Calibrating large-scale ABM models with Bayesian Emulation and History Matching
Arnau Quera-Bofarull
April 2022 - ABM Workshop, Oxford
JUNE Collaboration: Ian Vernon, Jonathan Owen, Joseph Aylett-Bullock, Carolina Cuesta-Lazaro, Jonathan Frawley, Aidan
Sedgewick, Difu Shi, Henry Truong, Mark Turner, Joseph Walker,
Tristan Caulfield, Kevin Fong, and Frank Krauss
A case study: the JUNE epidemiological model

June Dalziel Almeida
Modelling an epidemic
Two common approaches:
1. SIR models
Pros:
"cheap",
simple,
...
Cons:
only models "averages",
...
Two common approaches:
2. ABM models
Pros:
individual agents,
individual interactions,
...
Cons:
computational cost,
calibration,
...

Modelling an epidemic
The JUNE
agent-based model
github.com/IDAS-Durham/JUNE
Many other epi ABMs exist:
- Covid-sim
- Covasim
- OpenABM
- etc.
What makes JUNE special?
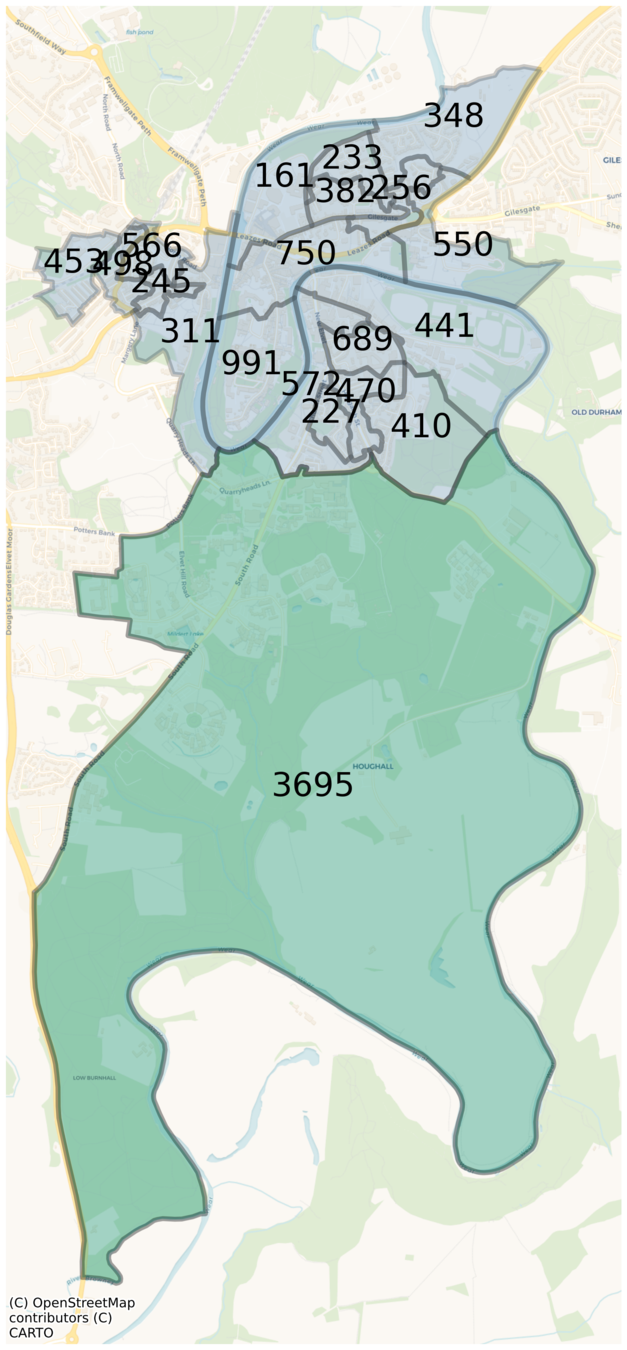
England digital twin
England Digital twin
Geography

England Digital twin
Demography
- age (27)
- sex (f)
- ethnic group (Caribbean)
- deprivation index 2 (1-10)
- work sector / subsector (healthcare/doctor)
- mode of transport (public)
- area of residence
- super area of work

