Exam 1 Review
Disclaimer
There is no way I can cram half a semester's worth of material into a 2 hour review.
Consider this a highlights reel. Some details have been missed that could appear on the exam.
Specimen Review
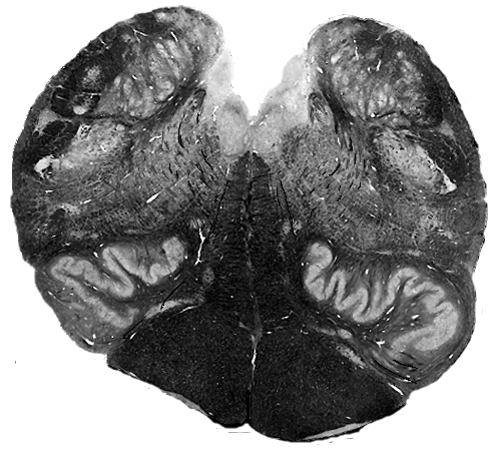
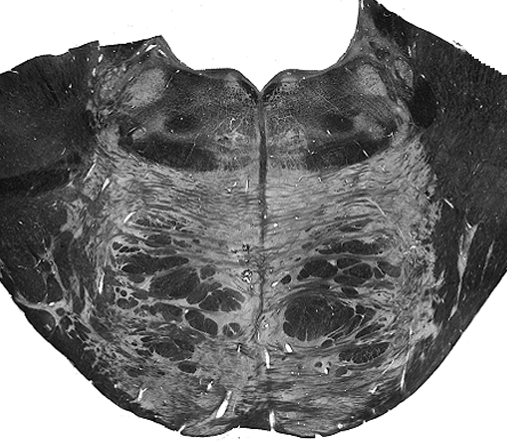
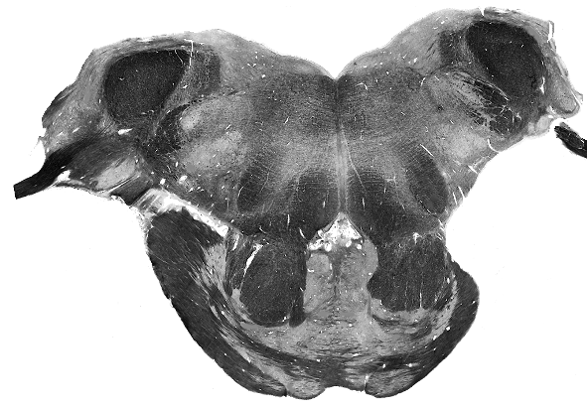
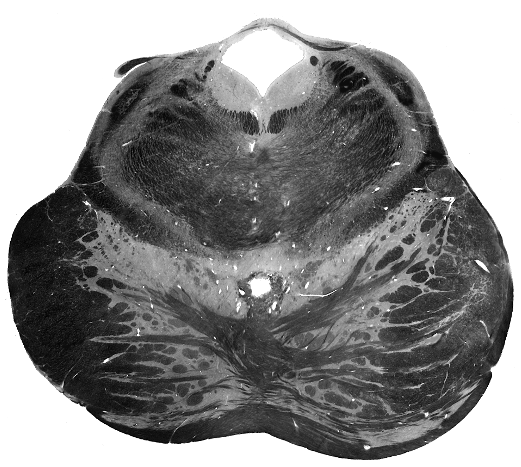
Brain darts!
Rules:
- We'll all take turns throwing magnets at the specimen picture.
- When the magnet lands on the target, write the:
- Name
- Function (if known)
- Signs/symptoms (if known)
- A correct answer is worth one point.
- Winner gets choice of candy bar at the end.

Which atlas should we use?
