ECMAScript 6
Neste versjon av JavaScript
- Mål
- Designprosess
- Funksjoner
- Når kan jeg bruke det?
Begreper
- TC39 (Ecma Technical Committee 39): komiteen som utvikler JavaScript.
- Medlemmer: bedrifter (bl.a. alle store browserleverandører).
- Ansatte og inviterte eksperter deltar på møtene.
- ECMAScript: språkets offisielle navn
- Versjoner: ECMAScript 5 er forkortelse for "ECMAScript Language Specification 5".
- ECMAScript Harmony: forbedringer etter ECMAScript 5 (ECMAScript 6 og 7)
JavaScript
- Folkemunne: språket
- Formelt: en implementasjon av ECMAScript
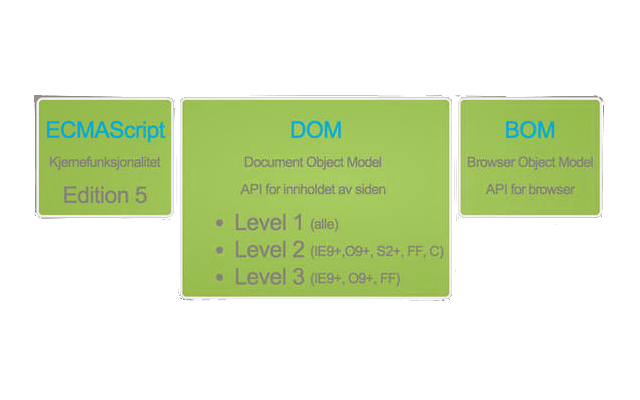
ECMAScript i seg selv er ikke bundet til nettlesere. For eksempel er NodeJS en implementasjon av ECMAScript.
JavaScript er blitt "farligere"
- Brukes overalt, browsere, servere, "devicer" osv.
- Brukes til mye mer enn det var laget for.
Mål
-
Være et bedre språk for å skrive:
- komplekse applikasjoner
- biblioteker for disse applikasjonene
- kodegeneratorer
Utforming av nye features
-
Unngå "design by committe":
- "design by champions" (1-2 eksperter).
- Feedback fra TC39 og community
- TC39 har siste ord for om/når nye funksjoner inkluderes
- Steg for å utforme en ny funksjon
- Strawman-forslag
- TC39 er interessert => forslag
- Field-testing via en eller flere implementasjoner
- TC39 godkjenner funksjonen => inkludert i ECMAScript utkast
- Inkludert i spesifikasjon => standard
Nye funksjoner
Block scope
// Function scoped var
function order(x, y) {
if (x > y) {
var tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
}
console.log(tmp === x);
// true
return [x, y];
}
// Block scoped let
function order(x, y) {
if (x > y) {
let tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
}
console.log(tmp === x);
// ReferenceError:
// tmp is not defined
return [x, y];
}Konstanter
const PI = 3.14;
PI = 10;
console.log(PI); // 3.14
Destructing
Destructing: Objekter
Hent ut data (mer enn en verdi) via patterns:
let obj = { first: "Jane", last: "Doe" };
let { first: f, last: l } = obj;
console.log(f + " " + l); // Jane Doe
Brukes til:
- Variabel-deklarasjon
- Tilordning
- Parameter-definisjon
Destructing: Forkortelse
{x, y} er det samme som {x: x, y: y}.
let obj = { first: "Jane", last: "Doe" };
let { first, last} = obj;
console.log(first + " " + last); // Jane Doe Destructing: Flere returverdier
function returnMultipleValues() {
return {
foo: 1,
bar: 2
};
}
var { foo, bar } = returnMultipleValues();
Destructing: Arrays
let [ x, y ] = [ "a", "b" ];
// x="a", y="b"
[ x, y ] = [ y, x ] // Swap values
var [,,third] = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(third);
// 3
var [head, ...tail] = [1, 2, 3, 4];
console.log(tail);
// [2, 3, 4]
Destructing: Refutable by default
Refutable (default):
{ a: x, b: y } = { a: 3 } // failsDefault Value:
{ a: x, b: y=5 } = { a: 3 } // x=3, y=5{ a: x, b: y=5 } = { a: 3, b: undefined } // x=3, y=5
Funksjonsparametre
Funksjonsparametre:
Standardverdier
Kan sette standardverdi for parametre som mangler
function func1(x, y=3) {
return [x, y];
}
Console:
# func1(1, 2);
[1, 2]
# func1(1);
[1, 3]
# func1();
[undefined, 3]
Funksjonsparametre: Restparametre
Legge etterfølgende parametre i en array:
function func2(arg0, ...others) {
return others;
}Console:
# func2(0, 1, 2, 3);
[1, 2, 3]
#func2(0);
[]
#func2();
[]
Fjerner behov for "arguments"
Funksjonsparametre: Spread operator (...)