Main data source: census data (NOMIS)
~56 million agents
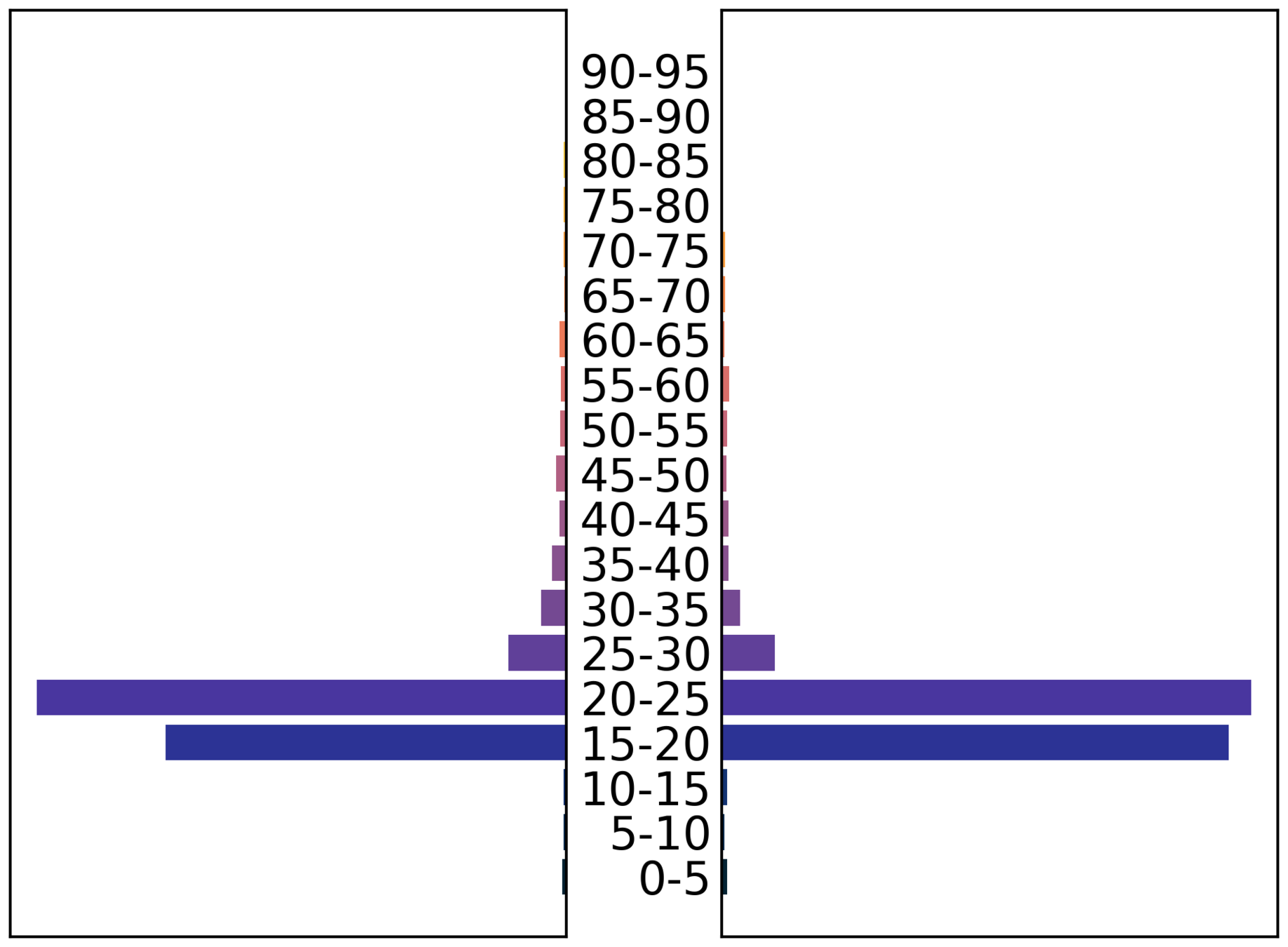
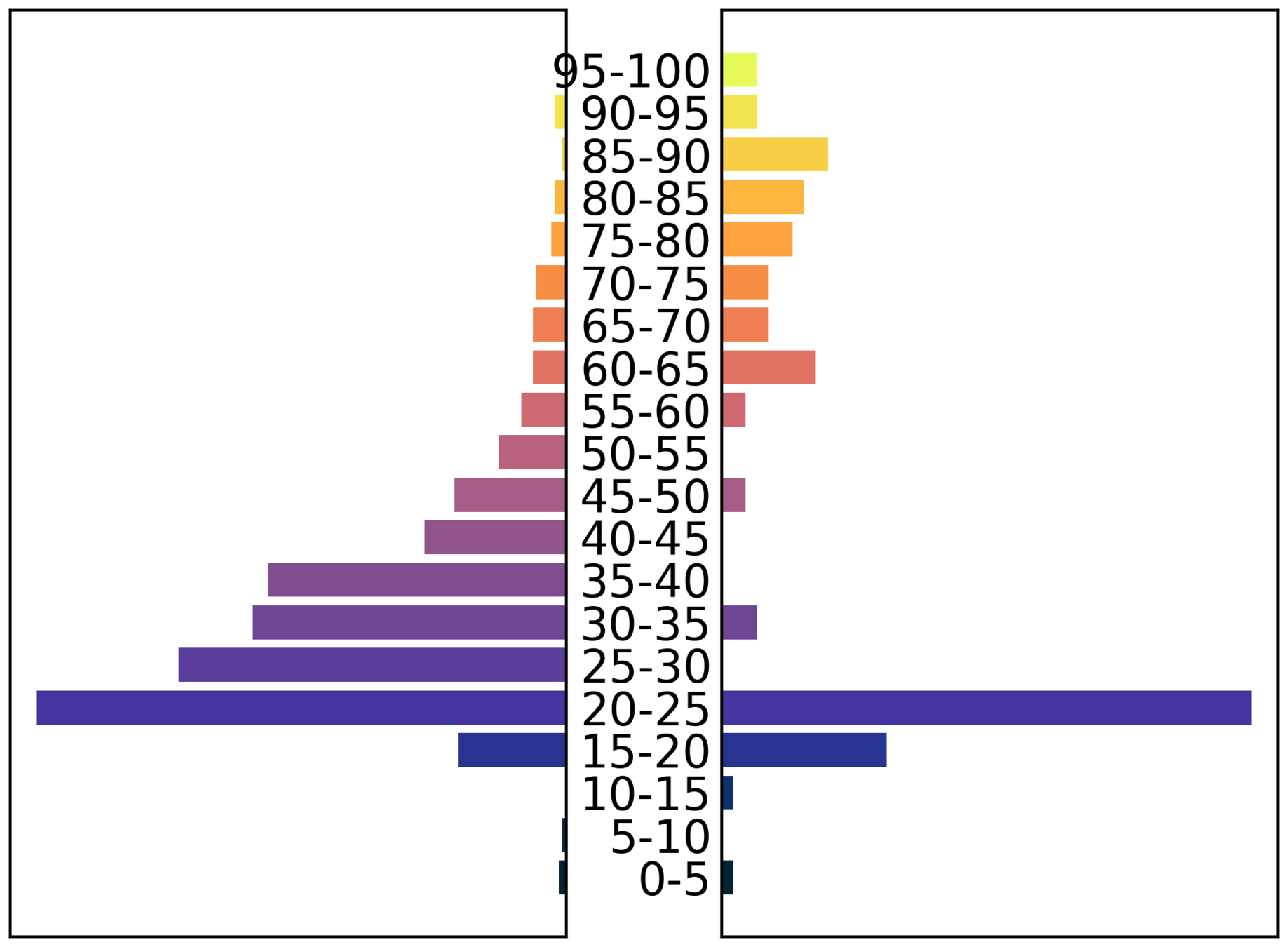
male
female
Demographic granularity
male
female
Some things are homogeneous, though...
Pubs in the UK
England Digital twin
Dynamics (where can people go?)
- Residence
- Care Home
- Household
- Primary activity
- Company
- Hospital
- School
- Care Home
- University

