JavaScript
Basics


We expect cooperation from all participants to help ensure a safe environment for everybody.
We treat everyone with respect, we refrain from using offensive language and imagery, and we encourage to report any derogatory or offensive behavior to a member of the JSLeague community.
We provide a fantastic environment for everyone to learn and share skills regardless of gender, gender identity and expression, age, sexual orientation, disability, physical appearance, body size, race, ethnicity, religion (or lack thereof), or technology choices.
We value your attendance and your participation in the JSLeague community and expect everyone to accord to the community Code of Conduct at all JSLeague workshops and other events.

Code of conduct

Whoami
Alexandru Albu
Trainer @JSLeague

frontend engineer @10yo
design: photoshop, illustrator, adobe xd, figma
development: javascript. python, sql, mongo
devops: docker
and gaming and basketball

Overview
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
Agenda
// Week 1
Overview of Web Technologies
Hello, JavaScript!
Comments
Variables
Data Types
Operators
Statements
Iterators
Functions

JavaScript Basics
Agenda
// Week 2
Closures
Browser & DOM Events
Forms
Server Requests
From ES5 to ESNEXT
Error Handing

JavaScript Basics
Agenda
// Week 3
Developer tools
Cross browser tools
DOM panel
Monitoring Events
Functions panel
Network panel
Performance panel
Data panel

Overview of Web Technologies
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics


JavaScript Basics
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
JavaScript Basics


JavaScript Basics
h1 {
font-size: 60px;
text-align: center;
}
p, li {
font-size: 16px;
line-height: 2;
letter-spacing: 1px;
}
JavaScript Basics


JavaScript Basics
let myImage = document.querySelector('img');
myImage.onclick = function() {
let mySrc = myImage.getAttribute('src');
if(mySrc === 'images/icon.png') {
myImage.setAttribute('src','images/icon2.png');
} else {
myImage.setAttribute('src','images/icon.png');
}
}
JavaScript Basics
IDEs
(Integrated Development Environment)



Hello, JavaScript!
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
JavaScript's purpose is
to make web pages dynamic

JavaScript Basics
What?
lightweight
programming
language
object oriented
interpreted
prototype
based
dynamic
functional

JavaScript Basics
Using JavaScript in HTML as:
- inline
- infile
- external

JavaScript Basics
// inline
<body>
<button onclick="
function doSomething() { /* code goes here */ };
doSomething()
">
Click me!
</button>
</body>Inline

JavaScript Basics
// infile
// index.html
<body>
<button onclick="doSomething()">
Click me!
</button>
<script>
function doSomething() { /* code goes here */ }
</script>
</body>Infile

JavaScript Basics
// external
// index.html
<body>
<button onclick="doSomething()">
Click me!
</button>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</body>
// script.js
function doSomething() { /* code goes here */ }External

JavaScript Basics
Coding styles


Comments
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
Comments are text we put in our code that doesn't get executed

JavaScript Basics
// This is a single line comment
function doSomething() {
return true;
}
// We can add code between single line comments
var value = 2; // Or even add comments at the end of a line
// A comment
// can be added after another comment
// but this is not really a multiline commentSingle line comments

JavaScript Basics
/**
* This is a proper multi line comment
*
* We can have blank lines in the comment
* but we can't have code inside a multi line comment
*/
function doSomethingElse() {
}
var test = /* some comment goes here */ 2;Multi line comments

Variables
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
Declaration
var

JavaScript Basics
Naming
camelCase
PascalCase
_camelCase
_PascalCase
public
private

JavaScript Basics
Scope
global
local
var global = "This is a global var";
function doSomething() {
var local = "This is a local var";
}
Data Types
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
primitive types
vs.
object types

JavaScript Basics
primitive types
number
string
boolean
undefined
null
object
typeof

JavaScript Basics
var number = 5; // typeof number === 'number'
var value; // typeof value === 'undefined';
var dictioary = {
"word": "description"
} // typeof dictionary
var list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ...]; // typeof list
JavaScript Basics
Conversion
- "" + 1 + 0
- "" - 1 + 0
- true + false
- 6 / "3"
- "2" * "3"
- 4 + 5 + "px"
- "$" + 4 + 5
- "4" - 2
- "4px" - 2
- 7 / 0
- " -9 " + 5
- " -9 " - 5
- null + 1
- undefined + 1