Omgjøre en array til funksjon-/metodeparametre:
# Math.max(7, 4, 11);
11
# Math.max(...[ 7, 4, 11 ]);
11
- Det motsatte av restparameter
- Erstatter Function.prototype.apply()
Kan også brukes til å slå sammen arrays
var parts = ['shoulder', 'knees'];
var lyrics = ['head', ...parts, 'and', 'toes'];
Navngitte parametre
Bruk av destructing for navngitte parametre opt1 og opt2:
function func3(arg0, { opt1, opt2 }) {
return [opt1, opt2];
}
func3(0, {opt1: "a", opt2: "b"});
// ["a", "b"]Arrow-funksjoner
Arrow-funksjoner: syntax
Kortere syntaktisk form (function () {} vs () => {})
let squares = [1, 2, 3].map(function(x) { return x * x });let squares = [1, 2, 3].map(x => x * x);Arrow-funksjoner:
Slutt på that = this
`=>` har leksikalsk `this` istedenfor dynamisk`this`
var that = this,
button = document.getElementById("myButton");
button.addEventListener("click", function() {
that.handleClick();
});
let button = document.getElementById("myButton");
button.addEventListener("click", () => {
this.handleClick();
});Arrow-funksjoner
Generell form:
(arg1, arg2, ...) => expr
(arg1, arg2, ...) => { statment1; statment2; ...}Kortversjon - kun en parameter
arg => expr
arg => { statment1; statment2; ...}Objektorientering
OO: Objektlitteraler
__proto__ gjør det mulig å definere prototypisk arv:
// ECMAScript 6
let obj = {
__proto__: someObject, // special property
myMethod(arg1, arg2) { // method definition
...
}
};
// ECMAScript 5
var obj = Object.create(someObject);
obj.myMethod = function (arg1, arg2) {
...
};OO: Klasser
ECMAScript 6
class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
toString() {
return "(" + this.x + ", " + this.y + ")";
}
}ECMAScript 5
function Point(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
Point.prototype.toString = function() {
return "(" + this.x + ", " + this.y + ")";
};
OO: Subklasser
ECMAScript 6
class ColorPoint extends Point {
constructor(x, y, color) {
super(x, y);
this.color = color;
}
toString() {
return this.color + " " + super();
}
}
ECMAScript 5
function ColorPoint(x, y, color) {
Point.call(this, x, y);
this.color = color;
}
ColorPoint.prototype = Object.create(Point.prototype);
ColorPoint.prototype.constructor = ColorPoint;
ColorPoint.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.color + " " + Point.prototype.toString.call(this);
};OO: Statiske metoder
class Point {
static zero() {
return new Point(0, 0);
}
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
} let p = Point.zero();Moduler
Moduler: Import og export
// lib/math.js
export function sum(x, y) {
return x + y;
}
export var pi = 3.141593;
// app.js
import {sum, pi} from 'lib/math';
alert("2π = " + sum(pi, pi));// app.js
module Math from 'lib/math';
alert("2π = " + Math.sum(Math.pi, Math.pi));
Moduler: Bundling
module 'lib/math' {
export function sum(x, y) {
return x + y;
}
export var pi = 3.141593;
}
module 'lib/string' {
export function capitalize(string) {
return string.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + string.substr(1);
}
}
import {sum, pi} from 'lib/math';
import {capitalize} from 'lib/string';
alert("2π = " + sum(pi, pi));
alert(capitalize("evry"));Moduler: API
- I tillegg til deklarativ syntax finnes det et API for å laste moduler programatisk.
- System.load laster script-filer.
- System.import importerer moduler.
- Syntax ligner AMD
System.import([
'module1',
'module2'
], function (module1, module2) { // success
...
}, function (err) { // failure
...
});Moduler: Konfigurasjon
APIet har forksjellige "hooks" man kan bruke til f.eks.:
- Tilpasse hvordan modulIDer blir mappet til modulfiler.
- Kjøre f.eks. JSHint på moduler som importeres.
- Automatisk oversette moduler, f.eks. CoffeeScript eller TypeScript
- Bruke f.eks. AMD- eller Nodejsmoduler.
Loader : function(options = {}) -> Loader
options: {
global: Object = Object.create(null),
intrinsics: Loader | null = null,
strict: boolean = false,
normalize: function,
resolve: function,
fetch: function,
translate: function,
link: function
}Templatestrings
Templatestrings:
Forsøker å løse flere problemer
- Strenger over flere linjer
- Formatering
- HTML-escaping
- Lokalisering
Templatestrings: Syntax
`literal${substitution}literal`Substitusjon skjer mot variabler tilgjengelig i samme scope som templatestrengen
var name = "Evry",
msg = `Hello, ${name}!`;
console.log(msg); // "Hello, Evry!"Kan gjøre mer avanserte substitusjoner
var total = 30,
msg = `The total is ${total} (${total*1.25} with tax)`;
console.log(msg); // "The total is 30 (37.5 with tax)"Templatestrings: Tags
- Forslaget inneholder flere innebygde tags
- safehtml, msg, raw...
