An Introduction to Pandas
ayush1997


a skill to be mastered......

About me
-
CS Sophomore
-
Pythonista !
-
Hackathon Lover
-
FOSS Enthusiast
-
Mentor @ DevSocMSIT




What is it?
Pandas is a powerful data analysis toolkit providing fast, flexible, and expressive data structures designed to make working with "relational" or "labeled" data both easily and intuitively.

Pandas = Python + Numpy + R
Why Pandas?
-
Highly optimized for performance, with critical code paths written in Cython or C.
-
Easy handling of missing data (represented as NaN)
-
Robust IO tools for loading/saving data from/to different formats(CSV,HDF5,JSON.....)
-
Intuitive merging and joining of data sets
-
Easy label-based slicing, indexing, and subsetting of large data sets
-
Powerful, flexible group by functionality to perform split-apply-combine operations on data sets
-
Combined with the excellent IPython toolkit and other libraries
Installation
Using Pip
pip install pandasUsing Conda
conda install pandasimport pandas as pdAgenda
- Data Structures
- I/O Tools
- Basic Functions
- Indexing and selecting data
- Working with missing data
- GroupBy
- Merge,Join and Concatenate
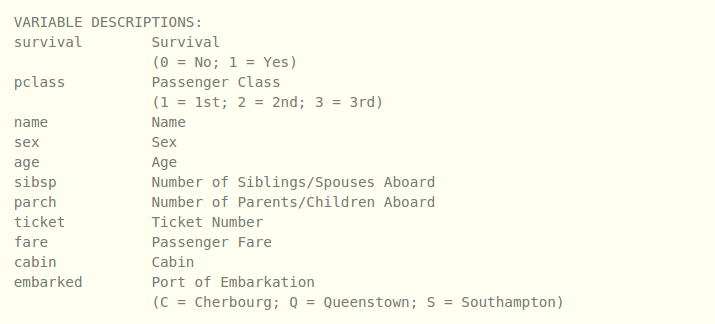
The Data

DATA STRUCTURES
DataFrame
It is a tablular data structure comprised of rows and columns.
Series
A Series is a one-dimensional object similar to an array, list, or column in a table.
Series
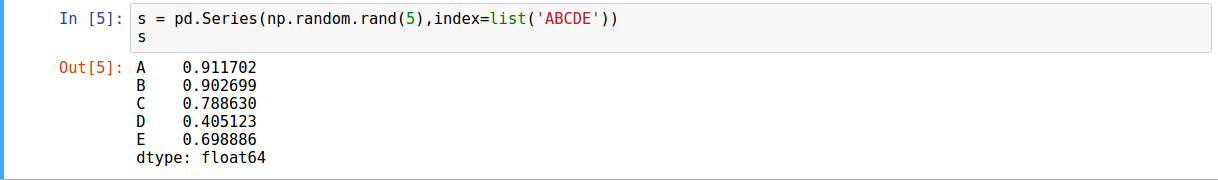
- Using random list
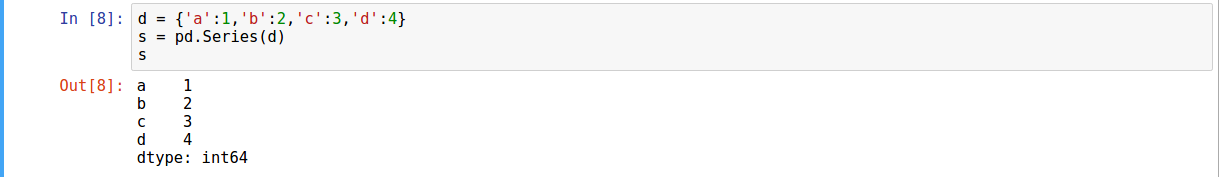
- Using Dictionary
DataFrame
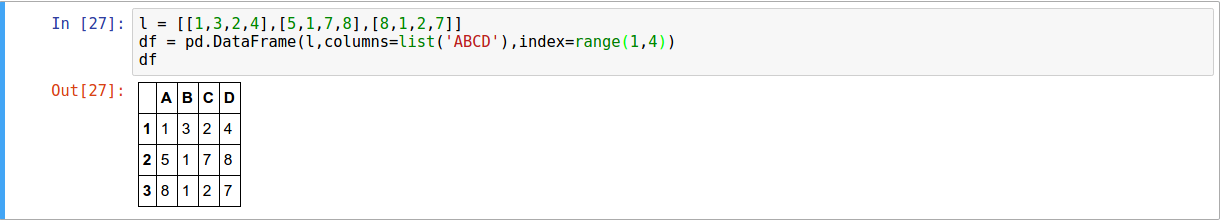
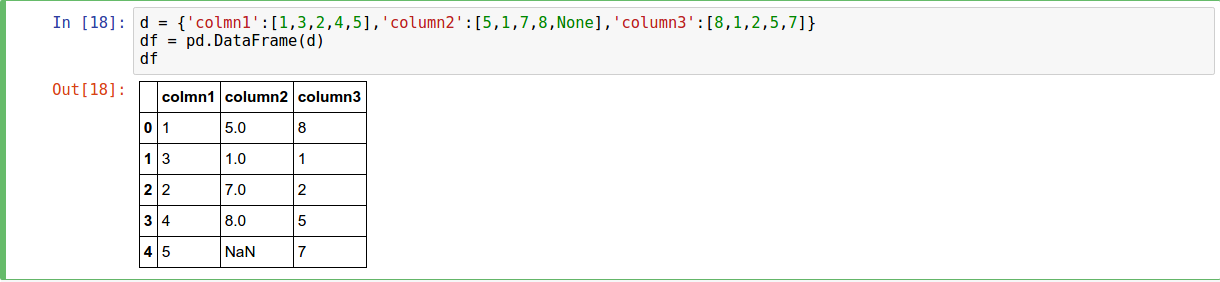
- From Dictionary
- Using list of lists
I/O Tools
The pandas I/O API is a set of top level reader and writer functions that generally return a pandas object.
