Attention and Task Switching
The farce and folly of multitasking
Benjamin T. Carter, PhD
Collaborative Science & Innovation
Objectives
- Basic understanding attention theory.
- What is it? What types are there?
- How does it work?
- How it relates to productivity.
- Methods for leveraging/protecting it.
Attention
Attention
Refers to the allocation of neurological resources to the sensing, processing and interpretation of specific, discrete stimuli to the exclusion of all other stimuli of a lesser priority. This is usually coupled with action directly associated with the stimulus of interest.

Selective Attention
- Attentional processes we have conscious control over.
- Multiple models
- Broadbent's Filter Model
- Treisman's Attenuation Model
- Late Selection Model
- Multimode Model
- All models contain the following elements
- Sensory input
- Processing
- Filtering
- Semantic analysis/Perception
- Short term memory/awareness
- Response (output)

Models of Selective Attention
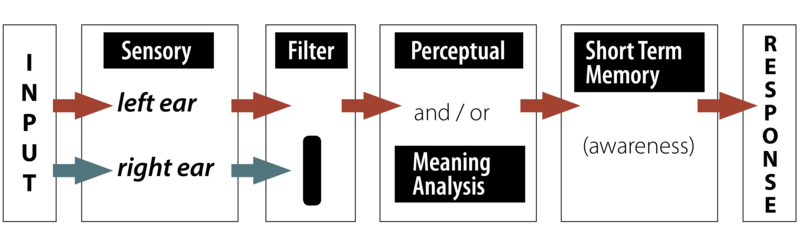
Broadbent's filter model
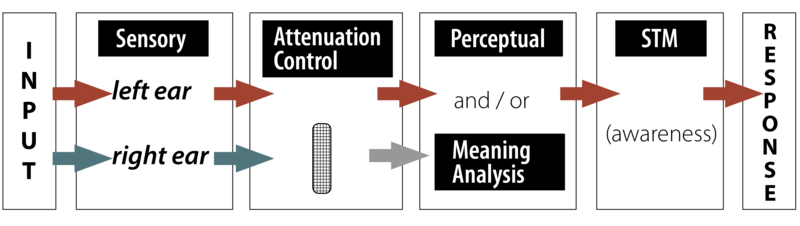
Treisman's Attenuation
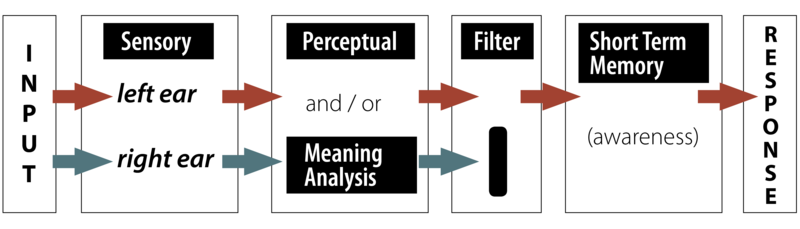
Late Selection Model
Divided Attention
Studies of divided attention tasks (i.e. multitasking) demonstrate decreases in task performance in terms of accuracy, skill and even memory of the task.
The effect is modulated by task complexity and relatedness but does not disappear.

Divided Attention
Strayer 2007, Cell phone induced driver distraction.
- Hands-free cellphone use
- Pre-smartphone (iPhone came out in 2006).
- Dual-task drivers
- Blindness - less likely to remember seeing objects they looked at.
- Brake-check ERP for P300 decreased by 50% (reduced cognitive resources).


Strayer, 2007, Cell Phone Induced Driver Distration
Texting While Walking
Courtemanche, 2019
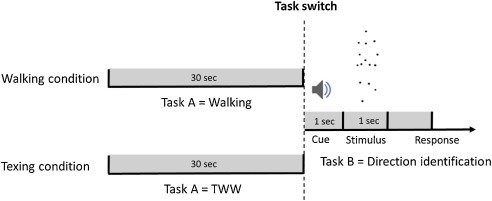

