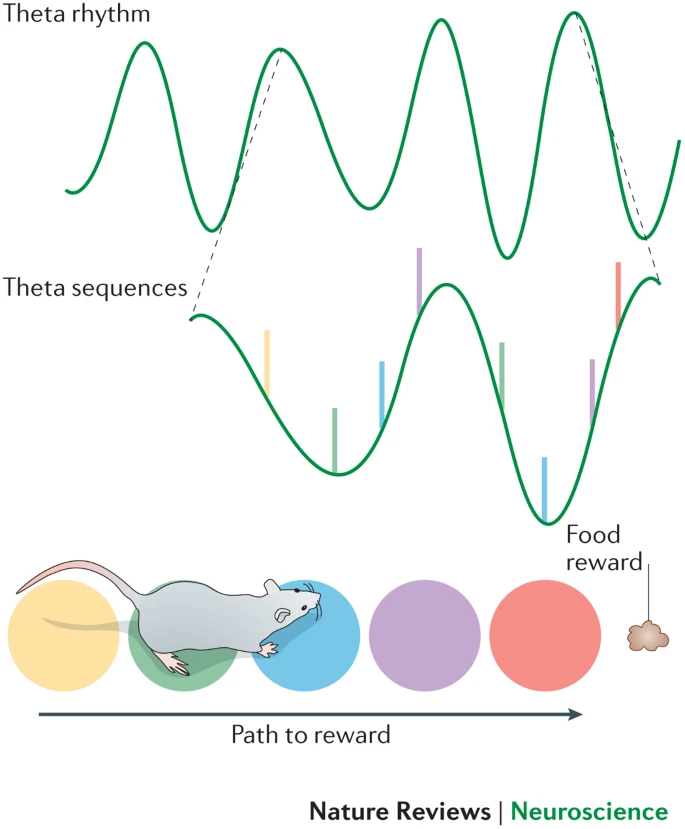
Theta Oscillations
- Formation of sequential memories
- Allows brain to accept new information
- Observed during activity and REM
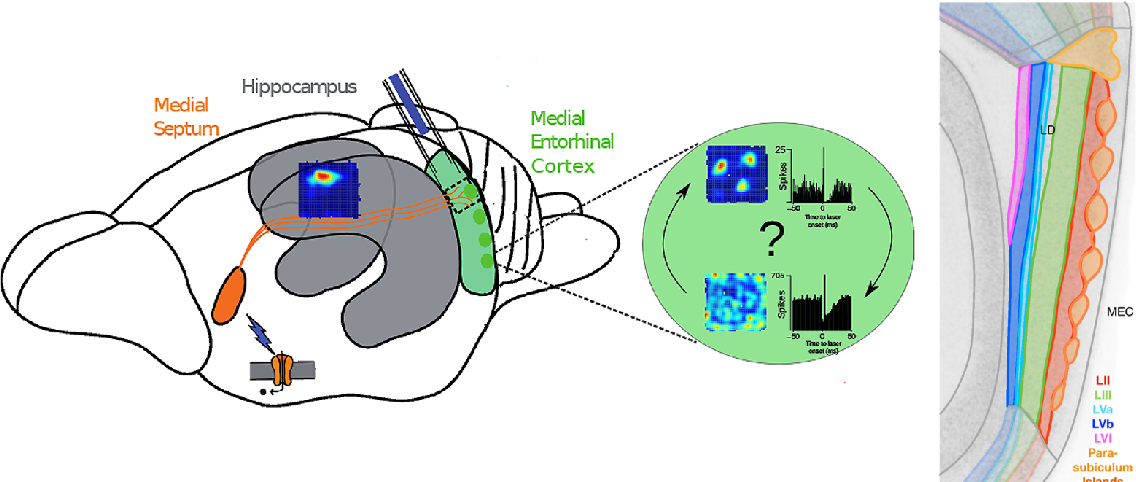
- Septum impacts firing in DG, CA1 & CA3
- Theta sequences
- Required for memory, not place fields
Gamma Oscillations
- Slow gamma driven by CA3, fast driven by EC
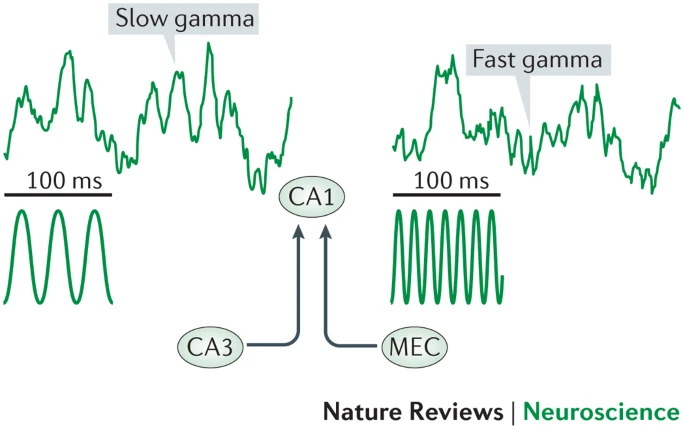
- Theta and gamma couple to each other
- Phase-locking observed both in awake and REM
- Fast gamma related to current trajectory and recent locations
- Slow gamma retrieves spatial memories from CA3 network
- Upcoming locations when re-running

Sharp Wave Ripples (SWRs)
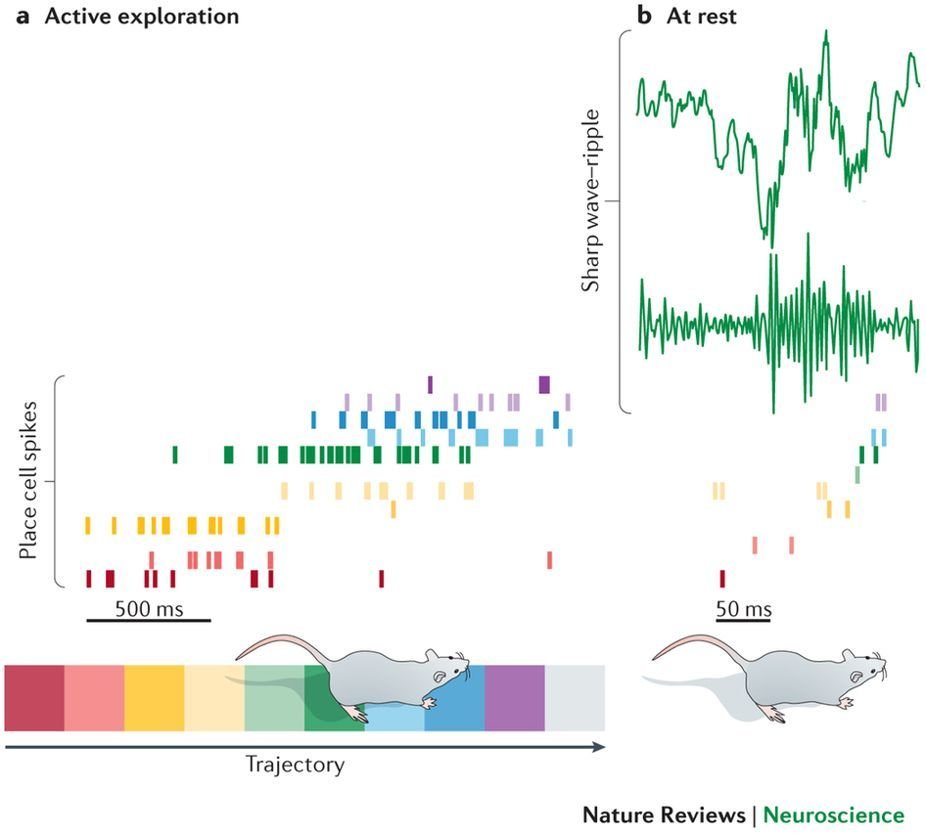
raw LFP
ripple band filtered
SWR
CA3 propagates to CA1, to produce SWRs

Adapted from Laura Colgin
Responsible for consolidation of spatial memories
def sosfiltfilt(timeseries, *, fl=None, fh=None, fs=None, inplace=False, bandstop=False,
gpass=None, gstop=None, ftype=None, buffer_len=None, overlap_len=None,
parallel=True,
**kwargs):
# make sure that fs is specified, unless AnalogSignalArray is passed in
if isinstance(timeseries, (np.ndarray, list)):
if fs is None:
raise ValueError("Sampling frequency, fs, must be specified!")
elif isinstance(timeseries, core.RegularlySampledAnalogSignalArray):
if fs is None:
fs = timeseries.fs
else:
raise TypeError('Unsupported input type!')
try:
assert fh < fs, "fh must be less than sampling rate!"
except TypeError:
pass
try:
assert fl < fh, "fl must be less than fh!"
except TypeError:
pass
if inplace:
out = timeseries
else:
out = deepcopy(timeseries)
if overlap_len is None:
overlap_len = int(fs*2)
if buffer_len is None:
buffer_len = 4194304
if gpass is None:
gpass = 0.1 # max loss in passband, dB
if gstop is None:
gstop = 30 # min attenuation in stopband (dB)
if ftype is None:
ftype = 'cheby2'
try:
if np.isinf(fh):
fh = None
except TypeError:
pass
if fl == 0:
fl = None
# Handle cutoff frequencies
fso2 = fs/2.0
if (fl is None) and (fh is None):
raise ValueError('Nonsensical all-pass filter requested...')
