ABM vs MARL
ABMs:
- Many agents
- Simple behaviour
MARL:
- Few agents
- Complicated behaviour ( lots of learning )
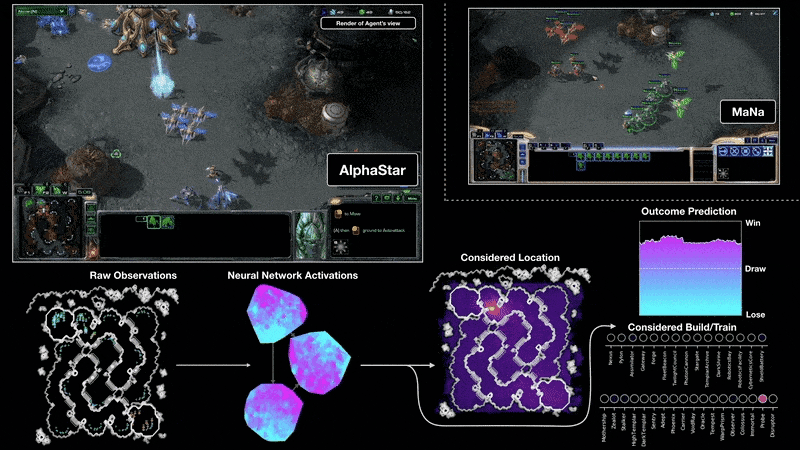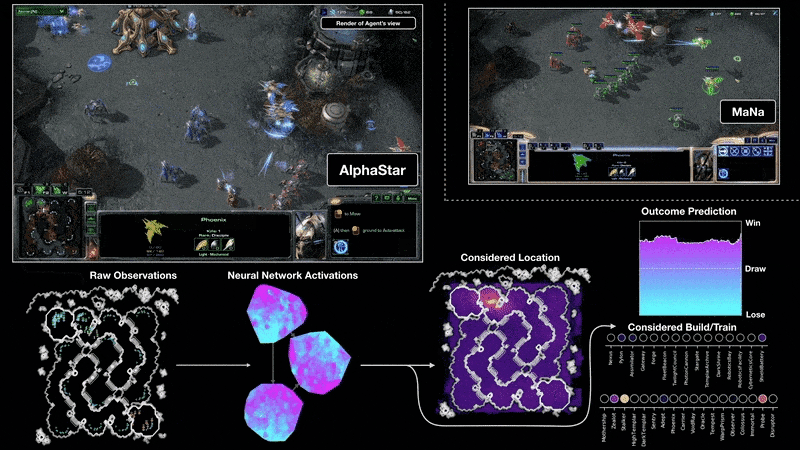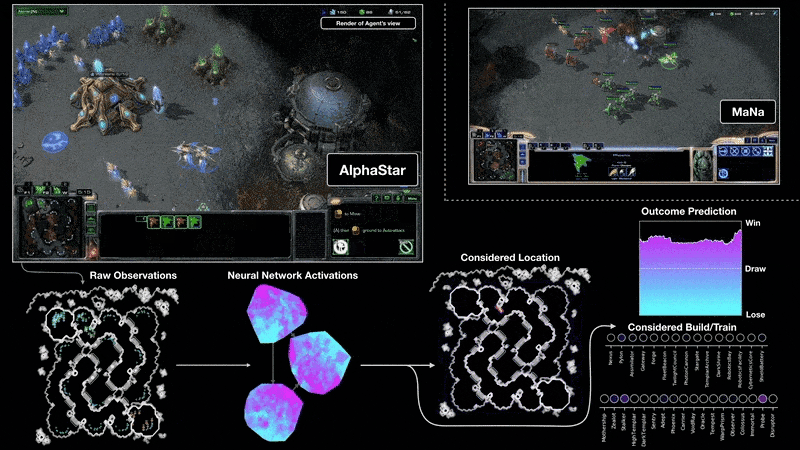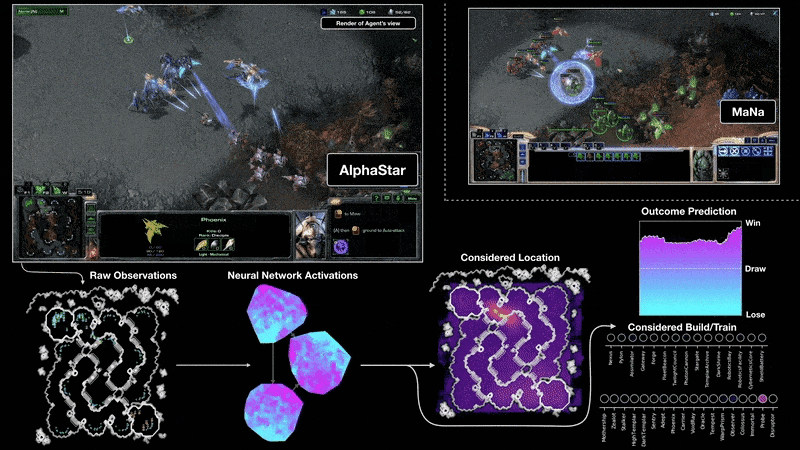
ABM vs MAS
ABMs:
- Goal is to study emergence
MAS:
- Engineering goal (coordination, cooperation, etc.)
Examples of ABMs
SIR on a graph
Parameters
- Infection probability
- Recovery probability
