GMS6850 FOUNDATIONS OF BIOMEDICAL INFORMATICS

The Exposome: Concept, Utility, and Challenges
Hui Hu Ph.D.
Department of Epidemiology
College of Public Health and Health Professions & College of Medicine
October 1, 2020
Phenotypes are a function of inherited and environmental factors
P = f( G , E )
Phenotype
Genome
Environment
The Genome
- Well-established tools to sequence the human genome and to examine individual susceptibility through genome-wide association studies (GWAS)
- Thousands of GWAS
A lack of comparable tools in relation to environmental exposure assessment
Traditional environmental health studies almost uniquely focused on single exposure-outcome relationships and no global view of how various types of coexisting exposures may jointly affect health
Concept
The Exposome

To draw attention to the critical need for more complete environmental exposure assessment
"encompasses all life-course environmental exposures from the prenatal period onwards, complementing the genome"
"in a broader sense of all lifestyle, infections, radiation, natural and man-made chemicals and occupational exposures"
Environmental Exposures
The Health and Environment-wide Associations based on Large population Surveys (HEALS)
Aims to develop an integrated methodology for compiling and organizing exposure data across multiple domains, and using these factors to predict health outcomes

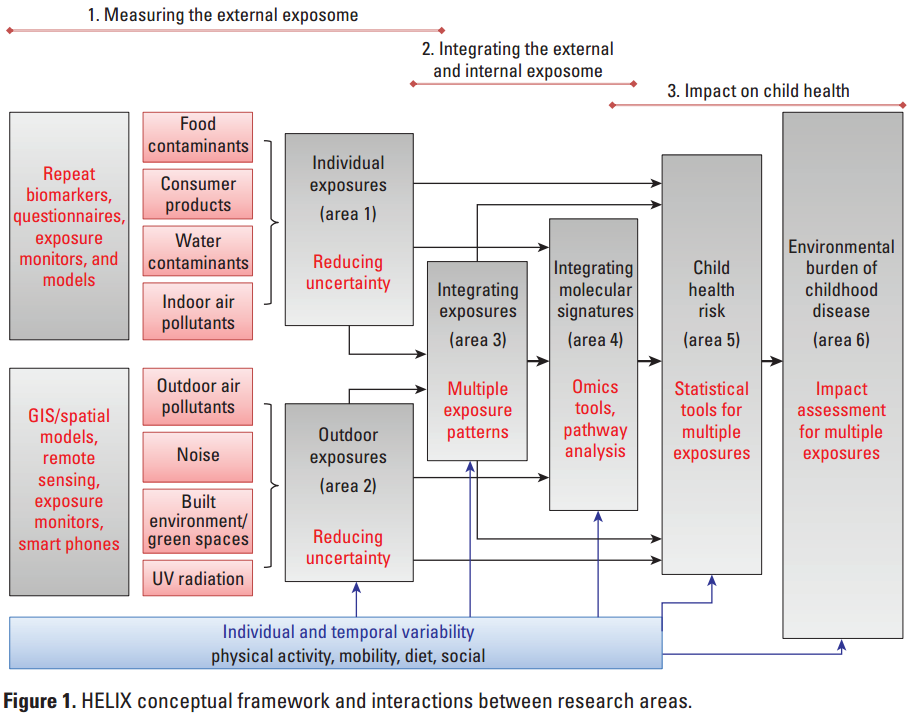
Human Early-Life Exposome (HELIX) Project
Aim to implement tools and methods to characterize early-life exposure to a wide range of chemical and physical environmental factors and associate with data on major child health outcomes
- early-life exposome approach

Source: Vrijheid et al. The human early-life exposome (HELIX): project rationale and design. Environmental health perspectives. 2014 Jun;122(6):535-44.

HHEAR - NIEHS/NCI/NHLBI/ECHO

HERCULES Exposome Research Center - Emory

The Institute for Exposomic Research - Mount Sinai

Center for the Investigation of Environmental Hazards - NYU


Source: Wild CP. The exposome: from concept to utility. International journal of epidemiology. 2012 Feb 1;41(1):24-32.

