Gestion d'exceptions
Définition
Il permet de gérer les conditions exceptionnelles pendant l'exécution du programme. Lorsqu'une exception se produit, l'exécution normale du programme est interrompue et l'exception est traitée.
Types
- arithmétique (débordement, division par zéro…) ;
- collections (débordement d'indices) ;
- allocation mémoire (mémoire insuffisante) ;
- signaux système (interruption du programme par le système d'exploitation).
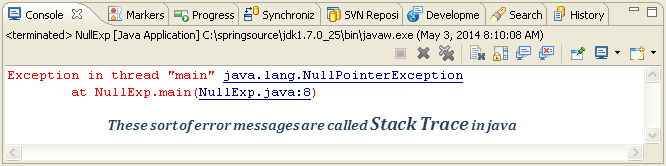
Création des Exceptions

Exemple
class ProgramLog
{
System.IO.FileStream logFile = null;
void OpenLog(System.IO.FileInfo fileName, System.IO.FileMode mode) {}
void WriteLog()
{
if (!this.logFile.CanWrite)
{
throw new System.InvalidOperationException("Logfile cannot be read-only");
}
// Else write data to the log and return.
}
}Gestion des Exceptions

Exemple
static int GetValueFromArray(int[] array, int index)
{
try
{
return array[index];
}
catch (System.IndexOutOfRangeException ex)
{
System.ArgumentException argEx = new System.ArgumentException("Index is out of range", ex);
throw argEx;
}
}Exemple
static void CodeWithCleanup()
{
System.IO.FileStream file = null;
System.IO.FileInfo fileInfo = null;
try
{
fileInfo = new System.IO.FileInfo("C:\\file.txt");
file = fileInfo.OpenWrite();
file.WriteByte(0xF);
}
catch(System.UnauthorizedAccessException e)
{
System.Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
finally
{
if (file != null)
{
file.Close();
}
}
}