Washington Brain atlas
Brain Atlas
BrainStorm
My brain
Cortex
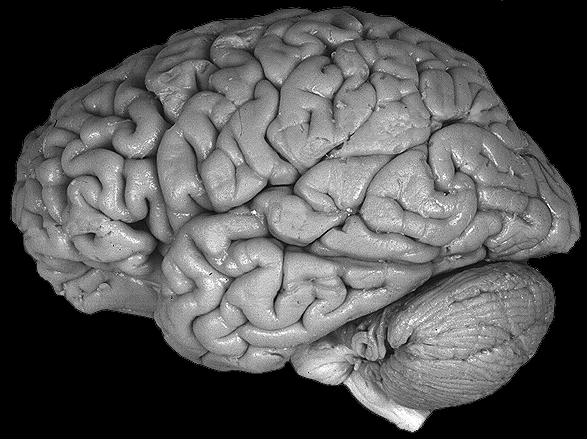
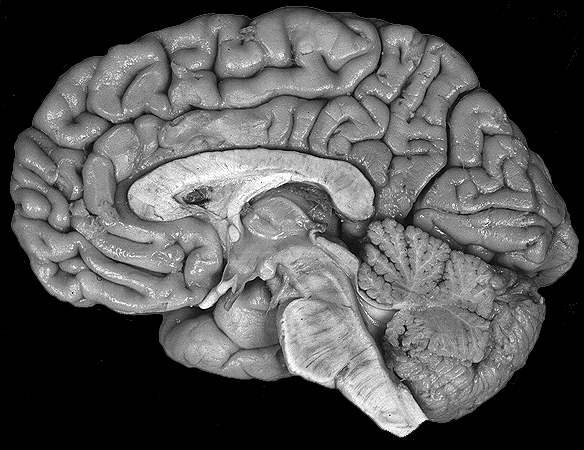
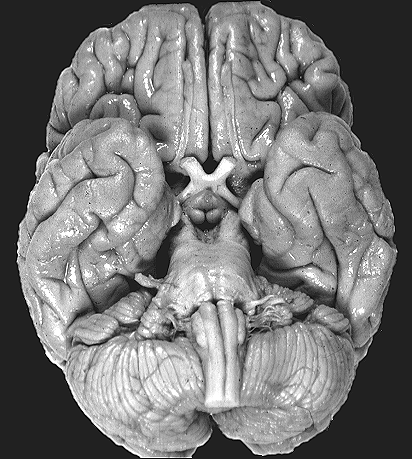
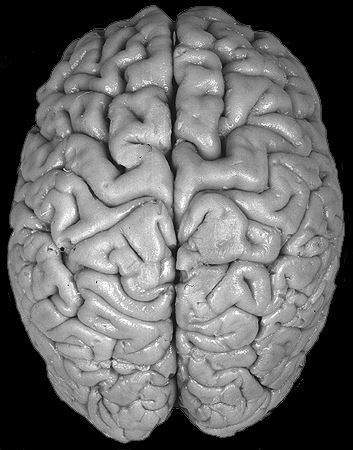
Subcortical
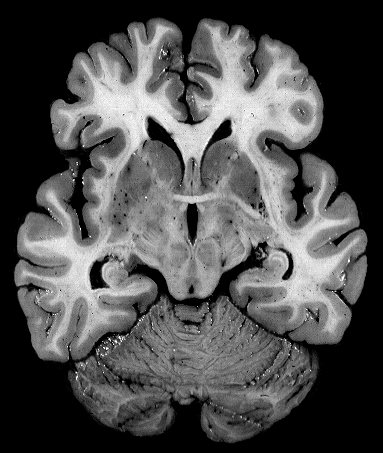
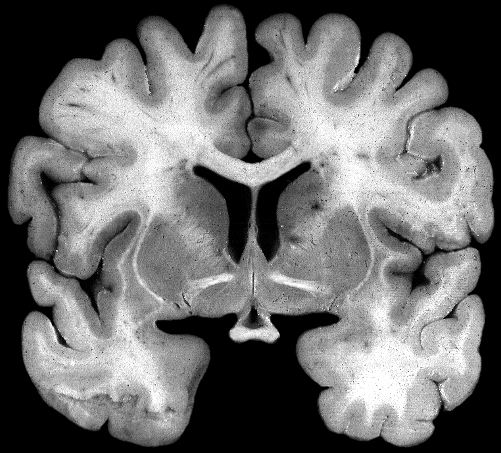
