Analysis of Scientific Paper
OpenSIP : Toward Software-Defined SIP Networking
Wai Yan Kyaw
211AEM007
Agenda
-
Traditional SIP Networks
-
Problems of legacy SIP networks
-
OpenSIP
-
Contributions
-
Software Defined Networking
-
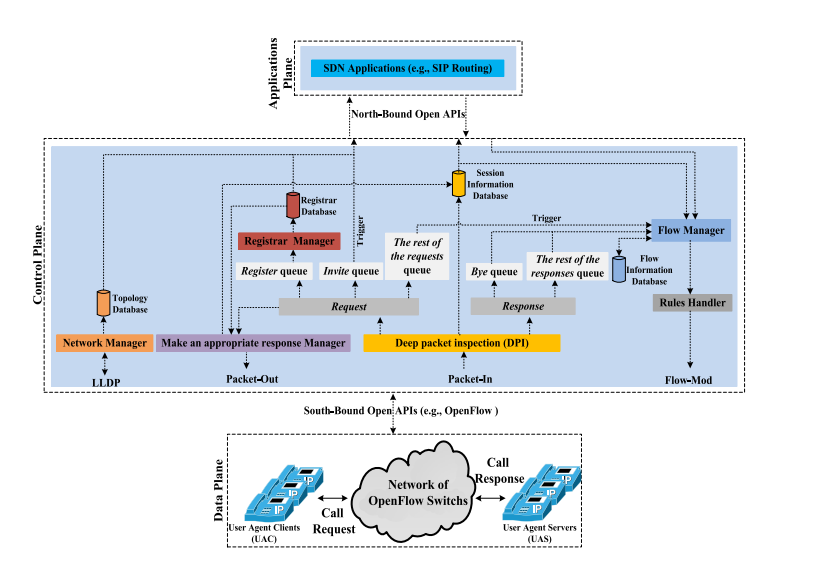
Partial SDN-based Architecture
-
Full SDN-based Architecture
-
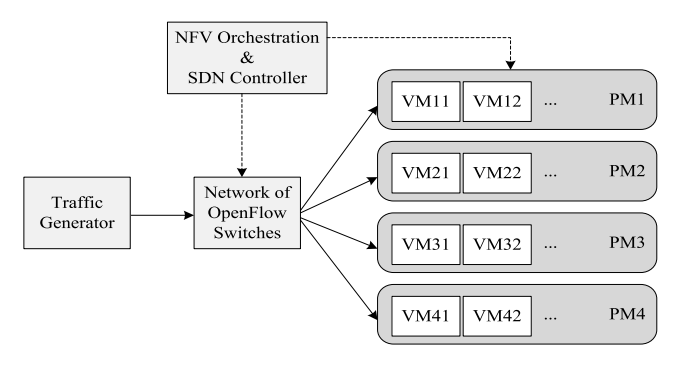
Software-Defined NFV-Based Architecture
-
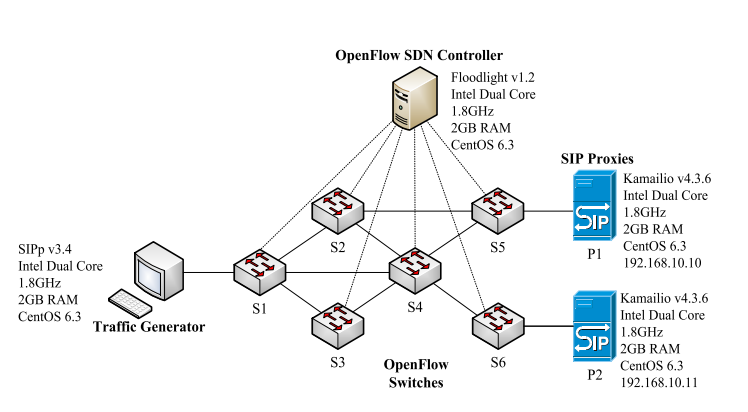
Implementation and Performance Evaluation
-
Conclusions
Session Initiatoin Protocol (SIP)
SIP is extensively deployed for significantly growing session-oriented applications on the Internet, such as Internet telephony or voice over IP.
