Lab 5
Agenda
- Turn in Lab 4 by the staplers on the North bench.
- Needs a name and group number
- ~10 min.: Q&A on Lab 4 material
- 20 min.: Quiz 4
- ~2 hrs.: Lab 5: Action Potentials and Neurons
- ~30 min.: Next lab reminders/questions/review
Lab 4 Q&A
Core principles
What is diffusion?
- How is it affected by:
- Temperature
- Molecule size
How to calculate osmolarity
Osmolarity = Molarity \times n
n is the number of particles the solute dissociates into when dissolved
\% solution = grams/milliliter
Osmotic Pressure
\pi = 19,300 mmHg \times \Delta C
\Delta C = Osm_{solution_1} - Osm_{solution_2}
Normal Osmolarity of Human Plasma
- 0.9% NaCl
- 5.0% Glu
The Effect of Tonicity

Quiz 4

Action Potentials & Neurons
Lab 5
Lab Purpose
To allow students to experiment with principles of neuron function, the generation of action potentials and nerve potentials and how they may be modified.
Lab objectives
- Explain the location of the major parts and channels of a neuron.
- Understand the parts of an action potential and what causes them.
- Define the electrical properties of a nerve, including threshold.
- Observe the relationship between stimulus intensity and action potential strength in a nerve and how
this may or may not differ from the activity of a single neuron. - Be able to explain refractory periods and what causes them.
Lab Safety
- Half the lab is computer based. Just be patient with the software and follow the instructions and you'll be fine.
Experiment 1-3
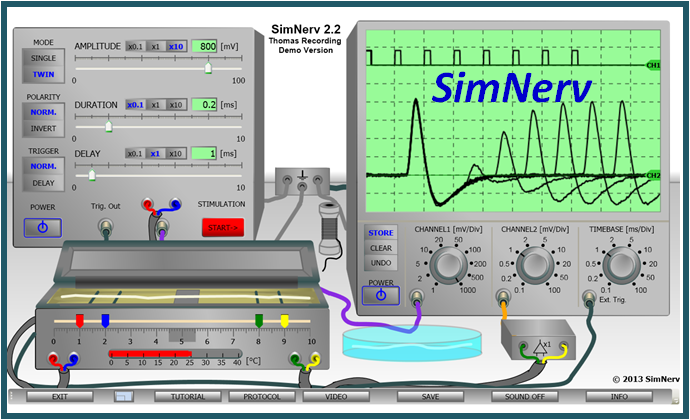
Experiment 4 & 5

Core Principles
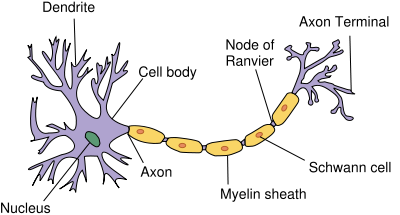
Neuron Anatomy
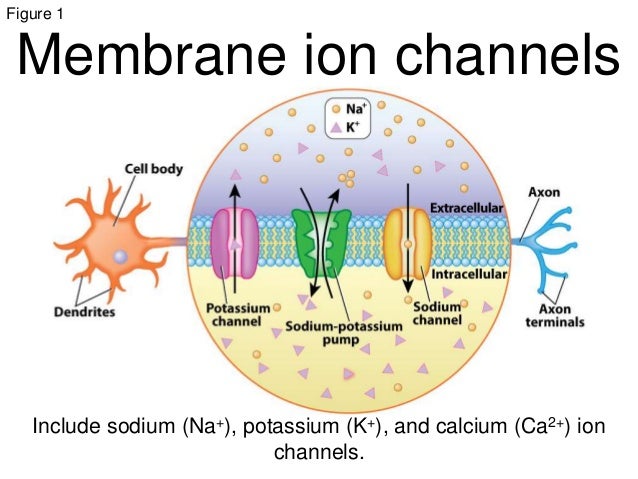
Ion Channels and Pumps
Action Potentials
- What is an action potential (AP)?
- Can you label/define the parts?
- Define threshold.
- Describe the action of these ions during an AP.
- Na+
- K+
- Ca++
- Cl-
- How are APs similar to nerve potentials? How are they different?

Summation
- What kinds are there?
- Temporal
- Spatial
- Can you define them?
Drug Effects
- Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) - glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter
- Nicotine - activates nicotinic ACh receptors
- Calcium chloride - increases voltage dependence of Na and K channels, increasing threshold.
Lab 6: Sensory Physiology
- Read:
- Stanfield pgs. 256-299
- Silverthorn pgs. 291-294, 314-353
- Bring:
- Calculator
