Intro to
Angular


We expect cooperation from all participants to help ensure a safe environment for everybody.
We treat everyone with respect, we refrain from using offensive language and imagery, and we encourage to report any derogatory or offensive behavior to a member of the JSLeague community.
We provide a fantastic environment for everyone to learn and share skills regardless of gender, gender identity and expression, age, sexual orientation, disability, physical appearance, body size, race, ethnicity, religion (or lack thereof), or technology choices.
We value your attendance and your participation in the JSLeague community and expect everyone to accord to the community Code of Conduct at all JSLeague workshops and other events.

Code of conduct

Whoami
Alexandru Albu
Trainer @JSLeague

frontend engineer @10yo
design: photoshop, illustrator
development: javascript. python, sql, mongo
devops: docker
and gaming and basketball

Overview
Intro to Angular

Intro to Angular
Agenda
Components & Modules
Services
Observables
Requests
Routing
Forms
Testing

Components &
Modules
Intro to Angular

Services
Intro to Angular

Observables
Intro to Angular

Intro to Angular

System complexity

Intro to Angular
Product
Vendor
Cart
Invoice
Sale
Coupon
User profile
Payment

Intro to Angular
Cart
Invoice
Add product...
...update the total

Intro to Angular
Cart
Invoice
Proactive
Passive
import { Invoice } from './invoice';
class Cart {
constructor(invoice: Invoice){ ... }
addProduct(product) {
...
this.invoice.update(product); // needs to be public
...
}
}

Intro to Angular
Cart
Invoice
Listenable
Reactive
import { Cart } from './cart';
class Invoice {
constructor(cart: Cart){ ... }
init() {
...
this.cart.onCartChange( callback )
}
}

Intro to Angular
Cart
Invoice
Sale
Coupon
Payment
Passive programming
- remote setters and updates
- What does it affect? - look inside
- How does it work? - find usage

Intro to Angular
Cart
Invoice
Sale
Coupon
Payment
Reactive programming
- events, observation and self updates
- What does it affect? - find usages of events
- How does it work? - look inside

Intro to Angular


Intro to Angular

Intro to Angular
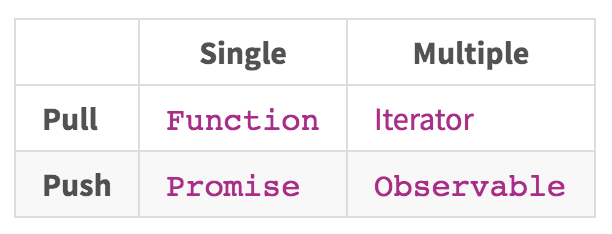
Observables

- A stream of data ( 0 or more values of any type)
- Pushed over any amount of time (can end, but not necessarily)
- Cancelable ( can be stopped from emitting a value - unsubscribed)
- Lazy - won't emit values until we subscribe to them

Intro to Angular
Iterator pattern


Intro to Angular
Observer pattern


Intro to Angular
Async with callbacks?
getData(
function(successResult) {
// do something with the data
},
function(faliureError) {
// handle the error
},
);
Intro to Angular


Intro to Angular
Request with promise
let result = fetch('api/users.json');
// what we think it is
result
.then(success => {
// handle success
})
.catch(error => {
// handle error
})
// what it actually is
result
.then(...)
.then(...)
.then(...)
Intro to Angular
Async / await
function asyncTask(i) {
return new Promise(resolve => resolve(i + 1));
}
async function runAsyncTasks() {
const res1 = await asyncTask(0);
const res2 = await asyncTask(res1);
const res3 = await asyncTask(res2);
return "Everything done"
}
runAsyncTasks().then(result => console.log(result));
Intro to Angular
Observables
Unifying callbacks, promises and event handlers.
Shape of an observable:
- A function
- accepts an observer ( an object with `next`, `error` and `complete` methods on it)
- returns a cancellation function