- read_csv
- read_excel
- read_hdf
- read_sql
- read_json
- read_html
- read_pickle
- to_csv
- to_excel
- to_hdf
- to_sql
- to_json
- to_html
- to_pickle
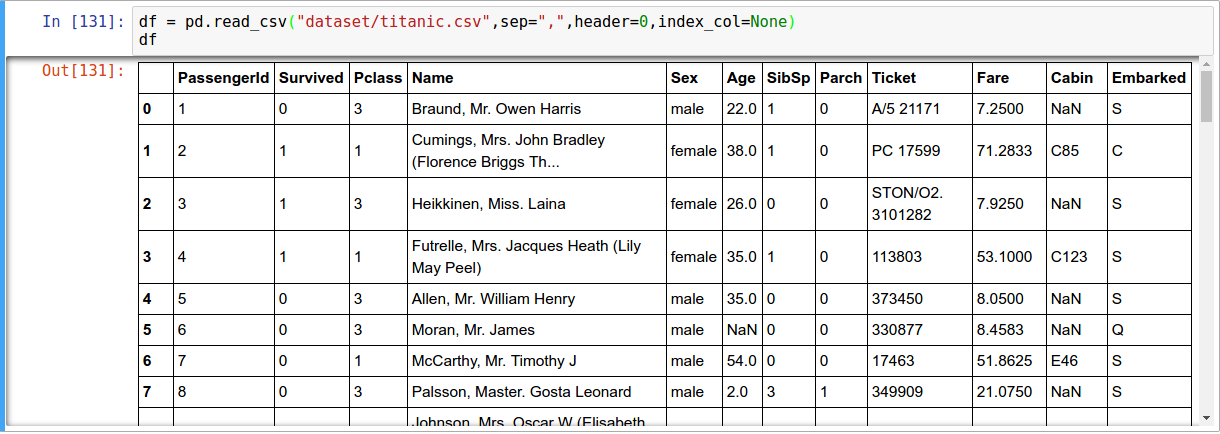
- Reading CSV
- Writing to CSV

Essential Basic Functions
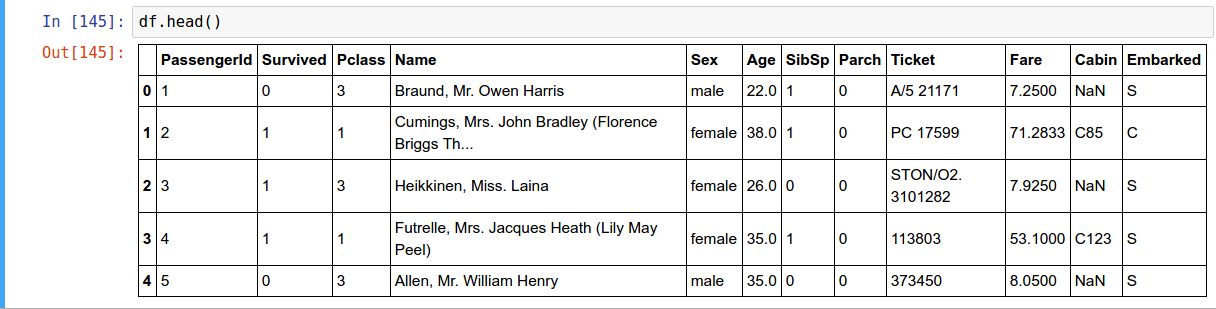
Head and Tail

Columns and indexes
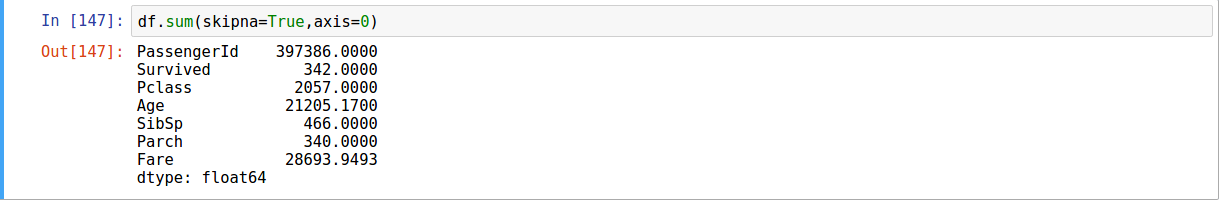
Descriptive Statistic
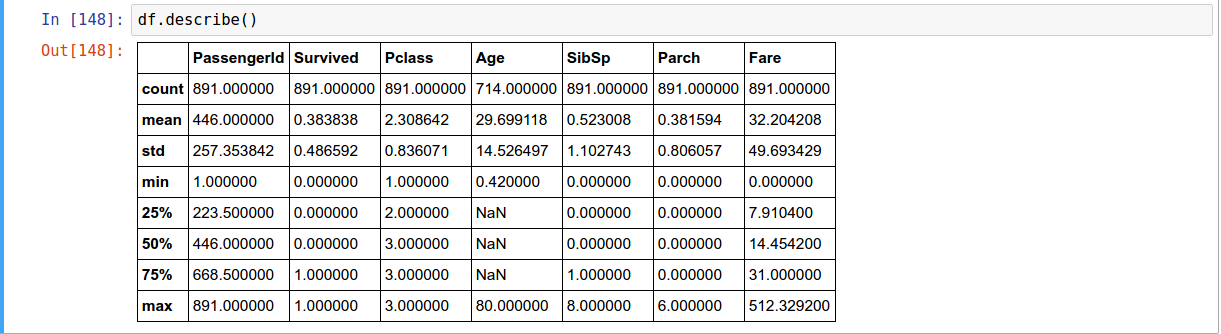
Data Summary
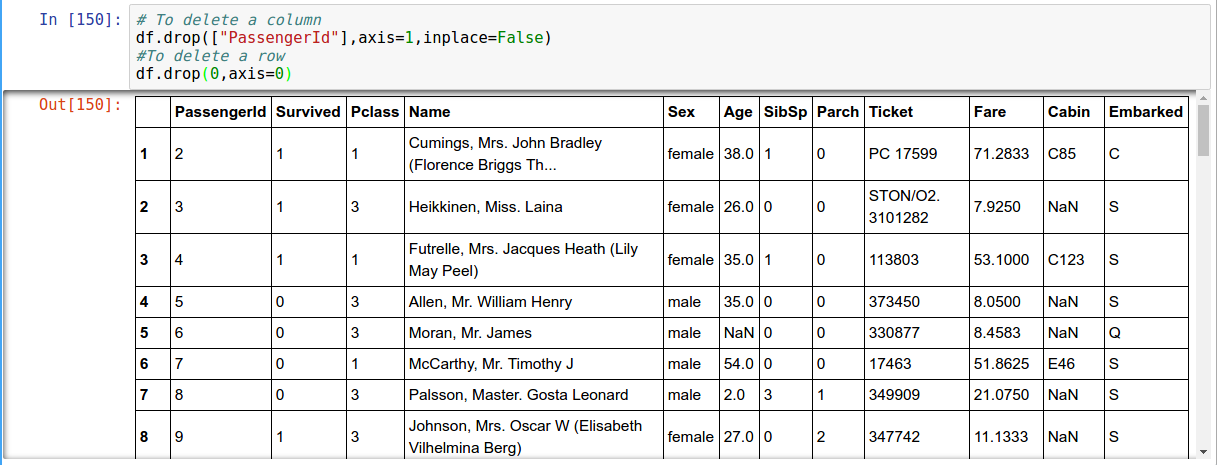
Deleting
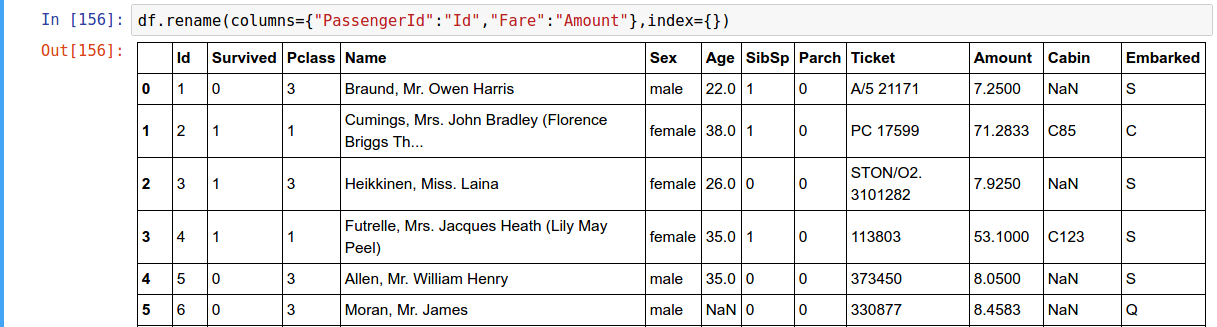
Rename

