Turn Down For What?
A Beginner's Guide To Digital Music-Making
About Me
- Choirboy from age 4-18
- French Horn from age 10
- Guitar from age 12
- Recording music since age 16
- Drums from age 21
- Introduction to piano in college
- Sound recording and design classes in college
- MIDI sound recording class in college
About You?
- Know some music theory basics?
- Recorded music before?
- Taken piano lessons?
- Worked with Garageband?
- Worked with another Software? Which?
The DAW
(Digital Audio Workspace)
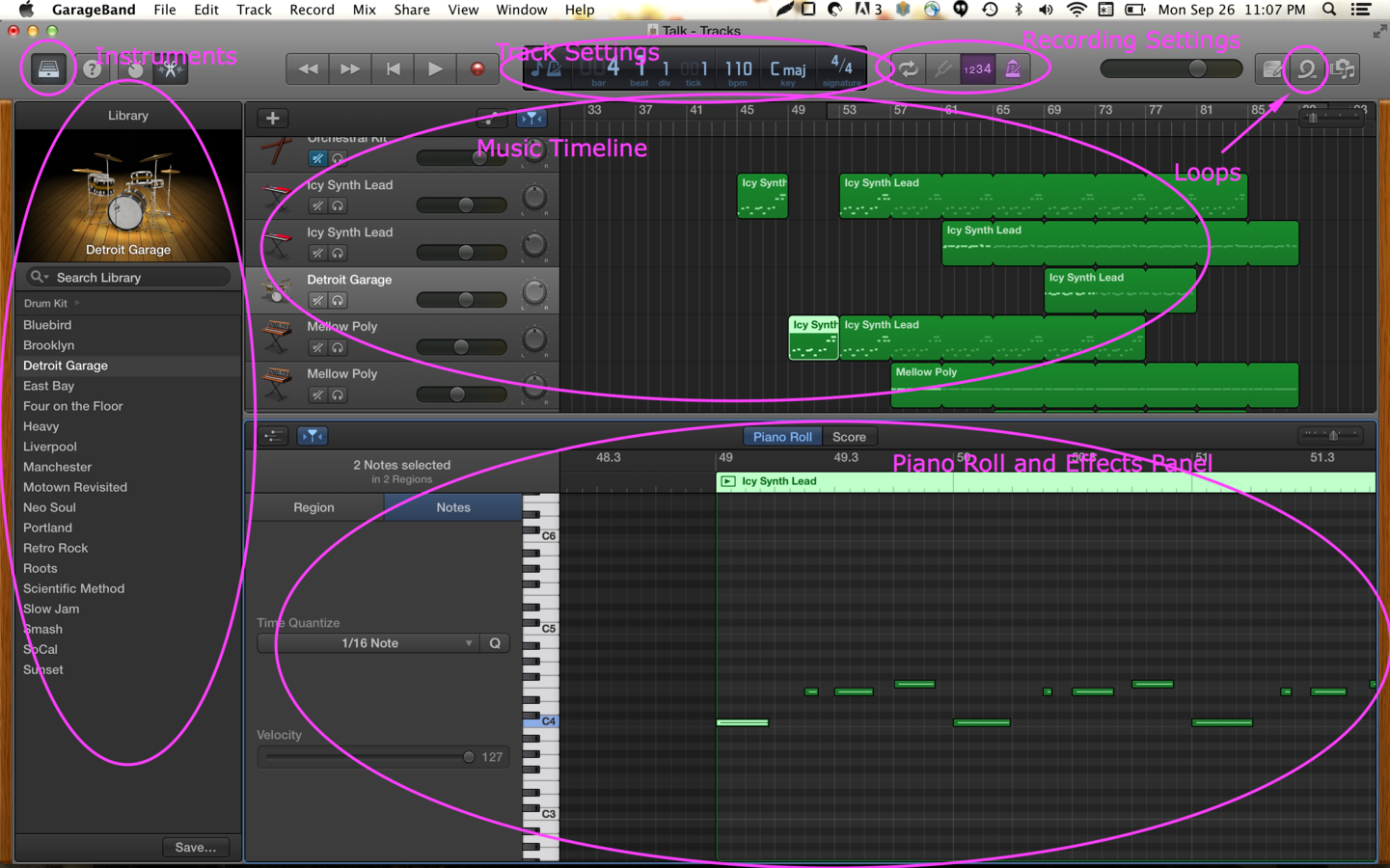
Some Music Theory Basics
Scale
A scale is any set of musical notes ordered by fundamental frequency or pitch. A scale ordered by increasing pitch is an ascending scale, and a scale ordered by decreasing pitch is a descending scale.
C Major Scale:

Chords
A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of usually three or more notes (also called "pitches") that is heard as if sounding simultaneously.
Usually three or more notes played together.
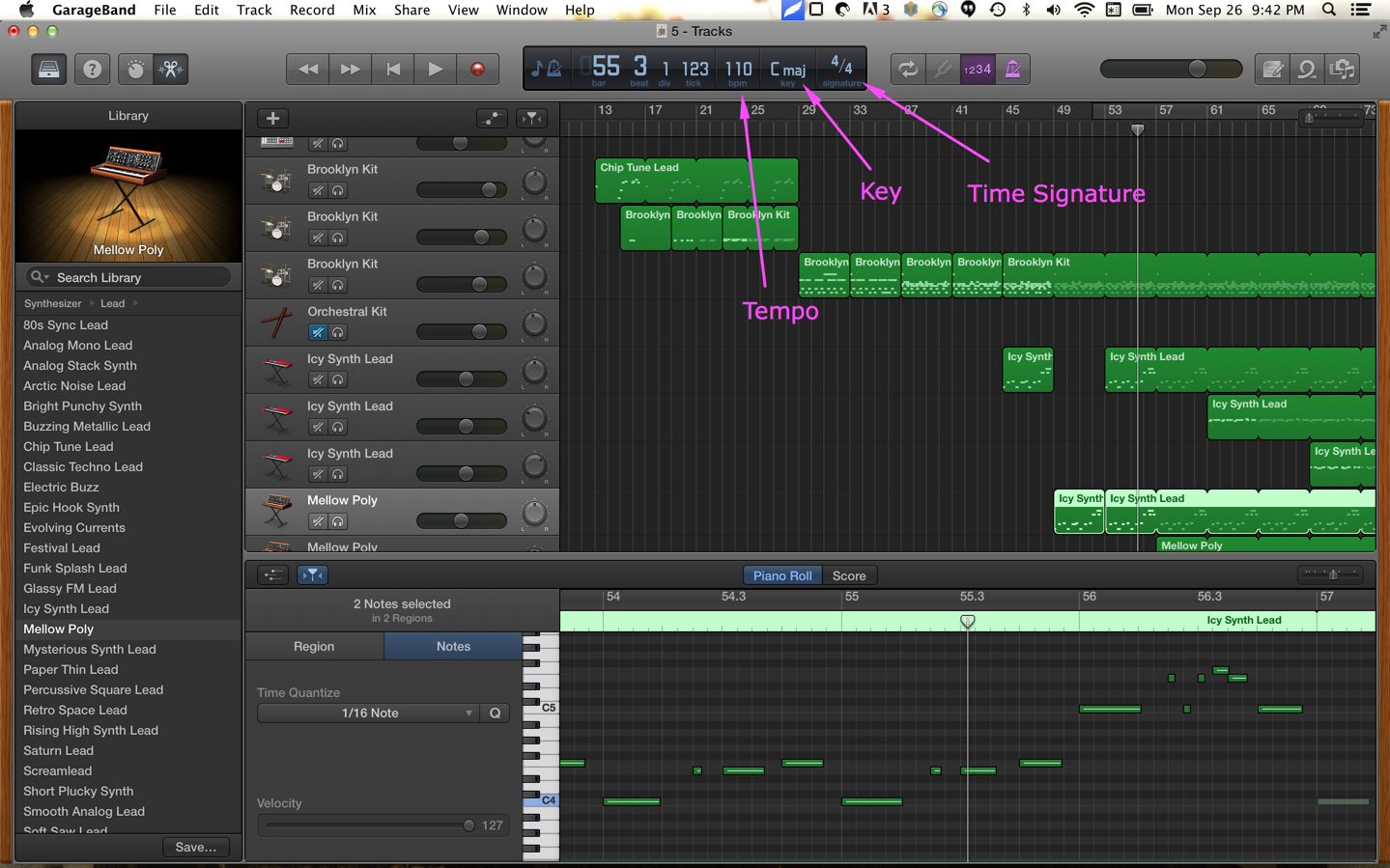
Tempo
The "speed" of the music or beats per minute.
