- Authentication & Password Management
- Token & Session Management
- Authorization & Access Management
Security Considerations

Asjad Saboor
$whoami
- Full-stack JS developer
- Associate Software Architect @ 10pearls
- Betts Recuriting
Agenda
- Authentication vs Authorization
- Authentication methods and security
- Securing User Session & JWT
- Authorization models
Authentication != Authorization

How to do Authentication?
- Password based
- Biometrics
- Passwordless
- 2FA or MFA
- Certificate Based
Best Security Practices

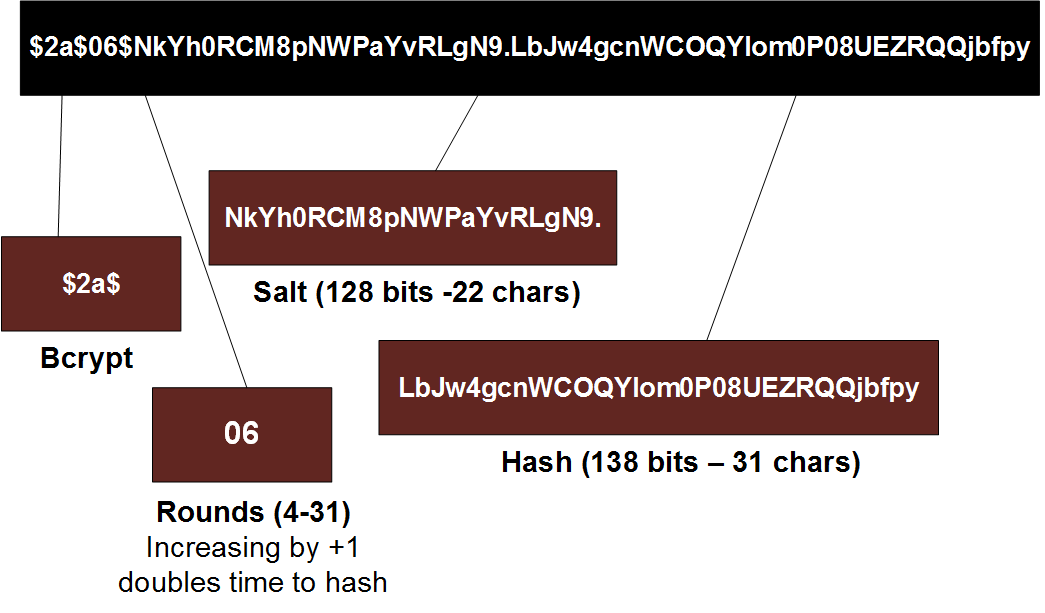
Salting & Hashing Passwords
- No Plain text
- Strongly hashed and salted that cannot be reversed
- Use Bcrypt ,Scrypt, Argon2 and avoid using deprecated algorithms such as md5 or SHA
- Make sure the hashing algo library / version is dont have any open vulnerability.
Why salting is necessary?
- Hashing without salt create same results
- Hashes will become predictable
- Salt is a random string.
- Salt + Plain text = unpredictable hash

bcrypt
Strong Passwords
- Weak passwords with Salt+Hash can still be compromised.
- Ensure Minimum length of password to be 8.
- Ensure complexity (uppercase, lowercase,number,special characters)
- Password rotation.
Stopping Brute-force attacks
- Logging all attempts (IP/Useragent)
- Blocking account / login limits
- Auth Challenge i.e Captcha
- Notifying user of invalid attempts
Error Messages/Codes ?
- Email Not found.
- Password in invalid.
- User is not active.
- Invalid Credentials.
- We have sent you reset password link.
- If your email is registered, you should have received a password reset email.

Forgot/Reset Password
- Show not look like spam or phishing email
- Link Should Expire after use
- Should contain
- password reset link
- Expiry information
- Support contact information
- Images should be public
- Should Not
- secure resources /assets.
- Go to Have
- Who requested the reset(IP/Agent)
Are Passwords
Good enough?

Not for High risk / sensitive application!
MFA or 2FA
- Verifies user’s identities using multiple methods of authentication
- SMS/Email
- Phone Call
- Tokens
Security and usability go hand in hand
- Should not choose between security and usability
- Security should support and enable better business and should not hinder business functioning
- Provide a Variety of Authentication Factors.
- One time pin-code
- Easypaisa Frauds
- Whatsapp scams
- Biometric Fails
- Face ID in the age of Covid.