Unique
Indexing & Selecting Data
Different selection methods
pandas provides a suite of methods in order to get integer and label based indexing. The semantics follow closely python and numpy slicing
- Some Basic indexing
- .loc is used for label based selection
- .iloc is basically integer position based
- .ix is for mixed label and integer position based
- Boolean indexing
Basic Indexing [ ]
- To get columns
- Slicing rows
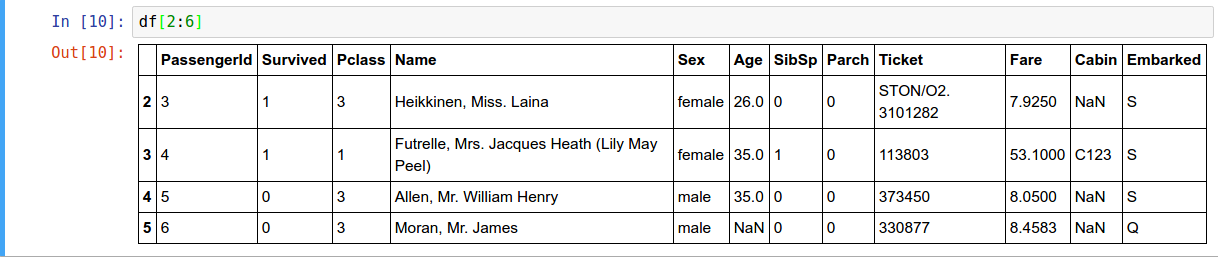


- To get a cell
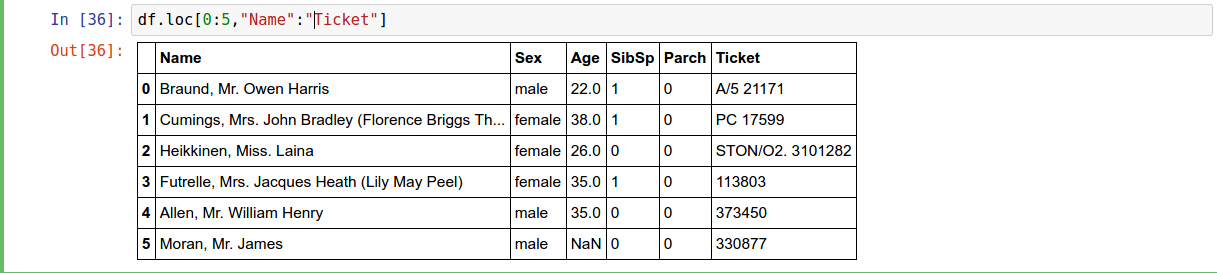
.loc
Selection by Label