- slow - 80 bmp
- medium - 110 bpm
- fast - 160 bpm
Key
- The notes that the song centers around
- You can play a song, in different keys
Time Signature
- Number of beats in a measure
Some Audio Recording Basics
Stereo vs Mono
Stereo is a method of sound reproduction that creates an illusion of multi-directional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two or more independent audio channels through a configuration of two or more loudspeakers (or stereo headphones) in such a way as to create the impression of sound heard from various directions, as in natural hearing.
It is often contrasted with mono sound, where audio is heard as coming from one position, often centered in the sound field.
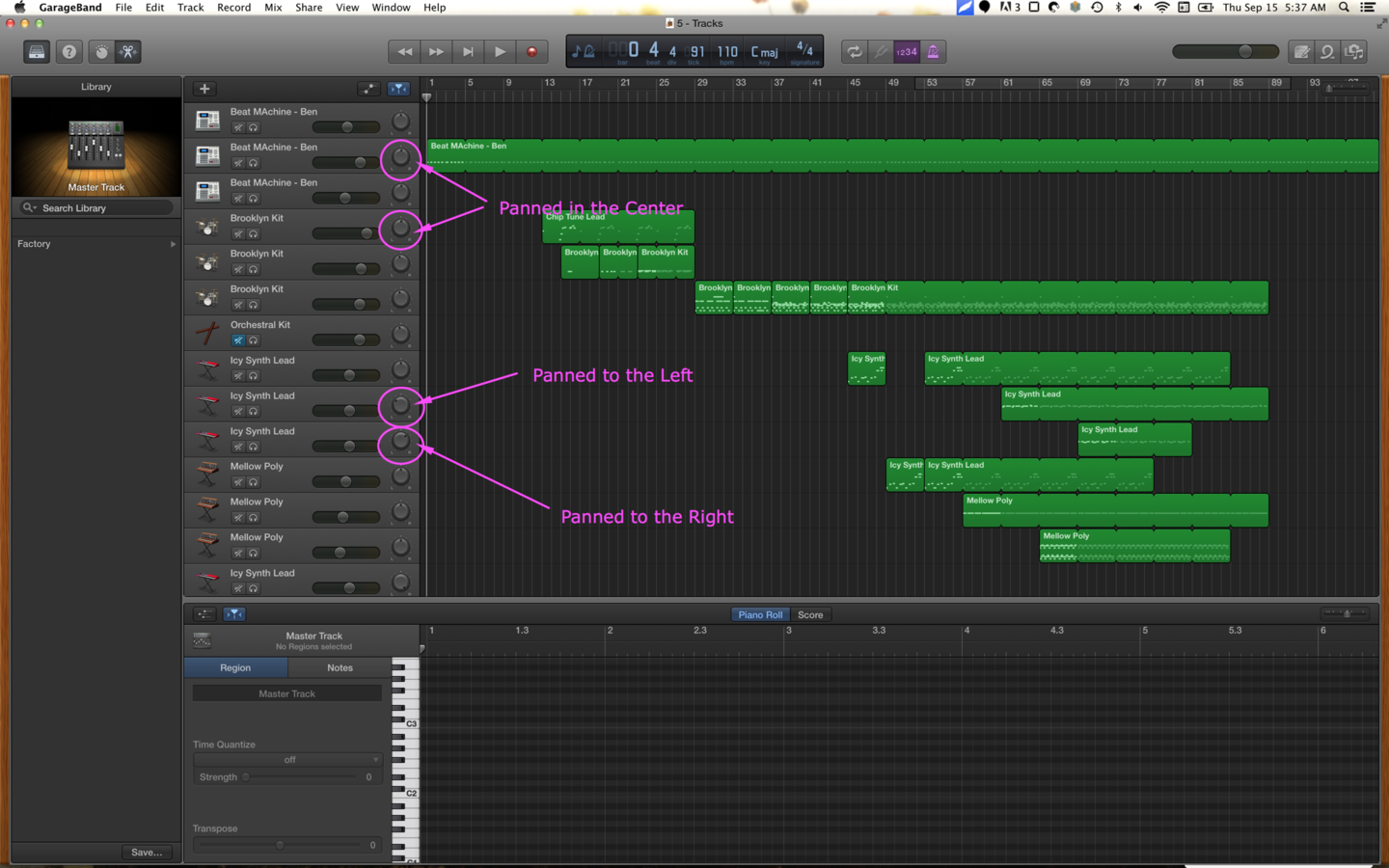
Panning
The distribution of a sound signal into a new stereo or multi-channel sound field determined by a pan control setting (ie. some sounds comes from the left speaker, some come from the right speaker, and some come from both [sounds like it comes from the middle]).
You might pan guitar #1 one to the right, guitar #2 to the left, and leave the bass, drums, and vocals centered (coming out of both speakers equally).
Double Tracking
Double tracking or vocal doubling is an audio recording technique in which a performer sings or plays along with his or her own prerecorded performance, usually to produce a stronger or "bigger" sound than can be obtained with a single voice or instrument.