Reinvent the wheel or use popular identity providers?
Securing Sessions & Token
User Session Recap
- Http is Stateless
- Tracking user interaction with the server
- session is a sequence of network HTTP request and response transactions associated with the same user.
- Stored in cookies
- Session ID - Unique Identifier

Securing User Sessions
- session ID
- should not offer unnecessary details.
- Change default session Id of frameworks.
- Long enough and unpredictable to prevent brute force (128 bytes).
- Always use TLS / HTTPS
- use build-in session management in frameworks
- Only use cookies for session exchange
Securing Cookies

Securing Cookies
- Set Attributes
- secure -prevents MitM
- HttpOnly - prevents XSS
- SameSite: Strict - Prevents CSRF
- Domain
- Expiry / Max-Age
<html>
<body>
<form action="https://vulnerable-website.com/email/change" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" name="email" value="pwned@evil-user.net" />
</form>
<script>
document.forms[0].submit();
</script>
</body>
</html>CSRF attack
JSON Web Token
- A way to exchange authentication information
- Stateless
- Signed(base64 url) - Not encrypted but payload can be(JWE).
- Structure
- Header
- Payload
- Signature

No Built in Token revocation
Storing JWT
Local Storage or Cookies?
Storing JWT
- Local /Session Storage
- XSS attacks
- Short lived
- Cookies
- httpOnly else prone to CSRF attacks
Which one to choose?
Authorization Models
Authorization Models
-
Set of rules that governs
-
what actions some users or Group of users can perform.
-
Who uses what resource,when and in what amounts
-
-
Defined by Business needs / Requirements.
-
ACL, RBAC, ABAC ...
-
Ideal to follow the principle of least privilege.
-
Adopt zero-trust security model.
-
Check on every request at back-end.
Access Control Levels
- Enforce multiple levels of authentication
- Specific IP / Location
- Domain / Business / Service / Data layer
- Database
- In Short - each layer should have some security measures in place.
ACL
- Simplest model - gatekeeper
- Security is tied to an individual.
- List of users with simple yes/no permissions.
- Each user can have list of some permissions
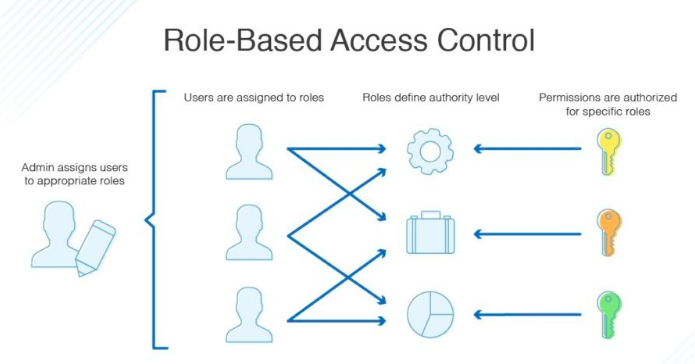
RBAC
- More granular control than ACL
- Based on roles in Business / Organizations
- Manager, Director, Team Lead
- All permissions are assigned via Roles.
- Standard for Most business applications.
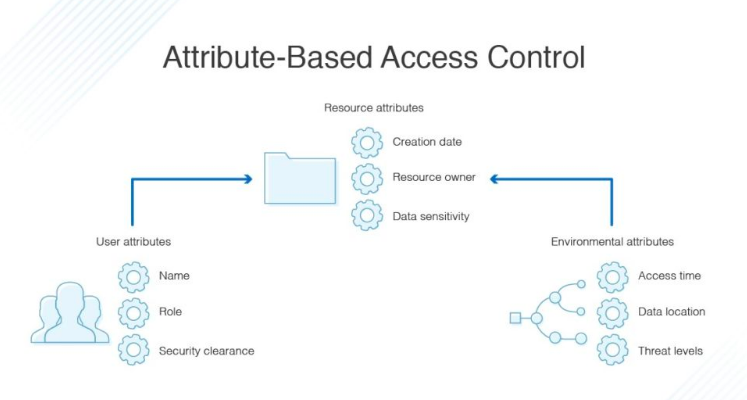
ABAC
- More Fine grained than RBAC
- Provides access based on user, environment and resource attributes.
- User Attributes: role / organization /security Clearance
- Environment: time of access, location, type of data
- Resource: owner, creation date