JavaScript Basics
object types
Number
String
Boolean
Math
Date
RegExp
instanceof

JavaScript Basics
object types
Object
Array
JSON
instanceof

JavaScript Basics
// example 1
var number = Number(5);
typeof number // 'number'
number instanceof Number // false
// example 2
var number2 = new Number(5);
typeof number2 // 'object'
number2 instanceof Number // true
JavaScript Basics
Number object properties
| MAX_VALUE | The largest possible value a number in JavaScript can have 1.7976931348623157E+308 |
| MIN_VALUE | The smallest possible value a number in JavaScript can have 5E-324 |
| NaN | Equal to a value that is not a number. |
| NEGATIVE_INFINITY | A value that is less than MIN_VALUE. |
| POSITIVE_INFINITY | A value that is greater than MAX_VALUE |

JavaScript Basics
Number object methods
| toExponential() | Forces a number to display in exponential notation, even if the number is in the range in which JavaScript normally uses standard notation. |
| toFixed() | Formats a number with a specific number of digits to the right of the decimal. |
| toLocaleString() | Returns a string value version of the current number in a format that may vary according to a browser's local settings. |
| toPrecision() | Defines how many total digits (including digits to the left and right of the decimal) to display of a number. |
| toString() | Returns the string representation of the number's value. |

JavaScript Basics
String object properties
| length | Returns the length of the string. |

JavaScript Basics
String object methods
| charAt() | Returns the character at the specified index. |
| concat() | Combines the text of two strings and returns a new string. |
| indexOf() | Returns the index within the calling String object of the first occurrence of the specified value, or -1 if not found. |
| match() | Used to match a regular expression against a string. |
| replace() | Used to find a match between a regular expression and a string, and to replace the matched substring with a new substring. |
| search() | Executes the search for a match between a regular expression and a specified string. |

JavaScript Basics
String object methods (cont.)
| slice() | Extracts a section of a string and returns a new string. |
| split() | Splits a String object into an array of strings by separating the string into substrings. |
| substr() | Returns the characters in a string beginning at the specified location through the specified number of characters. |
| substring() | Returns the characters in a string between two indexes into the string. |
| toLowerCase() | Returns the calling string value converted to lower case. |
| toUpperCase() | Returns the calling string value converted to uppercase. |

JavaScript Basics
Date object parameters
| Date | Current day of the month |
| Day | Day of the week |
| FullYear | Year |
| Hours | Hours |
| Minutes | Minutes |
| Milliseconds | Milliseconds |
| Month | Month |
| Seconds | Seconds |

JavaScript Basics
Date object methods
| get<param>() | Returns data based on param requested |
| getUTC<param>() | Returns data based on param requested according to UTC |
| set<param>() | Updates the value |
| getTimezoneOffset() | Returns the time-zone offset in minutes for the current locale. |
| toLocaleFormat() | Converts a date to a string, using a format string. |
| toUTCString() | Converts a date to a string, using the universal time convention. |

JavaScript Basics
Math object properties
| E | Euler's constant and the base of natural logarithms, approximately 2.718. |
| LN2 | Natural logarithm of 2, approximately 0.693. |
| LN10 | Natural logarithm of 10, approximately 2.302. |
| LOG2E | Base 2 logarithm of E, approximately 1.442. |
| LOG10E | Base 10 logarithm of E, approximately 0.434. |
| PI | Ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, approximately 3.14159. |
| SQRT1_2 | Square root of 1/2; equivalently, 1 over the square root of 2, approximately 0.707. |
| SQRT2 | Square root of 2, approximately 1.414. |

JavaScript Basics
Math object methods
| floor() | Returns the largest integer less than or equal to a number. |
| ceil() | Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to a number. |
| max() | Returns the largest of zero or more numbers. |
| min() | Returns the smallest of zero or more numbers. |
| pow() | Returns base to the exponent power, that is, base exponent. |
| random() | Returns a pseudo-random number between 0 and 1. |
| round() | Returns the value of a number rounded to the nearest integer. |

JavaScript Basics
Regex object properties
| global | Specifies if the "g" modifier is set. |
| ignoreCase | Specifies if the "i" modifier is set. |
| multiline | Specifies if the "m" modifier is set. |

