Version Control
Dylan Gregersen
What is version control?
Version control is a system for tracking changes to a file or files over time

Something we've probably all done in one form or another

Versioning Concepts: Tracking
If you're a version jedi:
In version control, helps to by having a system to keep track of the changes


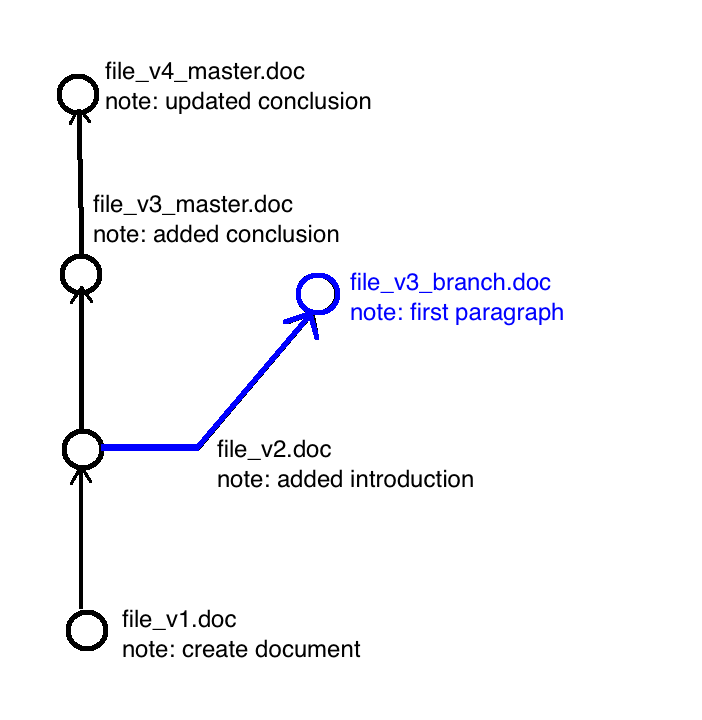
Versioning Concepts: Branching
If you're a version
jedi master:
Branching when you make two different changes to the same committed version
This happens especially if you have multiple people working on a document(s)

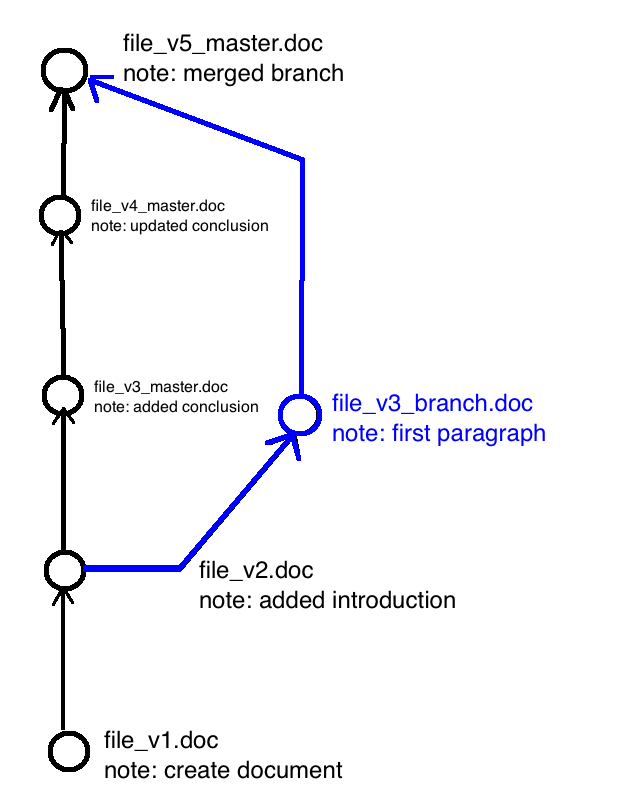
Versioning Concepts: Merging
When you've branched you'll eventually want to merge again
Some changes are easy to merge
Generally merging requires you to make decisions about what changes to keep
Programs help with versioning
Software both enterprise and open source provide tools for version control sometimes called document management software
Git is a computer program which provides version control to files


Git is NOT GitHub which is a web service that hosts/stores projects tracked by git and provides tools to manage those projects.
As developers we use git to track our code changes and we host a main repository on github
We have separate branches called develop and master which contain the primary divisions between our code


+
Git basics
Interactive time! Open a terminal, navigate to the git_an_adventure directory
git status -- current status of repository
git log -- log of changes
git show -- show changes for a particular commit

