iOS Pentesting For Beginners


n|u
Arun.S
Senior Security Consultant @ IBM - ISL
What not to expect?
-
OWASP Mobile TOP 10 -
Dynamic Analysis -
Advanced Application Runtime Analysis -
Exploiting iOS Applications etc.,
Agenda
-
iOS_Architecture - Using_Xcode
-
Device_Jailbreaking -
Setting_up_the_Test_Environment -
References
iOS Architecture
iOS Basics
-
iOS Operating System is based on the Darwin OS, which was originally written by Apple in C, C++ and Objective-C.
-
iOS recently introduced Swift, an alternate programming language that greatly simplifies the process of building fast and effective native applications.
-
Unlike Android, the iOS operating system is not open source..
-
To Know more visit : goo.gl/c7X7aX
iOS Architecture

iOS Security Architecture

iOS Boot Chain Process
-
When an iOS device is turned on, its application processor immediately executes code from read-only memory known as the Boot ROM. -
The boot ROM contains the firmware that is permanently installed by Apple on every iOS and cannot be altered, once manufactured. -
It also contains the Apple Root CA public key, which is used to verify that the Low-Level Bootloader (LLB) is signed by Apple before allowing it to load. -
Each step ensures that the next step is signed by Apple.

iOS Boot Chain Process Contd.,
Low-level boot loader :
- This is the lowest level of code that can be updated.
- It also verifies the signatures of firmware of iBoot before loading it.
iBoot :
- It verifies the signature of the iOS kernel before starting the kernel.
For More Info visit :
- goo.gl/H8OVUJ