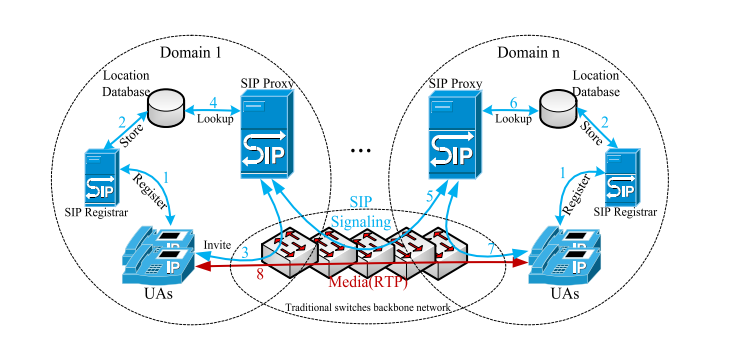
Traditional SIP Netowork
With the incresing use of SIP,
-
Ineffective routing
-
un-optimized management of proxy resources
-
overload conditions
OpenSIP
The gold of the current study is to separate the main functionalities of the SIP networks into a software logically centralized controller.
Contributions
This paper intruduces three approaches: First approach:Partial SDN-Based Architecture (OpenSIP_Partial) Second approach:Partial SDN-Based Architecture (OpenSIP_Full)
Third approach:Software-Defined NFV-Based Architecture(OpenSIP_NFV+)
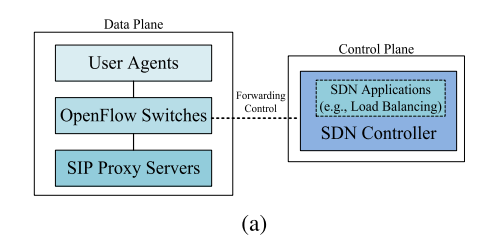
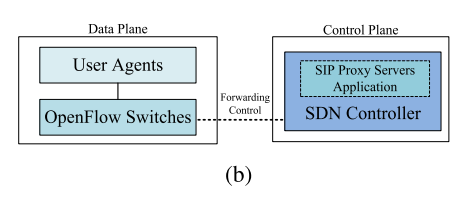
