
Multilevel Approaches
Hui Hu Ph.D.
Department of Epidemiology
College of Public Health and Health Professions & College of Medicine
October 17, 2019
PHC6016 Social Epidemiology
Introduction
Linear Mixed-Effects Model
Generalized Linear Mixed-Effects Model
Introduction
- We usually assume the samples drawn from targeted population are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.).
- This assumption does not hold when we have data with multilevel structure:
- clustered and nested data (i.e. individuals within areas)
- longitudinal data (i.e. repeated measurements within individuals)
- non-nested structures (i.e. individuals within areas and belonging to some subgroups such as occupations)
- Samples within each group are dependent, while samples between groups stay independent

- A longitudinal study:
- n = 3
- t = 3
- Complete pooling
- poor performance
- No pooling
- infeasible for large n
- Partial pooling
- An alternative solution: include categorical individual indicators in the traditional linear regression model.
- Why do we still need mixed-effects models?
- Why do we still need mixed-effects models?
- Account for both individual- and group-level variations when estimating group-level coefficients.
- Easily model variations among individual-level coefficients, especially when making predictions for new groups.
- Allow us to estimate coefficients for specific groups, even for groups with small n
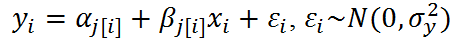
Fixed and Random Effects
- Fixed Effects: parameters are fixed
- Random Effects: parameters are random variables
Two extreme cases:
- when the group-level variation is very little
- reduce to traditional regression models without group indicators (complete pooling) - when the group-level variation is very large
- reduce to traditional regression models with group indicators (no-pooling)
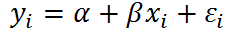
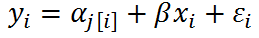
Little risk to apply a mixed-effects model
What's the difference between no-pooling models and mixed-effects models only with varying intercepts?
- In no-pooling models, the intercept is obtained by least squares estimates, which equals to the fitted intercepts in models that are run separately by group.
- In mixed-effects models, we assign a probability distribution to the random intercept:
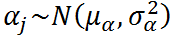
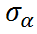
Intraclass Correlation (ICC)
shows the variation between groups
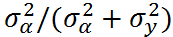
ICC ranges from 0 to 1:
- ICC -> 0: the groups give no information (complete-pooling)
- ICC -> 1: all individuals of a group are identical (no-pooling)
Intraclass Correlation (ICC)
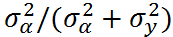
ICC ranges from 0 to 1:
- ICC -> 0: "hard constraint" to
- ICC -> 1: "no constraint" to
- Mixed-effects model: "soft constraint" to
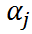
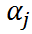
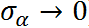
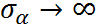
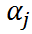
This constraint has different effects on different groups:
- For group with small n, a strong pooling is usually seen, where the value of is close to the mean (towards complete-pooling)
- For group with large n, the pooling will be weak, where the value of is far away from the mean (towards no-pooling)
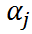
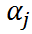


Linear Mixed-Effects Model
Pull the codes and dataset: https://github.com/benhhu/R-Mixed-Effects-Model
Load the Packages and Data

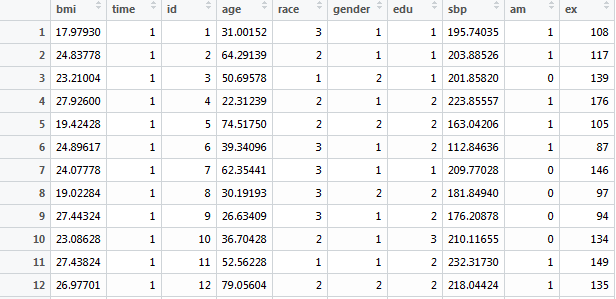
1,000 participants
5 repeated measurements
bmi
time
id
age
race: 1=white, 2=black, 3=others
gender: 1=male, 2=female
edu: 1=<HS, 2=HS, 3=>HS
sbp
am: 1=measured in morning
ex: #days exercised in the past year
Varying-intercept Model with No Predictors
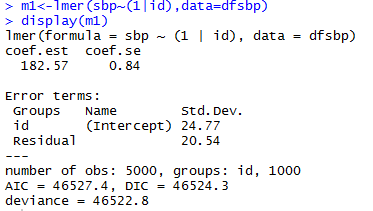
allows intercept to vary by individual
estimated intercept, averaging over the individuals
estimated variations
Varying-intercept Model with an individual-level predictor
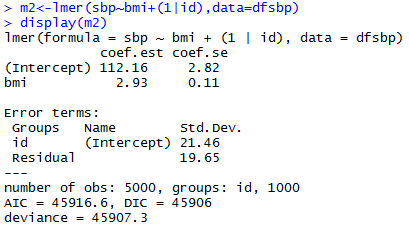
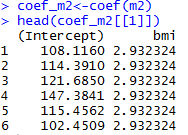
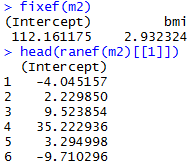
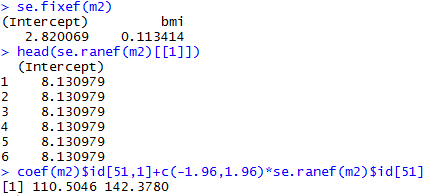
Varying-intercept Model with both individual-level and group-level predictors
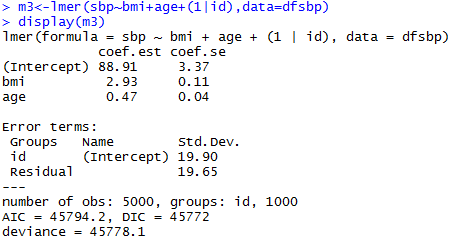