JavaScript Basics
Regex object methods
| exec() | Executes a search for a match in its string parameter. |
| test() | Tests for a match in its string parameter. |

JavaScript Basics
Encapsulation
Aggregation
Inheritance
Polymorphism
Objects

JavaScript Basics
Object methods
| entries() | Transforms the object into an array containing arrays of key, value pairs |
| keys() | Returns an array of keys |
| values() | Returns an array of values |
| freeze() | Marks the object as frozen and cannot be modified |
| assign() | Concatenates object keys and values |
| defineProperty() | Adds a property to the object |

JavaScript Basics
Array properties
| length | Reflects the number of elements in an array. |

JavaScript Basics
Array methods
| concat() | Returns a new array comprised of this array joined with other array(s) and/or value(s). |
| forEach() | Calls a function for each element in the array. |
| indexOf() | Returns the first (least) index of an element within the array equal to the specified value, or -1 if none is found. |
| join() | Joins all elements of an array into a string. |
| pop() | Removes the last element from an array and returns that element. |
| push() | Adds one or more elements to the end of an array and returns the new length of the array. |

JavaScript Basics
Array methods (cont.)
| reverse() | Reverses the order of the elements of an array -- the first becomes the last, and the last becomes the first. |
| shift() | Removes the first element from an array and returns that element. |
| slice() | Extracts a section of an array and returns a new array. |
| sort() | Sorts the elements of an array |
| splice() | Adds and/or removes elements from an array. |
| unshift() | Adds one or more elements to the front of an array and returns the new length of the array. |

JavaScript Basics
JSON object Methods
| parse() | Transform a string to a JSON object |
| stringify() | Transform JSON object into string |

Operators
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
Arithmetic
Comparison
Logical
Assignment

JavaScript Basics
Arithmetic
| Addition (+) | Adds two operands |
| Subtraction (-) | Subtracts the second operand from the first |
| Multiplication (*) | Multiply both operands |
| Division (/) | Divide the numerator by the denominator |
| Modulus (%) | Outputs the remainder of an integer division |
| Increment (++) | Increases an integer value by one |
| Decrement (--) | Decreases an integer value by one |

JavaScript Basics
Comparison
| Equal (==) | Checks if the value of two operands are equal or not, if yes, then the condition becomes true. |
| Not Equal (!=) | Checks if the value of two operands are equal or not, if the values are not equal, then the condition becomes true. |
| Greater than (>) | Checks if the value of the left operand is greater than the value of the right operand, if yes, then the condition becomes true. |
| Less than (<) | Checks if the value of the left operand is less than the value of the right operand, if yes, then the condition becomes true. |

JavaScript Basics
Comparison (cont.)
| Greater than or Equal to (>=) | Checks if the value of the left operand is greater than or equal to the value of the right operand, if yes, then the condition becomes true. |
| Less than or Equal to (<=) | Checks if the value of the left operand is less than or equal to the value of the right operand, if yes, then the condition becomes true. |

JavaScript Basics
Logical
| Logical AND (&&) | If both the operands are non-zero, then the condition becomes true. |
| Logical OR (||) | If any of the two operands are non-zero, then the condition becomes true. |
| Logical NOT (!) | Reverses the logical state of its operand. If a condition is true, then the Logical NOT operator will make it false. |

JavaScript Basics
Assignment
| Simple Assignment (=) | Assigns values from the right side operand to the left side operand |
| Add and Assignment (+=) | It adds the right operand to the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. |
| Subtract and Assignment (-=) | It subtracts the right operand from the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. |
| Multiply and Assignment (*=) | It multiplies the right operand with the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. |
| Divide and Assignment (/=) | It divides the left operand with the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand. |
| Modules and Assignment (%=) | It takes modulus using two operands and assigns the result to the left operand. |

JavaScript Basics
// example 1
var sum = 0;
sum += 3;
console.log(sum) // 3;
var value = 5;
sum += value;
console.log(sum) // ?
JavaScript Basics
// example 2
var sum = "0";
sum += 3;
console.log(sum) // "03"
var value = 5;
sum += value;
console.log(sum) // ?
Statements
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
if..then..else
switch
for
while
until