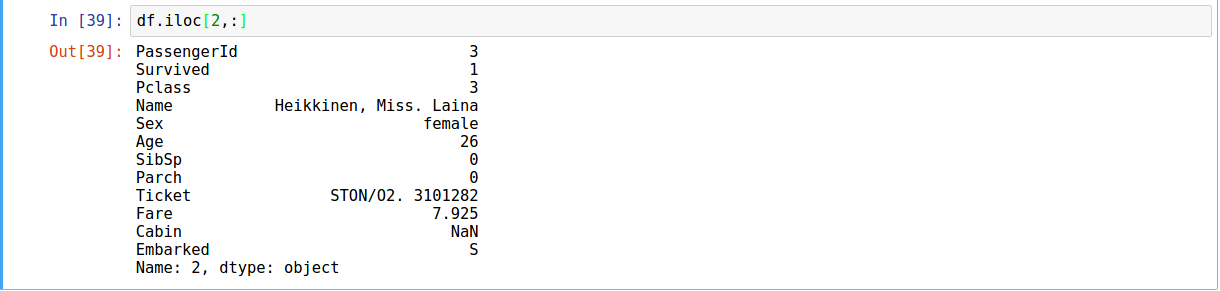
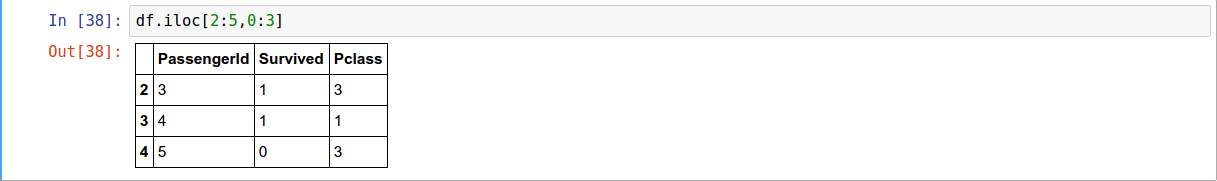
Selection by Position
.iloc
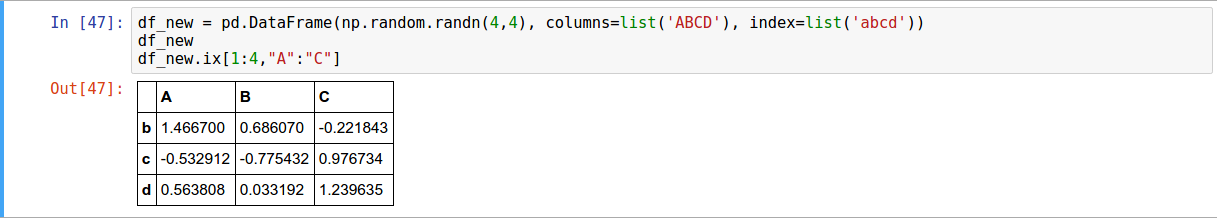
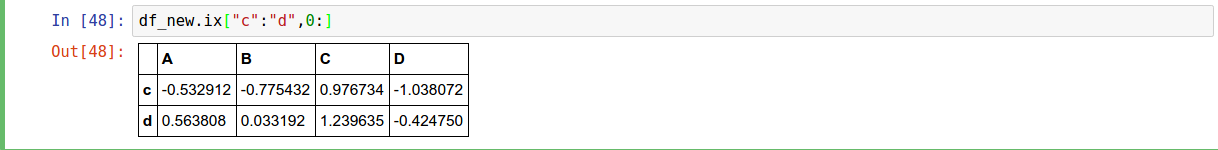
.ix
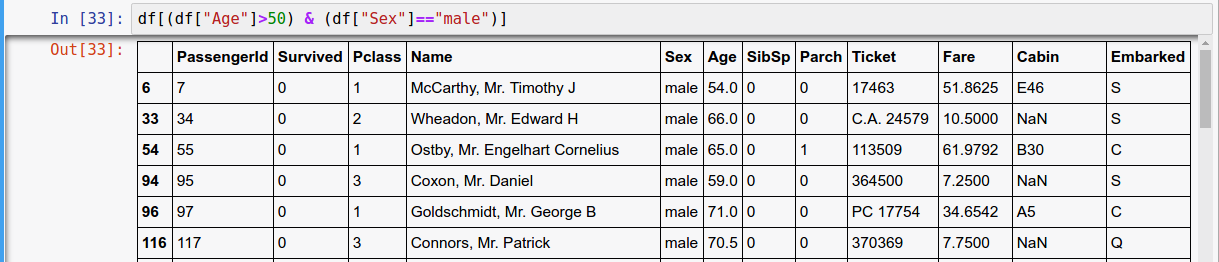
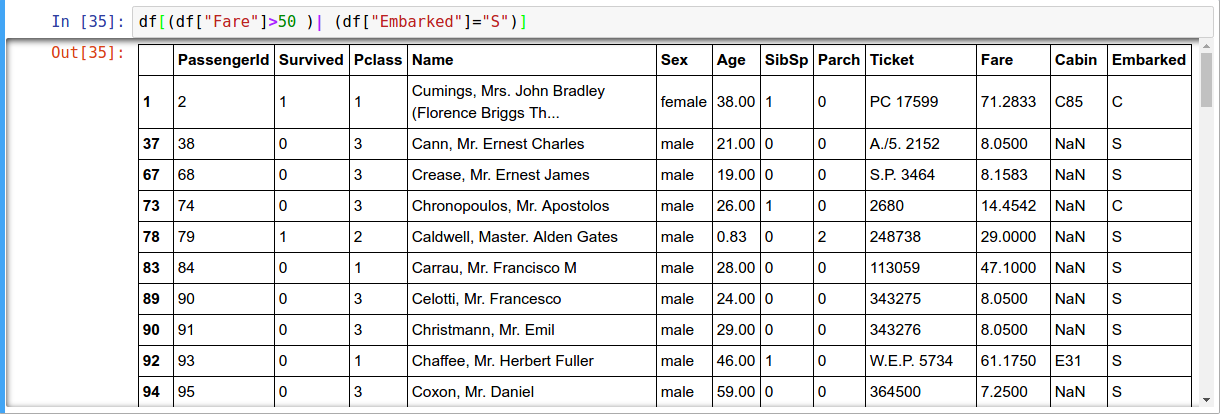
Boolean Indexing
Boolean vector to filter data
| fo r or & for and ~ for not
Working With Missing Data
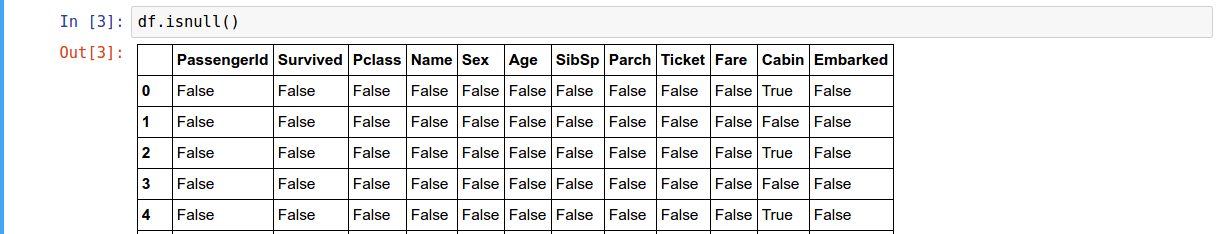
In pandas the missing data is represented by NaN
Check for Null values
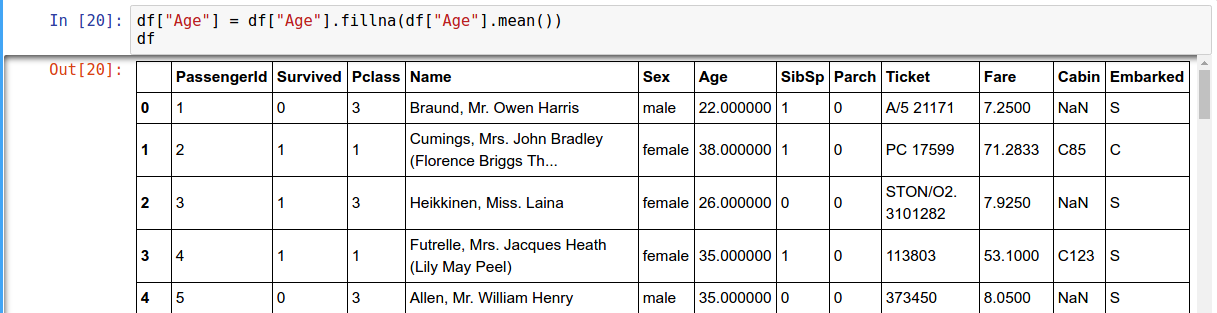