-
Travel
- Commute
- National travel
- Leisure
- Shopping
- Pubs / restaurants
- Cinema
- Gyms
- Residence visits
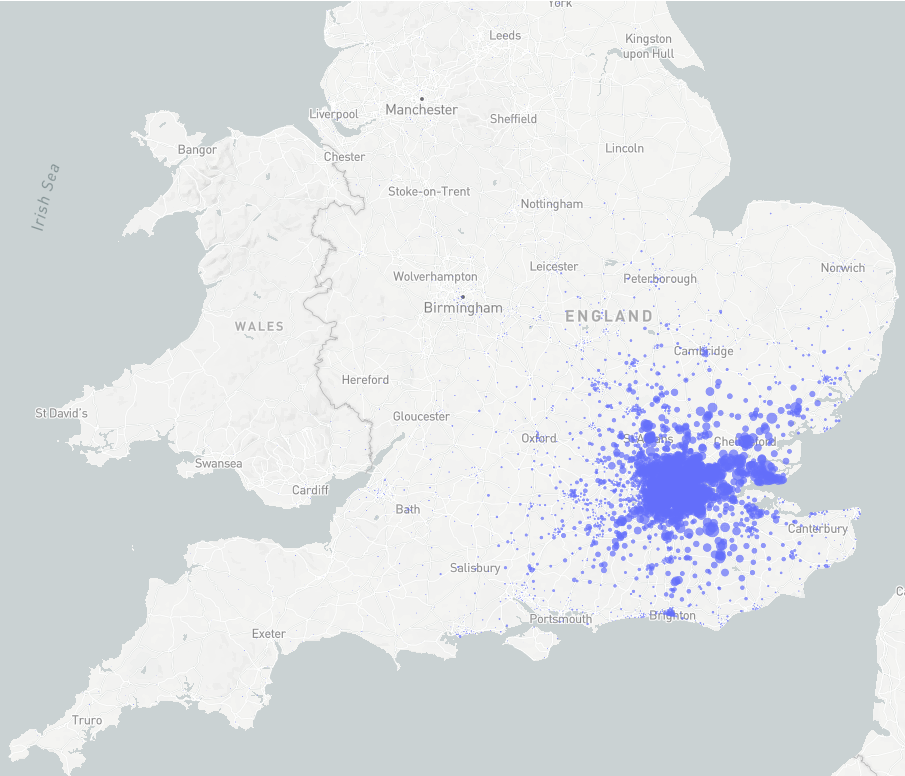
City of London workers' usual residence
Matching workplace and residence
Commute
-
Census -> method of transportation.
-
Two kinds: Inner city commute, outer city commute