JavaScript Basics
if..then..else
// if..then..else
if (condition) {
action()
} else {
alternative()
}
// short if
condition
? action()
: alternative()
JavaScript Basics
switch
// switch
switch(variable) {
case 'value':
action(params);
break;
case 'value2':
action2(params);
break;
default:
action3(params);
break;
}
JavaScript Basics
switch alternative
// alternative to switch with objects
var actions = {
'value': action,
'value2': action2
};
var defaultAction = action3;
(actions[varaible] || defaultAction)(params);
JavaScript Basics
for
// for
var values = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
for(var i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
console.log(values[i]);
}
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
// 5
JavaScript Basics
while
// while
var items = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
while(items.length) {
var current = items.shift();
console.log(current);
}
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
// 5
JavaScript Basics
until
// while
var items = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
while(items.length) {
var current = items.shift();
console.log(current);
}
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
// 5until doesn't exist in javascript

Iterators
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
var colors = ["red", "green", "blue"];
for (var i = 0, len = colors.length; i < len; i++) {
console.log(colors[i]);
}For loop
Tend to get complicated when complex logic and nesting is required

JavaScript Basics
// example
let values = [1, 2, 3];
for (let num of values) {
console.log(num);
}
// 1
// 2
// 3for...of iterator

JavaScript Basics
// example
let person = { firstName: 'John', lastName: 'Doe' };
for (var prop in person) {
console.log(prop);
}
// 'firstName'
// 'lastName'
// ES5
var properties = Object.keys(person);
for (var i = 0; i < properties.length; i++) {
console.log(properties[i])
}for...in iterator

Functions
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
Definition
Params
Arguments
Calls

JavaScript Basics
Definition
// first we define a function name and the parameters
function doSomething(params) {
// then we define the function body
// functions do not need a return statement but one is preferred
}
doSomething(values); // for our function to work, we need to call it
JavaScript Basics
Params
// params are always in the paranthesis following a function name
// they can be any type of data or even other functions
function doSomething(params) {
}
JavaScript Basics
Arguments
// arguments is a special key-word in javascript
// it takes over and contains all data being sent to the function as an input
function doSomething() {
var params = arguments;
}
doSomething(input);
JavaScript Basics
Calls
function doSomething(params) {
// ...
}
var doSomethingElse = function(params) {
// ...
}
var doSomethingMore = doSomethingElse;
// calling a function can be done on any kind of function
// even if it is a named, annonymouse or just a cloned function body
doSomething(input);
JavaScript Basics
Pure functions
based on input => output
no mutation
=> easy to test
=> predictability
=> no "wild" bugs

JavaScript Basics
Pure functions vs mutation
function doSomething(input) {
// doing some magic processing here
return output;
}
// vs
var output;
function doSomething(input) {
// doing the same magic here
output = values;
}
JavaScript Basics
Pure functions vs mutation
function doSomething(input) {
// doing some magic processing here
return output;
}
function doSomethingElse(input) {
return output;
}
// vs
var output;
function doSomething(input) {
// doing the same magic here
output = values;
}
function doSomethingElse(input) {
// doing the same magic here
output = values;
}
Closures
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
A closure is the combination of a function bundled together (enclosed) with references to its surrounding state (the lexical environment)

JavaScript Basics
function sayHello() {
var name = 'John';
function withGreeting() {
console.log('Hello, ' + name);
}
withGreeting();
}
sayHello(); // Hello, JohnScope

JavaScript Basics
function sum(a) {
return function(b) {
return function(c) {
return function (d) {
return function (e) {
console.log(a + b + c + d + e);
}
}
}
}
}
sum(1)(2)(3)(4)(5); // 15Depth

JavaScript Basics
var numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
function asyncLog(arr) {
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(i, arr[i]);
}, 1000 * i)
}
}
asyncLog(numbers);Evaluation

JavaScript Basics
// IIFE
var id = (function() {
var current = 0;
function next() {
return ++current;
}
function reset() {
current = 0;
}
return { next, reset }
})();
id.next(); // 1
id.next(); // 2
id.reset();
id.next(); // 1
id.current // undefinedEncapsulation

Browser & DOM Events
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
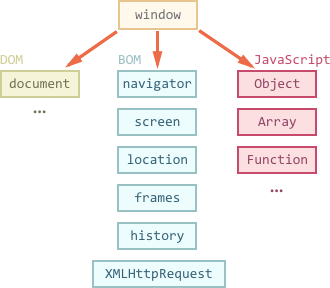
BOM vs. DOM

JavaScript Basics
Browser Object Model
Not a standard itself but a collection of methods and properties that browsers expose to JavaScript.