Filling Missing Data
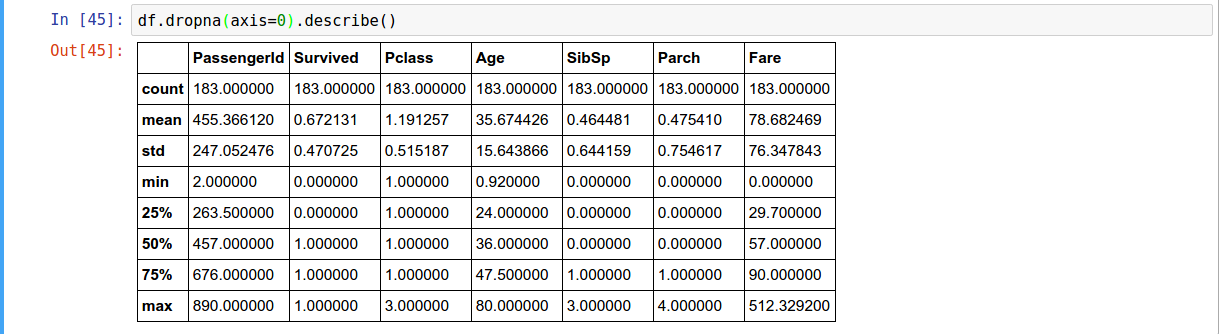
Droping Data
GroupBy
split-apply-combine
By “group by” we are referring to a process involving one or more of the following steps
- Splitting the data into groups based on some criteria
- Applying a function to each group independently
- Combining the results into a data structure
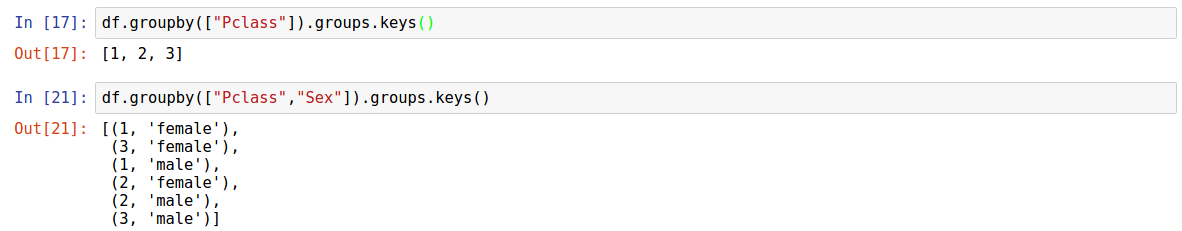
Splitting an object into Groups
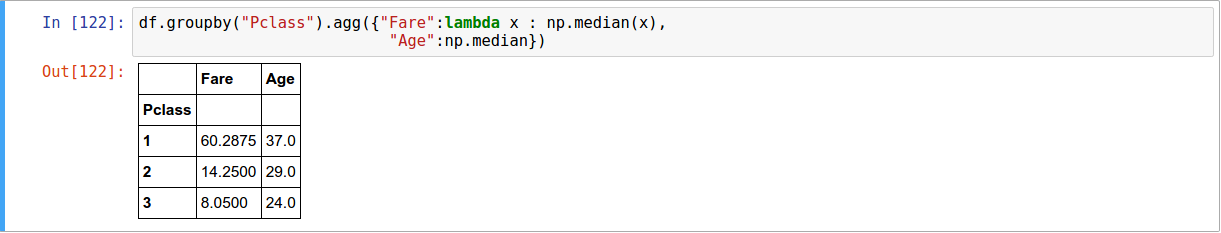
df.groupby(["Pclass"])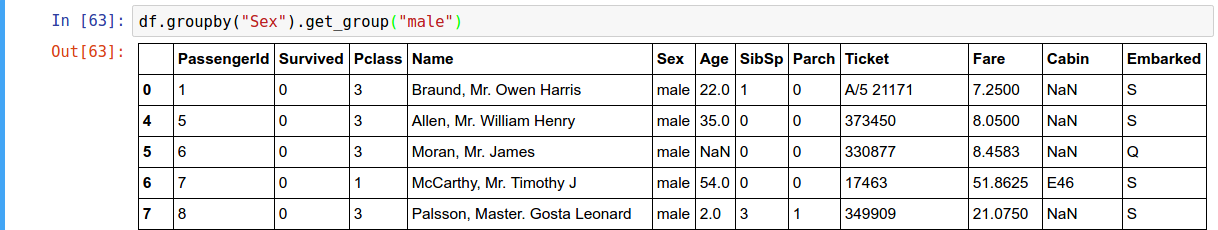
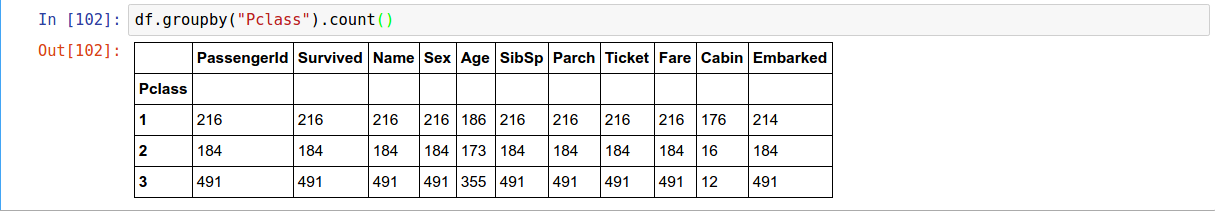
