Haskell
Lessons learned and Applications to Front End Development
by Camilo Orrego

Why should I learn Functional Programming?
It will open your mind to a different way of thinking about solving problems.
It'll help you to write solid, simple and maintainable code.
You're gonna look as a Popstar!
But you'll feel as a Noob too.


Let's see the good stuff!
Recursion
Recursion in computer science is a method where the solution to a problem depends on solutions to smaller instances of the same problem (as opossed to iteration).
Graham, Ronald; Donald Knuth; Oren Patashnik (1990). Concrete Mathematics. Chapter 1: Recurrent Problems.
First Example: Factorial of a number
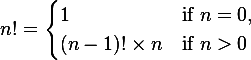
1! = 1 * 0!
0! = 1
2! = 2 * 1!
3! = 3 * 2 * 1!
3! = 3 * 2 * 1 * 0!
3! = 3 * 2!
Example
3! = 3 * 2 * 1 * 1 = 6
Factorial: Imperative way
function getFactorial(num) {
var rval = 1;
for (var i = 2; i <= num; i++) {
rval = rval * i;
}
return rval;
}Factorial: Haskell Way
factorial :: Integer -> Integer
factorial 0 = 1
factorial n = n * factorial (n - 1)Quicksort Algorithm
[8, 4, 3, 10, 15, 7]
[8]
[4, 3, 7]
[10, 15]
[4]
[3]
[7]
[10]
[15]
[3, 4, 7, 8, 10, 15]
Explanation
/**
* @source https://gist.github.com/tamask/1080446
*/
function qsort(a, k, l, r) {
// a: array to sort, k: key to sort by,
// l, r: optional array index array range
// i: stack index, s: stack,
// p: pivot index, v: pivot value,
// t: temporary array item,
// x, y: partion low/high
var i, s, p, v, t, x, y;
l = l || 0;
r = r || a.length - 1;
i = 2;
s = [l, r];
while (i > 0) {
r = s[--i];
l = s[--i];
if (l < r) {
x = l;
y = r - 1;
p = l;
v = a[p];
a[p] = a[r];
while (true) {
while (
x <= y &&
a[x] != undefined &&
a[x][k] < v[k])
x++;
while (
x <= y &&
a[y] != undefined &&
a[y][k] >= v[k])
y--;
if (x > y)
break;
t = a[x];
a[x] = a[y];
a[y] = t;
}
a[r] = a[x];
a[x] = v;
s[i++] = l;
s[i++] = x - 1;
s[i++] = x + 1;
s[i++] = r;
}
}
}Quicksort: Imperative Way
QuickSort: The Haskell Way
qsort :: (Ord a) => [a] -> [a]
qsort [] = []
qsort (x:xs) = qsort [a | a <- xs, a <= x] ++ [x] ++ qsort [a | a <- xs, a > x]
This is cool... but the Javascript engine is not optimized to do recursion efficiently.
Functions!
Pure Functions
A function is pure when it returns the same result after using the same input.
F(x)
1
7
2
6
2
6
6
13
Advantages
- Memoizable
- Very testable
- Reusable
Impure Functions
Following this order of ideas, impure functions don't return always the same value.
Functions are First Class Citizens
Functions can pass as arguments in other functions.
Higher Order Functions
They can receive functions as input and return them as output.
f(x)
1
1
2
4
3
9
5
25
[1, 2, 3, 5]
[1, 4, 9, 25]
MAP
Example
square :: Int -> Int
square x = x ^ 2
map square [1..5] -- [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].map(x => x * x);
// [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
Partial Application
Each time a function is called with an argument, returns a new function until it receives all the arguments, returning the expected result.
Example
const join = curry(function join(delimiter, list) {
return Array.prototype.join.call(list, delimiter);
});
const joinByDash = join('-');
joinByDash([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]); // "1-2-3-4-5"Composition!!!
With composition, you can create complex functions with simple blocks.
-- Haskell!
-- get the sum of squares of the odd numbers of a list.
sumOddSquares :: Integral a => [a] -> a
sumOddSquares = sum . map (\x -> x * x) . filter odd
main :: IO()
main = print $ sumOddSquares [1,3,2,8,5] -- 1 + 9 + 25 = 35
Example
// Javascript!
const getUpperName = compose(toUpper, get('name'));
getUpperName({ name: "Maximus" }); // MAXIMUSType System
Static Typing
Types are checked in compilation time. This approach reduces a lot of runtime errors.
Strongly Typed
There's no coercion. Instead, you have to compare the values manually through functions.
Type Inference to the rescue!
Haskell type system can deduce the type of the expressions without defining it, making it as clean as dynamic languages.
Not in Javascript???
Think Again!


Example
/**
* Gets the first element of a list.
* @param {Array} list List of elements.
* @returns {*} First element of the list.
*/
export default function head(list: Array<any>): any {
const [x] = list;
if (x == null) {
throw Error('List must have at least one element');
}
return x;
}What else?
Fantasy Land