JavaScript Basics
BOM Browser API
navigator

JavaScript Basics
BOM Window API
closed
frames
opener
parent

JavaScript Basics
BOM Display / Device API
devicePixelRatio
alert, confirm, prompt

JavaScript Basics
BOM Elements API
customElements
document

JavaScript Basics
BOM Navigation API
history
location

JavaScript Basics
BOM Storage API
localStorage
sessionStorage

JavaScript Basics
BOM Debugging API
console
performance

JavaScript Basics
Document Object Model
DOM connects JavaScript to the actual HTML rendered structure that we see on the screen.

JavaScript Basics
DOM Access
body, head
children
forms, images, links, scripts
cookies, location

JavaScript Basics
DOM Query API
querySelector
querySelectorAll
getElementById
getElementsByClassName
getElementsByTagName

JavaScript Basics
DOM Manipulation API
createElement
append

JavaScript Basics
Element / Node Manipulation API
append
insertBefore
replaceWith
remove
remove

JavaScript Basics
Events API
elements / document can dispatch events
native events
custom events
elements / document can listen to events
cancel events

JavaScript Basics
Native Events
Pre-defined events by the browser that are available for us to listen, capture and react to.
These events are bubbling, can be canceled but they are not composed.

JavaScript Basics
Mouse Native Events
click
contextmenu
mouseover / mouseout
mousedown / mouseup
mousemove

JavaScript Basics
Form Native Events
submit
focus

JavaScript Basics
Keyboard Native Events
keyup
keydown

JavaScript Basics
Custom Events
Events defined and emitted by the application. They are not available out of the box by the browser.
These events have to be configured for bubbling, canceling and compose.

JavaScript Basics
Custom Events
Events defined and emitted by the application. They are not available out of the box by the browser.
These events have to be configured for bubbling, canceling and compose.

JavaScript Basics
Event Definition
// native event
var clickEvent = new MouseEvent('click');
var submitEvent = new SubmitEvent('submit');
// Same event can be defined from a specific interface
// or a generic interface
// looses some properties that are specific to mouse events
var genericEvent = new Event('click');
// custom event
var customEvent = new CustomEvent('mycustomevent', {
bubbles: true,
cancelable: true,
composed: true
});
JavaScript Basics
Event Dispatch
// define event
var clickEvent = new MouseEvent('click');
var customEvent = new CustomEvent('appcustomevent', {
bubbles: true,
cancelable: true,
composed: true
})
// get element that is dispatching
var element = document.querySelector('button');
// dispatch
element.dispatchEvent(clickEvent);
element.dispatchEvent(customEvent);
JavaScript Basics
Event Handling
// get element that is dispatching
var element = document.querySelector('button');
// handler
element.addEventListener('click', function(event) {
// do something when a button is clicked
});
document.addEventListener('appcustomevent', function(event) {
// do something when a custom event is emitted
// take note that the event needs to bubble all the way to the document
});
JavaScript Basics
Event Stopping
// handler
form.addEventListener('submit', function(event) {
if(event.bubbles) {
event.stopPropagation(); // stops the event from going further
};
if(event.cancelable) {
event.preventDefault(); // cancel the native action
}
// do something when the form submits
});
Forms
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
Forms are the way HTML
communicates data with a 3rd party

JavaScript Basics
<form name="login" action="/authentication" method="post">
<label for="user">
Username:
<input type="email" id="user" name="user">
</label>
<label for="pass">
Password:
<input type="password" id="pass" name="pass">
</label>
</form>
JavaScript Basics
var loginForm = document.querySelector('[name="login"]');
var loginForm = document.forms.login;Accessing forms from JavaScript

JavaScript Basics
Form Elements
input, textarea
select, options
label
fieldset, legend
button

JavaScript Basics
var loginForm = document.querySelector('[name="login"]');
var loginForm = document.forms.login;
// elements
var username = loginForm.querySelector('[name="user"]');
var password = loginForm.elements.pass;Accessing form elements from JavaScript