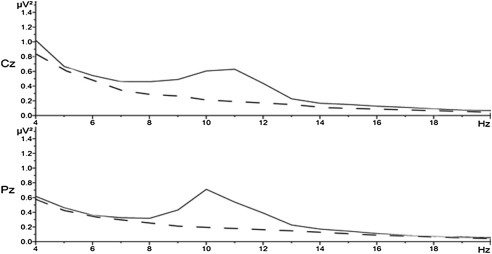
Texting While Walking
Courtemanche, 2019
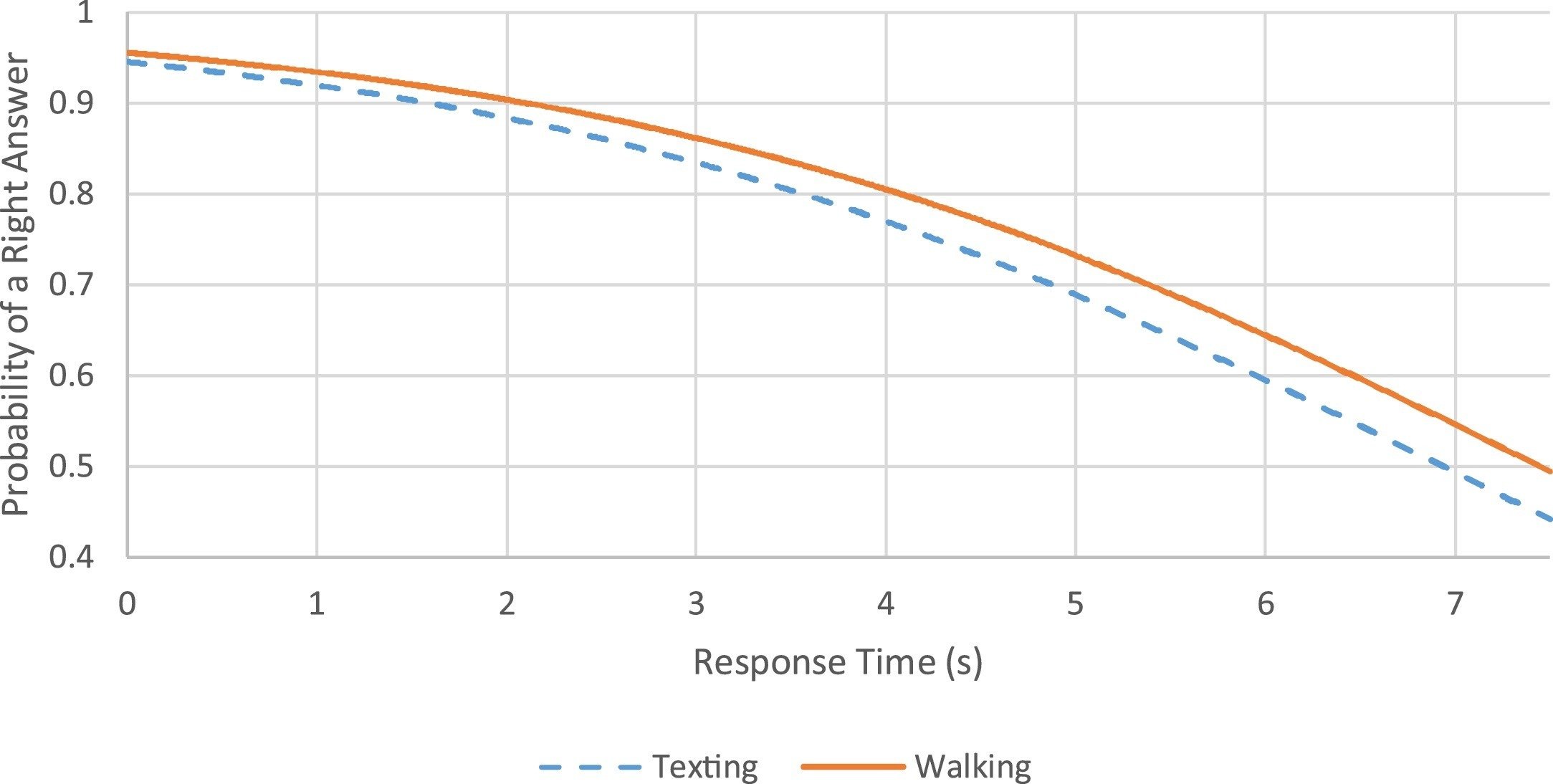
Why is there a performance loss when dividing our attention?
Attentional Bottleneck
Human cognition has a limited processing power - we only have some many neurons available.
There are also sensory constraints - e.g. fovea = thumb
Attentional Inertia
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Morbi nec metus justo. Aliquam erat volutpat.
Attention & Productivity
Task Switching
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Morbi nec metus justo. Aliquam erat volutpat.
Myths of Digital Native and Multitasker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Morbi nec metus justo. Aliquam erat volutpat.
Attention & Productivity
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Morbi nec metus justo. Aliquam erat volutpat.
Parting Thoughts
Want
more?
- Attention, NOBA Project
- Inattentional Blindeness, NOBA Project
Benjamin T. Carter, PhD
Collaborative Science & Innovation






u/LiteratusSimiae

aReadingApe
Attention and Task Switching
The farce and folly of multitasking

