正規表達式
Regular Expressions
Date: Nov. 17th, 2019
Lecturer: Chia

Outline
- 什麼是 Regular Expressions?
- 創建一個正規表達式 (Creating a regular expression)
- 比對測試 (Testing for matches)
- 字元的集合 (Sets of characters)
- 重複部分的模式 (Repeating parts of a pattern)
- 群組子表達式 (Grouping subexpressions)
Outline
- 匹配與群組(Matches and groups)
- 日期類 (The Date class)
- 單詞和字串的邊界 (Word and string boundaries)
- 選擇模式 (Choice patterns)
- 匹配機制 (The mechanics of matching)
- 回溯 (Backtracking)
Outline
- 取代方法 (The replace method)
- 貪婪式比對 (Greed)
- 動態創建RegExp物件 (Dynamically creating RegExp objects)
- 搜尋方法 (The search method)
- lastIndex屬性 (The lastIndex property)
- 解析一個INI文件 (Parsing an INI file)
- 國際字符 (International characters)
什麼是 Regular Expressions?
-
正規表達式
-
被用來匹配字串中字元組合的模式。 -
一個描述字串資料之模式(patterns)的方式。
-
let animalCount = /\b\d+ (pig|cow|chicken)s?\b/;
console.log(animalCount.test("15 pigs"));
// → true
console.log(animalCount.test("15 pigchickens"));
// → false創建一個正規表達式
- 正規表達式的型別(type)為物件(object)。
- 創建方式:
// (方式一) 使用 RegExp()
let re1 = new RegExp("abc");// (方式二) 使用 正斜杠 / 包覆所描述的模式
let re2 = /abc/;創建一個正規表達式
若 ? 和 + 的前面添加反斜線 \,代表將之當成一般字元,
意即表示字元本身,沒有特殊用途。
let eighteenPlus = /eighteen\+/;
// + 原本是特殊字元,但這裡要當成非特殊字元比對測試
-
test() 方法
- 回傳布林值,說明該字串是否符合欲比對的模式。
- 若正規表達式中只包含非特殊字元,比對字元本身。
console.log(/abc/.test("abcde"));
// → true
console.log(/abc/.test("abxde"));
// → false字元的集合
console.log(/[0123456789]/.test("in 1992"));
// → true
console.log(/[0-9]/.test("in 1992"));
// → true若將一組字符放在 [ ] 內,表示匹配[ ]內的所有字符。
意即只要符合 [ ] 內所列出的字符,就算匹配成功。
字元的集合
- 內建快捷表達方式(built-in shortcuts)
- 如:\d 與 [0-9] 含義相同(匹配所有數字)。
| 特殊字元 | 解說 |
|---|---|
| \d | 任何數字 |
| \w | 任何字母和數字(“文字字符”) |
| \s | 任何空白字符(space, tab, newline… |
| \D | 非數字的字符 |
| \W | 非字母和數字字符 |
| \S | 非空白字符 |
| . | 除換行字符以外的任何單一字元。 |
字元的集合
let dateTime = /\d\d-\d\d-\d\d\d\d \d\d:\d\d/;
console.log(dateTime.test("01-30-2003 15:20"));
console.log(dateTime.test("30-jan-2003 15:20"));let notBinary = /[^01]/;
console.log(notBinary.test("1100100010100110"));
// → false
console.log(notBinary.test("1100100010200110"));
// → true 1100100010`2`00110- 若 ^ 存在於 [ ] 內,表示匹配非方括號內的字符。
重複部分的模式
console.log(/'\d+'/.test("'123'"));
console.log(/'\d+'/.test("''"));
console.log(/'\d*'/.test("'123'"));
console.log(/'\d*'/.test("''"));- 如何匹配一個或多個數字的序列?
| + | 該字符重複出現至少1次 |
|---|---|
| * | 該字符重複出現0次以上 |
| ? | 該字符重複出現出現0次或1次 |
let neighbor = /neighbou?r/;
console.log(neighbor.test("neighbour"));
console.log(neighbor.test("neighbor"));重複部分的模式
let dateTime = /\d{1,2}-\d{1,2}-\d{4} \d{1,2}:\d{2}/;
console.log(dateTime.test("1-30-2003 8:45"));
// → true- 為了精確匹配該字符的出現次數,使用 { } 放在某個字符後面。
| {4} | 該字符需出現4次,即符合。 |
|---|---|
| {2,4} | 該字符出現至少2次、最多4次,即符合。 |
| {5,} | 該字符出現至少5次,即符合。(開放式範圍) |
群組子表達式
let cartoonCrying = /boo+(hok+)+/i;
console.log(cartoonCrying.test("BoohoooohooHooo"));
console.log(cartoonCrying.test("Boohokoohokhook"));
>>> `i`是指`不區分大小寫`-
括號 ( ) 用於驗證字符串,以及提取字串的一部分。
- 若一次要對多個字符使用特殊符號(+ 或 *),則必須使用 ( )。
- 若沒有使用 ( ) 包起來,則代表其是針對前面的一個字符。
匹配與群組
let match = /\d+/.exec("one two 100");
console.log(match);
// → ["100"]
console.log(match.index);
// → 8- test()方法:最簡單的匹配方式,只回傳True或False。
-
exec()方法:沒有匹配時,回傳null;否則傳回匹配資訊。
- index屬性:回傳成功匹配的字符從何處開始。
- match()方法:處理字串的方法,與exec()方法類似。
console.log("one two 100".match(/\d+/));
console.log("one two 100".match(/\d?/));
console.log("one two 100".match(/\d*/));匹配與群組
let quotedText = /'([^']*)'/;
// '([^']*)' -> 字串外面使用''包裹。群組裡面沒有`'`出現0次以上。
// 'hello' or hello
console.log(quotedText.exec("she said 'hello'"));
// → ["'hello'", "hello"]const regexp = /(\w+)\.jpg/;
console.log(regexp.exec('File name: cat.jpg'));
// ["cat.jpg", "cat"]匹配與群組
console.log(/bad(ly)?/.exec("bad"));
// → ["bad", undefined]
// 先比對 bad(ly)? 再比對 (ly)?