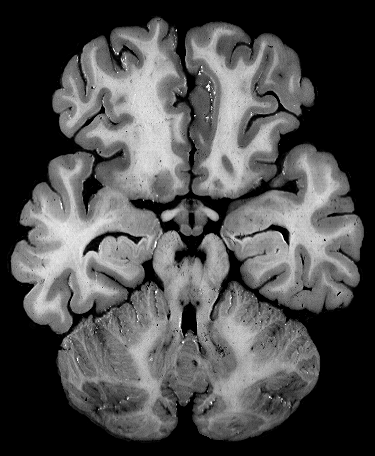
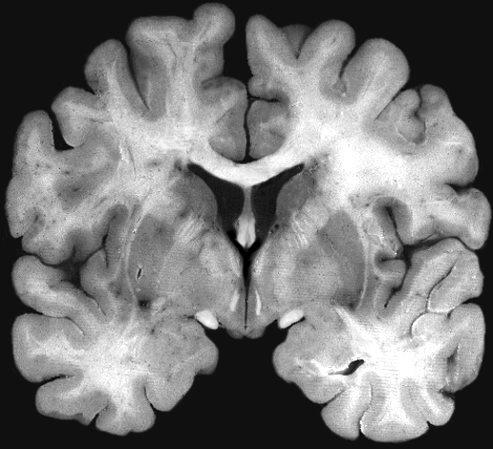
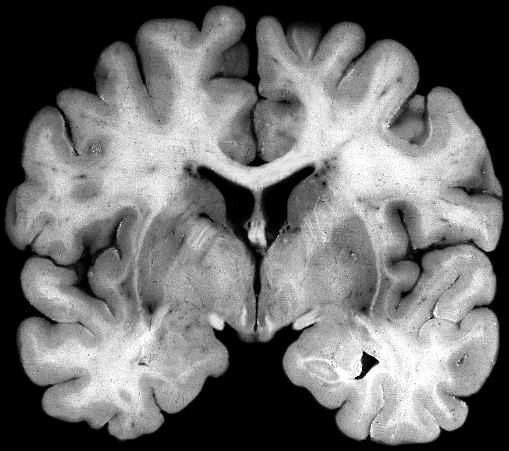
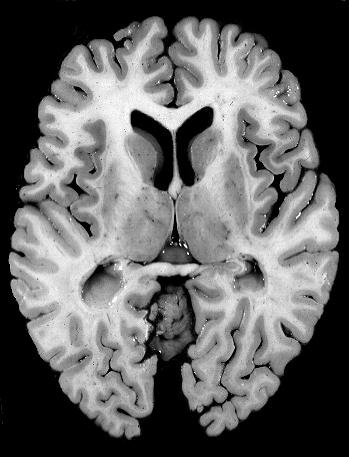
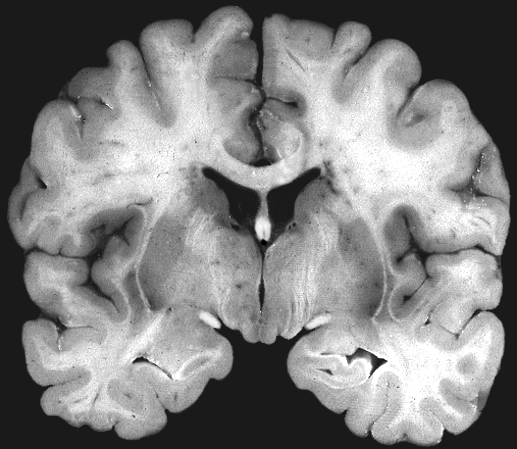
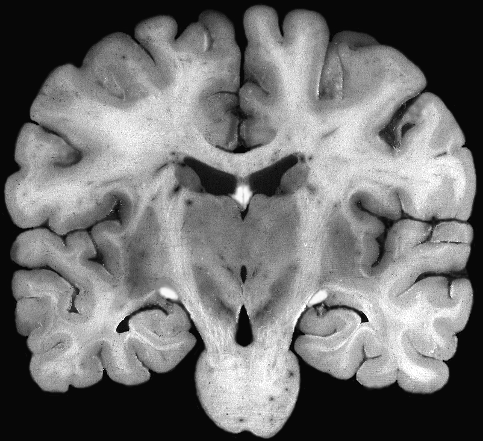
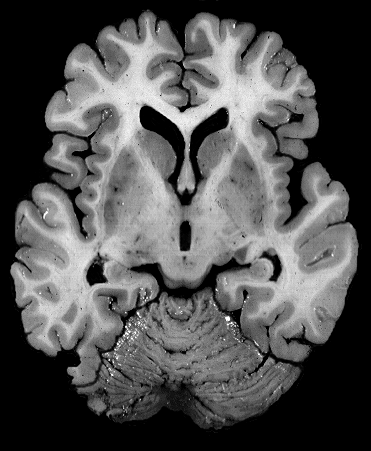
