Web APIs 101
Web Programming Course
SUT • Fall 2018
TOC
-
Document Object Model (DOM)-
Introduction
-
Data Types
-
Selectors -
DOM Manipulation -
Events
-
DOM Tree
-
-
Asynchronous JavaScript And XML (AJAX)
-
XMLHttpRequest -
Fetch API
-
Promise (ES2015)
-
- Web Storage
cookielocalStoragesessionStorage
DOM
document.getElementById("img1")
.style
.borderWidth = '1px';Is this JavaScript?
document.addEventListener('click', function () {
// some stuff
}, false);What about this?
Intro
More on MDN
DOM
What is DOM
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming interface for HTML and XML documents. It represents the page so that programs can change the document structure, style, and content. The DOM represents the document as nodes and objects. That way, programming languages can connect to the page.
Intro
DOM
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>
Hello World
</p>
<div>
<img src="example.png"/>
</div>
</body>
</html>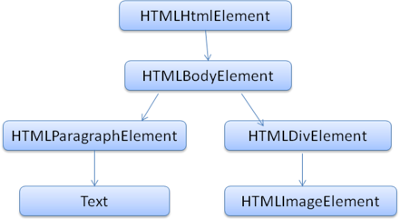
Parsing
Intro
More on MDN
DOM
More on MDN
// the document object
window.document;
// returns an Element
document.getElementById('foo');
// returns a NodeList
document.getElementsByTagName('a');Data Types
DOM
More on JavaScript.info
Selectors
-
document.getElementById()
-
document.getElementsByClassName()
-
document.getElementsByTagName()
-
document.querySelector()
-
document.querySelectorAll()
- ...
Also on an element
To match an element or a NodeList collection
DOM
More on JavaScript.info
Manipulation
- Styles:
- Read/Write width, height, ...
- Attributes:
- Read/Write class attribute value, data-*, ...
- Add element:
- Creating children tree, moving an element, ...
- ...
DOM
More on MDN
Example
Manipulation
DOM
More on JavaScript.info
Events
A signal that something has happened.
3 ways to assign event handlers:
- HTML attribute