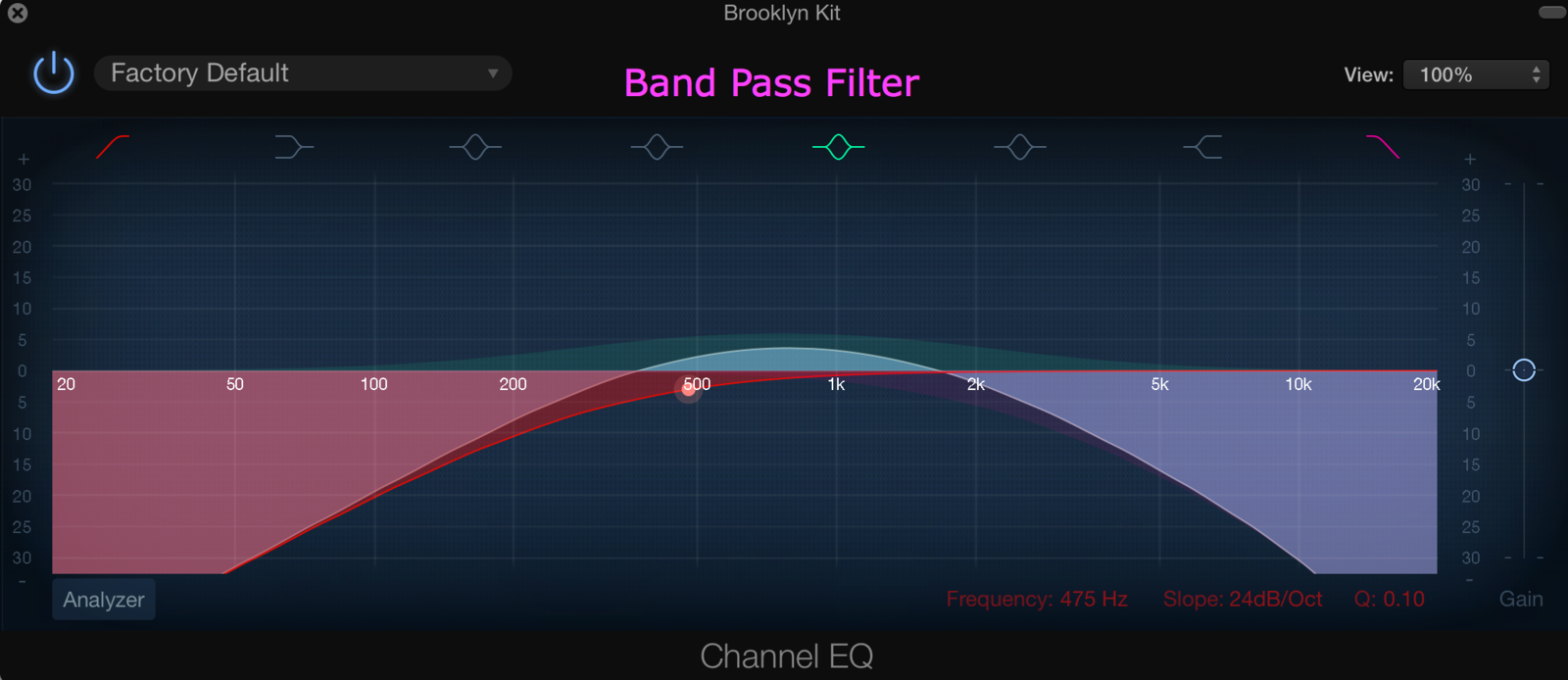
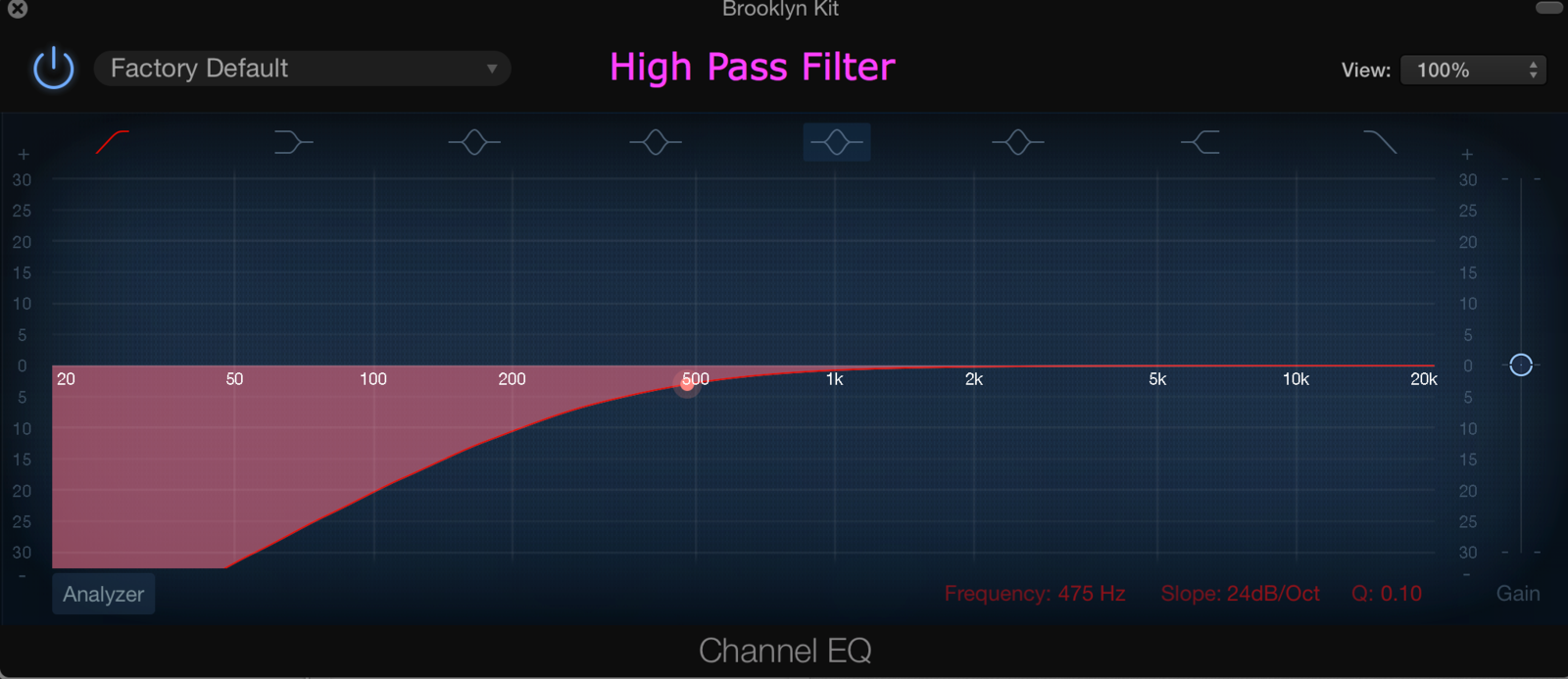
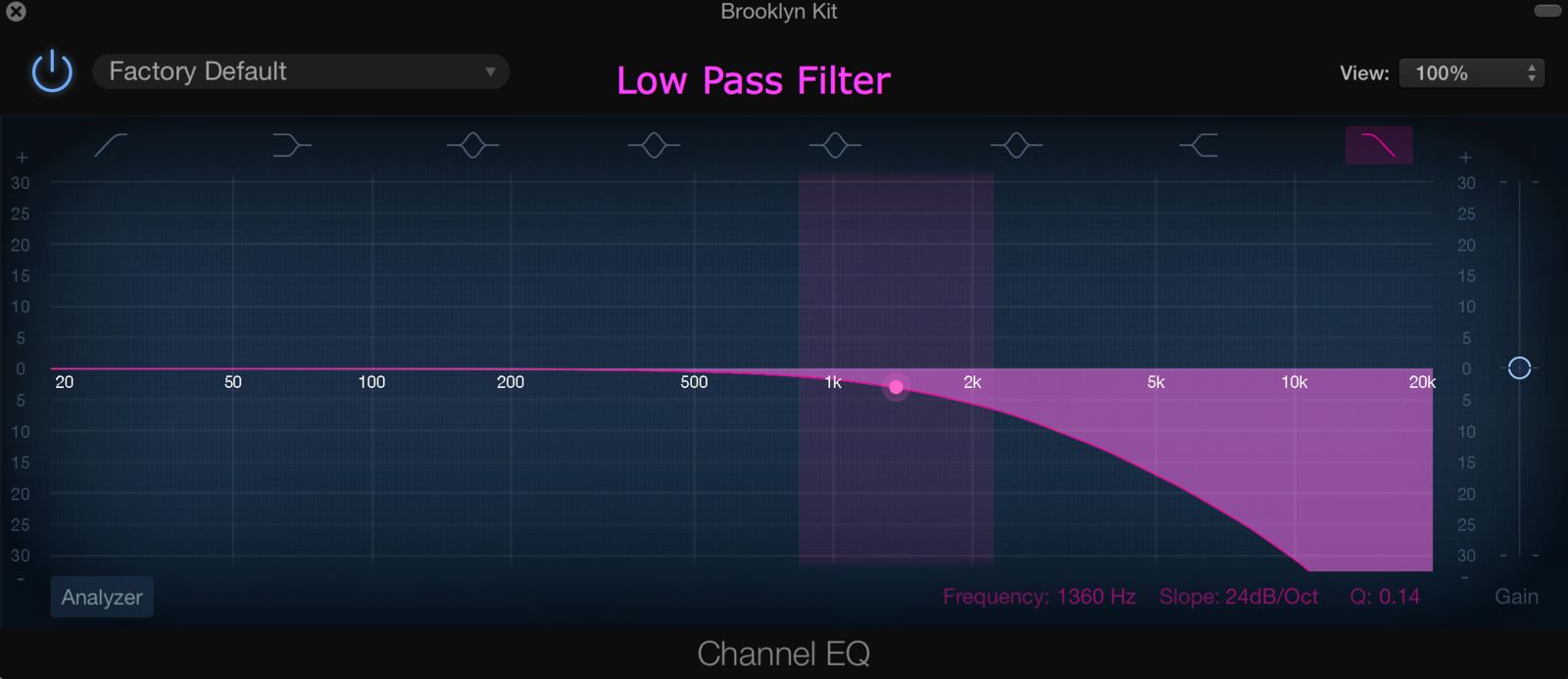
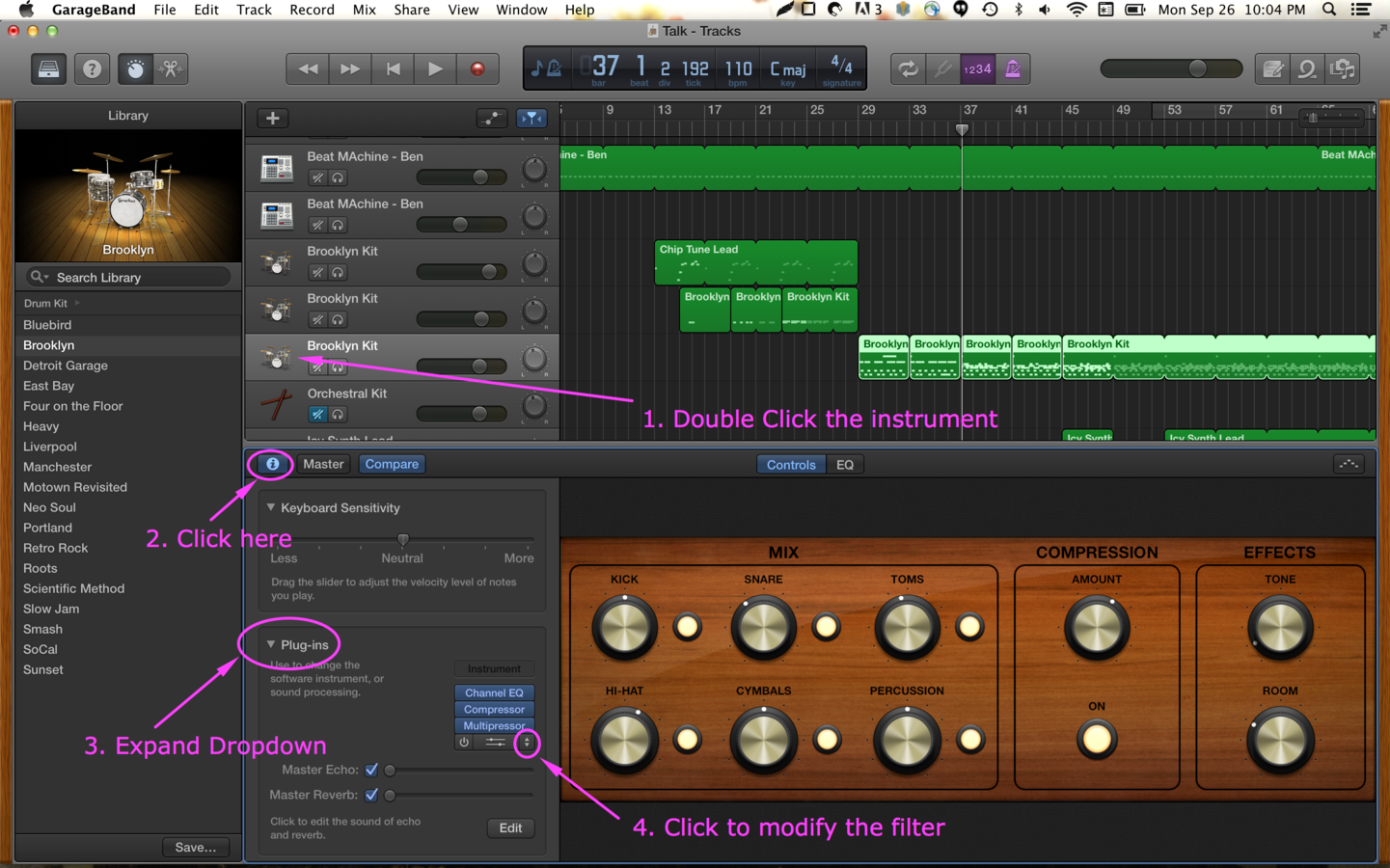
High/Low/Band Pass Filters
Audio filters can boost, pass cut some frequency ranges
Auto-Tune
An audio processor which measures and alters pitch in vocal and instrumental music recording and performances. It was originally intended to disguise or correct off-key inaccuracies, allowing vocal tracks to be perfectly tuned despite originally being slightly off-key. The processor slightly shifts pitches to the nearest semitone (or note).