Intro to Angular
Observable with rxJS
let observable$ = new Observable(() => {
})Observable
- read-only - consumer
- plain function
- exposes 3 channels: next, error and complete

Intro to Angular
Observable with rxJS
let observable$ = new Observable(observer => {
observer.next(1);
observer.next(2);
})Observer
- write-only - producer
- instance passed to observable
- provide next, error and complete methods
- just an interface

Intro to Angular
Observable with rxJS
let observable$ = new Observable(observer => {
observer.next(1);
observer.next(2);
})
observable$.subscribe(value => {
console.log(value)
}Subscription
- triggers the observable execution
- returns an unsubscribe() method that stops the observable

Intro to Angular
let observable$ = new Observable(observer => {
observer.next(1);
observer.next(2);
return () => {
// cleanup resources when done
};
})
const subscription = observable$.subscribe(value => {
console.log(value)
})
subscription.unsubscribe(); // stop emitting values
Intro to Angular
Other ways to create observables
Creation functions
-
of (value1, value2, value3)
-
from(promise/itterable/observable)
-
fromEvent(target, eventName)
-
interval(time)
-
timer(time)

Intro to Angular
HOT vs COLD observables
COLD is when your observable creates the producer
- producer is created and activated during subscription
- unicast => everyone gets their own instance
- observables are "cold" by default
// COLD
var cold = new Observable((observer) => {
var producer = new Producer();
// have observer listen to producer here
});
Intro to Angular
HOT vs COLD observables
HOT is when your observable closes over the produce
- producer is created and activated outside and independent of subscription
- multicast => shared reference to the producer
// HOT
var producer = new Producer();
var cold = new Observable((observer) => {
// have observer listen to producer here
});
Intro to Angular
Subjects
Observables are unicast - each subscriber manages its own execution context
Subjects are multicast observables - values are multicasted to many Observers
Types of subjects
- BehaviorSubject - has the notion of "current value"
- ReplaySubject - can record part of it's execution

Intro to Angular


Intro to Angular
Operators
Observables are collections of pushed values or events that we can:
- query (filter)
- transform (map)
- accumulate (reduce)
- join
- flatten
- more...

Intro to Angular
let array = [1,2,3,4,5];
array
.map(v => v * v)
.filter(v => v > 5 && v < 20)
.reduce((acc, curr) => acc + curr, 0)
// 25Array functions

Intro to Angular
let observable$ = from([1,2,3,4,5]);
observable$
.pipe(
map(v => v * v),
filter(v => v > 5 && v < 20),
reduce((acc, curr) => acc + curr, 0)
)
.subscribe(val => console.log(val))
// 25Observable operators

Intro to Angular
const buttonObs$ = fromEvent(querySelector('button'), 'click');
// anti-pattern
buttonObs$.subscribe(() => {
http$.get('/api/users').subscribe( data => {
// handle loaded data
})
})
// better
buttonObs$.pipe(
concatMap(
event => http$.get('/api/users')
)
).subscribe(data => {
// handle loaded data
})Higher-order observables
Higher-order operators:
- concatMap
- switchMap
- mergeMap

Intro to Angular
// when stream completes
const obs$ = new Observable(observer => {
observer.closed; // false
observer.next(1); // emit 1
observer.complete();
observer.closed; // true
observer.next(2); // won't emit
});Error handling

Intro to Angular
// streams error only once
const obs$ = new Observable(observer => {
observer.closed; // false
observer.next(1); // emit 1
observer.error(new Error('Bad!'));
observer.closed; // true
observer.next(2); // won't emit
});
obs$
.subscribe({
next: v => console.log(v),
error: e => console.log(e.message)
});Error handling

Intro to Angular
// intercepting errors
const obs$ = new Observable(observer => {
observer.next(1);
observer.error(new Error('BANG!'));
}).pipe(
catchError(err => {
console.log('Intercepted error:' + err);
return of('I got this');
})
)
obs$.subscribe(v => console.log(v));
// 1 'I got this'Error handling

