Test
Advanced Programming
SUT • Spring 2019
Review
-
Java Programming Language
-
Principles of Object Oriented Programming
-
Characteristics of objects
-
Encapsulation
-
-
Objects in memory
-
References
-
Heap
-
Stack
-
-
Parameter Passing
Review
- Initialization and Cleanup
- Constructor
- finalize()
- Order of initialization
- Initialization blocks
- Access specifiers
- Public
- Private
- Package access
Review
- Package
- Static
- The this reference
- Method overloading
- toString()
- equals()
- Refactoring
- Bad smells
- Refactoring techniques
Agenda
-
Software Quality
-
Characteristic of a good software
-
Test
-
Unit Testing
-
Refactoring
Software Quality
Quality of Product
-
The producer should ensure about the quality of the products
-
Quality Control
-
Any business, any product
A Cook

In surgery
A Car Maker


Quality Control
- Quality should be tested
- A product is not finalized, before the test
- Different kinds of test, check different kinds of quality

Software Quality
- We are programmers
- Programmers produce software
- What are characteristics of a good software?
- Many parameters. E.g.
- Conformance to requirements
- Performance
- Time
- Memory
- Maintainability
- Changeability
- Different kinds of test, check different kinds of quality
Test in Other Industries
- Test side effects
- A damage to the product
- Test of a building
- Test of a car
- Test of a part of a product
Test Side Effects

What to do with Test Side Effects?
- Testing a sample of the product
- Simulation
- Mathematical analysis
- In software testing
- Along with all of these techniques
- And we can also test the software itself!
- (Usually) no damage to the software
Test Target
- System Test
- Test the system as a whole
- For performance, correctness and conformance.
- Unit Test
- Test the units and modules
- Test of a component
- Test of a class
- Test of a method
How to Test Software
- Manual Test
- Try it!
- Test Tools
- Performance Test
- Profiling
- JProfiler, TPTP
- Load Test
- Jmeter
- Test Code
- Unit Tests
- Test Teams
Test Code
- Business Code
- The code, written for implementation of a requirement
- The code, written for implementation of a requirement
- Test Code
- The code, written for test of an implementation
Unit Testing
- A process for the programmer
- Not a test team procedure
- For improving the code quality
- Reduces bugs
- Test of units of software
- before the software is completed
- Unit: method, class
Classical Unit Testing
- Writing main() method
- Some printlns
- Drawbacks?
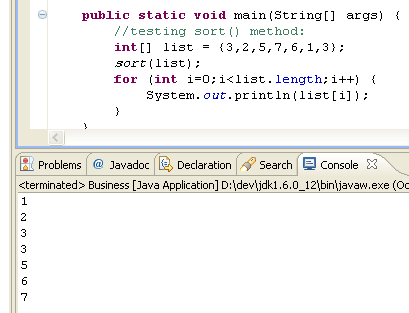
Drawbacks
- Test code coupled with business code
- In the same class
- Written tests are discarded
- One test at a time
- The programmer executes the tests himself
- Test execution is not automatic
- The programmer should check the result of each test himself
- The test is passed or failed?
- The test result interpretation is not automatic
A Good Unit Test Code
- Repeatable
- Automatic
- Invocation
- Acceptance (Pass/Failure)
- JUnit helps you write such tests
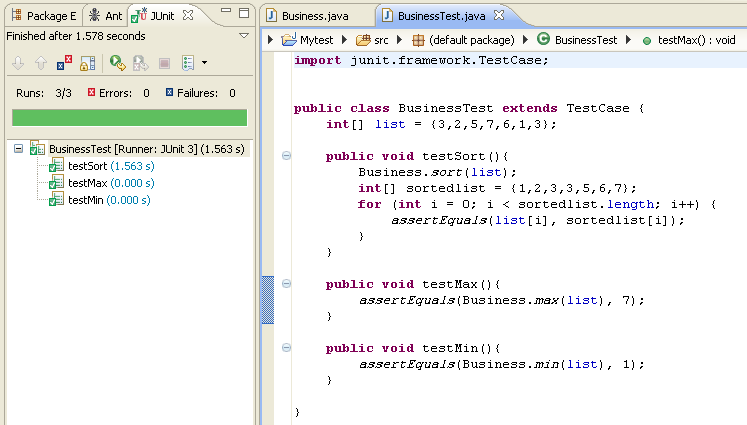
JUnit, First Example
public class BusinessTest extends TestCase {
public void testSort(){
int[] list = {3, 2, 5, 7, 6, 1, 3};
Business.sort(list);
int[] sortedList = {1, 2, 3, 3, 5, 6, 7};
for (int i = 0; i < sortedList.length; i++){
assertEquals(list[i], sortedlist[i]);
}
}
}JUnit, The Green Bar
What is the output of:
public class Testing {
@Test
public void testNormal() {
int[] array = {3, 2, 1, 4};
int[] sorted = {1, 2, 3, 4};
Business.sort(array);
for (int i = 0; i < sorted.length; i++) {
Assert.assertEquals(sorted[i], array[i]);
}
}
@Test
public void testEmptyArray() {
int[] array = {};
try {
Business.sort(array);
} catch (Exception e) {
Assert.fail();
}
Assert.assertEquals(array.length, 0);
}
}Assertions
- assertNull(x)
- assertNotNull(x)
- assertTrue(boolean x)
- assertFalse(boolean x)
- assertEquals(x, y)
- Uses x.equals(y)
- assertSame(x, y)
- Uses x ==y
- assertNotSame
- fail()
Annotations
- @Test
- @Before
- @After
- @BeforeClass
- @AfterClass
What is the output of:
@Test
public void theTestMax() {
System.out.println(" testMax()");
assertEquals(Business.max(list), 7);
}
@Test
public void theTestMin() {
System.out.println(" testMin()");
assertEquals(Business.min(list), 1);
}
@Before
public void theTestMax() {
System.out.println(" setUp()");
}
@After
public void theTestMax() {
System.out.println(" tearDown()\n");
}
A Good Unit Test is
- Automated
- Through
- Repeatable
- Independence
- Professional
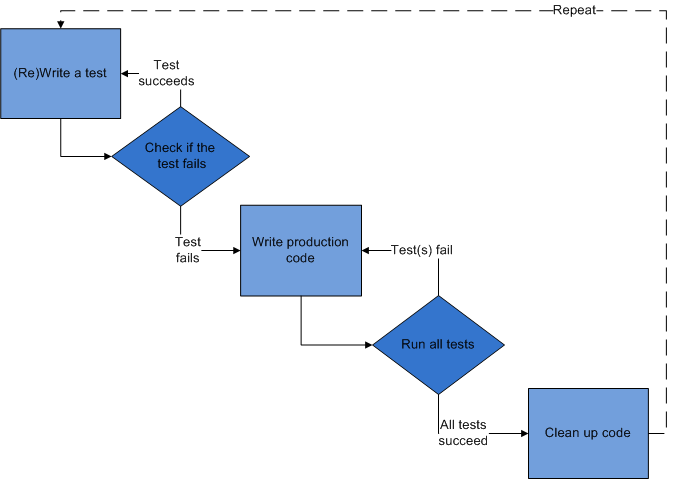
Test Driven Development
- Test First Development
- Before writing a code, write the tests!
TDD
Title Text
