Semantic Web 101
(A Work in Progress)
Anna-Sophia Zingarelli-Sweet
LIS 2975 - Digital Scholarship
School of Information Sciences, University of Pittsburgh
September-October 2013
Guns, Raf. "Tracing the Origins of the Semantic Web."
Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 64:10 (2013): 2173-2181
“Although the web is mainly known for documents
in HTML, even the earliest proposals hint at ambitions
beyond a simple document formatting language… The Semantic Web therefore does not represent
a radical paradigm shift but rather the externalization of an undercurrent that has existed since the beginning
of the web. Throughout the first decade of the web, several proposals were developed
to enable 'semantic' relationships on the
web.”
www design documents from early '90s discuss:
- whether links should have "types"
- what types should be available
"In a keynote speech at
INET’95, the Internet Society’s 1995 International Net-
working Conference, Berners-Lee outlined four points on
the way to a “semantic web.”
The full text of the presentation is not available, but the four points mentioned in the surviving slides are:
• Link typing
• Knowledge representation content types
• Meta language for trait investigation
• Bootstrapping class structures.
It is not entirely clear what exactly was meant by each of these points, but the first one is quite clear: Typed links imply semantics."
- relations between items
- web of documents, but also people and companies
- (Friend of a Friend)
- importance of ontologies
- problem of compatibility among ontologies
HTML2
- introduced 1995
- includes for the first time "the seeds" of embedded metadata and typed links
SHOE
- allows specification of "data objects, their classes, and their relations"
- Guns identifies as first major addition of semantic elements to HTML
Tim Berners-Lee
September 1998: Semantic Web Roadmap
"A road map for the future, an architectural plan untested by anything except thought experiments."
"a plan for achieving a set of connected applications for data on the Web in such a way as to form a consistent logical web of data (semantic web)"
Basic Assertion Model
- RDF (Resource Description Framework)
- Assertions
- Quotation (an assertion about an assertion)
"Being simple there is
nothing much you can do
with the model itself without layering many things on top."
- Schema Layer
- Conversion Language
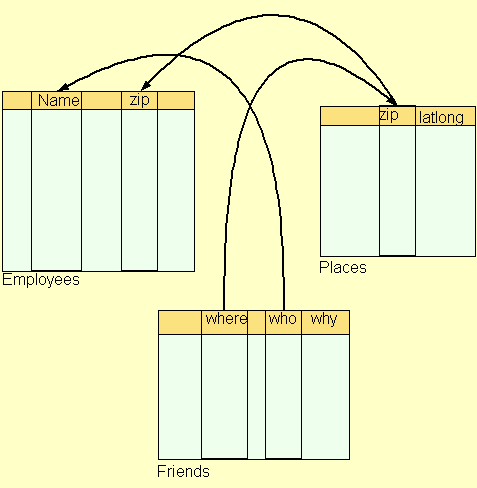
- Logical Layer
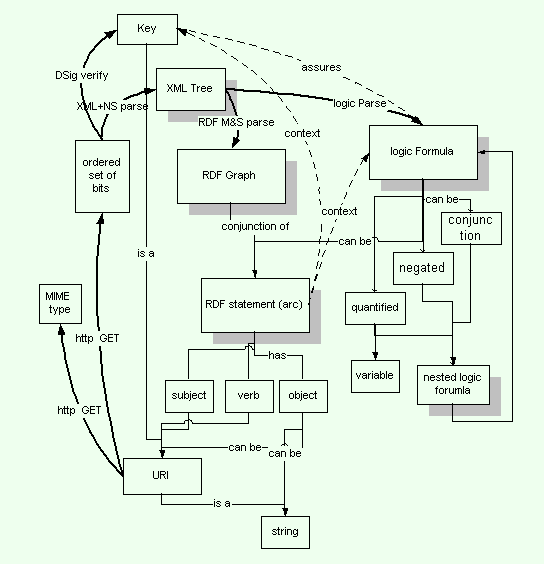
Continued to update through 2009
- Read-Write Linked Data
- Socially Aware Cloud Storage
- Government Data on the Web
Implications for Scholarship?
- Scholarly communication vs. accessibility of scholarly documents
- Focus on structuring information to be machine-readable
"the WWW was originally developed with the goal to be a collaborative space in which people could collectively design, discuss, share and manage things. Being able to impart one's knowledge, or put down a new design or correct or annotate existing work, is I think a key functionality of the Web."
(Berners-Lee, "Read Write Linked Data")