Garageband
Live Playing Demo
- Set a looped spot
- Turn on/off metronome
- cmd+k to bring up keyboard
- Click record
- Play your stuff
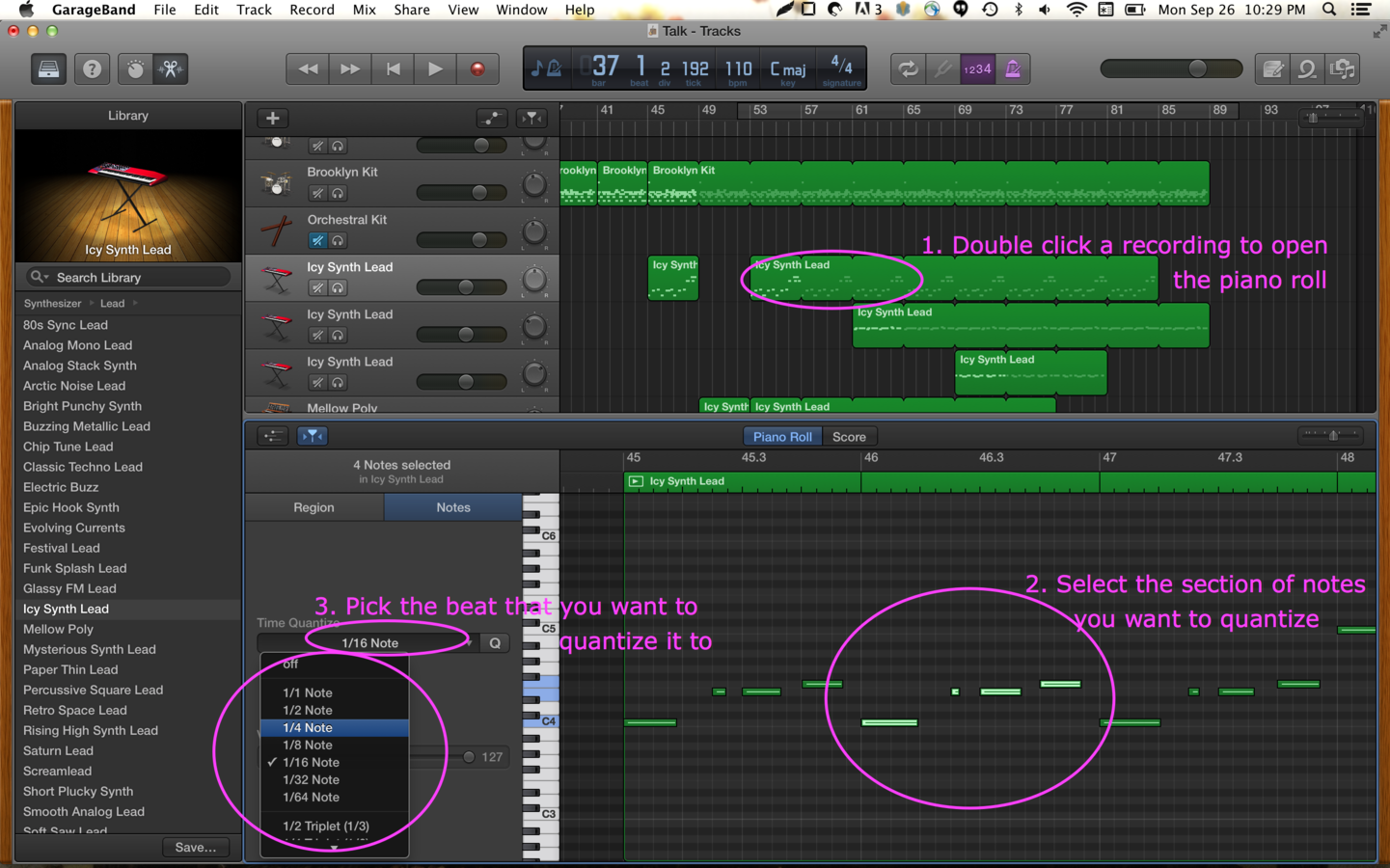
In digital music processing technology, quantization is the process of transforming performed musical notes, which may have some imprecision due to expressive performance, to an underlying musical representation that eliminates this imprecision. The process results in notes being set on beats and on exact fractions of beats.