Applying
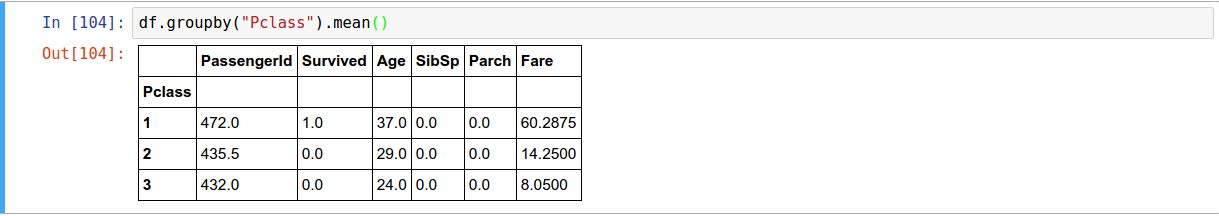
Once GroupBy objects have been created we can compute a summary statistic (or statistics) about each group
Once GroupBy objects have been created we can compute a summary statistic (or statistics) about each group
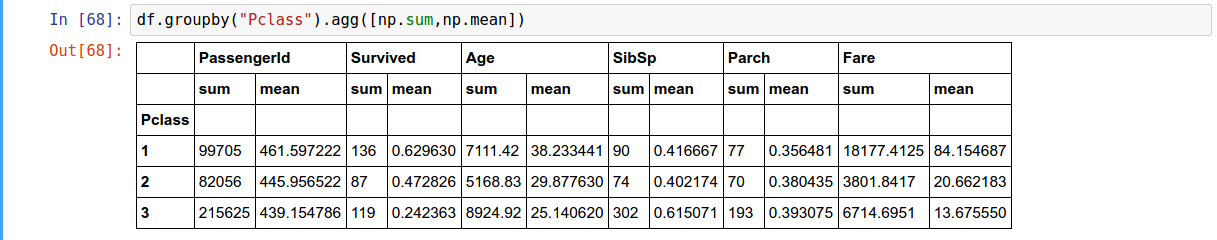
aggregate( )
-
Applying multiple functions at once
-
Applying different functions to DataFrame Columns
Merge,Join
and Concatenate
Concatenating Objects