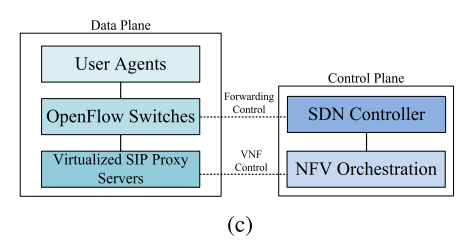
OpenSIP_Partial
OpenSIP_Full
OpenSIP_NFV+
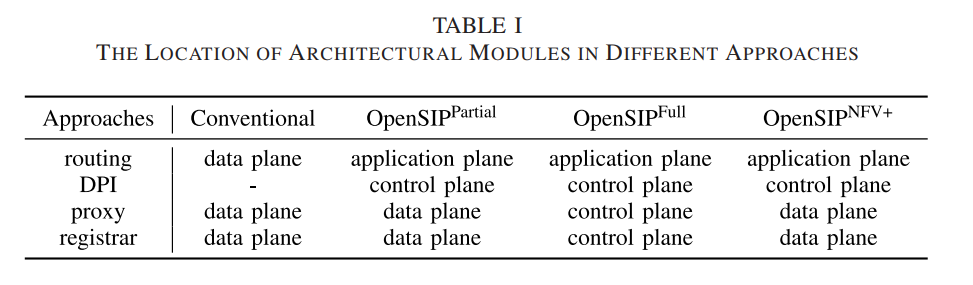
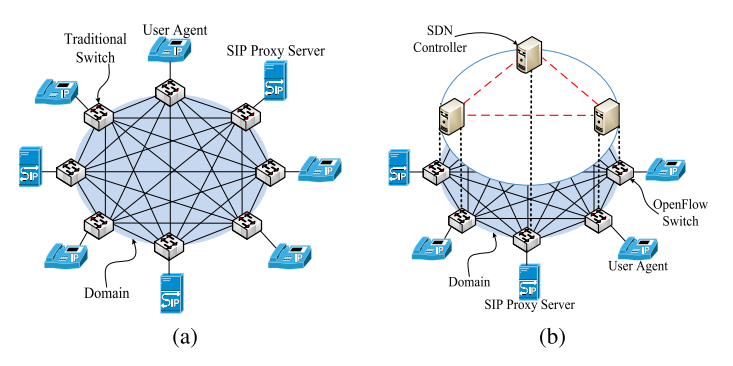
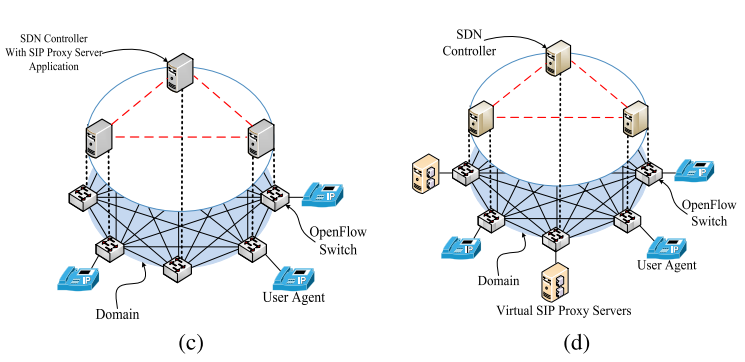
(a) Traditional SIP network
(b) OpenSIP_Partial
(c) OpenSIP_Full
(d) OpenSIP_NFV+
Partial SDN-based Architecture
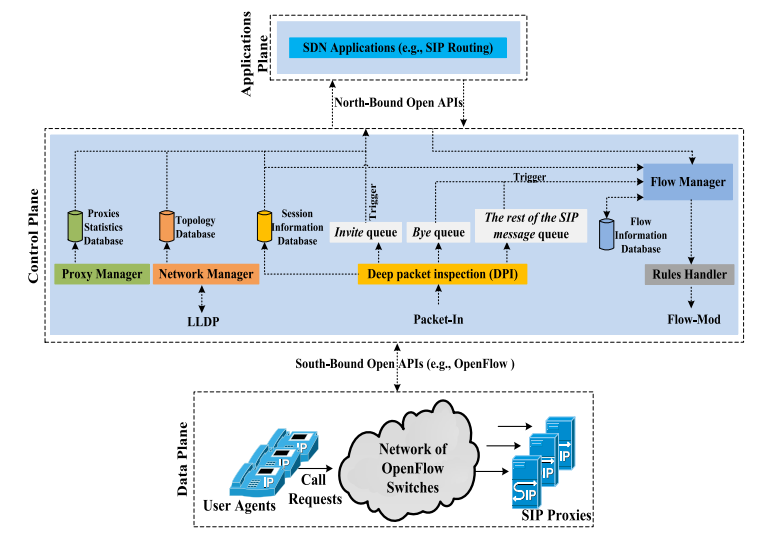
Full SDN-based Architecture
Software-Defined NFV-Based Architecture
Implementation and Performance Evaluation
For OpenSIP_Partial
-
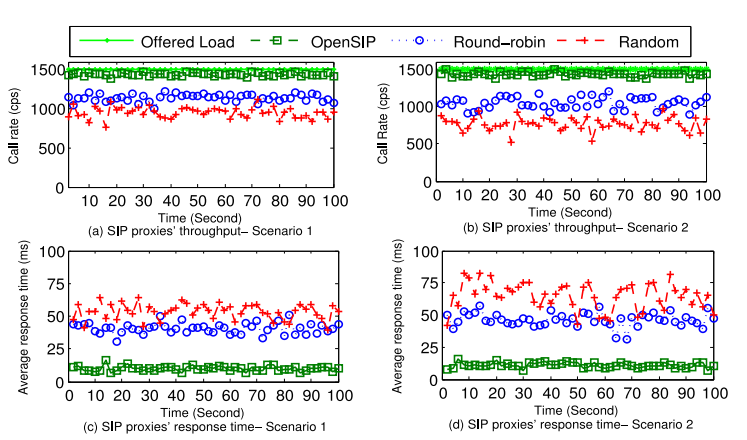
Scenario_1: Background traffic of each proxy is equal -
Scenario_2:Backgound traffic of P1 is as double as P2.