Examples of ABMs
Flocking model
Parameters
- Speed
- Cohere factor
- Separation
- Separate factor
- Match factor
- Visual distance

Calibration of ABMs
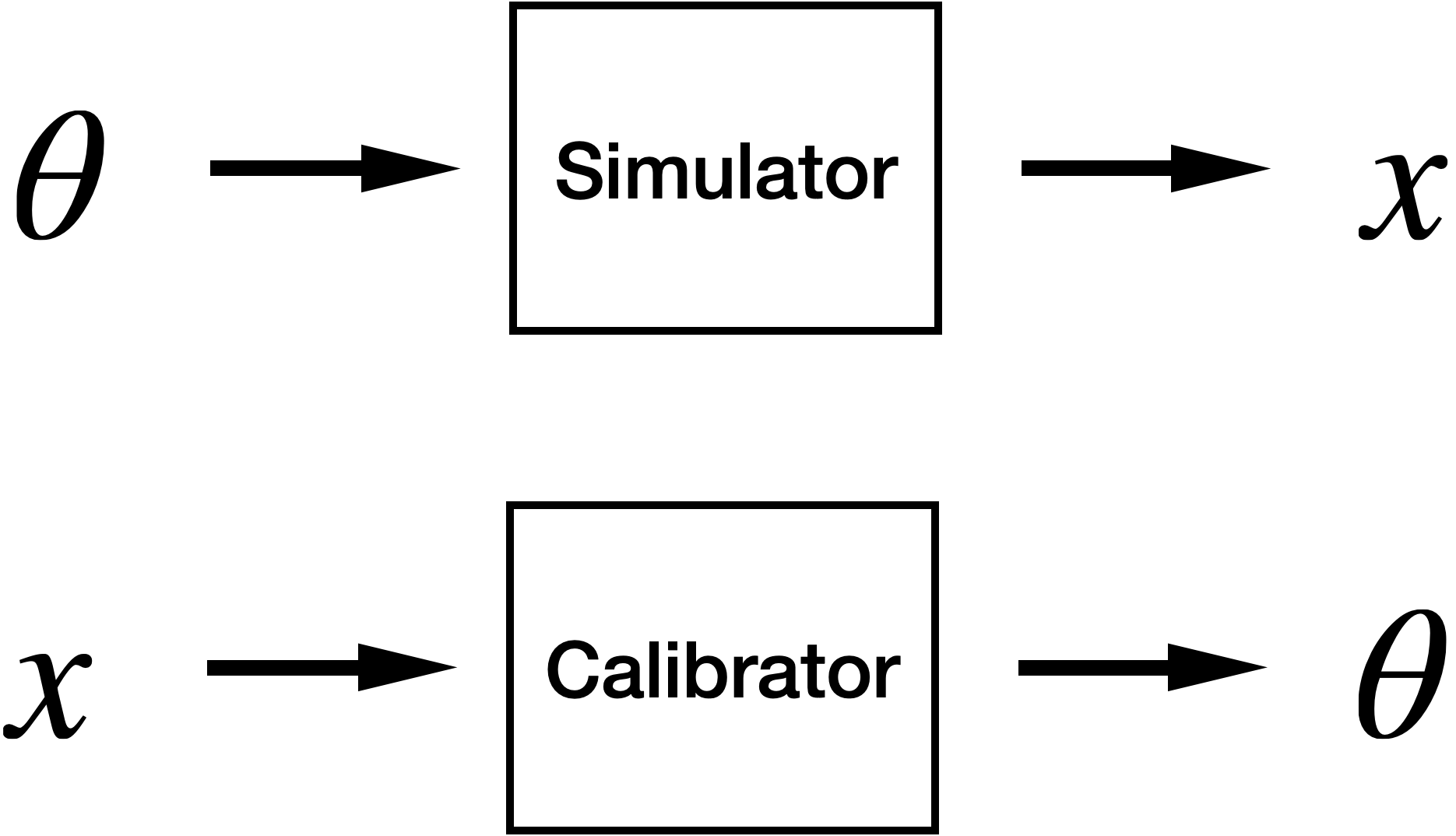
Typically hard because
- No access to the likelihood.
- Simulator is slow to run.
- Large parameter space.
Simulated minimum distance (SMD)
observed data
ABM parameters
Calibration of ABMs,
the standard way
Limitations: Not a Bayesian approach, so no proper uncertainty quantification