Varying Slopes Models
With only an individual-level predictor
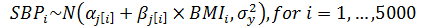
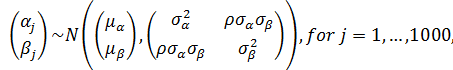
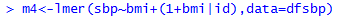
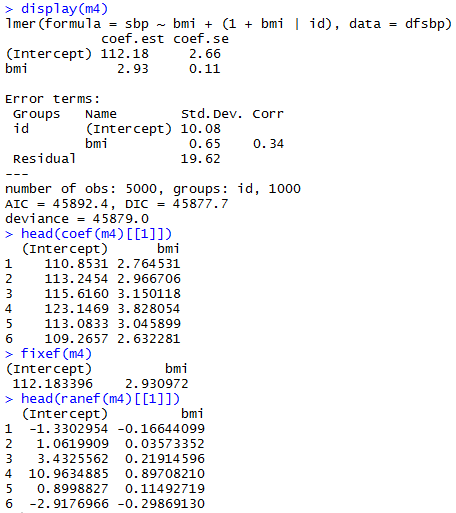
Varying Slopes Models
Add a group-level predictor
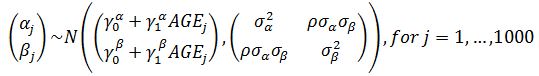
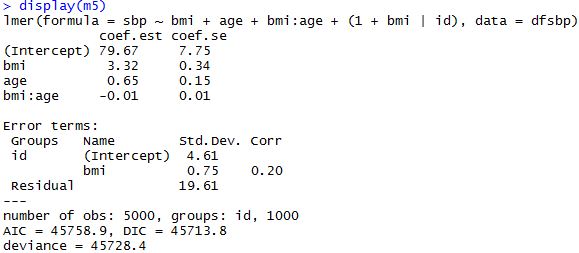
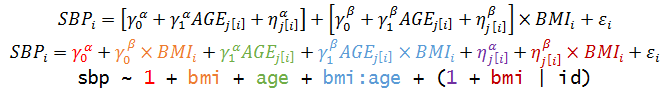
Non-nested Models
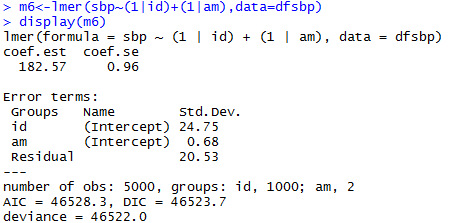
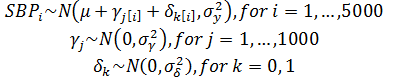
Generalized Linear Mixed-Effects Model
Mixed-Effects Logistic Model
Empty model


Mixed-Effects Logistic Model
Add bmi and race


Mixed-Effects Poisson Model
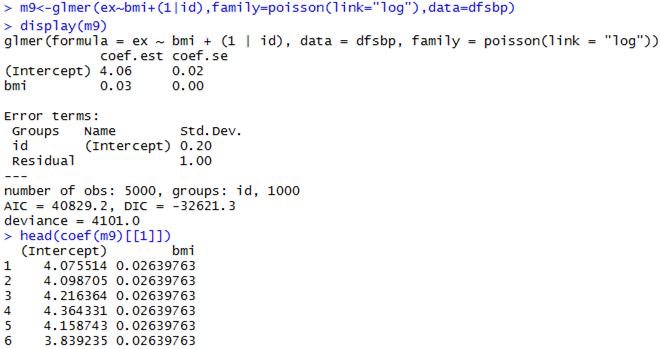

Parameter Estimation Algorithms
- ML: maximum likelihood
- REML: restricted maximum likelihood
- default in lmer() - PQL: pseudo- and penalized quasilikelihood
- Laplace approximations
- default in glmer() - GHQ: Gauss-Hermite quadrature
- McMC: Markov chain Monte Carlo

Bolker BM, Brooks ME, Clark CJ, Geange SW, Poulsen JR, Stevens MHH, et al. 2009. Generalized linear mixed models: A practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends in ecology & evolution 24:127-135.
Mixed-Effects Model vs. GEE
| Mixed-Effects Model | Marginal Model with GEE | |
|---|---|---|
| Distributional assumptions | Yes | No |
| Population average estimates | Yes | Yes |
| Group-specific estimates | Yes | No |
| Estimate variance components | Yes | No |
| Perform good with small n | Yes | No |