Week 8 TA Review
Week 9 Preview
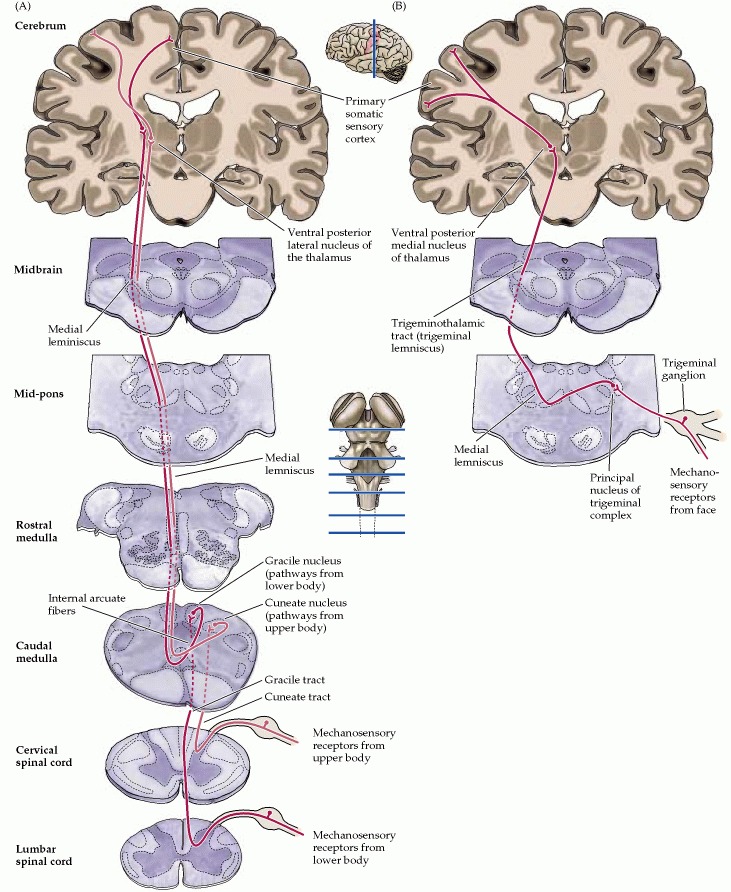
Pathways
Spinal touch, vibration and proprioception
- Draw the pathway.
- Include the first, second and third order neurons.
- Label the decussation.
Spinal Pain and Temperature Pathway
- Draw the pathway.
- Include the first, second and third order neurons.
- Label the decussation.

Trigeminal Somatosenation
- Draw the pathway.
- Include the first, second and third order neurons.
- Label the decussation.

Trigeminal Fast Pain and Temperature
- Draw the pathway.
- Include the first, second and third order neurons.
- Label the decussation.

Questions
Your nipples are associated with which dermatome?
- T2/T3
- T4/T5
- T6/T7
- T9/T10
- Right C7
- Left C7
- Right C8
- Left C8
A 35 YOM rolls into your ER on a gurney after a fight at the local bar, which he lost (his opponent made judicious use of a bar stool).
Upon examination you observe the patient is unable to detect changes in joint position in his middle finger, and is no longer sensitive to light touch from a cotton ball in the region of his left clavicle and neck. Also he cannot distinguish between a hot or cold pack on his right thumb, shoulder and neck.
Where is the lesion?
A 35 YOM rolls into your ER on a gurney after a fight at the local bar, which he lost (his opponent made judicious use of a bar stool).
In addition to the previous signs and symptoms, you also observe flaccid paresis of the left middle finger, little finger and spastic paralysis of the left leg. He can still sense changes in temperature and pain in the left leg and has an exaggerated patellar reflex. He still has voluntary muscle control of the right leg without weakness, has normal reflexes and is sensitive to touch, vibration and proprioception but can no longer sense temperature or pain.
Where is the lesion?
Which pathway is responsible for the emotional, attentional and arousing aspects of pain?
- Fast pain pathway
- Slow pain pathway
- Squirrel pain pathway

The ability to identify letters or other graphical symbols as they are traced on your skin is called:
- Stereognosis
- Graphesthesia
- Prioprioception
- Orthoaethsia