In Short: if you quantize your performance, it cleans up the timing of your notes.
Quantization
Common Effects
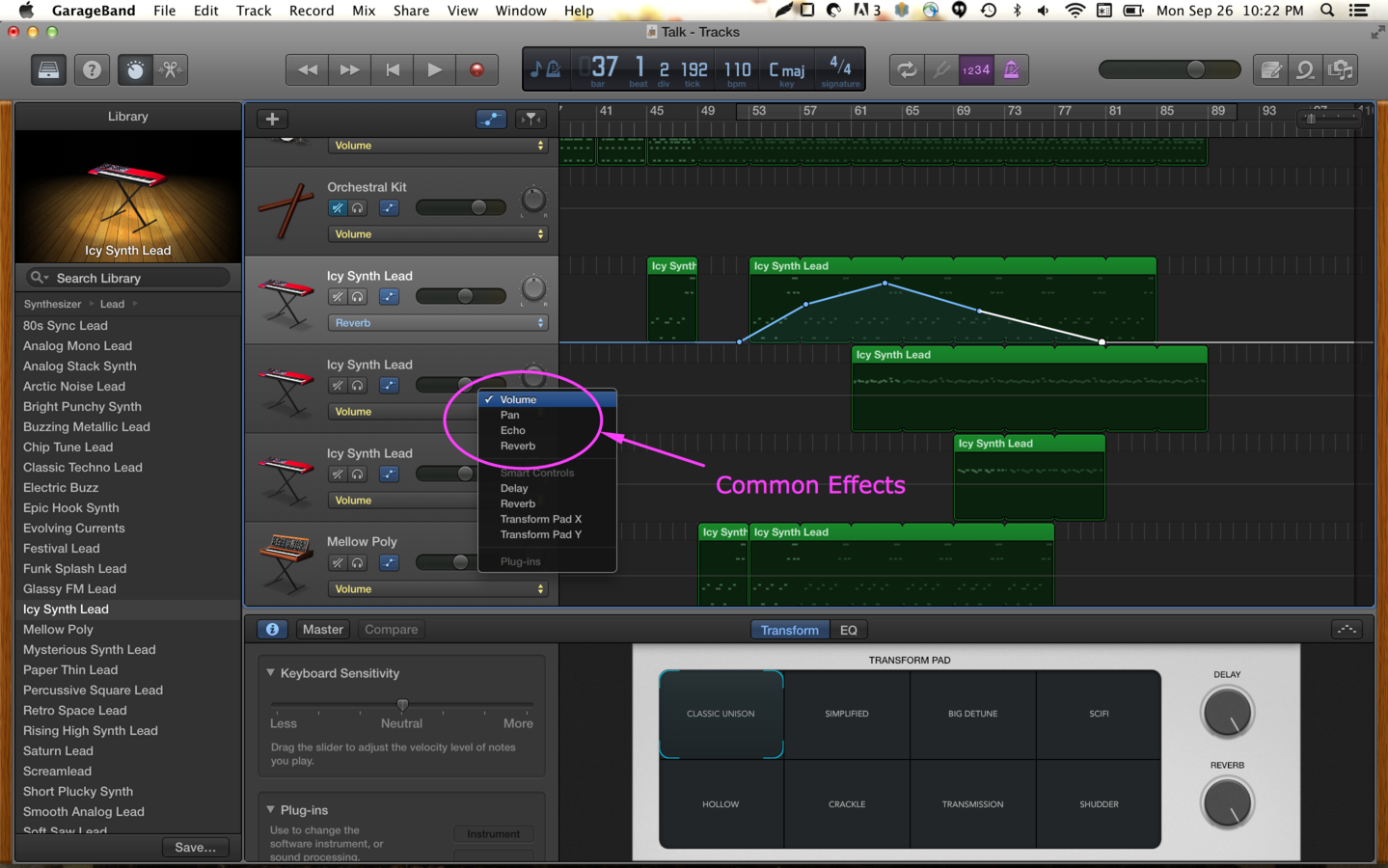
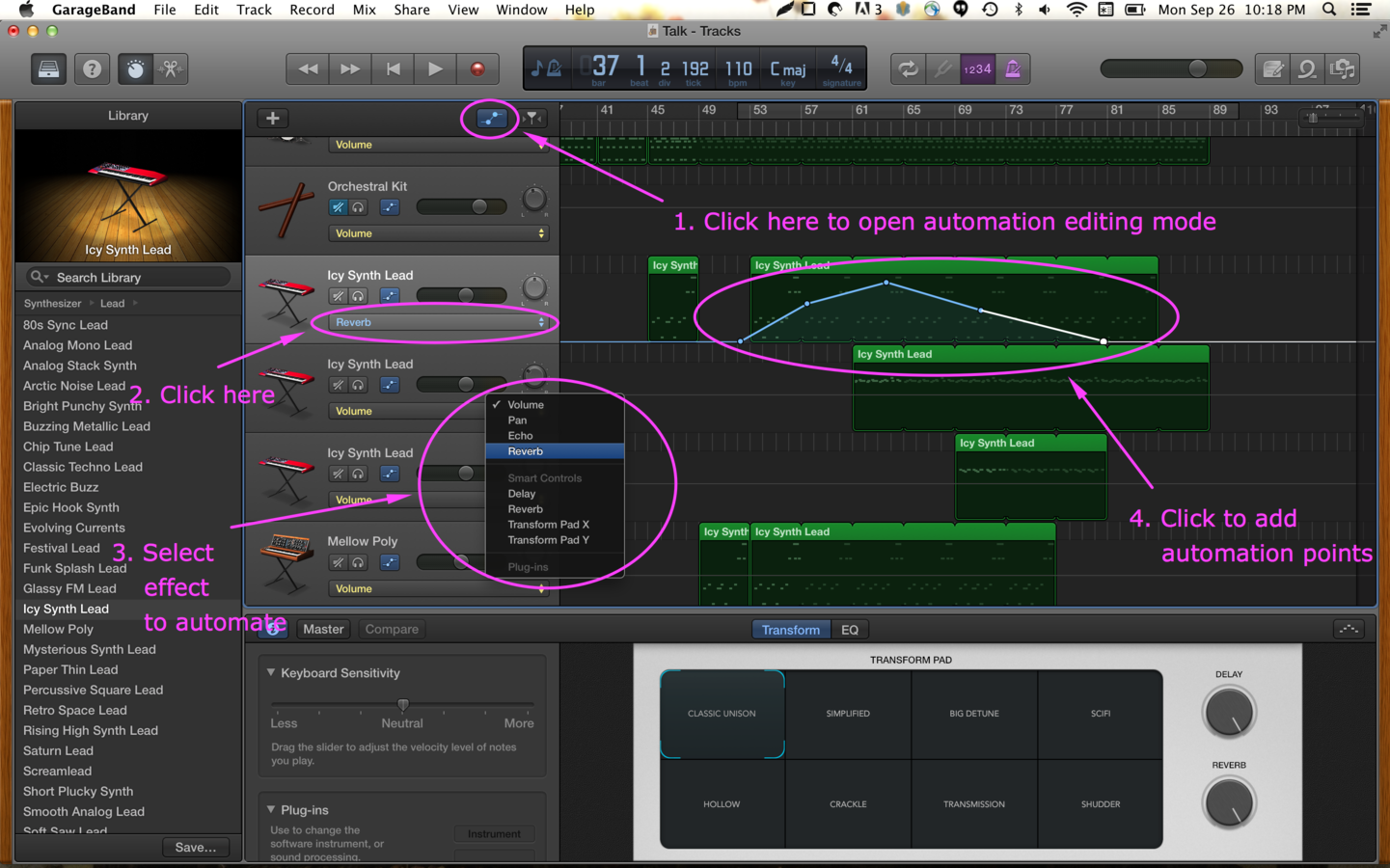
Automating Effects
When an effect is automated, the console or DAW remembers the audio engineer's adjustment of the effect.
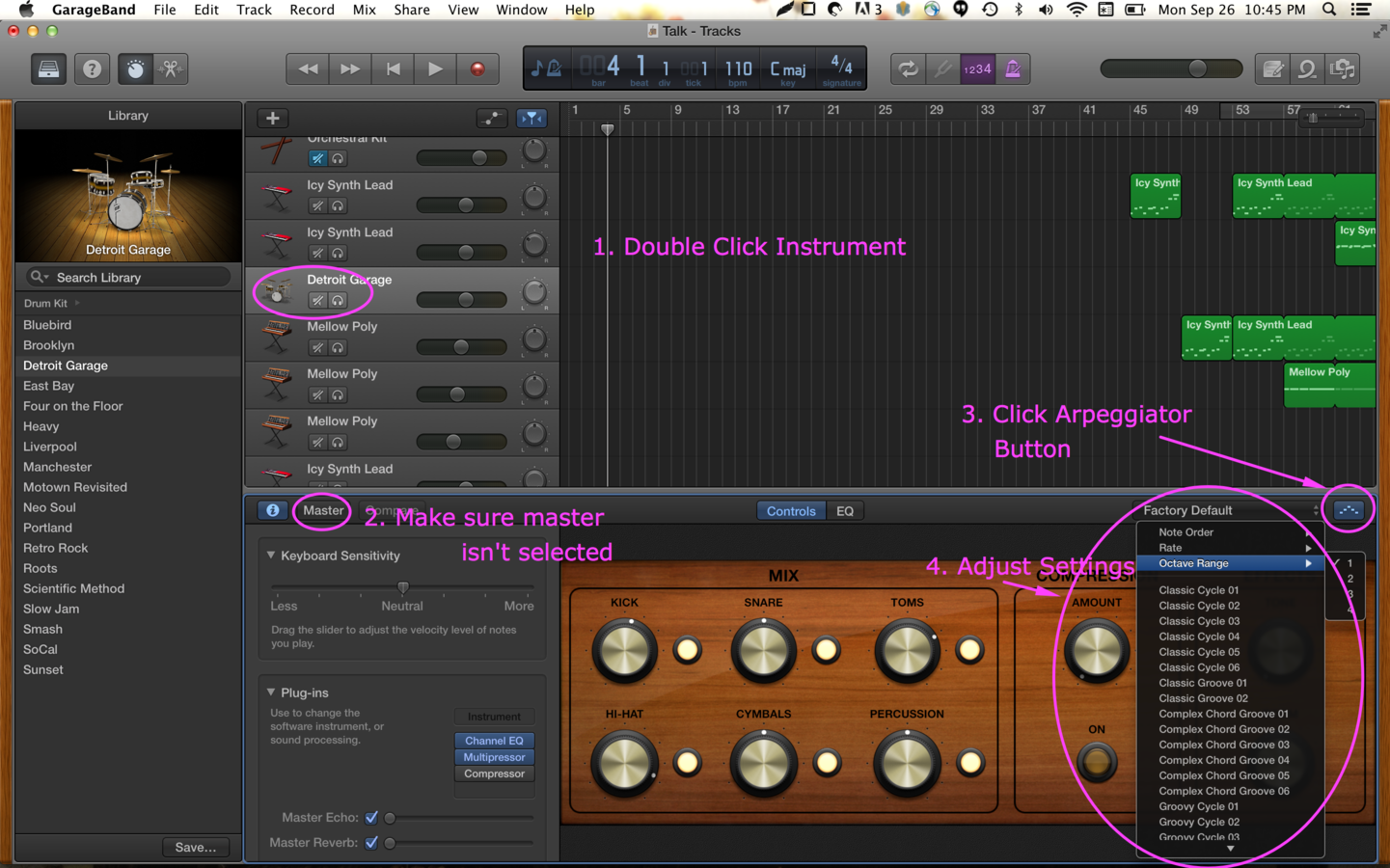
Arpeggiators
Customizing Instruments
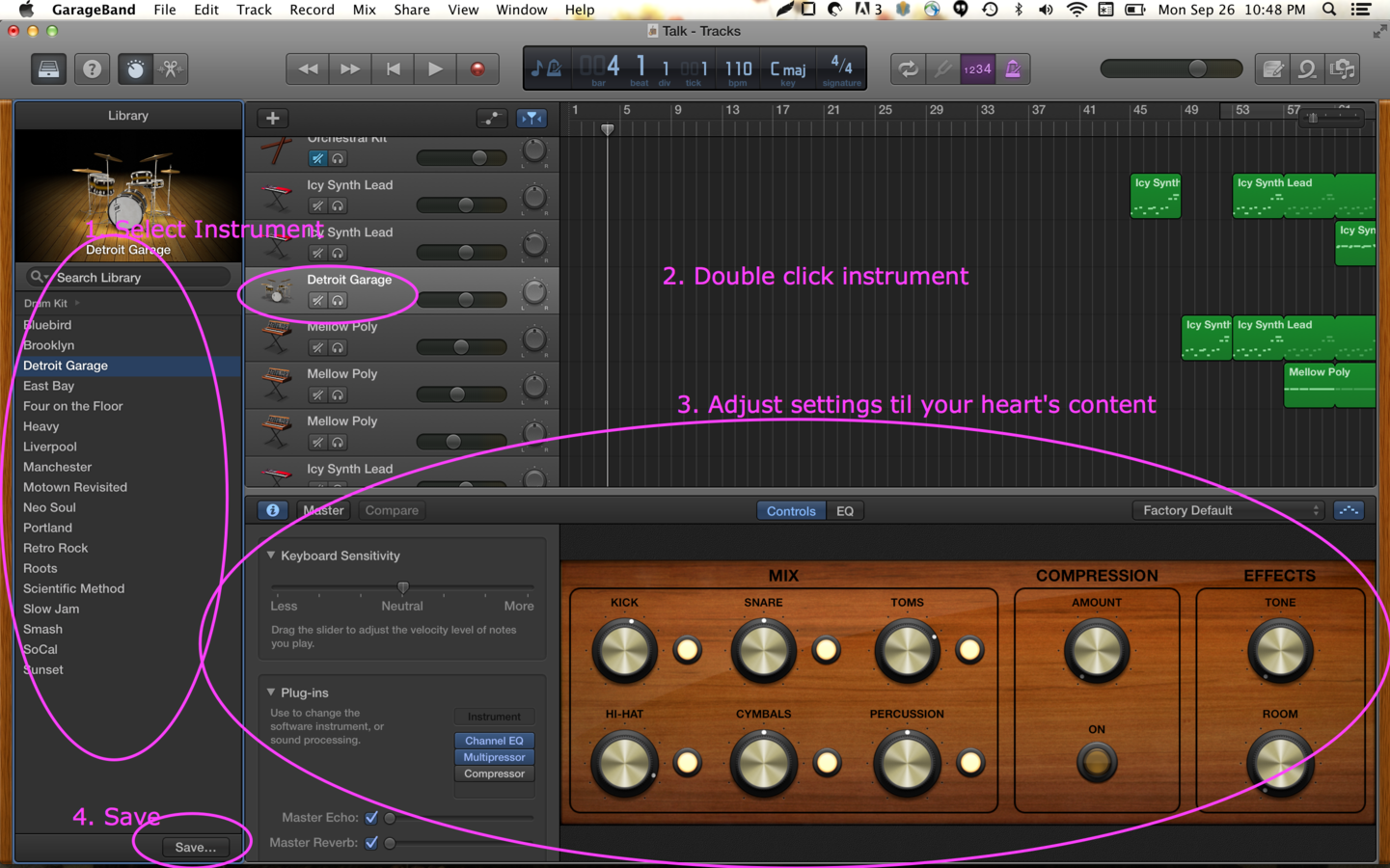