- Tag er en funksjon som endrer templatestrengen
- Mulig å lage egne tags
tag`literal${substitution}literal` someFunc`literal${substitution}literal`Symboler
Symboler
- Ny primitiv verdi
- Inspirert av bl.a. Lisp, Smalltalk.
- Hvert symbol er unikt
> let sym = Symbol();
> typeof sym
'symbol'
Symboler:
Enum-style-verdier
let red = Symbol();
let green = Symbol();
let blue = Symbol();
function handleColor(color) {
switch(color) {
case red:
...
case green:
...
case blue:
...
}
}Symboler: Property keys
let specialMethod = Symbol();
let obj = {
// computed property key
[specialMethod]: function (arg) {
...
}
};
obj[specialMethod](123);- Ingen navnekonflikter
- Konfigurering av objekter for ECMAScript og rammeverk via kjente symboler.
Standardbibliotek
Standardbibliotek: Maps
Enkel lagringsmekanisme for å lagre verdier knyttet til unike nøkler
let map = new Map();
let obj = {};
map.set(obj, 123);
console.log(map.get(obj)); // 123
console.log(map.has(obj)); // true
map.delete(obj);
console.log(map.has(obj)); // false- Kan iterere over keys, values og items.
- Nøkler må ikke være strenger
Standardbibliotek: Sets
En samling av verdier uten duplikater
let set1 = new Set();
set1.add('hello');
console.log(set1.has('hello')); // true
console.log(set1.has('world')); // false
let set2 = new Set([3,2,1,3,2,3]);
console.log(set2.values()); // 1,2,3
Standardbibliotek: Object.assign
Gir mulighet for å slå sammen objekter
class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
Object.assign(this, { x, y });
}
}Standardbibliotek:
Nye strengmetoder
# 'abc'.repeat(3)
'abcabcabc'
# 'abc'.startsWith('ab')
true
# 'abc'.endsWith('bc')
true
# 'foobar'.contains('oo')
trueStandardbibliotek:
Nye arraymetoder
# [13, 7, 8].find(x => x % 2 === 0)
8
# [1, 3, 5].find(x => x % 2 === 0)
undefined
# [13, 7, 8].findIndex(x => x % 2 === 0)
2
# [1, 3, 5].findIndex(x => x % 2 === 0)
-1Standardbibliotek: for-of
- Erstatter
- for-in
- Array.prototype.forEach()
- Virker for iterabler
- Arrays, Maps, Sets
Standardbibliotek: for-of Arrays
let arr = [ 'hello', 'world' ];
for (let elem of arr) {
console.log(elem);
}Output - elementer, ikke indekser
hello
worldStandardbibliotek: for-of Objekter
key-value
import items from "@iter";
let obj = { first: "Jane", last: "Doe" };
for (let [k,v] of items(obj)) {
console.log(k + " = " + v);
}Sets
var s = Set([1, 3, 4, 2, 3, 2, 17, 17, 1, 17]);
for (var v of s) {
console.log(v);
}Maps
let m = new Map;
m.set("one", 1);
m.set("two", 2);
for (let [name, value] of m) {
console.log(`the value of ${name} is ${value}`);
}Standardbibliotek:
Array comprehension
Brukes for å gjøre en array om til en annen.
let numbers = [1,2,3];
let squares = [for (x of numbers) x * x];
[for (i of document.querySelectorAll('.item'))
i.textContent]
[for (x of a) for (y of b) if (x > y) [x,y]]tilsvarer
function arrayComprehension() {
let result = [];
for (let x of a) {
for (let y of b) {
if (x > y) {
result.push([x,y]);
}
}
}
return result;
}Annet
-
Også en del av ECMAScript 6
- Promises
- Bedre støtte for Unicode (strenger, regulæruttrykk)
- Standardmoduler (@iter...)
- Sannsynligvis i ECMAScript 7
- Håndtering av binærdata
- Object.observe()
- Integers (64 bits, 32 bits, osv)
Når?
Tidsplan
- November 2013: siste gjennomgang av utkastet
- July 2014: redaksjonelt ferdig
- Desember 2014: Godkjennes av ECMA
Bruke ECMAScript 6 i dag
- Noen features er allerede på plass i browsere i dag. Flere kommer senere i 2014.
- Traceur fra Google: kompilerer ECMAScript 6 til ECMAScript 5
- Dynamisk on the fly
- statisk via tools
- TypeScript fra Microsoft
- es6-shim: funskjoner fra ECMAScript 6 biblioteket backported til ECMAScript 5.