onclick="..." - DOM property
elem.onclick = function(){};. - Methods
elem.addEventListener(event, handler[, phase])to add,removeEventListenerto remove.
DOM
More on JavaScript.info
Example
Events
DOM
More on JavaScript.info
Bubbling & Capturing
Events
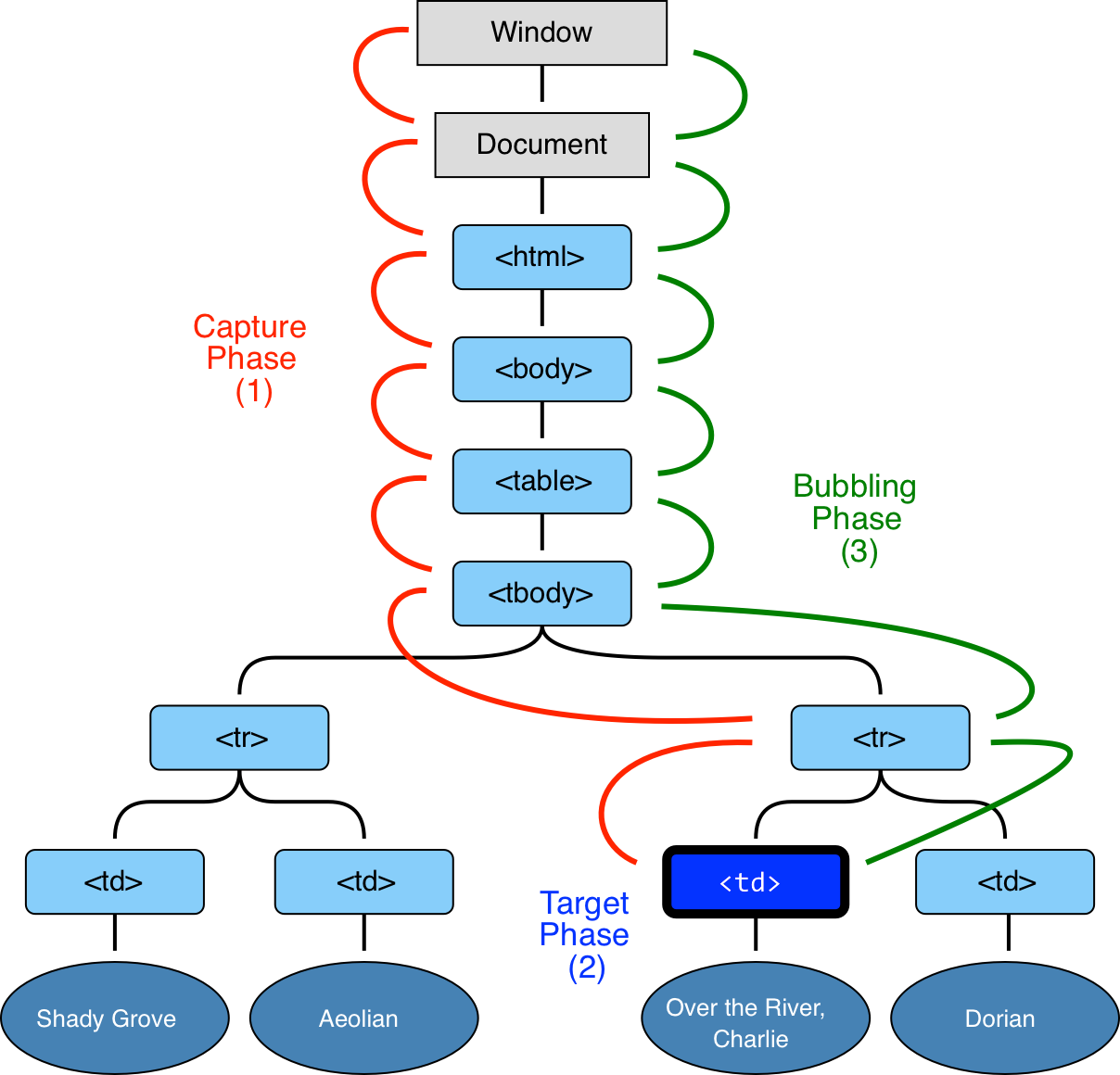
1. Capturing Phase
2. Target Phase
3. Bubbling Phase
event.stopPropagation()
DOM
More on JavaScript.info
Tree
Creating new elements "on the fly", modifying the page
AJAX
To partially updating the web page
More on MDN
... is a set of Web development techniques using many Web technologies on the client side to create asynchronous Web applications [that] can send and retrieve data from a server without interfering with the display and behavior of the existing page. By decoupling the data interchange layer from the presentation layer, Ajax allows Web pages to change content dynamically without the need to reload the entire page.[3] ... modern implementations utilize JSON instead of XML due to the advantages of JSON being native to JavaScript.
AJAX
XMLHttpRequest API
More on MDN
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET', '/my/url');
xhr.send();
xhr.onload = function() {
// we can check
// status, statusText - for response HTTP status
// responseText, responseXML (content-type: text/xml)
if (this.status != 200) {
// handle error
alert( 'error: ' + this.status);
return;
}
// get the response from this.responseText
};
xhr.onerror = function() {
// handle error
};AJAX
fetch API
More on MDN
fetch('/my/url', { method: 'GET' })
.then(function(response) {
if (response.ok) {
return response.json();
}
throw new Error('Network response was not ok.');
})
.then(function(data) {
// do something with data
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.error(error);
});AJAX
A future value for the completion of an asynchronous operation.