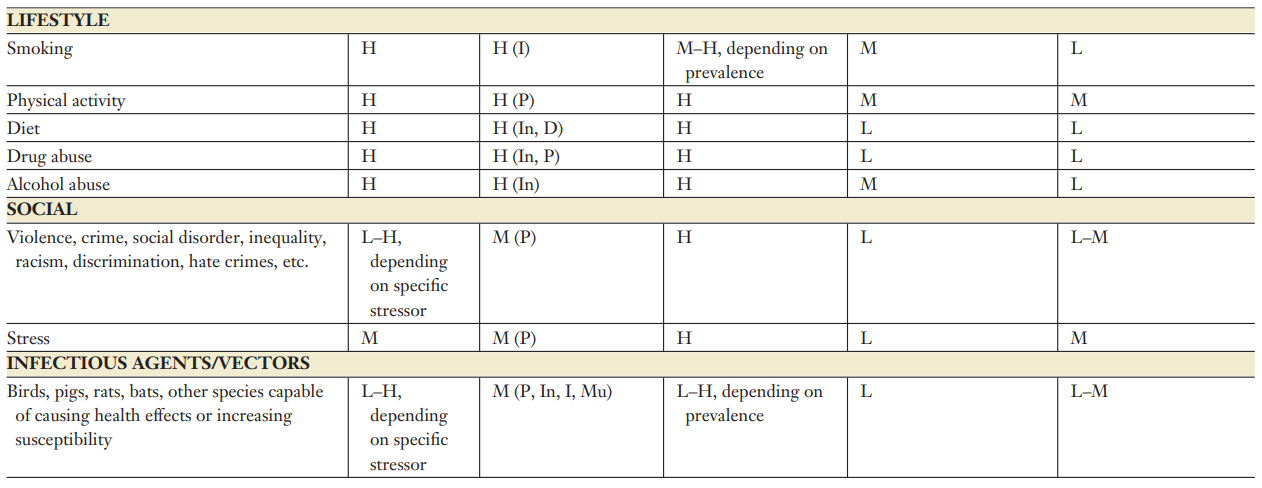
Exposures that impact the internal environment of the body
Social, cultural and ecological contexts in which the person lives their life
The specific external agents to which one is exposed
- There can be overlaps in the three domains
“the difficulty in placing a particular exposure in one domain or another; for example, one can debate whether physical activity should be in the internal or specific external domains”
- The domains can also be considered as intertwined
- the internal may at least partially be a response to the external
- Measures in one domain or another may reflect to differing degrees one component of the exposome:
- the urban environment (general external)
- air pollution (specific external)
- inflammation (internal)

Source: Wild CP. The exposome: from concept to utility. International journal of epidemiology. 2012 Feb 1;41(1):24-32.
Two domains:
- The internal exposome
- The external exposome
Bottom-up vs. top-down


Approaches and Tools to Measure the Exposome
Source: Wild CP. The exposome: from concept to utility. International journal of epidemiology. 2012 Feb 1;41(1):24-32.


Source: Turner MC, et al. Assessing the exposome with external measures: commentary on the state of the science and research recommendations. Annual review of public health. 2017 Mar 20;38:215-39.
- Genome sequencing has been closely followed by analogous tools to characterize downstream biological event:
- RNA expression (transcriptomics)
- proteins (proteomics)
- metabolites (metabolomics)
- epigenomics
- Each of the omics provides information on thousands of individual component parts, and can be linked to disease outcomes in analogous fashion to GWAS
- Some of the limitations to use these approaches in the exposome framework:
- the 'top-down' approach lacks a crucial link between exposure to a given agent and the molecular profiles observed
- this is required to identify risk factors and to implement prevention strategies
Source: Wild CP. The exposome: from concept to utility. International journal of epidemiology. 2012 Feb 1;41(1):24-32.

Approaches and Tools to Measure the Exposome
Source: Wild CP. The exposome: from concept to utility. International journal of epidemiology. 2012 Feb 1;41(1):24-32.


Source: Turner MC, et al. Assessing the exposome with external measures: commentary on the state of the science and research recommendations. Annual review of public health. 2017 Mar 20;38:215-39.

GIS

Remote Sensing

GPS and Geolocation Techs

Smartphone-based sensors and assessments

Portable and Personal Sensing



Utility
Source: Zheng et al. Design and methodology challenges of environment-wide association studies: A systematic review. Environmental Research. 2020 Feb 19:109275.

Environment-Wide Association Studies (EWAS)
aka Exposome-Wide Association Studies (ExWAS)


Source: Zheng et al. Design and methodology challenges of environment-wide association studies: A systematic review. Environmental Research. 2020 Feb 19:109275.