Intro to Angular
// recovering from an error with retry operator
const getData$ = http.get('/api/users')
.pipe(
retry(3),
catchError(() => of('Something went wrong');
)
getData$.subscribe(value => console.log(value));Error handling

Requests
Intro to Angular

Routing
Intro to Angular

Forms
Intro to Angular

Testing
Intro to Angular

Intro to Angular
Automated testing

Intro to Angular
Why do we (automatically) test?
-
Documented Intentions
-
Improved Design
-
Fewer Bugs into Production
-
No Regressions
-
Safer Refactoring

Intro to Angular
Tools
-
Test frameworks - where you write your test
-
Jasmine, Mocha, Tape
-
-
Test environment - where your tests are executed
-
browsers - Chrome, Firefox, etc
-
headless browsers - JSDom, PhantomJS, Puppeteer
-
-
Test runners - where you run your tests
-
Karma, Jest
-

Intro to Angular
Jasmine
-
A behavior-driven development framework for testing JavaScript code.
-
Create hierarchical suites of test - describe(‘', function)
-
The tests are written as specifications - it('', function)
-
Expectations and Matchers (built-in and custom) - expect(x).toBe(expected)
-
Spies - a test double pattern
-
Asynchronous operations support

Intro to Angular
Jasmine - a basic example
describe("A resource",() => {
const resource;
// runs before each test - good for initializing data
beforeEach(() => {
resource = new Resource();
resource.allocateSpace();
});
// runs after each test - good for cleanup
afterEach(() => {
resource.free();
});
// test
it("should have allocated 100 units of space",() => {
expect(resource.space).toEqual(100);
});
});
Intro to Angular
Jasmine - Matching functions
- not
- toBe
- toEqual
- toMatch
- toBeDefined
- toBeUndefined
- toBeNull
- toBeTruthy
- toBeFalsy
- toContain
- toBeLessThan
- toBeGreaterThan
- toBeCloseTo
- toThrow

Intro to Angular
Jasmine - Spies
// example.ts
class Person {
helloSomeone(toGreet) {
return `${this.sayHello()} ${toGreet}`;
};
sayHello() {
return 'Hello';
};
}
// example.spec.ts
describe('A Person', () => {
let fakePerson;
beforeEach( () => {fakePerson = new Person();})
it('should call the sayHello() function', () => {
spyOn(fakePerson, 'sayHello');
fakePerson.helloSomeone('world');
expect(fakePerson.sayHello).toHaveBeenCalled();
});
it('should greet the world', () => {
spyOn(fakePerson, 'helloSomeone');
fakePerson.helloSomeone('world');
expect(fakePerson.helloSomeone).toHaveBeenCalledWith('world')
});
});
Intro to Angular
Jasmine - Spies
// Actually calling the method
spyOn(fakePerson, 'sayHello').and.callThrough();
// Set a return value for a call
spyOn(fakePerson, 'sayHello').and.returnValue('Hello World');
// Set a return value for a call
spyOn(fakePerson, 'sayHello').and.returnValue('Hello World');
// Call a different function
spyOn(fakePerson, 'sayHello').and.callFake(
(arguments, can, be, received) => ...);
// Get number of calls
spyOn(fakePerson, 'sayHello')
expect(fakePerson.sayHello.calls.count()).toBe(3)
fakePerson.sayHello.calls.reset() // reset the counts
// Create a "bare" spy
spy = jasmine.createSpy('whatAmI');
expect(spy).toHaveBeenCalled();
// Create a spy object
tape = jasmine.createSpyObj('tape', ['play', 'pause', 'stop', 'rewind']);
Intro to Angular
Jasmine - async tests
describe('Asynchronous specs', () => {
let value;
beforeEach(() => {
value = 0;
});
it('should support async execution', done => {
setTimeout(() => {
value++;
expect(value).toBeGreaterThan(0);
done();
}, 1000);
});
});
Intro to Angular
Karma
- JavaScript test runner that integrates with a browser environment
- Created by the AngularJS team
- Configuration file to set:
- browser launchers
- test framework
- reporters
- preprocessors