More on JavaScript.info
Promise Intro
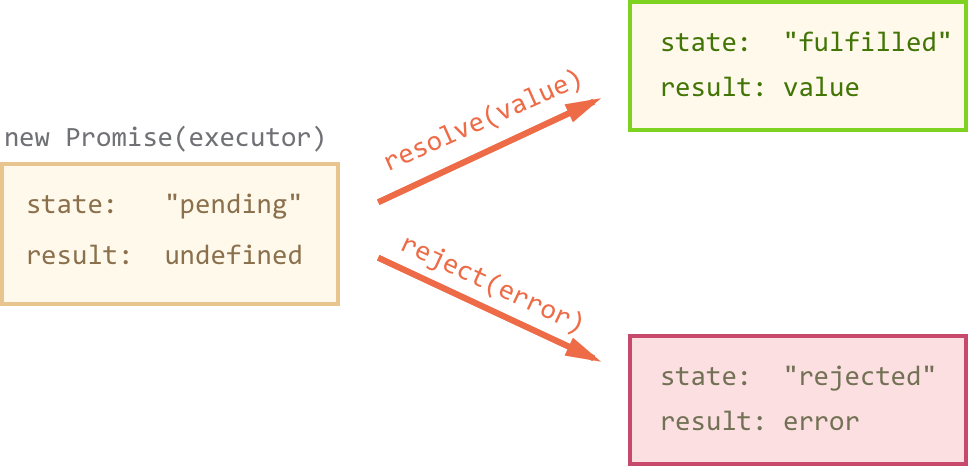
new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// the function is executed automatically with `new Promise`
// after the async job: call resolve(value) or reject(reason)
});AJAX
More on JavaScript.info
Promise Example
Web Storage
Mechanisms by which browsers can store data
More on MDN
Use-cases
- Authentication (persist token)
- To keep user's preferences
- ...
Web Storage
More on MDN
Cookie
Response (Set-Cookie header)
Set-Cookie: <cookie-name>=<cookie-value>
Set-Cookie: yummy_cookie=choco
Set-Cookie: tasty_cookie=strawberryRequest (Cookie header)
Cookie: <cookie-list>
Cookie: name=value
Cookie: name=value; name2=value2; name3=value3Web Storage
More on MDN
Cookie
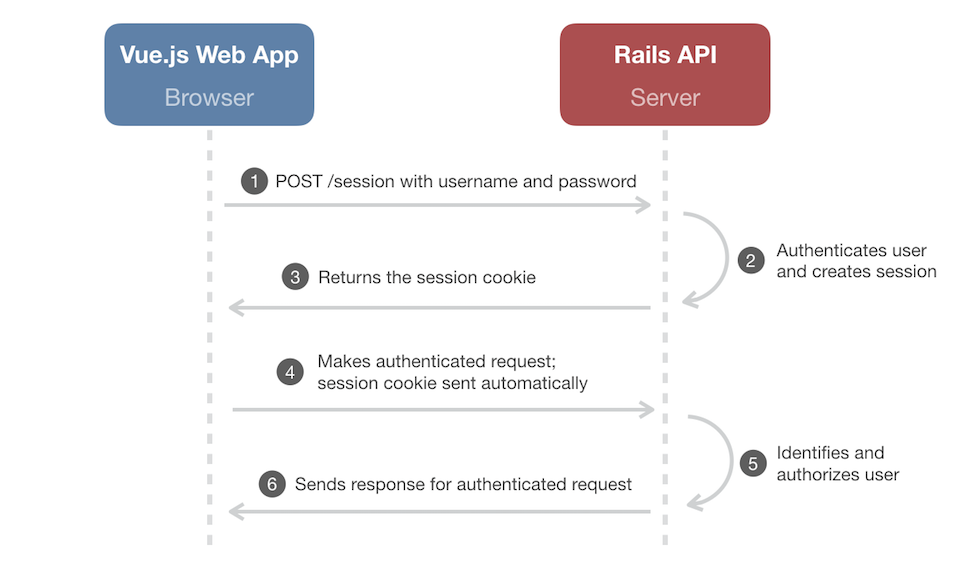
Web Storage
More on MDN
// getting all cookies
// semicolon-separated list of all cookies
// (e.g. "key1=value1; key2=value2")
allCookies = document.cookie;
// writing a new cookie
document.cookie = newCookie;Cookie
API
Web Storage
More on MDN
// adding a data item
localStorage.setItem('myCat', 'Tom');
// reading an item
var cat = localStorage.getItem('myCat');
// removing an item
localStorage.removeItem('myCat');
// clear all items
localStorage.clear();
Storage
Web Storage
More on MDN
Storage