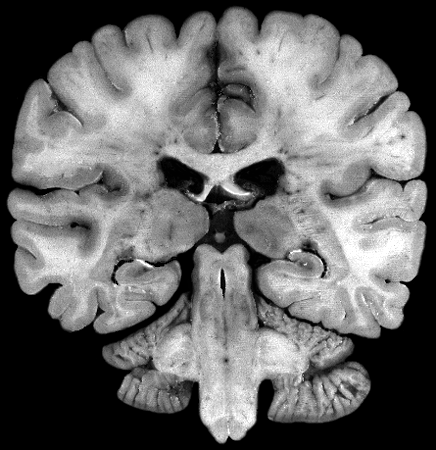
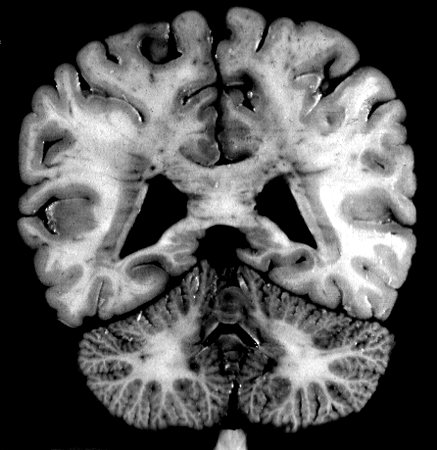
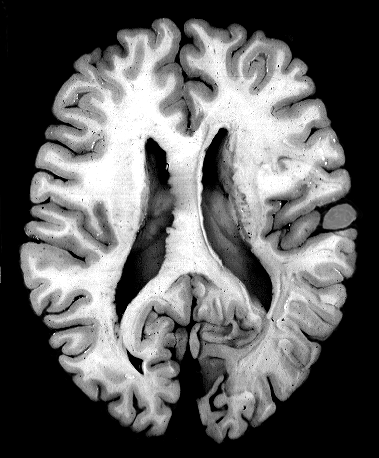
Brainstem
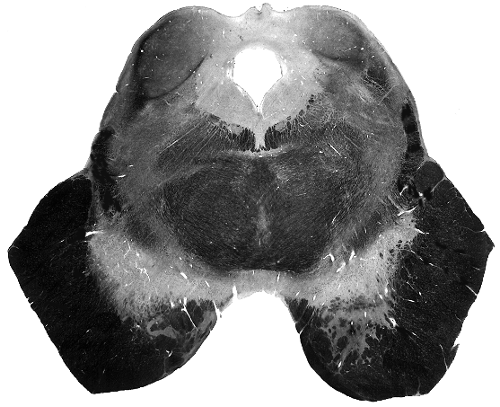
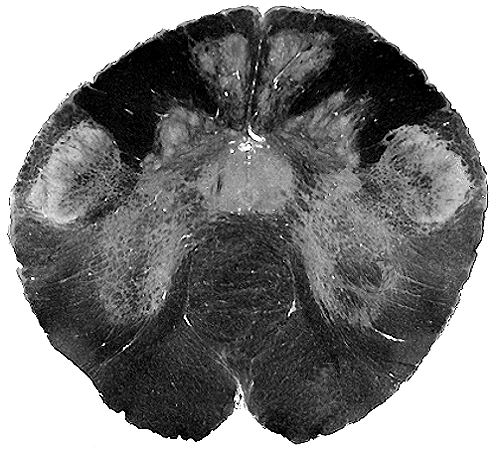
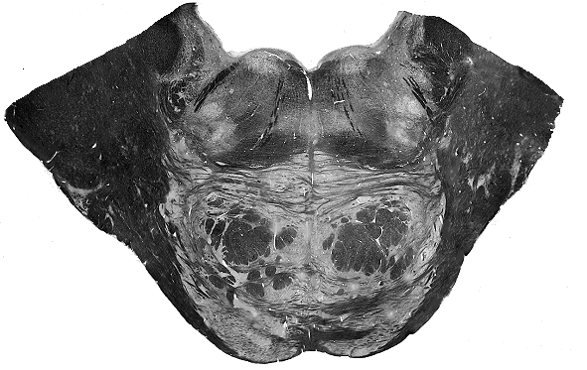
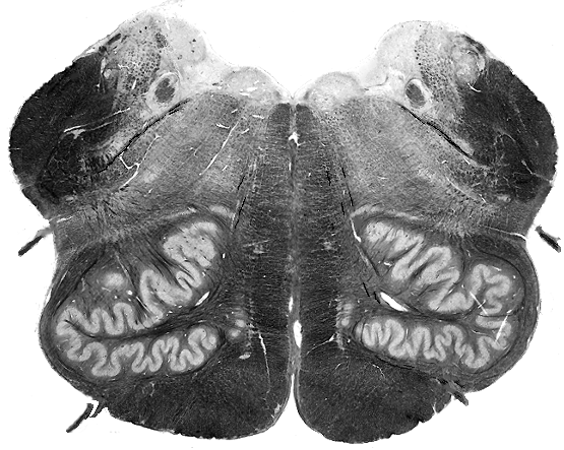