Intro to Angular
Writing (good) tests

Intro to Angular
-
Arrange all necessary preconditions and inputs.
-
Act on the object or method under test.
-
Assert that the expected results have occurred.
Structuring tests

Intro to Angular
DRY vs DAMP
RULES
- Repeat yourself if necessary to make it easier to read
- A test should be a complete story, all within the it()
- You shouldn’t need to look around much to understand the test
- Minimize logic out of tests (what will test the tests?)
TECHNIQUES
- Remove less interesting setup to beforeEach()
- Keep critical setup within the it()
- Include all of the "Act" and "Assert" test parts are in the it() clause

Intro to Angular
DRY Test
describe("Hero Detail Component", function() {
var heroDetCmp;
beforeEach(function() {
heroDetCmp = createComponent();
heroDetCmp.ngOnInit();
});
describe('ngOninit' function() {
it("should set the hero", function() {
expect(heroDetCmp.hero).toBeDefined()
});
it("should set the heroId", function() {
expect(heroDetCmp.heroId).toBe(3));
});
});
});

Intro to Angular
DAMP Test
describe("Hero Detail Component", function() {
var heroDetCmp;
beforeEach(function() {
heroDetCmp = createComponent();
});
describe('ngOninit' function() {
it("should set the hero", function() {
heroDetCmp.ngOnInit();
expect(heroDetCmp.hero).toBeDefined()
});
it("should set the heroId", function() {
heroDetCmp.ngOnInit();
expect(heroDetCmp.heroId).toBe(3));
});
});
});

Intro to Angular
DRY vs DAMP


Intro to Angular
-
Isolated tests: only the class, mocking everything
-
Integration tests: compiling components and using the injector
-
Shallow: mock out related components
-
Deep: include all components
-
How much testing?

Intro to Angular
Angular Testing

Intro to Angular
Utilities
-
TestBed - a harness for compiling components
-
inject() - provides access to injectables
-
waitForAsync() & fakeAsync() - async Zone control

Intro to Angular
TestBed
// component.spec
describe('Testing GreetComponent', () => {
let component: GreetComponent;
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [ HeroComponent ],
imports: [ ... ],
providers: [ ... ],
schemas: [ ... ]
});
});
});TestBed configures a temporary NgModule for testing

Intro to Angular
TestBed
// component.spec
describe('Testing GreetComponent', () => {
let component: GreetComponent;
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({...});
TestBed.overrideComponent(GreetComponent, {
set: {
template: '<div>Overridden template here</div>'
// ...
}
});
});
});TestBed configurations can be overriden

Intro to Angular
Component fixture
// component.spec
describe('Testing GreetComponent', () => {
let component: GreetComponent;
let fixture: ComponentFixture<GreetComponent>;
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({...});
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(GreetComponent);
});
});- creates an instance of the component to test
-
returns a component fixture
- access to the component instance
- access to Native DOM Element
- control Change Detection
- closes current TestBed configurations

Intro to Angular
Component fixture methods
Access to the component, its DOM and change detection
-
componentInstance - the instance of the component created by TestBed
-
debugElement - provides insight into the component and its DOM element
-
nativeElement - the native DOM element at the root of the component
-
detectChanges() - trigger a change detection cycle for the component
-
whenStable() - returns a promise that resolves when the fixture is stable

Intro to Angular
Change detection
describe('Testing message state in greet.component', () => {
beforeEach(...)
it('should display original greet', () => {
fixture.detectChanges();
expect(element.textContent).toContain(component.message);
});
})- tells Angular to perform change detection
- TestBed.createComponent() does not trigger change detection

Intro to Angular
Change detection - automatically
import { ComponentFixtureAutoDetect } from '@angular/core/testing';
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
providers: [
{ provide: ComponentFixtureAutoDetect, useValue: true }
]
})Configure automatic change detection

