Interface
Advanced Programming
SUT • Spring 2019
Outline
-
interface
-
Multiple Inheritance
Interface
Abstract Example
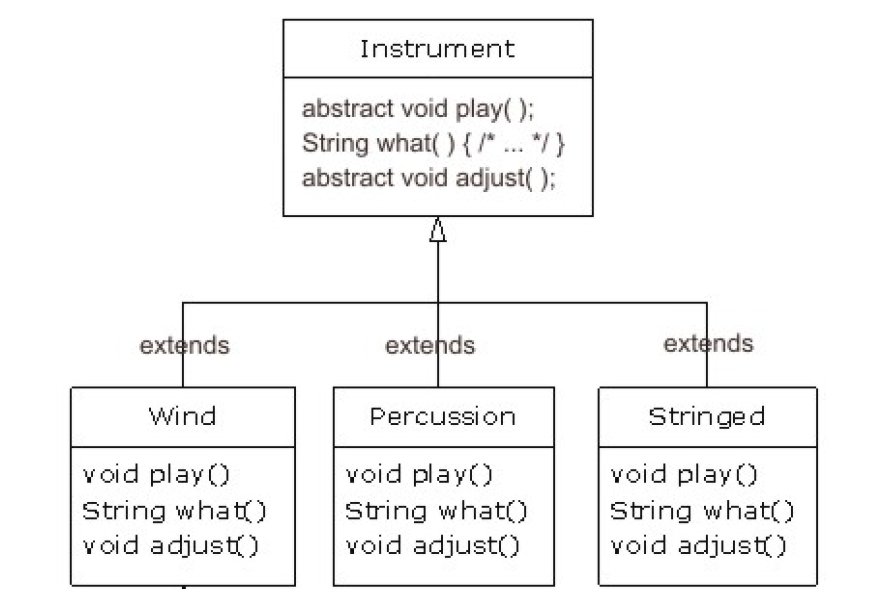
Abstract Method
- All subclasses have the method
- But we can not implement the method in super-class
- So why we define it in super-class?
- Polymorphism
Interface
- Sometimes we have an abstract class, with no concrete method
- interface: pure abstract class
- no implemented method
Interface
interface Shape {
int getColor();
double getArea();
double getPrimeter();
}Interface
-
All the methods are implicitly abstract
-
No need to abstract specifier
-
-
All the methods are implicitly public
-
No need to public specifier
-
interface Shape {
int getColor();
double getArea();
double getPrimeter();
}Interface Implementation
-
Some classes may inherit abstract classes
-
Some classes may implement interfaces
-
-
Is-a relation exists
-
If a class implements an interface
-
But does not implement all the methods
-
What will happen?
-
The class becomes an abstract class
-
class Rectangle implements Shape {...}Example
class Rectangle implements Shape {
private double width, length;
private int color;
public Rectangle(double width, double length, int color) {
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
this.color = color;
}
public int getColor() {
return color;
}
public double getArea() {
return width * length;
}
public double getPrimeter() {
return 2 * (width + length);
}
}Multiple Inheritance in Java
-
A class can inherit one and only one class
-
A class may implement zero or more interfaces
interface CanFight {
void fight();
}
interface CanSwim {
void swim();
}
interface CanFly {
void fly();
}
class ActionCharacter {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
class Hero extends ActionCharacter implemenets CanFight, CanSwim,
CanFly {
public void fly() {}
public void swim() {}
public void fight() {}
}A Question
-
Why multiple inheritance is not supported for classes?
-
Why multiple inheritance is supported for interfaces?
What About Name Collision?
-
The return types are incompatible for the inherited methods B.f(), A.f()
interface A {
int f();
}
interface B {
void f();
}
public abstract class TestCase implements A, B {};interface CanFight {
void fight();
void move();
}
interface CanSwim {
void swim();
}
interface CanFly {
void fly();
void move();
}
class ActionCharacter {
public void fight() {}
}
class Hero extends ActionCharacter implemenets CanFight, CanSwim,
CanFly {}Example
Interface Extension
-
Interfaces may inherit other interfaces
-
Code reuse
-
Is-a relation
-
interface CanSee{
void move();
void see();
}
interface CanMove{
void move();
}
interface CanFight{
void fight();
}Interface properties
-
No member variable
-
Variables: implicitly final and static
-
Usually interfaces declare no variable
-
-
Only operations are declared
-
No constructor
-
Why?