Drum Machines and Sequencers
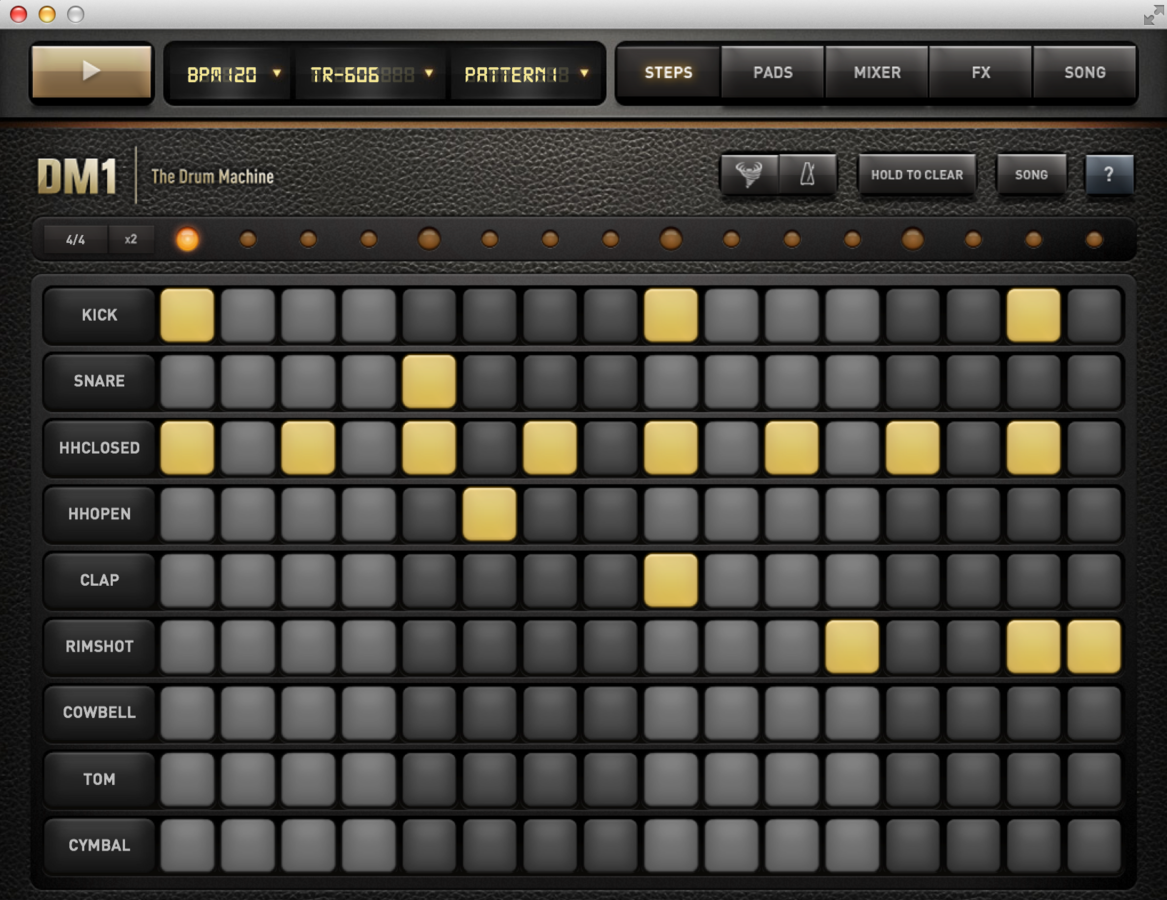
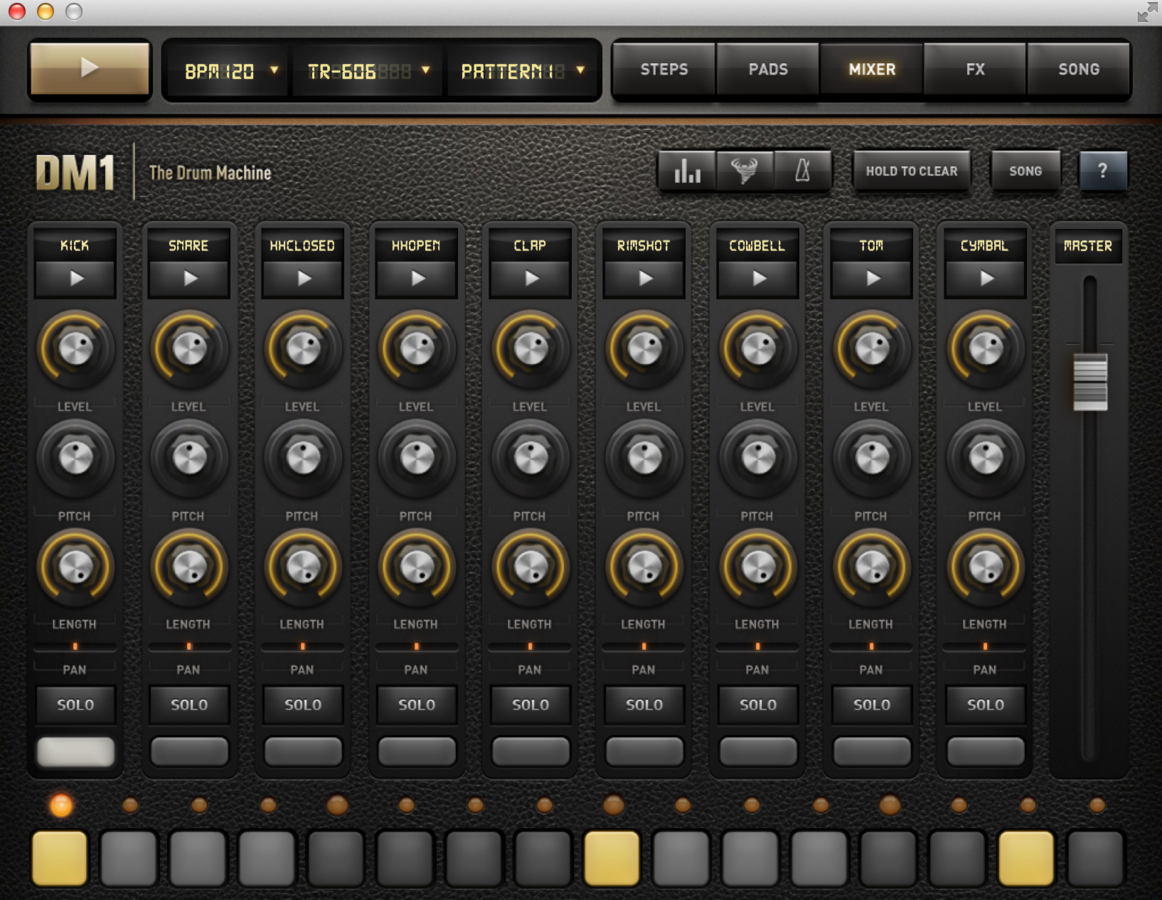
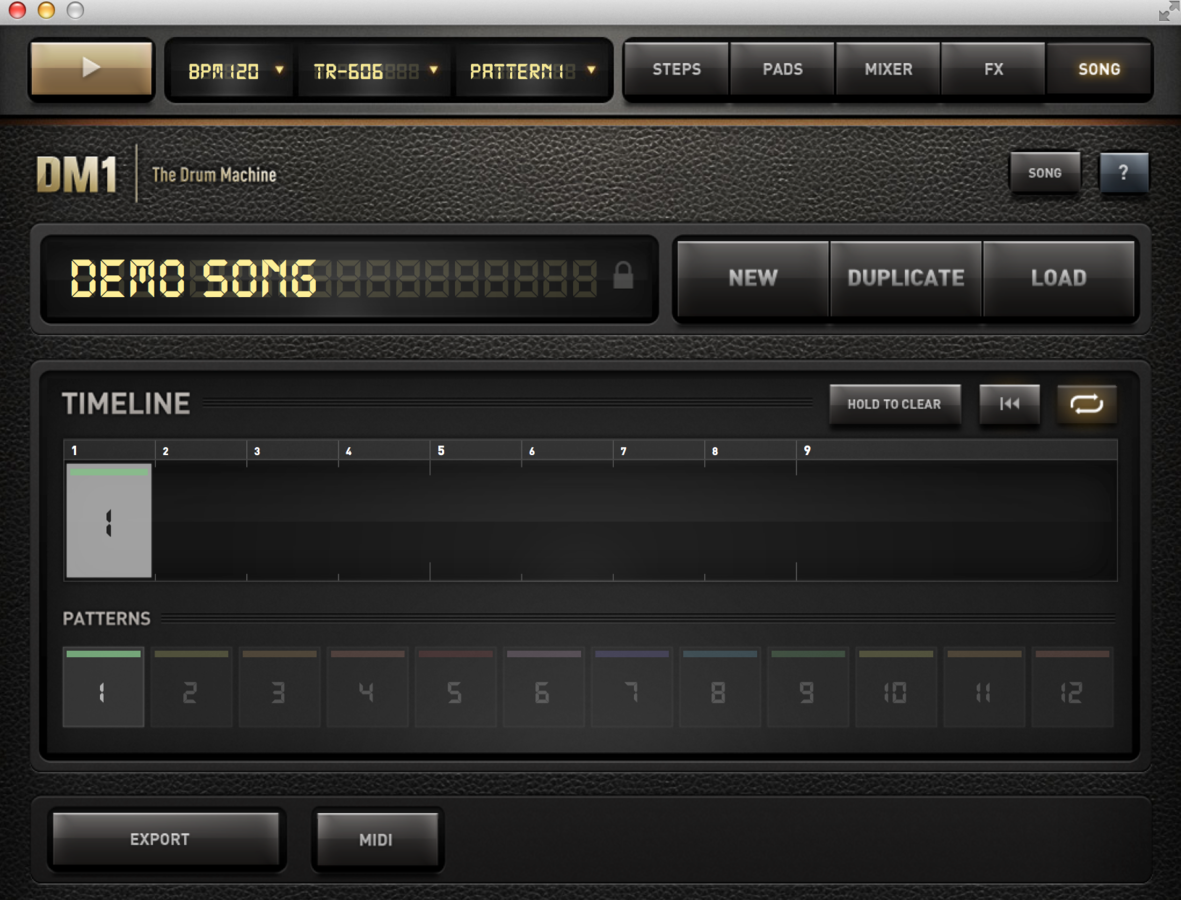
Some Fun Things for When You're Stuck
- Try dropping out drums
- Try dropping out bass
- Try dropping out leads
- Try transferring melody to a different instrument
- Try adding background "soundscapes" or effects
- Try panning instruments
More things for when you're stuck remember
- Instrument choices make a big difference to your sound
- The easiest way to make your stuff sound more interesting is panning and double tracking
- When you get stuck, just layer and record stuff with yourself
- Set a short looped spot
- Select one sequence to repeat
- click some things
- copy/paste
End.
Sources
https://www.classicalguitarcorner.com/l106-extended-scale-in-c-major/882/
I pulled many of the definitions from various sites from the internet (mostly wikipedia).