RNN and its Types
- by Ashwin Hegde
Agenda
1. The basic structure of a neuron and neural network.
2. What is RNN?
3. Types of RNN
4. Bidirectional RNN
5. Vanishing Gradients Problem with RNN
Structure of single neuron
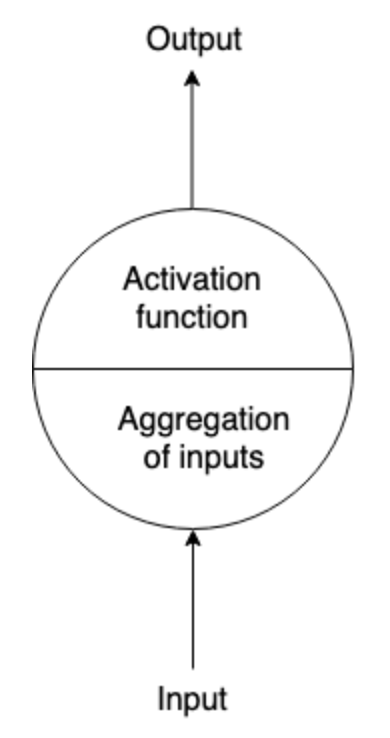
Single Neuron
A neuron using Python
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(x):
# Our activation function: f(x) = 1 / (1 + e^(-x))
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
class Neuron:
def __init__(self, weights, bias):
self.weights = weights
self.bias = bias
def feedforward(self, inputs):
# Weight inputs, add bias, then use the activation function
total = np.dot(self.weights, inputs) + self.bias
return sigmoid(total)
weights = np.array([0, 1]) # w1 = 0, w2 = 1
bias = 4 # b = 4
n = Neuron(weights, bias)
x = np.array([2, 3]) # x1 = 2, x2 = 3
print(n.feedforward(x)) # 0.9990889488055994Structure of neural network
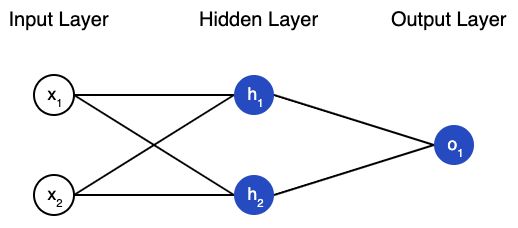
Feed Forward Neural Network
Notes:
1. Cannot remember the things it learns.
2. Pre-determined sizes
What is RNN?
RNN
1. Helps to model memory units (hidden state) that enable to persist data.
2. Context to be able to provide the output based on the input.
3. Next word prediction, music composition, speech recognition, times series and stock market prediction, etc.
4. The idea behind RNN is to connect previous info to the present task.
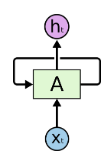
Unroll a Recurrent Neuron throughout time
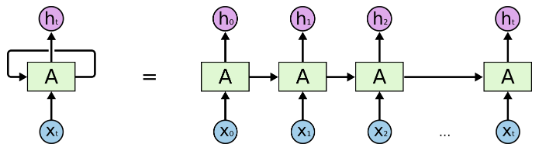
Type of RNN
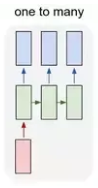
1. One-to-Many
- Single input and sequence of output.
- Eg. Image captioning, etc.
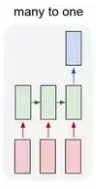
2. Many-to-One
- Sequence of input and single output
- Eg. Sentiment analysis etc.
Type of RNN
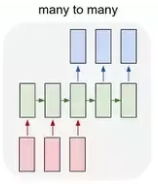
3. Many-to-Many
- Sequence input and sequence output.
- Eg. Machine translation, etc.
Bidirectional RNN
- A model can take into account both the previous as well as the later information of the sequence.
- Eg "Teddy bears are on sale!"
Vanishing Gradients problem with RNN
- Occurs due to a large number of layers, but this comes from the inability of the normal RNN unit to remember old values that appeared early in the sequence.
Eg.
The Cat, which already ate ..., was full.
The Cats, which already ate ..., were full.
Solutions:
1. GRU - Gated Recurrent Unit
2. LSTM - Long Short Term Memory

Find me on
Thank You
Happy Holidays
Merry Christmas & Happy New Year