Bayesian methods for ABM calibration
1. Approximate Bayesian Computation (ABC)
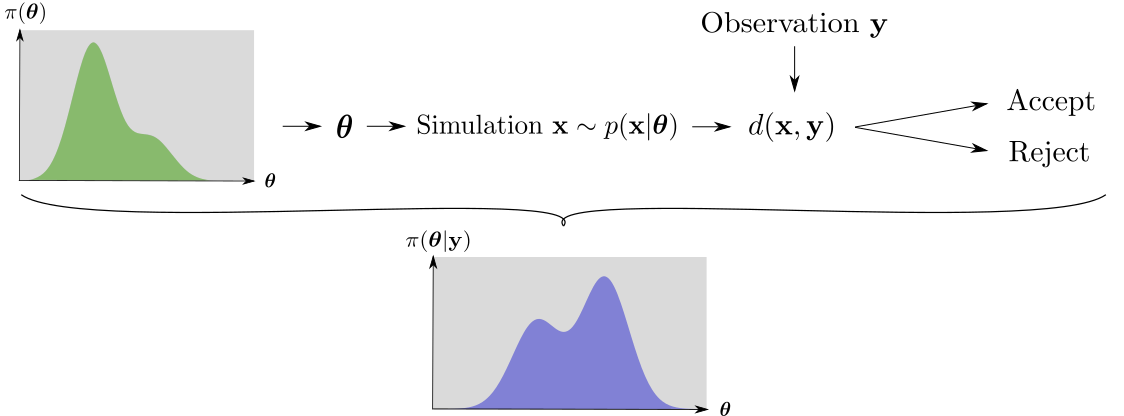
Typically x and y are summary statistics
Drawbacks:
- Choice of summary statistics
- Lots of simulations
Bayesian methods for ABM calibration
Advantages: black-box, simulation efficient, amortization
2. Neural methods
Idea: employ NN to estimate the posterior density
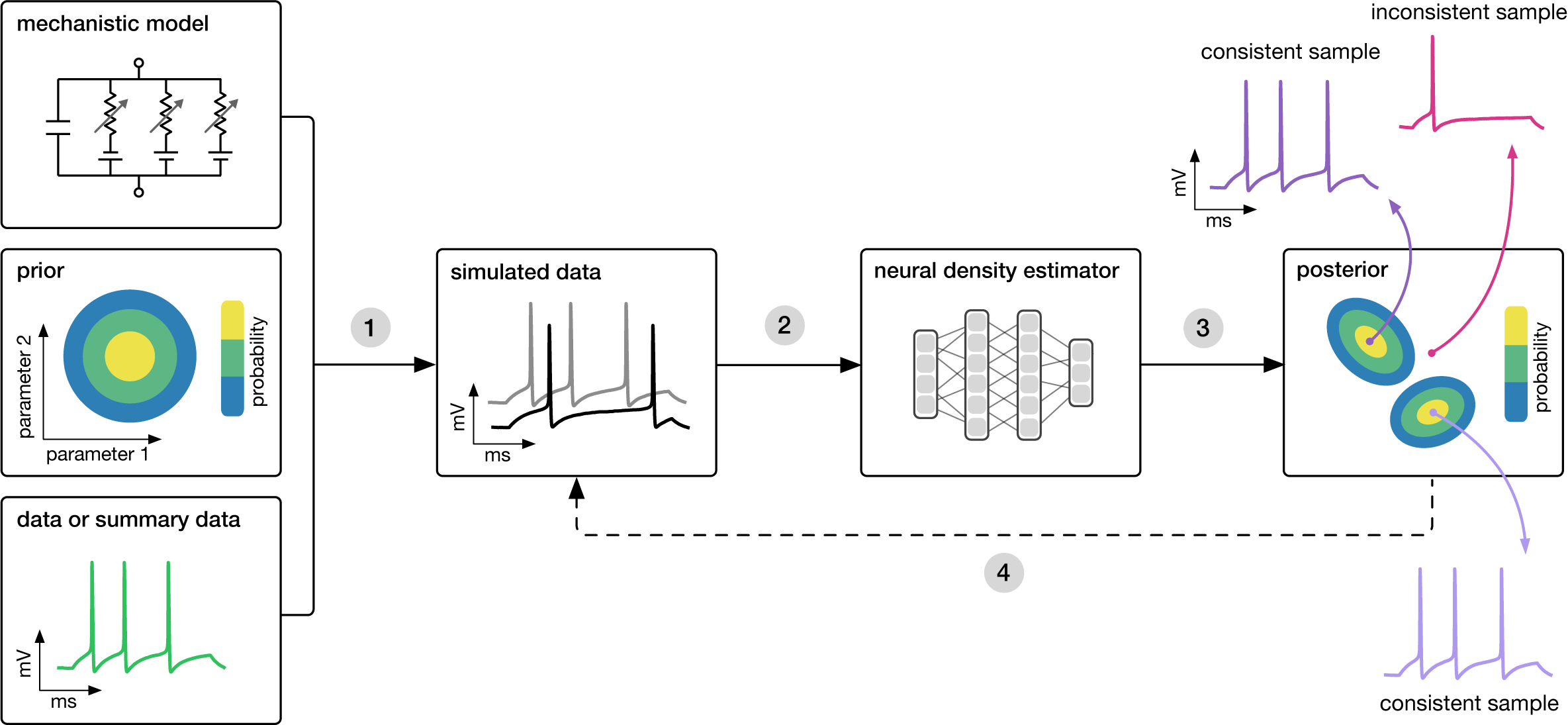
Bayesian methods for ABM calibration
3. Gradient-assisted methods
(Generalized) Variational Inference
Need the gradient:
Score function estimator
Pathwise estimator
Requires differentiable simulator
Advantages: Efficiency, scaling
Differentiable agent-based models
(current line of work)
Possible to differentiate through discrete randomness and control flow

Compartmental vs Agent SIR equivalence
No clear equivalence between
More infected -> More infections
Prob (infection) =
independent of number of infected neighbours