Git Structure
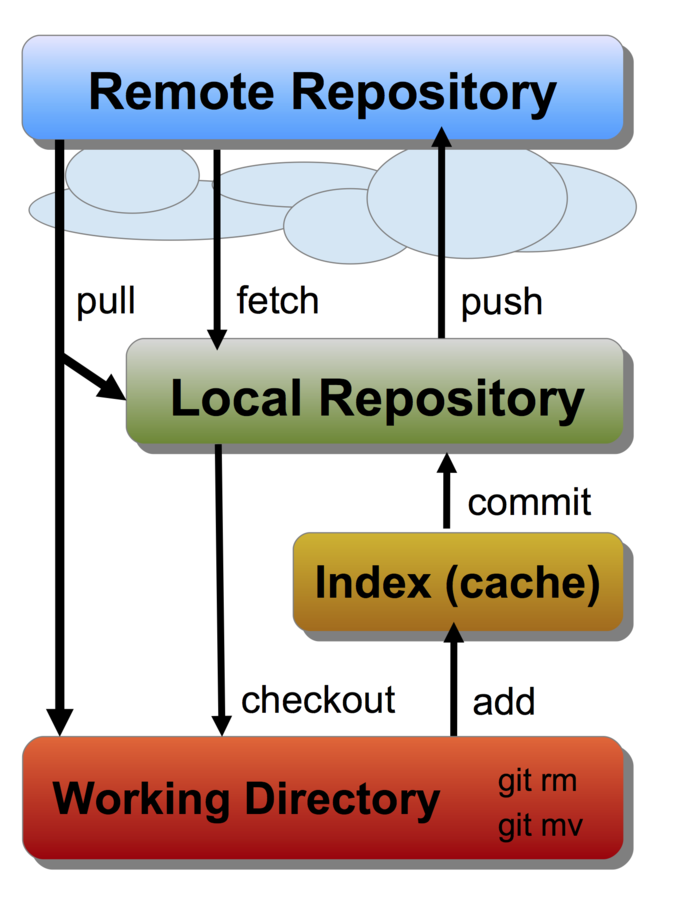
Git is distributed with many copies of your repository
Local repository lives on your computer and the working directory contains the current files
Remote repository might be stored on github
Git Flow

Primary flow for file changes:
1) edit a file
2) git add the changes
3) git commit the changes
4) git pull remote changes
5) merge (sometimes)
6) git push local changes

Git Checkout

Revert back to previous changes
git log
git checkout <commit>
git checkout -b <new_branch>
git checkout <old branch>

Git Flow : Jedi Version

Primary flow for file changes:
1) from clean branch git checkout -b <new branch>
2) edit file
3) git add, git commit
4) git branch to switch back
5) git merge
6) git pull, merge, git push

Git Flow : Merging

The most complicated part is merging changes together
git merge <other_branch>
git diff
git mergetool

Git Flow : Forking

git remote
git remote add
git pull <local> <branch>

Primary Repo
fork
Pull Request
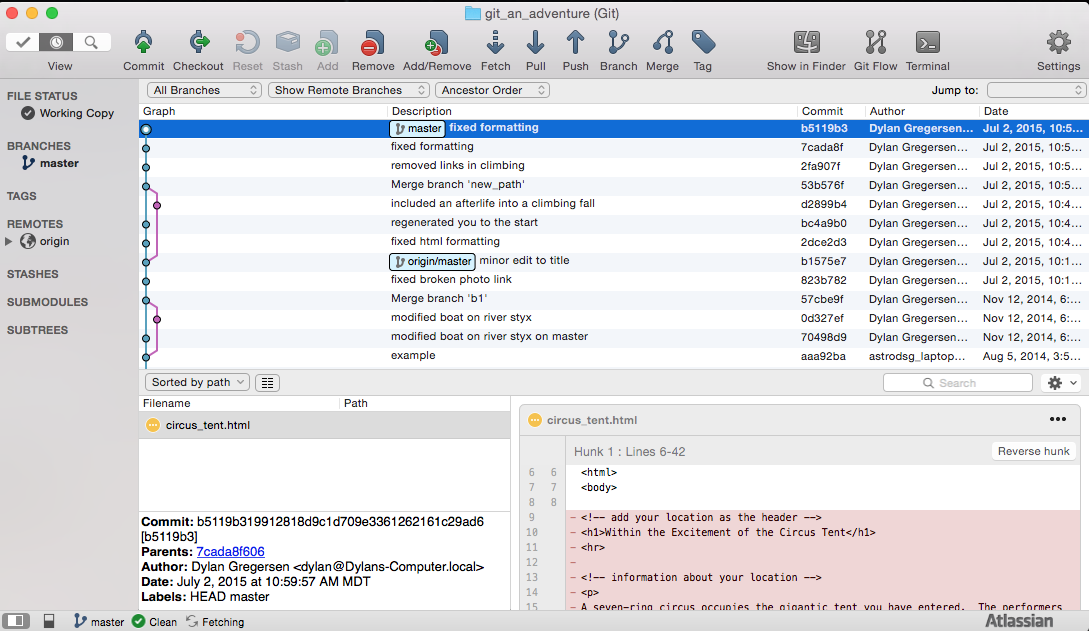
GUI Tools
Tools exist to help you with git pushes, pulls, comparisons, merges, etc.

Git GO!

git status
git checkout -b <new_branch>
edit file <file.html>
git add <file.html>
git commit -m "<message>"
git branch <old_branch>
git merge <new_branch>
git pull
merge if necessary
git push