Intro to Angular
Debug Element
Insights into the component's DOM representation
-
parent / children - the immediate parent or children of this DebugElement
-
query(predicate) - search for one descendant that matches
-
queryAll(predicate) - search for many descendants that match
-
injector - this component's injector
-
listeners - this callback handlers for this component's events and @Outputs
-
triggerEventHandler(listener) - trigger an event or @Output

Intro to Angular
Query the DOM
-
nativeElement provides:
-
querySelector(cssSelector)
-
-
debugElement provides:
-
query(predicate)
-
queryAll(predicate)
-
-
predicates can be created by helpers:
-
By.css(selector)
-
By.directive(DirectiveType)
-

Intro to Angular
Interacting with the DOM
-
nativeElement - can't use outside the browser
- dispatchEvent
- textContent
-
debugElement - doesn't have access to textContent
- triggerEventHandler
- properties
- attributes
- classes
- styles

Intro to Angular
Dependency Injection
let heroService;
beforeEach(() => {
heroService = TestBed.inject(HeroService);
}));
- Gets services from the root injector
- Can be placed in beforeEach or it blocks:

Intro to Angular
Isolated Tests

Intro to Angular
// example.component
@Component({
template: `
<h1>{{message}}</h1>
<button (click)="clearMessage">Clear</button>
`
})
export class GreetComponent {
public message = '';
constructor() {}
setMessage(newMessage: string) {
this.message = newMessage;
}
clearMessage() {
this.message = '';
}
}// Component

Intro to Angular
// example.sec
import {GreetComponent} from './greet.component';
describe('Testing message state in greet.component', () => {
let greetComponent: GreetComponent;
beforeEach(() => {
greetComponent = new GreetComponent();
});
it('should set new message', () => {
greetComponent.setMessage('Testing');
expect(greetComponent.message).toBe('Testing');
});
it('should clear message', () => {
greetComponent.clearMessage();
expect(greetComponent.message).toBe('');
});
});// Test

Intro to Angular
Deep Integration Tests

Intro to Angular
Deep component testing
- Nested Components need to be tested too
- Shallow testing (mocking all children) is not enough
- Deep tests check that
- the parent is rendering the children correctly
- the child is receiving the correct values in its inputs
- the parent handles output events correctly

Intro to Angular
Accessing child components
// Search for instances of the child component
movieElements = fixture.debugElement.queryAll(By.directive(MovieItemComponent));
// Check the value of @Input properties on the child component
expect(movieElements[0].componentInstance.movie).toBe(MOVIES[0]);
// Trigger @Output bindings
movieElements[0].triggerEventHandler('delete', null); 
Intro to Angular
Testing @Input and @Output
@Component({
selector: 'greet-message',
template: `<div class="greet">
{{message}}
<button (click)="handleClick()">LIKE</button>
</div>`
})
export class GreetComponent {
@Input() message: string;
@Output() onLiked = new EventEmitter<string>();
handleClick() {
this.onLiked.emit(this.message);
}
}-
Goal - Test if inputs and outputs work correctly
-
Approaches
-
test as a standalone component
-
test inside a container component
-

Intro to Angular
Testing @Input
it('should display greeting', () => {
expect(greetElementText.nativeElement.textContent).toBe(expectedMessage);
});set a value to the input property on the component object

Intro to Angular
Testing @Output
it('should raise selected event when clicked', () => {
let likedMessage: string;
component.onLiked.subscribe((message: string) => {
likedMessage = message;
});
greetElementButton.triggerEventHandler('click', null);
expect(likedMessage).toBe(expectedMessage);
});subscribe to EventEmitter, trigger click event

Intro to Angular
Testing in Host Component
@Component({
template: `
<greet-message [message]="greet" (onLiked)="handleLike($event)">
</greet-message>
`,
})
class TestHostComponent {
greet = 'Wassuuuup?!?';
handleLike(message: string) {
this.greet = 'New greet';
}
}create an on the fly component to test the target component