What happens if any one step of this boot process fails?
-
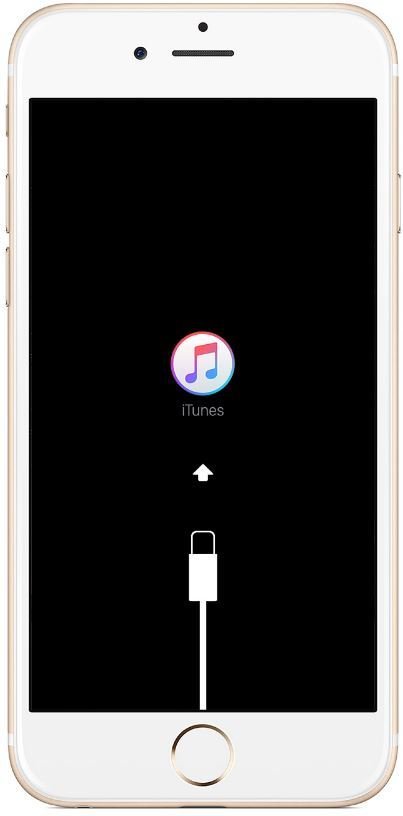
If one step of this boot process is unable to load or verify the next process, startup is stopped and the device displays the “Connect to iTunes” screen.
-
This is called recovery mode. If the Boot ROM is not able to load or verify LLB, it enters DFU (Device Firmware Upgrade) mode.
What happens if any one step of this boot process fails?Contd..
-
In both cases, the device must be connected to iTunes via USB and restored to factory default settings.
-
For more information on manually entering recovery mode, see https://support.apple.com/kb/HT1808.
Other Important Concepts
- Secure Enclave
- Touch ID
- Code Signing
Secure Enclave
-
On every Apple device that has an A7 and later processor, there exists a special processor, otherwise known as secure Enclave. -
Every device has a unique and non-iterable (non-repeatable) ID, that is fused into the Secure Enclave at the time of the device manufacturing. -
The Secure Enclave implements device passcode verification, file encryption, Touch ID fingerprint processing and matching , Apple Pay, and enforces security restrictions such as the escalating delays applied after excessive incorrect passcode attempts.
Touch ID
-
Touch ID is the fingerprint sensor that was first introduced by Apple on the iPhone 5S. It is a seamless way to use your fingerprint as your passcode. -
The touch ID is also responsible for encrypting keys generated in the device's secure enclave.Such keys are then, in turn, used to encrypt the device's lock-screen pass code or iOS app store account credentials, amongst other things. -
After 5 consecutive failed unlock attempts, using a fingerprint, the keys are deleted from the secure enclave. -
This secures the encrypted passcode/credentials from being decrypted(since the key that is required to decrypt the passcode, is now deleted) and forces the attacker to provide the actual pass-code/credentials in order to unlock the device/get access to iTunes account.