elif fl is None: # lowpass
wp = fh/fso2
ws = 1.4*fh/fso2
elif fh is None: # highpass
wp = fl/fso2
ws = 0.8*fl/fso2
else: # bandpass
wp = [fl/fso2, fh/fso2]
ws = [0.8*fl/fso2,1.4*fh/fso2]
if bandstop: # notch / bandstop filter
wp, ws = ws, wp
sos = sig.iirdesign(wp, ws, gpass=gpass, gstop=gstop, ftype=ftype, output='sos', **kwargs)
# Prepare input and output data structures
# Output array lives in shared memory and will reduce overhead from pickling/de-pickling
# data if we're doing parallelized filtering
if isinstance(timeseries, (np.ndarray, list)):
temp_array = np.array(timeseries)
dims = temp_array.shape
if len(temp_array.shape) > 2:
raise NotImplementedError('Filtering for >2D ndarray or list is not implemented')
shared_array_base = Array(ctypes.c_double, temp_array.size, lock=False)
shared_array_out = np.ctypeslib.as_array(shared_array_base)
# Force input and output arrays to be 2D (N x T) where N is number of signals
# and T is number of time points
if len(temp_array.squeeze().shape) == 1:
shared_array_out = np.ctypeslib.as_array(shared_array_base).reshape((1, temp_array.size))
input_asarray = temp_array.reshape((1, temp_array.size))
else:
shared_array_out = np.ctypeslib.as_array(shared_array_base).reshape(dims)
input_asarray = temp_array
elif isinstance(timeseries, core.RegularlySampledAnalogSignalArray):
dims = timeseries._data.shape
shared_array_base = Array(ctypes.c_double, timeseries._data_rowsig.size, lock=False)
shared_array_out = np.ctypeslib.as_array(shared_array_base).reshape(dims)
input_asarray = timeseries._data
# Embedded function to avoid pickling data but need global to make this function
# module-visible (required by multiprocessing). I know, a bit of a hack
global filter_chunk
def filter_chunk(it):
"""The function that performs the chunked filtering"""
try:
start, stop, buffer_len, overlap_len, buff_st_idx = it
buff_nd_idx = int(min(stop, buff_st_idx + buffer_len))
chk_st_idx = int(max(start, buff_st_idx - overlap_len))
chk_nd_idx = int(min(stop, buff_nd_idx + overlap_len))
rel_st_idx = int(buff_st_idx - chk_st_idx)
rel_nd_idx = int(buff_nd_idx - chk_st_idx)
this_y_chk = sig.sosfiltfilt(sos, input_asarray[:, chk_st_idx:chk_nd_idx], axis=1)
shared_array_out[:,buff_st_idx:buff_nd_idx] = this_y_chk[:, rel_st_idx:rel_nd_idx]
except:
raise ValueError(("Some epochs were too short to filter. Try dropping those first,"
" filtering, and then inserting them back in"))
# Do the actual parallellized filtering
if (sys.platform.startswith('linux') or sys.platform.startswith('darwin')) and parallel:
pool = Pool(processes=cpu_count())
if isinstance(timeseries, (np.ndarray, list)):
# ignore epochs (information not contained in list or array) so filter directly
start, stop = 0, input_asarray.shape[1]
pool.map(filter_chunk, zip(repeat(start), repeat(stop), repeat(buffer_len),
repeat(overlap_len), range(start, stop, buffer_len)),
chunksize=1)
elif isinstance(timeseries, core.RegularlySampledAnalogSignalArray):
fei = np.insert(np.cumsum(timeseries.lengths), 0, 0) # filter epoch indices, fei
for ii in range(len(fei)-1): # filter within epochs
start, stop = fei[ii], fei[ii+1]
pool.map(filter_chunk, zip(repeat(start), repeat(stop), repeat(buffer_len),
repeat(overlap_len), range(start, stop, buffer_len)),
chunksize=1)
pool.close()
pool.join()
# No easy parallelized filtering for other OSes
else:
if isinstance(timeseries, (np.ndarray, list)):
# ignore epochs (information not contained in list or array) so filter directly
start, stop = 0, input_asarray.shape[1]
iterator = zip(repeat(start), repeat(stop), repeat(buffer_len),
repeat(overlap_len), range(start, stop, buffer_len))
for item in iterator:
filter_chunk(item)
elif isinstance(timeseries, core.RegularlySampledAnalogSignalArray):
fei = np.insert(np.cumsum(timeseries.lengths), 0, 0) # filter epoch indices, fei
for ii in range(len(fei)-1): # filter within epochs
start, stop = fei[ii], fei[ii+1]
iterator = zip(repeat(start), repeat(stop), repeat(buffer_len),
repeat(overlap_len), range(start, stop, buffer_len))
for item in iterator:
filter_chunk(item)
if isinstance(timeseries, np.ndarray):
out[:] = np.reshape(shared_array_out, dims)
elif isinstance(timeseries, list):
out[:] = np.reshape(shared_array_out, dims).tolist()
elif isinstance(timeseries, core.RegularlySampledAnalogSignalArray):
out._data[:] = shared_array_out
return outNelpy Filtering