The concat function performs concatenation operations along an axis while performing optional set logic (union or intersection) of the indexes (if any) on the other axes.
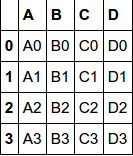
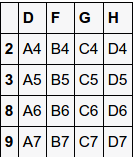
df1
df2
concat(objs, axis=0, join='outer', join_axes=None, ignore_index=False,
keys=None, levels=None, names=None, verify_integrity=False)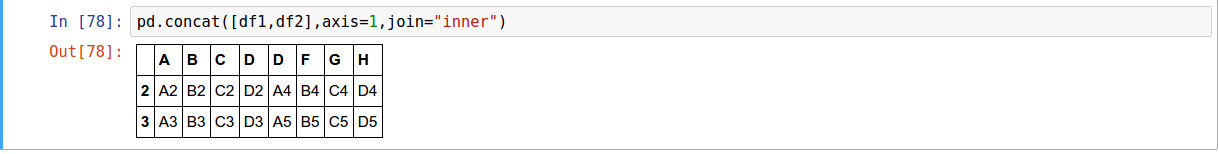
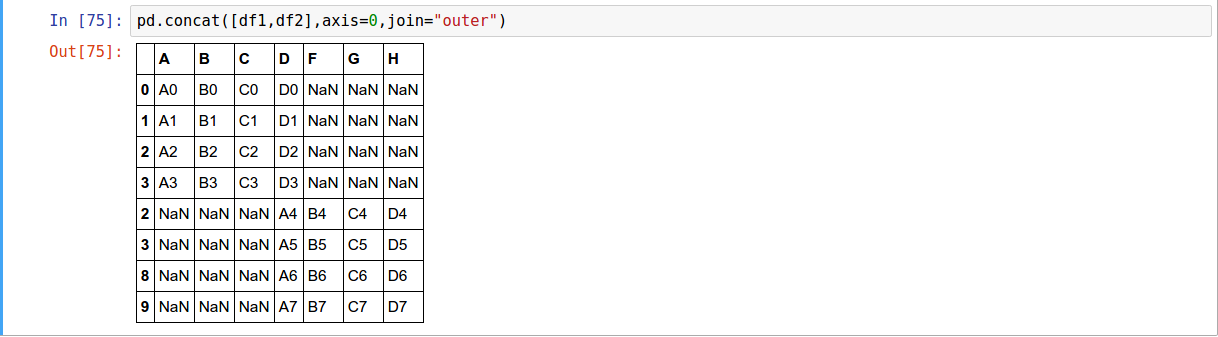
-
along column axis
-
along row axis
Concatenating Using append( )
A useful shortcut to concat are the append instance methods on Series and DataFrame.