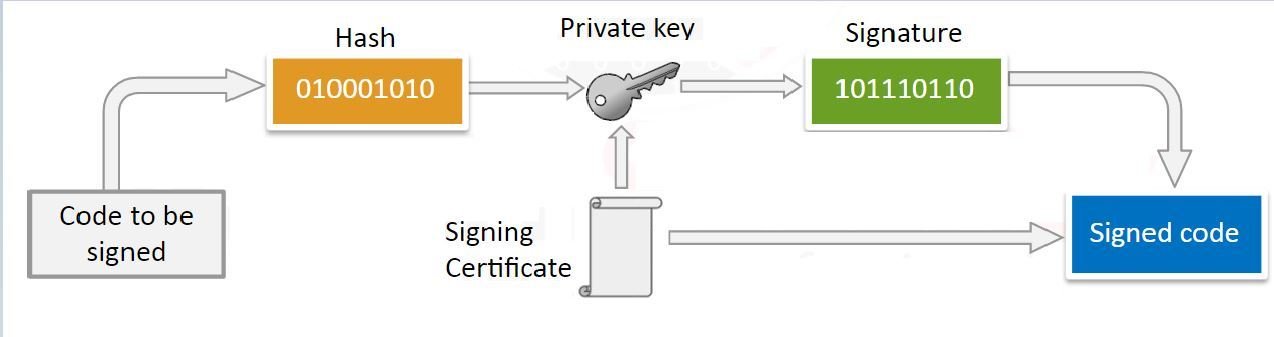
Code Signing
-
In general, all iOS apps must be signed by a signing certificate that was issued by Apple(this process is known as code signing) and must be distributed via the Apple app store.
Using Xcode
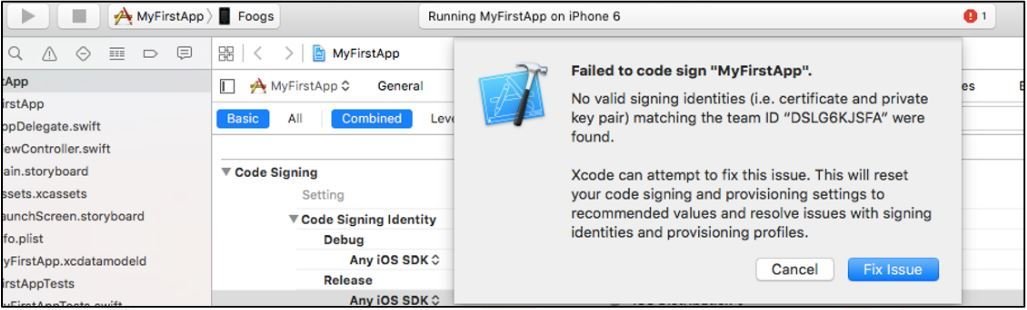
Provisioning Identity
- If you try the same in Real iDevice the application deployment will fail.
- Inorder to fix this issue, we would need to create a new provisioning identity.
Provisioning Profile
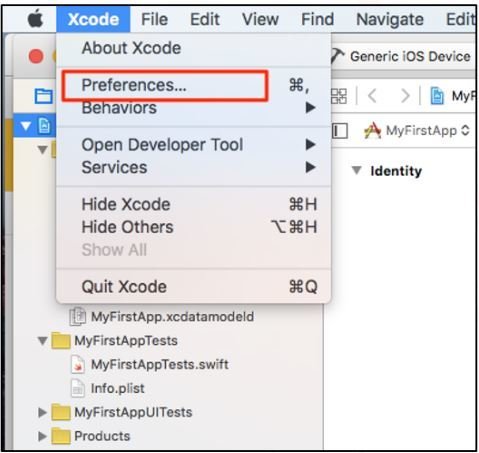
- Starting Xcode 7.2, Apple has provided an option to create a free iOS development provisioning profile. This allows you to write and test your application on a real iPhone.
- Navigating to Xcode > Preferences > Accounts > Select "View Details".
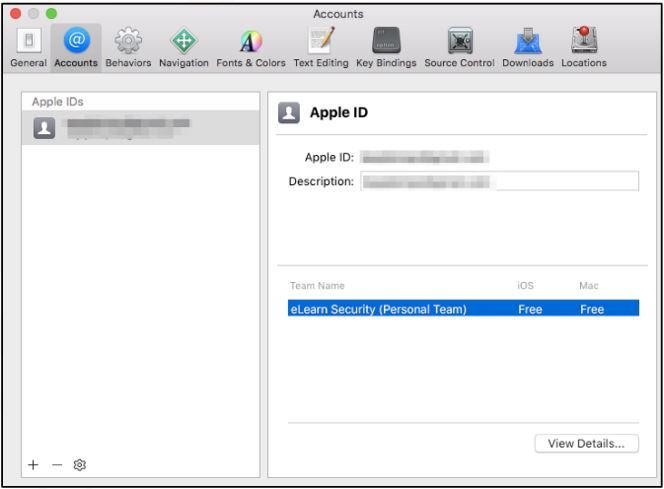
-
Create an iOS development Signing Identity and hit Done. -
goo.gl/pE9gMG
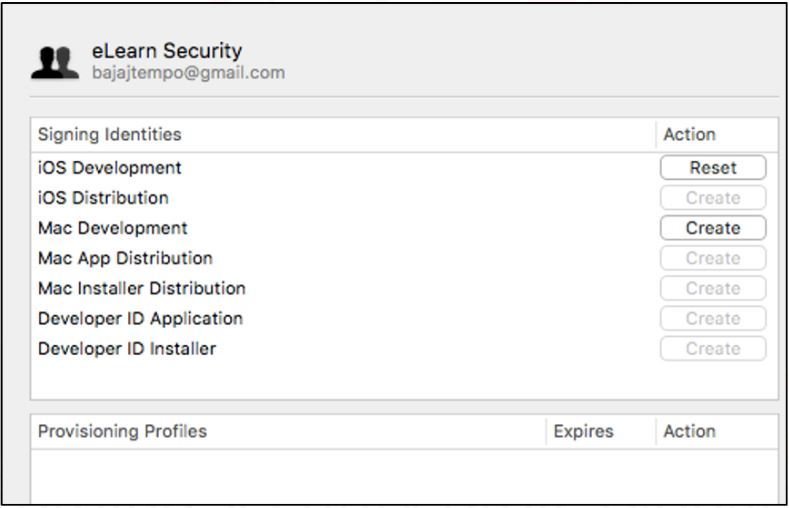
iOS Jailbreaking
iOS Jailbreaking
- Now we know that Apple strictly requires that the code running on the iPhone, be signed by a certificate issued by Apple.
- Jailbreaking is the process of actively removing such restrictions and other security controls put in place by the Operating system.
This allows user to;
- Install unapproved apps(apps not signed by a certificate issued by Apple).
- Accessing complete filesystem of iDevice.
Type of Jailbreaking
On a high level, there are two types of jailbreaks:
- Tethered - This is a temporary jailbreak and requires the device to be connected to a computer every time the device needs a restart. The jailbreak is revered otherwise.
- Untethered - This is the more sought after solution, where the device only needs to be connected to the computer at the time of initial jailbreak. Rebooting the device does not reset the jailbreak.