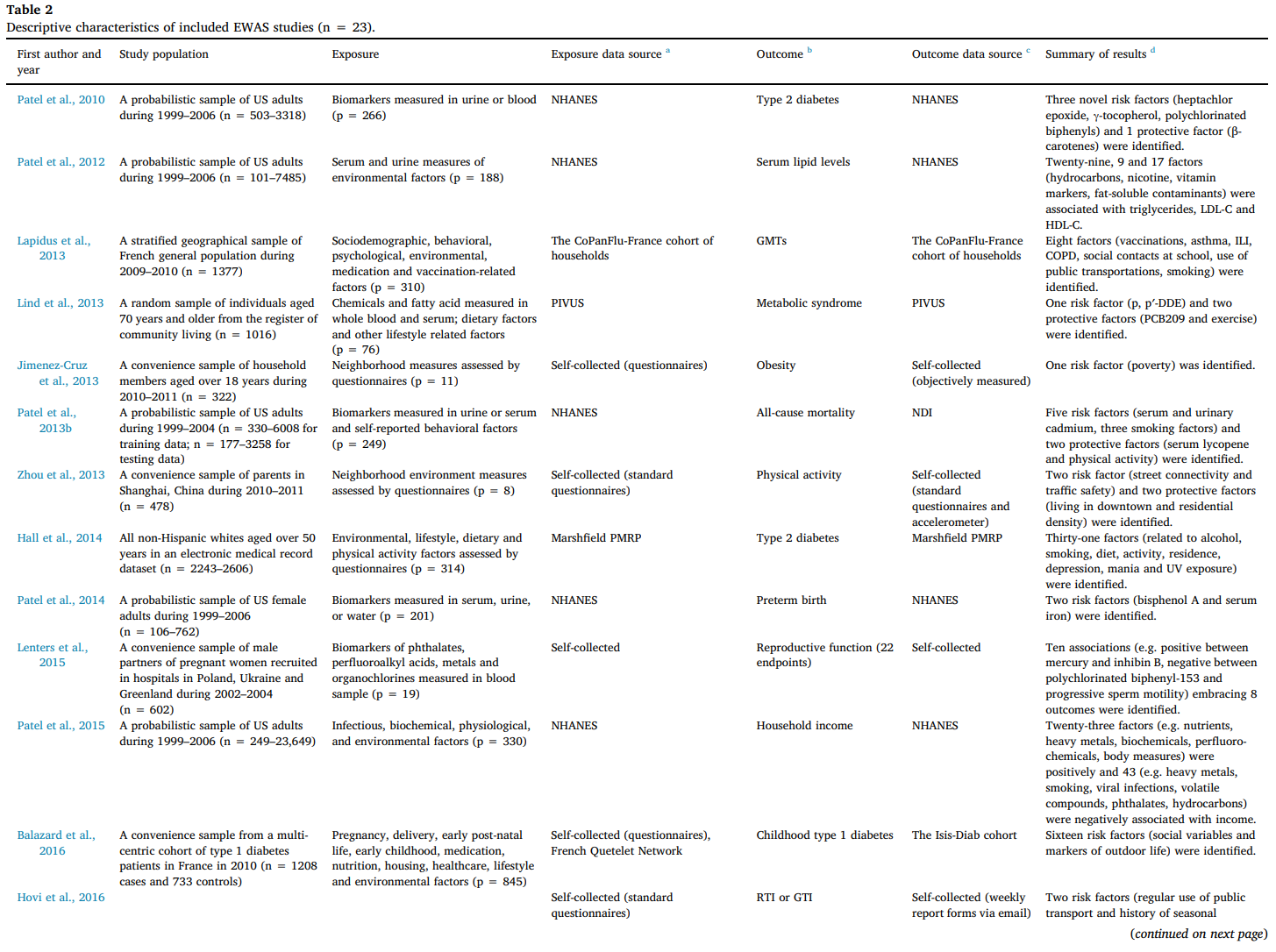
Among the 23 studies:
- 19 studies based on secondary data analyses
- 10 used data from the NHANES - 4 studies involved primary data collections
Top-down vs. bottom-up:
- 19 top-down studies
- 2 bottom-up studies
- 2 mixed

Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy (HDP)
One of the most common pregnancy complication (up to 10%), and major cause of morbidity and mortality








Individual's HDP Risk
Behavior and Intrinsic Biological Factors
Natural
Built



Social



Source: Hu et al. An external exposome-wide association study of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Environment International. 2020 Aug 1;141:105797.