-
Example
interface A {
int a = 5;
int f();
}
public class TestClass implements A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(a);
}
}Interfaces Applications
-
Pure Abstract classes
-
Describe the design
-
The architect designs interfaces, the programmer implements them
-
Only interfaces are delivered to code consumers
-
-
More powerful inheritance and polymorphism
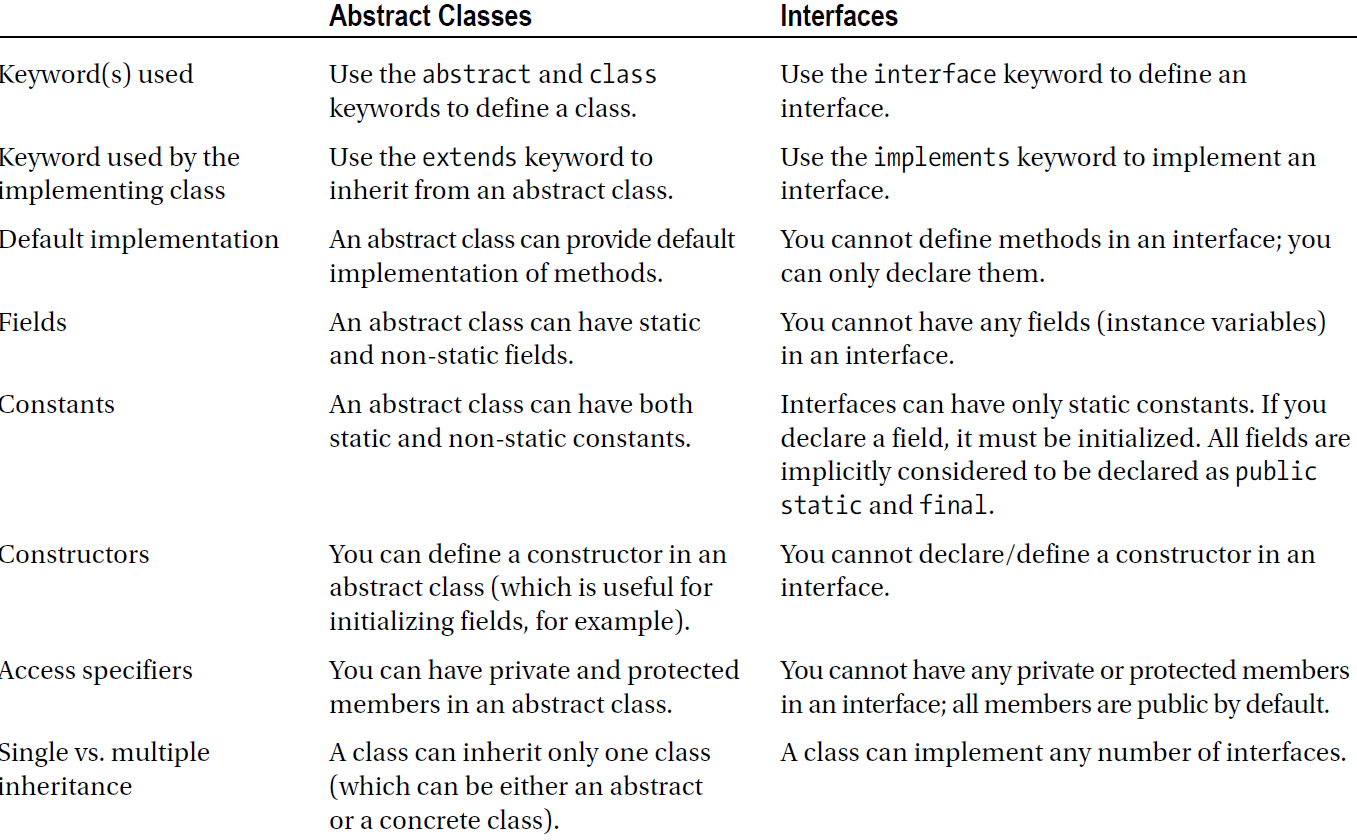
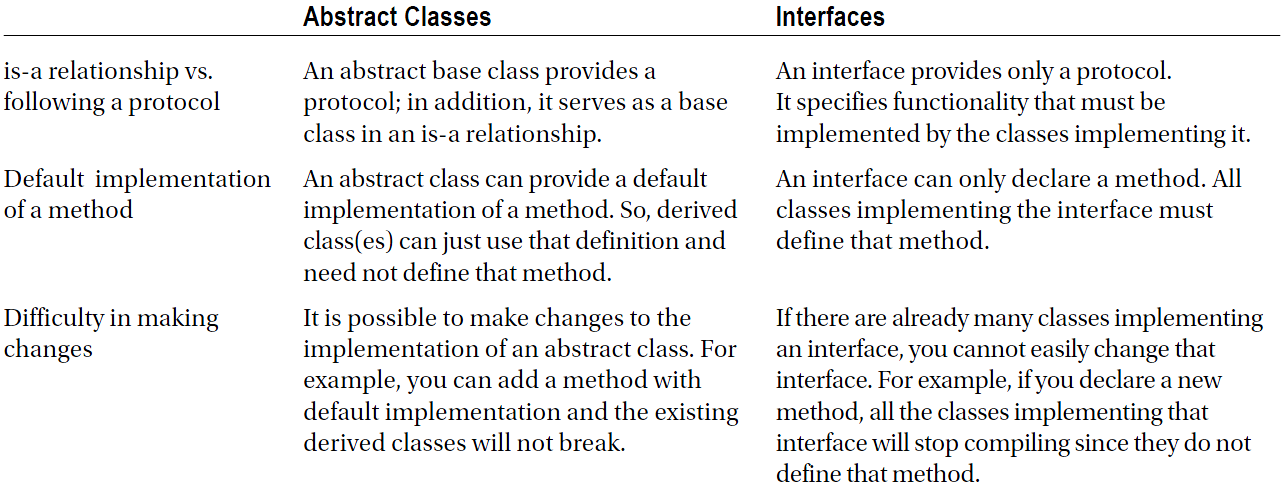
Default Method (Java 8)
public interface Interface {
void method(String str);
default void log(String str) {
System.out.println("logging::" + str);
Interface.print("abc");
}
}Default Method (Java 8)
public interface OtherInterface {
void otherMethod();
default void log(String str) {
System.out.println("Other logging::" + str);
}
}Default Method (Java 8)
public class Concrete implements Interface, OtherInterface {
@Override
public void method(String str) {
}
@Override
public void otherMethod() {
}
@Override
public void log(String str) {
System.out.println("MyClass logging::" + str);
}
}Static method
public interface Interface {
void method(String str);
default void log(String str) {
System.out.println("logging::" + str);
Interface.print("abc");
}
static void print(String str) {
System.out.println("Interface Print " + str + ".");
}
}Private Static method
public interface Interface {
void method(String str);
default void log(String str) {
System.out.println("logging::" + str);
Interface.print("abc");
}
private void print(String str) {
System.out.println("Interface Print " + str + ".");
}
}Title Text