This slide might help you....
- http://www.jailbreak-me.info/
- Jailbreaking iDevice is similar to installing a software. First, you need to check whether there is any jailbreak available for your iDevice that is running the specific version of iOS.
After Jailbreaking you can access Cydia.

iOS Sandbox/Privilege separation
- The sandbox allows better, more granular control, over the actions that processes and applications can perform.
- This is a critical security feature of the iOS, as it ensures that an application cannot get access to another application's private files unless the other application has given explicit permission via tightly controlled APIs.
iOS Sandbox/Privilege separation
- Each application is installed in its own directory, usually located under (private/var/mobile/Applications/{ID}), which acts as the app's home, and is identified with a random ID.
- Once installed, applications have limited read access to some system areas and functions (such as SMS, phone call, call logs etc.), and have no rights in the home directories of other such applications.
Sandbox
- If an application wants to access protected areas, permission for this specific functionality is granted through a pop-up to the user.

Pros & Cons of Jailbreaking
-
Jailbreaking removes any sandboxing put in place by the operating system.
-
By removing the sandbox protection, any app on the device has the potential to read any file on the filesystem, including other application's private files, tokens/cookies stored in plist files or keychain.
-
Jailbreak patches the integrity check, which is responsible for checking apps being installed and thus skips the code signing check(verifying that the app was signed by a certificate issued by Apple).
Pros & Cons of Jailbreaking
-