JavaScript Basics
Form Input Types
| button | checkbox | color |
| date | datetime-local | |
| file | hidden | image |
| month | number | password |
| radio | range | reset |
| search | submit | tel |
| text | time | url |
| week |

JavaScript Basics
Form Elements Events
change
input
cut
copy
paste

JavaScript Basics
Form Events
submit

JavaScript Basics
Form Validation
native built validation as attributes
javascript
3rd party libraries

JavaScript Basics
Native Validation
required
minlength / maxlength
min / max
type
pattern

JavaScript Basics
JavaScript Validation
// form.html
<form name="email" onsubmit="return validate()">
<label>
Email
<input name="email" type="email" required>
</label>
</form>
// script.js
validate() {
if (!document.forms.email.elements.email) {
return false;
}
}
document.forms.email.addEventListener('submit', function(event) {
if(!validate()) {
event.preventDefault();
event.stopPropagation();
}
})
JavaScript Basics
3rd Party Validation Libraries

Server Requests
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
XHR
fetch
3rd party libraries

JavaScript Basics
XHR
function reqListener () {
console.log(this.responseText);
}
var oReq = new XMLHttpRequest();
oReq.addEventListener("load", reqListener);
oReq.open("GET", "http://www.example.org/example.txt");
oReq.send();
JavaScript Basics
fetch
// native async
fetch('http://www.example.org/example.json')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data));
fetch('http://www.example.org/example.txt')
.then(response => response.text())
.then(data => console.log(data));
JavaScript Basics
axios
// native async
axios.get('http://www.example.org/example.json')
.then((response) => { console.log(response) });
From ES5 to ESNEXT
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
Variables
let
const

JavaScript Basics
// let
let number = 2;
console.log(number); // 2
function test() {
let number = 4;
console.log(number); // 4
}
test(); console.log(number); // 2
// const
const number = 2;
number = 4; // throws error, cannot reassign
JavaScript Basics
Data Types
template literals
destructuring, spread, rest
enhanced objects
Set, Map, WeakSet, WeakMap

JavaScript Basics
// template literals
const name = 'John'
let greeting = `Hello, ${name}!`;
console.log(greeting); // Hello, John!
// objects
const fiveKey = '5';
const numbers = {
2: 2,
3: 3,
four: 4,
[fiveKey]: 5,
sum: function() {
return Object.keys(this).reduce(
(sum, val) => {
const number = Number(this[val]);
if (Number.isFinite(number)) {
sum += number;
}
return sum;
}, 0
)
}
}
console.log(numbers.sum())
JavaScript Basics
// destructuring
const { four } = numbers;
const [ firstLetter, ...rest ] = 'works'; // firstLetter: 'w', rest: ['o', 'r', 'k', 's']
// map
const word = 'works';
const wordMap = new Map(Object.entries(word));
console.log(wordMap); // Map (5) {"0" => "w", "1" => "o", "2" => "r", "3" => "k", "4" => "s"}
const wordSet = new Set([...word]);
console.log(wordSet); // Set (5) {"w", "o", "r", "k", "s"} 
JavaScript Basics
Statements
for...of, for...in

JavaScript Basics
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
for (let number of numbers) {
console.log(number);
}
// 1 2 3 4 5
for (let index in numbers) {
console.log(index);
}
// 0 1 2 3 4
JavaScript Basics
Functions
arrow functions
classes
default params
promises

JavaScript Basics
// classes
class Example {
// implementation goes here
}
// arrow functions
let log = (msg = 'fallback') => { // default param
// function body
}
// native promises
let log = async (msg) {
// function body
}
Error Handling
JavaScript Basics

JavaScript Basics
function validate(input) {
if (!input) {
return new Error('input is required');
}
}
validate() // Error: input is requiredError interface

JavaScript Basics
function validate(input) {
if (!input) {
return new Error('input is required');
}
}
try {
validate()
} catch(e) {
console.log(e);
};Catching errors (sync)

JavaScript Basics
async function validate(input) {
if (!input) {
return new Error('input is required');
}
}
validate()
.then(() => { console.log('success!') })
.catch((e) => { console.error('failed! :(') });Catching errors (async)

Q&A
JavaScript Basics
Thank you!