Intro to Angular
Testing in Host Component
describe('Test input/output for components', () => {
let fixture: ComponentFixture<TestHostComponent>;
let testHost: TestHostComponent;
let greetElementText: DebugElement;
let greetElementButton: DebugElement;
beforeEach(
waitForAsync(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [GreetComponent, TestHostComponent],
}).compileComponents();
}),
);
beforeEach(() => {
fixture = TestBed.createComponent(TestHostComponent);
testHost = fixture.componentInstance;
greetElementText = fixture.debugElement.query(By.css('.greet span'));
greetElementButton = fixture.debugElement.query(By.css('.greet button'));
fixture.detectChanges();
});
...
});
Intro to Angular
Testing with Dependencies

Intro to Angular
Testing a service
import {Component} from '@angular/core';
import {UserService} from './user.service';
@Component({
selector: 'greet-message',
template: '<h1>{{message}}</h1>'
})
export class GreetComponent {
public message = 'Hello';
constructor(private userService: UserService) { }
ngOnInit(): void {
this.message = this.userService.isLoggedIn ?
'Welcome, ' + this.userService.user.name :
'Please log in.';
}
}
Intro to Angular
Testing a service
// service stub
userServiceStub = {
isLoggedIn: true,
user: { name: 'Test User'}
};
// configure stub
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
declarations: [ WelcomeComponent ],
// providers: [ UserService ]
providers: [{
provide: UserService,
useValue: userServiceStub
}]
});
// use service from injector
userService = TestBed.inject(UserService);

Intro to Angular
Mocking HTTP

Intro to Angular
Mocking HTTP
describe('HttpClient testing', () => {
let httpTestingController: HttpTestingController;
beforeEach(() => {
TestBed.configureTestingModule({
imports: [ HttpClientTestingModule ]
});
httpTestingController = TestBed.inject(HttpTestingController);
});
});-
HttpClientTestingModule - don't use the regular HttpClientModule
-
HttpTestingController - used to control the HTTP calls

Intro to Angular
Mocking HTTP
it('should get the proper todo\'s', () => {
const testData: Data = [{todo: 'Test Data'}];
// when call is made, observable emits
component.todos$.subscribe(data =>
expect(data).toEqual(testData)
);
// Match request URL's
const req = httpTestingController.expectOne('/data');
// Assert request method
expect(req.request.method).toEqual('GET');
// respond with mock data
req.flush(testData);
// make sure no outstanding calls
httpTestingController.verify();
});
Intro to Angular
Async Unit Tests

Intro to Angular
Zone.js
Intercepts and tracks asynchronous callbacks
- Intercept asynchronous task scheduling
- Wrap callbacks for error-handling and zone tracking across async operations.
- Provide a way to attach data to zones
- Provide a context specific last frame error handling
Configured by rules (or specs)
- AsyncTestZoneSpec - rules for async test zones
- FakeAsyncTestZoneSpec - rules for fake async test zones

Intro to Angular
Component with Async depedencies
@Component({
selector: 'greet-message',
template: '<h1>{{message}}</h1>'
})
export class GreetComponent {
public message = 'Hello';
constructor(private greetingsService: GreetingsService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.greetingsService.getGreets()
.then(greets => this.message = greets[0]);
}
}
Intro to Angular
Component with Async dependencies
it('should show message (async)',
waitForAsync(() => {
fixture.detectChanges();
fixture.whenStable().then(() => {
fixture.detectChanges();
expect(element.textContent)
.toBe(testGreetings[0]);
});
}),
);
it('should show message (fakeAsync)',
fakeAsync(() => {
fixture.detectChanges();
tick();
fixture.detectChanges();
expect(element.textContent)
.toBe(testGreetings[0]);
}),
);
Q&A
Intro to Angular
Thank you!