Week 8 Review
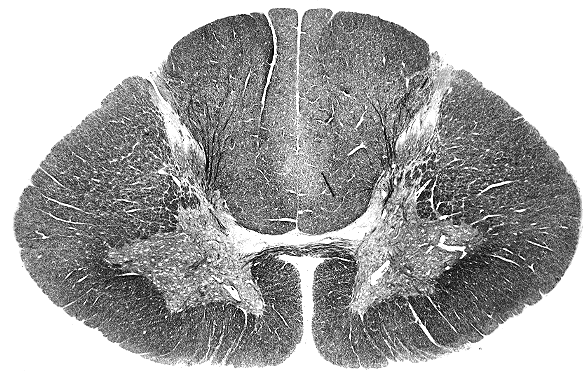
Name the structure
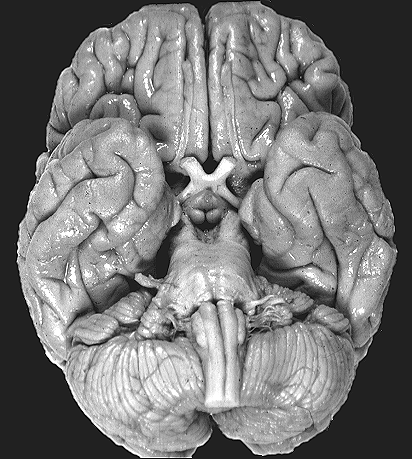
Name the structure
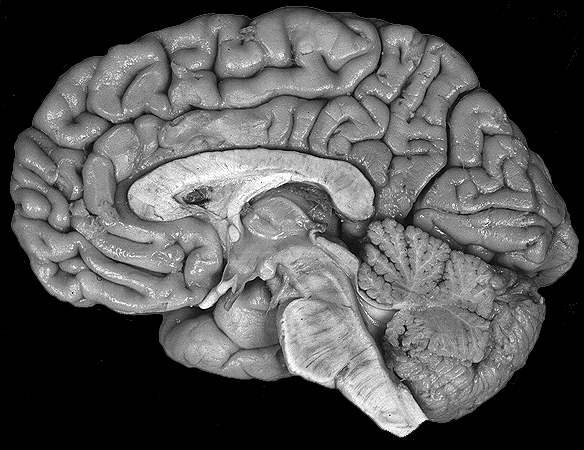
Name the structure
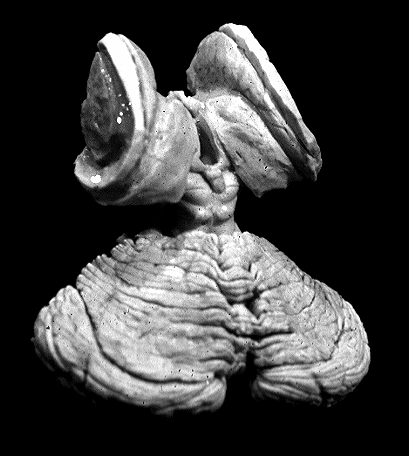
An individual with an intention tremor could have a lesion in which of the following structures?
- Fastigial nucleus
- Interposed nucleus
- Dentate nucleus
- Trigeminal nucleus
An individual is unable to maintain an unsupported sitting position. Which of the following structures could be damaged?
- Fastigial nucleus
- Interposed nucleus
- Dentate nucleus
- Trigeminal nucleus
An individual comes into your office with complaints of blurred, "jumpy" vision. After additional questioning, you discover it is most prominent when the patient is in motion. Which lobe of the cerebellum has been affected?
- Spinal cerebellum
- Neocerebellum
- Paleocerebellum
- Archicerebellum

This nucleus contains the secondary neuron for inputs to which lobe?
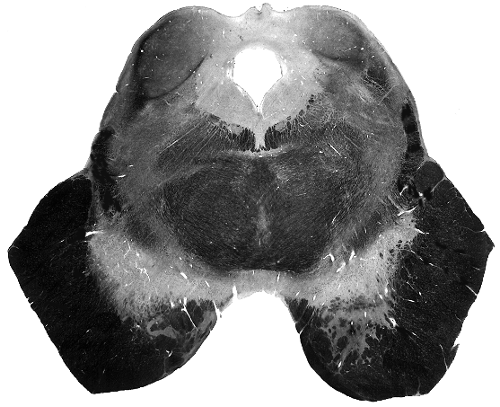
Name the sign(s)/symptom(s) produced by lesioning this structure.
Intention tremor, perpendicular to intended movement.