Implementation and Performance Evaluation
For OpenSIP_Full
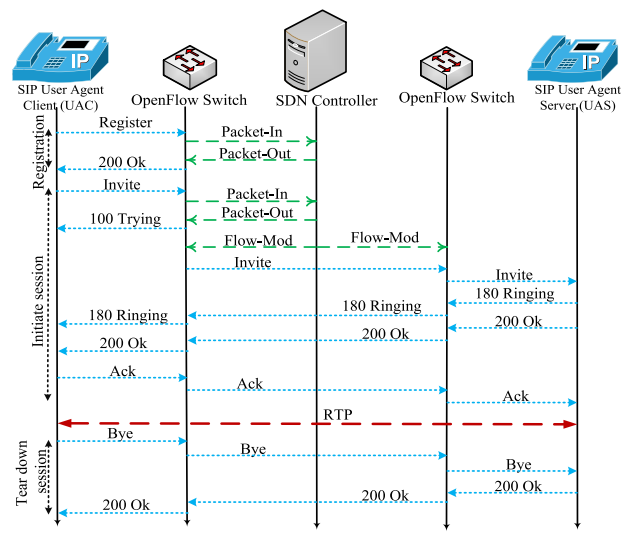
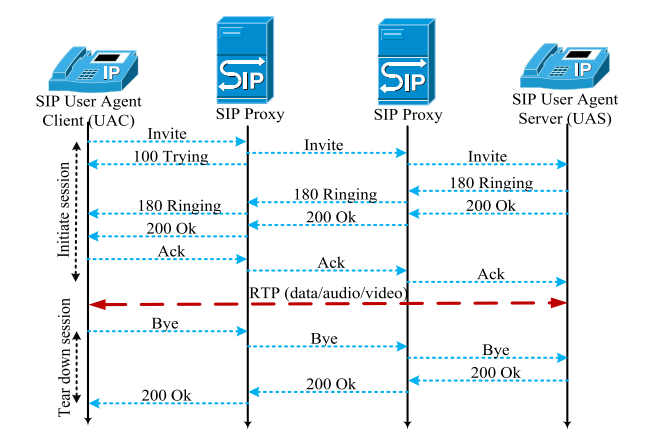
Basic SIP Flow
Advanced SIP Flow
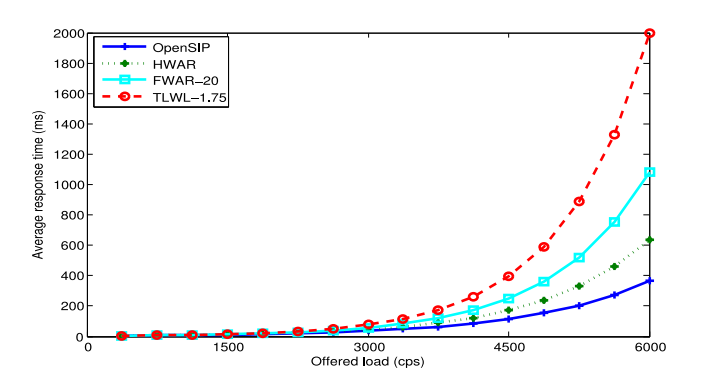
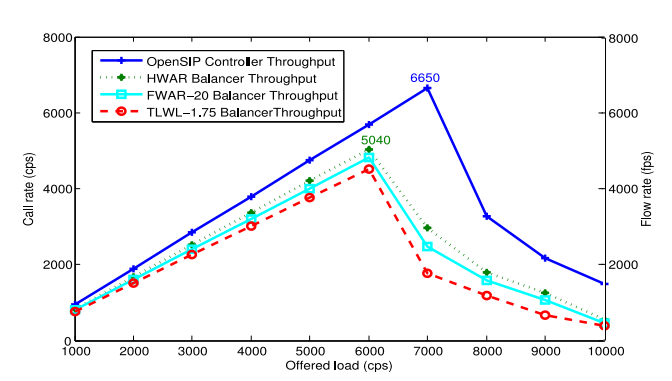
Simulation results
Conclusions
The simulation results confirmed that
-
high throughput, -
low response time -
resource efficiency. -
the scalability of the proposed controllers -
the proper routing of call requests