Hub





Hub





Venues geolocalisation
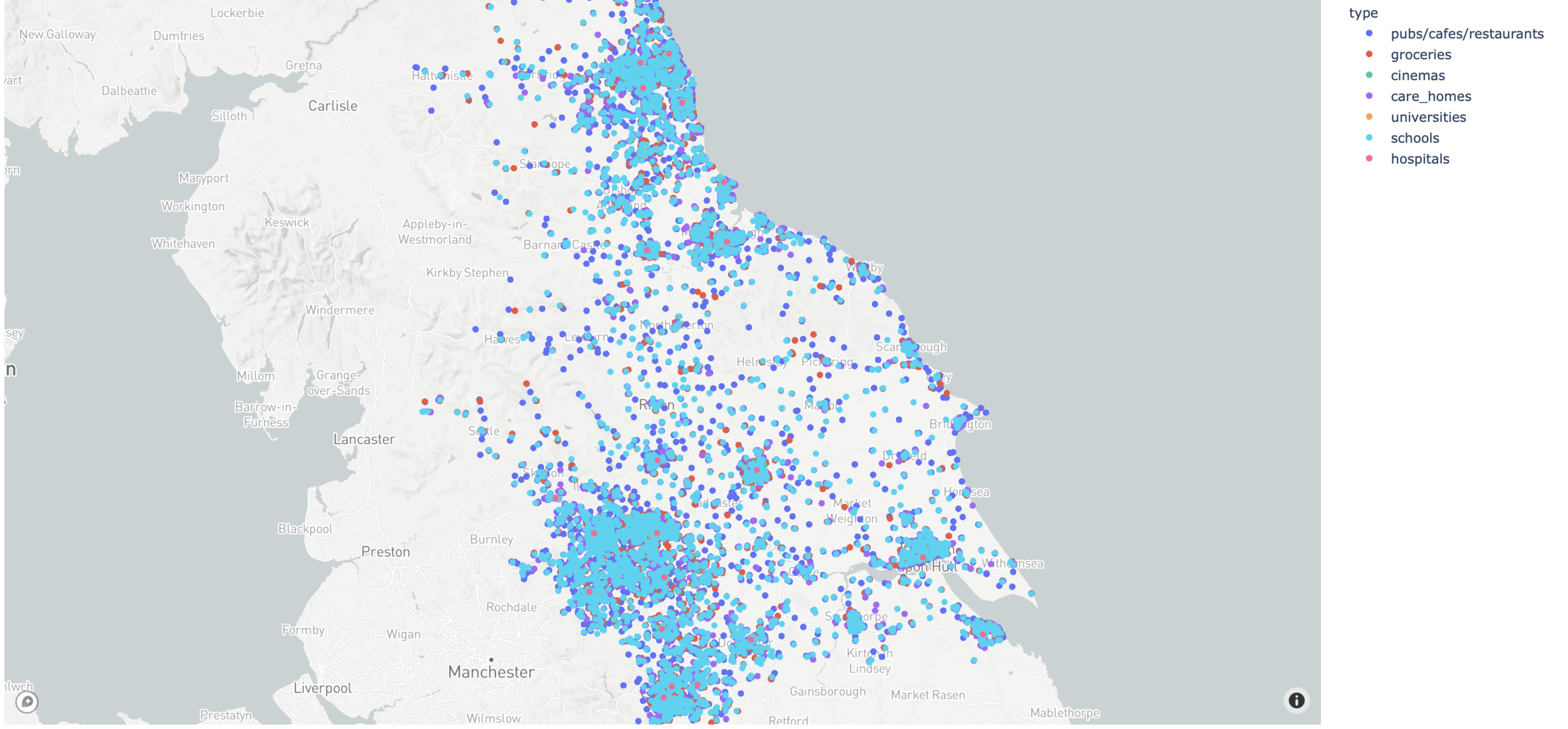

Durham student population




43 yo
38 yo
10 yo
Infection transmission
j
j
i
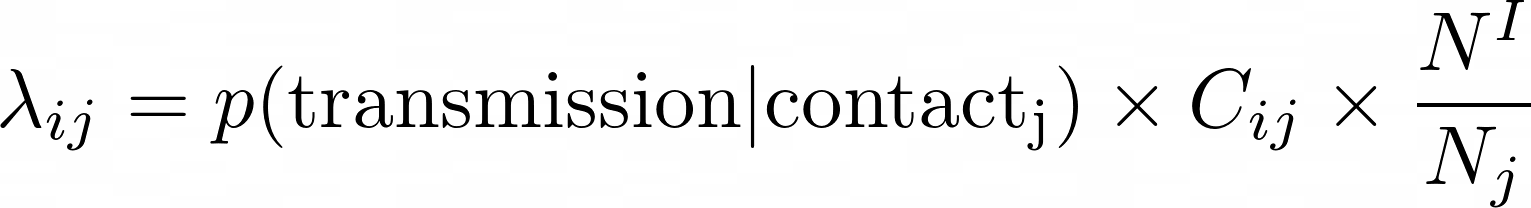
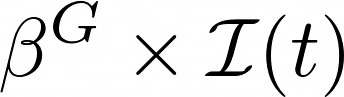
Intensity of contacts (per group)
Infectiousness profile

Contact
Matrix

Disease Trajectory
Odds calibrated to data

import scipy
Policies

The challenge of calibration
Very detailed model, but
is it useful?
is it realistic?
can we 'fit' it?
The challenge of calibration
Unknown parameters:
-
Location contact intensity (13)
-
Effectiveness of policies (5)
-
Seed cases (1)
19 parameters to fit
JUNE's computational cost
typical England run ~ 600 CPU hours / 100 GB RAM

Parallelisation by domains of equal population
JUNE's computational cost
Still too expensive
Build an emulator of the model
solution
Bayesian emulation
contact intensity in pubs
hospitalisations
Emulation:
Bayesian emulation
The emulator returns
on new unexplored points, but several orders of magnitude faster than the original model
Training the emulator
- Run the simulator on n points
and obtain:
2. Update the emulator's paramaters using Bayes linear methods

Linking the model to reality
-
Observational
-
Model discrepancy
History matching
Goal: Find all sets of input parameters that lead to acceptable matches.
Method: Iteratively rule out implausible parameter sets.

Reject when
The full picture
Train Bayesian emulator
Run emulator
O(500k) times
Run full simulation O(100) times
Discard implausible regions
Sample O(100) parameter sets from latin hypercube
Sample O(100) parameter sets from non-implausible region

Visualising the non-implausible regions

History matching in JUNE
Why we needed the complexity
JUNE reproduces infection disparities among various demographic groups thanks to its granularity.

Outlook
- High resolution ABM models are a powerful tool to understand social dynamics.
- ABM model calibration is often computationally prohibitive.
- Emulation + history matching enables global exploration of parameters and uncertainty quantification.
Slides: slides.com/arnauqb/abm_workshop
Paper: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.02.21.22271249v1