Among the total of 5,784 external exposome variables included, we identified 528 significant variables from the discovery set in Phase 1.

Under review: Science of the Total Environment



Linked data from:
- Florida Vital Statistics Birth Records (VSBR)
-
Florida Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS)
- We developed predictive models using information from:
- VSBR only
- VSBR + PRAMS
- VSBR + PRAMS + External Exposome
VSBR only: 0.63 (0.59, 0.67)
VSBR+PRAMS: 0.68 (0.65, 0.72)
VSBR+PRAMS+Environmental Factors: 0.74 (0.70, 0.77)



Gradient boosting decision trees models

Testing AUC

Challenges
-
Dynamic: one of the most challenging features of the exposome's characterization
- At any given time, an individual will have a particular profile of exposures
- To fully characterize an individual's exposome:
- sequential measures that spanned a lifetime
- a series of snapshot measures at specific times in the lifespan of an individual

Source: Wild CP. The exposome: from concept to utility. International journal of epidemiology. 2012 Feb 1;41(1):24-32.
- Periods of only gradual change in the exposure profile
- Periods with dramatic changes in specific components
- e.g. change in occupation
- Periods when there is a radical change in global exposure profile in a short period
- e.g. one is born or migrates
- Several key stages proposed for the snapshot approach:
- gestation
- early childhood
- puberty
- reproductive years




Source: Jiang et al. Dynamic human environmental exposome revealed by longitudinal personal monitoring. Cell. 2018 Sep 20;175(1):277-91.
Ontology
- Ontology: a formal, computational representation of a domain of knowledge based upon a controlled, standardized vocabulary for describing entities and the semantic relationships between them
- Several semantic standards developed for the internal exposome, e.g., Metabolomics Standards Initiative Ontology
- Few exists for the external exposome:
- Only 2 out of 882 ontologies found on
BioPortal focused on the external exposome

Source: Zhang et al. Semantic Standards of External Exposome Data. Under Revision.
Ontology for the external exposome is needed to answer these questions
Researchers may have many questions when conducting external exposome studies:
- What are the domains of the measures of interest?
- What are the spatial and temporal scales of the measures?
- How can we establish the susceptible spatial (e.g., buffer vs. administrative boundary) and temporal windows (e.g., short-term vs. long-term) to these external exposome measures?
- Are there similar measures (e.g., monitored vs. modelled PM2.5) from different sources?
- Which ones to use?
- Whether it make senses to combine these similar measures to a “better” (e.g., more reliable or representative) measure?
- How to interpret inconsistent results for similar measures from different sources; among many other practical considerations that are needed.
Statistical Methods for Exposome Studies (Inference)
- Numerous statistical methods for studies:
EWAS, EWAS-MLR, ENET, sPLS, GUESS, DSA, Tree-based models, etc.
- Performances for internal exposome studies have been assessed.


"There is no uniform dominance of one method across all simulation scenarios and all criteria."
"Although GUESS and DSA provided a marginally better balance between sensitivity and FDP, they did not outperform the other multivariate methods across all scenarios and properties examined, and computational complexity and flexibility should also be considered when choosing between these methods."
Statistical Methods for Exposome Studies (Inference)
- No established methods for external exposome studies
- External exposome data are more heterogeneous internal exposome data:
- unique correlation structures:
factors from the same data source are more likely to be highly correlated
- different spatiotemporal scales, leading to different aggregations and spatiotemporal linkages and subsequently different associations:
e.g., the MAUP bias
Methods for Exposome Studies (Prediction)
- Existing machine/deep learning models can be implemented for internal exposome data
- More efforts needed for predictive models using external exposome data:
- Traditional machine learning models fail to preserve spatiotemporal structures in external exposome data
- No existing deep learning model architectures can be directly applied to external exposome data
Other Challenges
- Selection of confounders:
- all existing exposome studies used common sets of confounders for all exposures
- External validations:
- can be easily carried out by internal exposome studies
- much more complicated for external exposome studies:
exposure-disease associations may vary by space when spatial stochastic
process is in presence