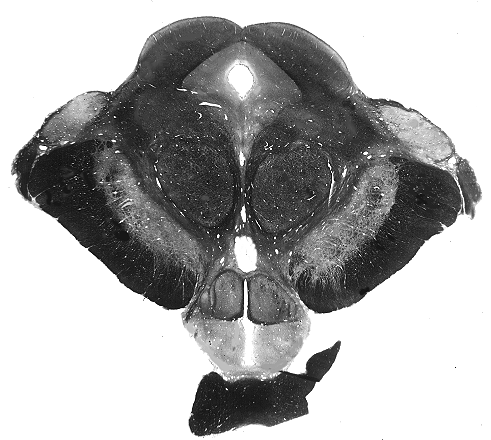
Spinal Cord
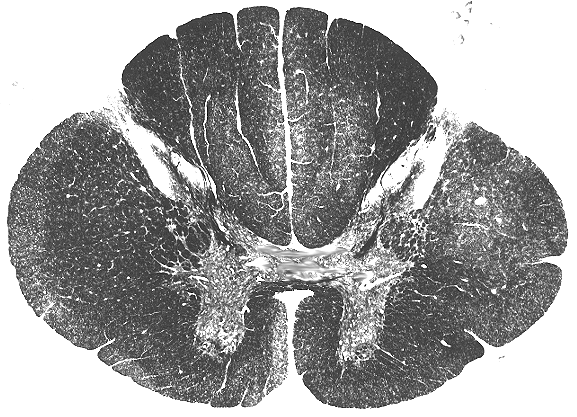
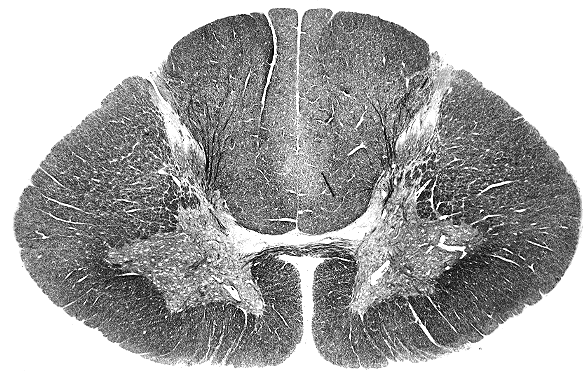
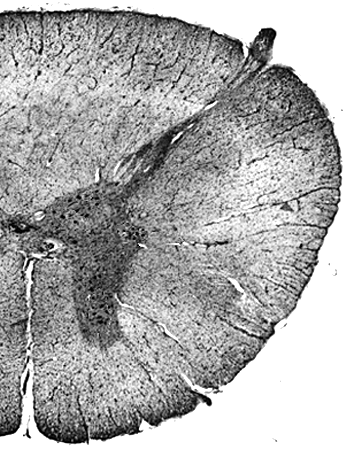
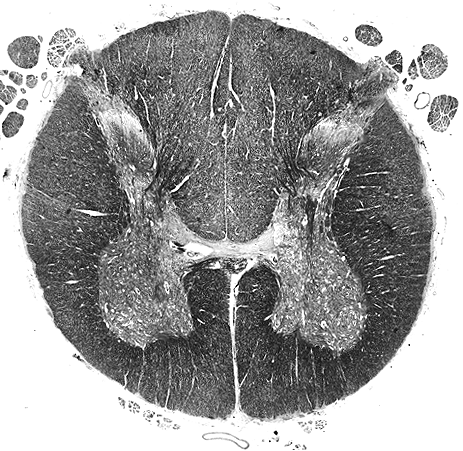
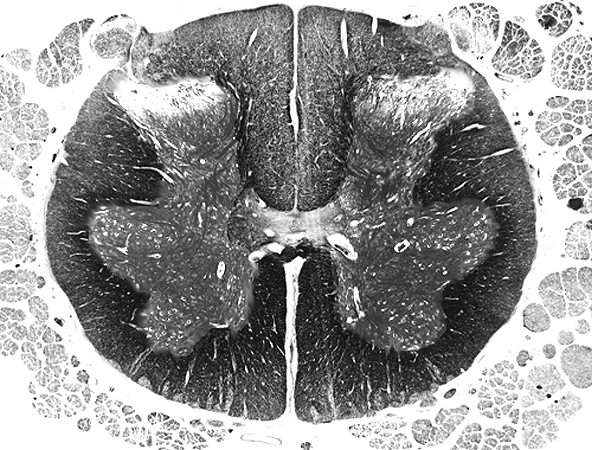
Question Bank
What are the signs and symptoms of LMN syndrome?