No need to pay $99 yearly fee for maintaining developer certificate as anyone can publish apps on Cydia for free.
-
Few applications check for signs of a jailbreak during the installation of the app or during normal usage.
-
When a jailbreak is detected, the apps may choose to cease operating, in order to prevent other apps from sniffing out sensitive data from this application.
Setting Up a Testing Environment
Prerequisites
- Jailbroken iPhone/iPad,
- Mac book or iMac with Xcode & iTunes.
Hardware Requirements :
Software Requirements :
- iFunbox or iExplorer
- OpenSSH
- Burpsuite
- IDB
Other useful tools : Otool,Cycript,Class-dump-z,Snoop-it,RET,Clutch,Filezilla - SFTP/Winscp,SQLite browser,Installipa,Veency etc.,
For More Visit : goo.gl/mgJZ6Q
iFunBox
-
Note: Starting iOS version 8.4, Apple has decided to restrict the third-party managers access to the application sandbox.
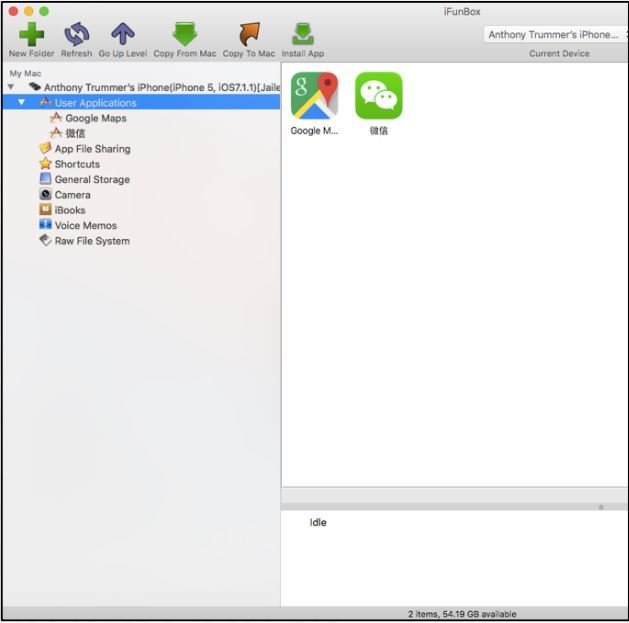
-
This tool allows you to retrieve sandbox files off the device for further inspection. - Available for both Windows & Mac @goo.gl/texZ9d
OpenSSH
-
Note: Starting iOS version 8.4, Apple has decided to restrict the third-party managers access to the application sandbox.
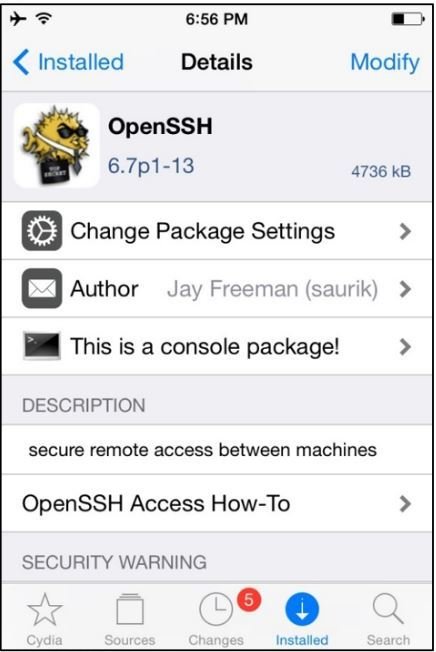
-
This tool is available as an app within the Cydia app store.
-
Once installed on the device, this will allows a user to SSH into the device, inspect the app sandbox & push/pull files on the filesystem etc.,
How to use OpenSSH?
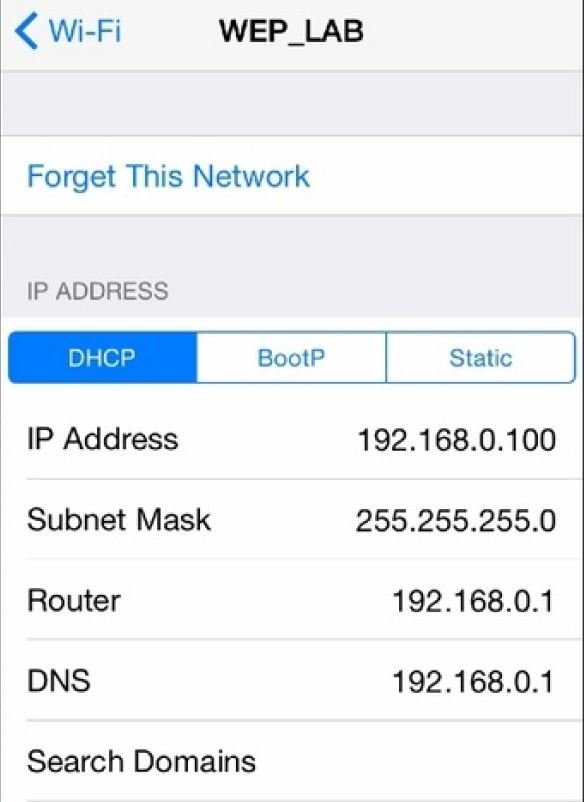
-
Connect the iPhone/iPad to Wi-Fi and check the IP address of the device.
-
Now, from our PC connect to this IP address Over SSH using any SSH Client. -
Default Username : root Password : alpine
Note: Change the default password as anyone in the same WiFi N/W can connect to our device using default credentials.
BurpSuite