They concatenate along axis=0
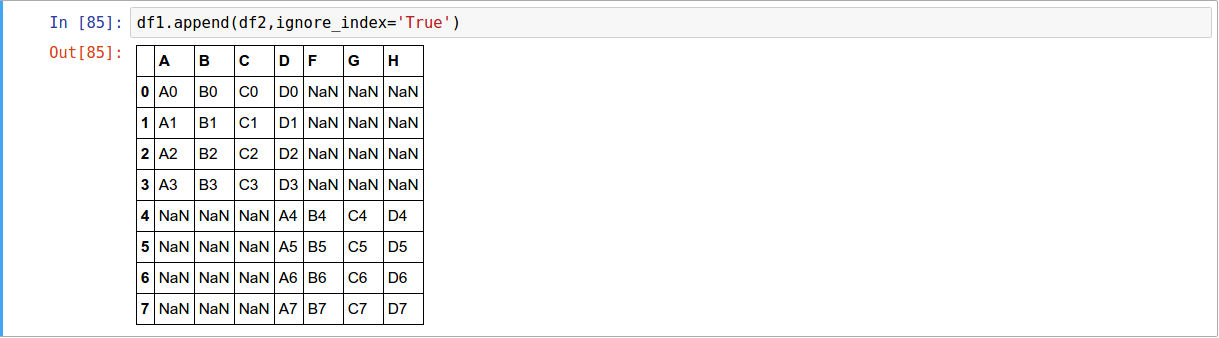
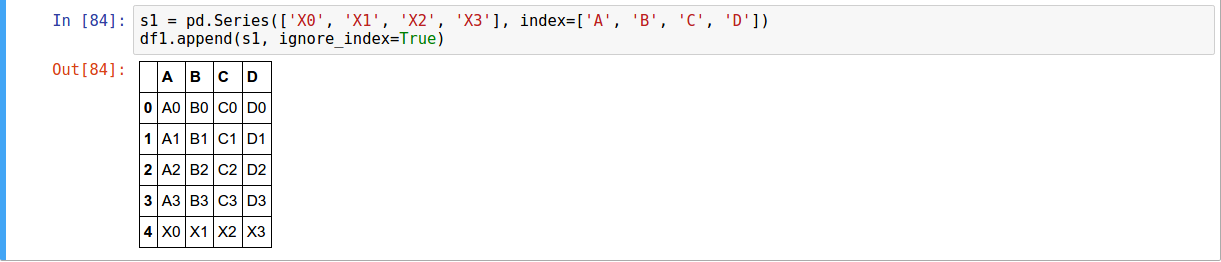
Text
To add a row
Merging/Joining
pandas has full-featured, high performance in-memory join/merge operations idiomatically very similar to relational databases like SQL
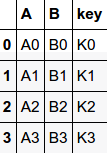
pd.merge(left, right, how='inner', on=None, left_on=None, right_on=None,
left_index=False, right_index=False, sort=True,
suffixes=('_x', '_y'), copy=True, indicator=False)df1
df2
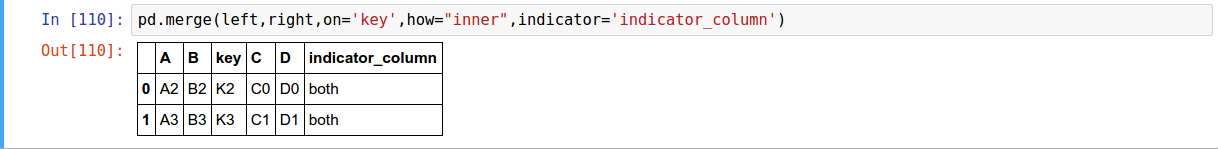
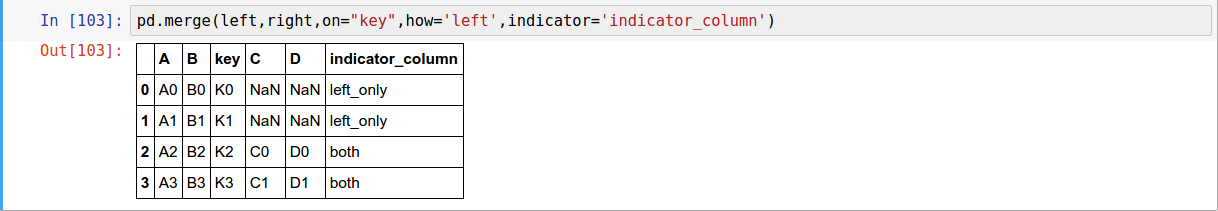
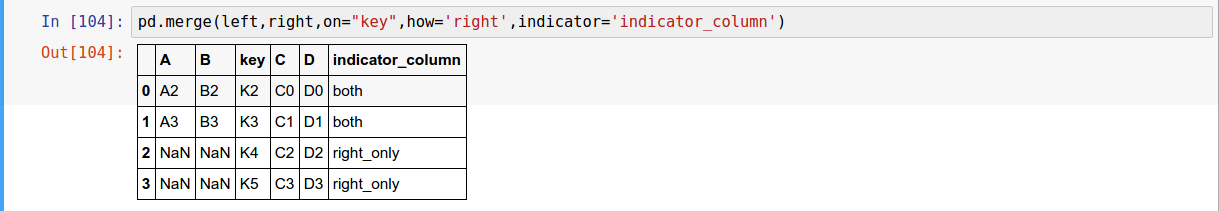
Text
Questions?



ayush0016
ayush1997
ayushkumar97
https://github.com/ayush1997/Pandas-Tutorial