Which cranial nerves are only sensory? motor? both?
Fill in the box
| Nerve/Nucleus | Function | Signs (I/B/C) |
|---|---|---|
| Oculomotor (CN III) | Superior levator, superior rectus, medial rectus, inferior rectus and inferior oblique eye muscles | Ipsilateral Ptosis (drooping eye lid) Mydriasis (dilated pupil) Opthalmoplegia (paralysis of eye muscles) Down & out eye |
| Trochlear (CN IV) | Superior oblique eye muscle | Contralateral to nuclues Ipsilateral to nerve Extorsion (hard to look down and in) Unconscious head tilt |
| Trigeminal (CN V) | Muscles of mastication Lateral pterygoid Medial pterygoid Masseter |
Ipsilateral Muscular atrophy Jaw deviation towards side of lesion Difficulty chewing |
| Abducens (CN VI) | Lateral rectus muscle | Ipsilateral Esotropia (cannot abduct eye) |
| Facial (CN VII) | Muscles of facial expression | Ipsilateral Paralysis of facial expression muscles Lack of salivation, lacrimation Hyperacusis |
| Glossopharyngeal (CN IX), Vagus (CN X), Accessrory (CN XI) | Palatal, pharyngeal, and laryngeal muscles, accesory spinal muscles | Ipsilateral Vocal muscle paralysis Dysphagia Contralateral deivation of uvula |
| Hypoglossal (CN XII) | Tongue muscles | Ipsilateral Atrophy Ipsilateral deviation of the tongue |
| Functional Area |
Function |
What occurs when it’s damaged? |
|---|---|---|
|
Primary Motor Cortex |
Discrete contralateral movements |
Paralysis or paresis |
|
Premotor Cortex |
Planning of complex movements |
Motor apraxia |
|
Prefrontal Cortex – Dorsolateral Region |
Concentration, planning, judgment, problem solving |
Loss of concentration, initiative, responsibility, judgment and foresight |
|
Prefrontal Cortex – Orbitofrontal Region |
Social behavior and emotion |
Abnormal social behavior, unstable emotions |
|
Broca’s Area |
Speech production |
Expressive aphasia (nonfluent aphasia) |
|
Primary Somatosensory Cortex |
Contralateral sensation (touch and proprioception) |
Anesthesia (loss of general sensation) |
|
Parietal Association Cortex |
Somatic and Visual Processing |
Astereognosis, asomatognosia, neglect syndrome |
|
Primary Visual Cortex |
Vision |
Contralateral homonymous hemianopsia |
|
Visual Association Cortex |
Complex visual perception, understanding what is seen |
Visual agnosia |
|
Primary Auditory Cortex |
Hearing |
Inability to localize sound |
|
Wernicke’s Area |
Understanding speech |
Receptive aphasia (fluent aphasia) |
|
Temporal Association Cortex |
Long-term memory, Recognition of objects and faces |
Anomia, prosopagnosia |
Can you fill in the blank?
| Symptom | Parkinson's | Huntington's |
|---|---|---|
| Chorea | ||
| Ballismus | ||
| Dyskinesia | ||
| Rigidity | ||
| Athetosis | ||
| Bradykinesia | ||
| Akinesia | ||
| Tremors | ||
| Tics |
Match the symptom with the disease.
Define each symptom
Define the following:
Corpus striatum
Striatum
Lentiform nuclei