Burp Suite is an HTTP proxy tool which comes in handy by inspecting an application's HTTP traffic, flowing through the device.
Burp Suite
- Create a new listening proxy on an interface which other devices can resolve, on the same network.
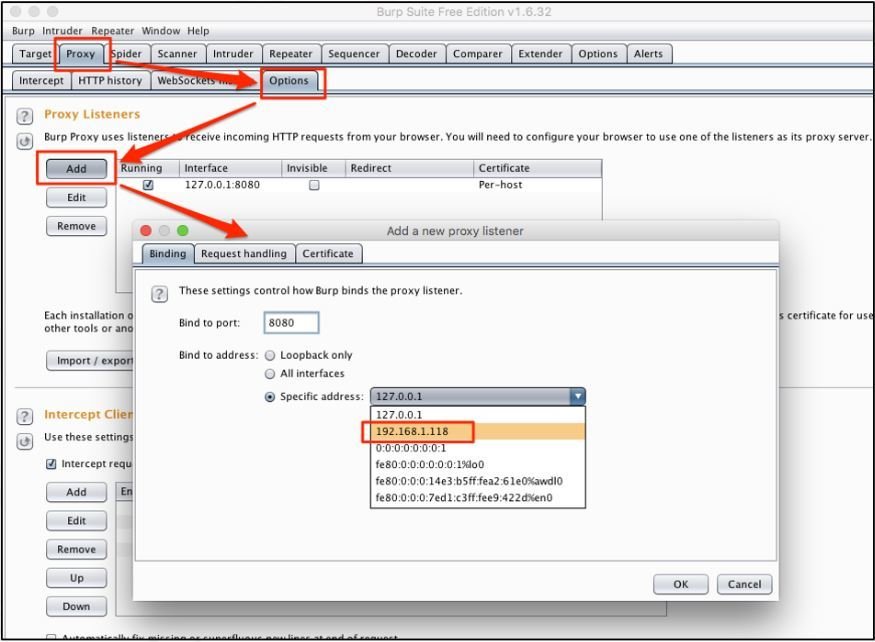
Burp Suite
- Now, configure an iPhone to pass its traffic through this proxy that we just set up.
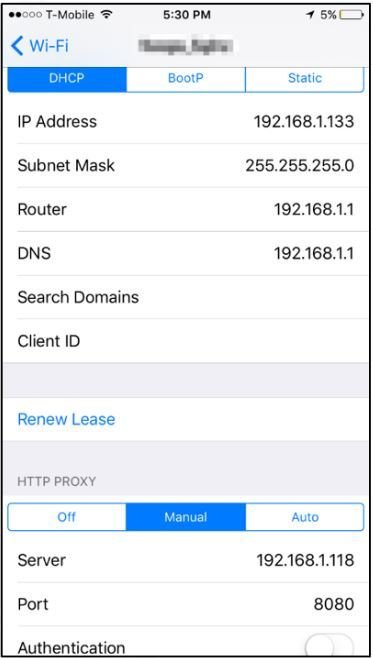
- On the iPhone, navigate to "Settings" > "Wi-Fi" > {select Wi-Fi} and set the HTTP proxy and port with the IP and port of the Burp proxy.
Burp Suite
- Now you will be able to intercept http traffic from device.
- To intercept https traffic we have to install the burp certificate.
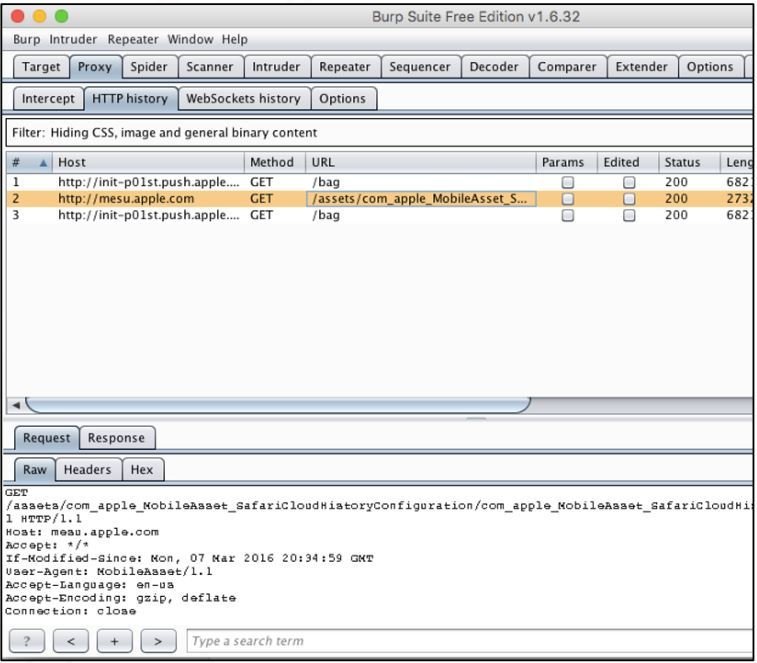
Burp Suite
- In order to add this rootCA to the device's trusted root CA list, navigate to http://burp using Safari on the iPhone.

- Click on "CA Certificate" and proceed with the instructions to install Burp's root CA on the iPhone.
- If you want to delete this certificate go to "Settings" > "General" > "Profile and Device Management" and delete the appropriate configuration profile.
Vulnerable Application to Practice
- Damn Vulnerable iOS App (DVIA): http://damnvulnerableiosapp.com
- ExploitMe Mobile iPhone Labs: http://securitycompass.github.io/iPhoneLabs
- OWASP iGoat: http://code.google.com/p/owasp-igoat
References
Cheat Sheet:
Books:
Testing Guide:
https://www.owasp.org/index.php/IOS_Application_Security_Testing_Cheat_Sheet
- Learning iOS Penetration Testing by Swaroop Yermalkar
- Mobile Application Penetration Testing by Vijay Kumar Velu
https://www.owasp.org/index.php/OWASP_Mobile_Security_Testing_Guide#tab=Main

Any Questions?