console.log(/bad(ly)?/.exec("badl"));
console.log(/bad(ly)?/.exec("badlyr"));- 當一個群組( )被成功匹配多次時,僅回傳最後一個匹配的項目,即"3"。
console.log(/(\d)+/.exec("123")); // (\d)+
// → ["123", "3"]日期類
console.log(new Date());
// → Tue Nov 12 2019 10:28:37 GMT+0800 (台北標準時間)Date 物件提供 getFullYear(), getMonth(), getDate(), getHours(), getMinutes(), and getSeconds()方法。
console.log(new Date(2019, 11, 12));
// → Thu Dec 12 2019 00:00:00 GMT+0800 (台北標準時間)
console.log(new Date(2009, 11, 12, 12, 59, 59, 999));
// 最後的四個參數為(小時,分鐘,秒和毫秒),預設皆為0。- 取得現在的日期和時間
- 創建特定時間的物件(object)
日期類
console.log(new Date(2019, 10, 12).getTime());
// → 1573488000000
console.log(Date.now());
// → 1573527038896
console.log(new Date(1573527038896));
// → Tue Nov 12 2019 10:50:38 GMT+0800 (台北標準時間)- JavaScript的月份從0開始(所以12月是11);日期從1開始。
-
getTime()方法,可回傳從1970年至某個時間點的毫秒數。
日期類
- 進行日期的處理
function processDate(string) {
let [_, month, day, year] = /(\d{1,2})-(\d{1,2})-(\d{4})/.exec(string);
// 底線 _ (underscore) 忽略,用於跳過由exec返回的陣列中匹配的物件。
return new Date(year, month - 1, day);
}
console.log(processDate("testing: 1-30-2003 in javascript."));
// → Thu Jan 30 2003 00:00:00 GMT+0800 (台北標準時間)備註:(匹配模式不夠嚴謹,於下一節 "單詞和字串的邊界" 說明)
console.log(processDate("100-1-30000")); // 匹配 "00-1-3000"
>>> Sun Dec 01 2999 00:00:00 GMT+0800 (台北標準時間)單詞和字串的邊界
| ^ | 匹配字串的開頭 |
|---|---|
| $ | 匹配字串的結尾 |
- 錯誤寫法:/x^/
| /^\d+$/ | 匹配開頭包含至少一個數字的字串 匹配結尾包含至少一個數字的字串 |
|---|---|
| /^!/ | 匹配開頭為!的字串 |
單詞和字串的邊界
| \b | 配對 word boundary(單詞邊界)。 單詞邊界是指一個字元的前後沒有其他字元。 |
|---|
let matchedResult = 'This is an apple.'.match(/\bis\b/);
// is 這個單字才會被選到
// This 中的 is 不會被選到,因為前有其他字元。
// [ 'is', index: 5, input: 'This is an apple.' ]console.log(/cat/.test("concatenate"));
console.log(/\bcat\b/.test("concatenate"));
console.log(/\bcat/.test("catenate"));選擇模式
| | | 在左側模式和右側模式之間進行選擇。 (一次匹配多種可選擇的類型) |
|---|
let animalCount = /\b\d+ (pig|cow|chicken)s?\b/;
console.log(animalCount.test("15 pigs"));
// → true
console.log(animalCount.test("15 pigchickens"));
// → false匹配機制
let animalCount = /\b\d+ (pig|cow|chicken)s?\b/;
console.log(animalCount.test("the 3 pigs"));
// → true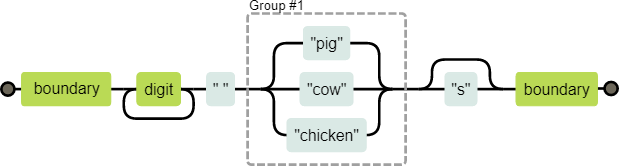
回溯
let reg = /\b([01]+b|[\da-f]+h|\d+)\b/;
console.log(reg.test("0 856 fr2 eah 1b"));
// → true
console.log(reg.exec("0m 856 fr2 eah 1b")); // 856 eah 1b 皆符合
// → ["856", "856"]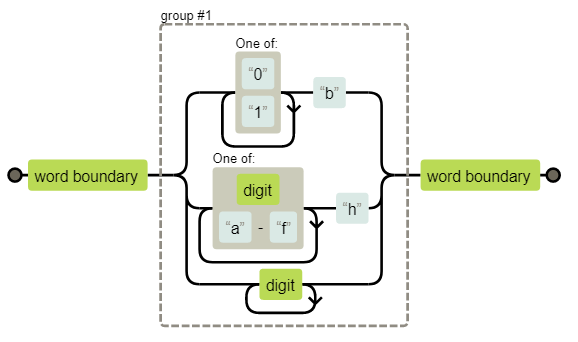
回溯
let reg = /^.*x/;
console.log(reg.test("."));
console.log(reg.test(""));
console.log(reg.test("x"));
console.log(reg.test(".x"));
console.log(reg.test(".xa"));
console.log(reg.test("abcxe"));let reg = /([01]+)+b/;
console.log(reg.test("01 123"));
console.log(reg.test("0 reg"));
console.log(reg.test("01b 123"));
console.log(reg.test("0b reg"));取代方法
console.log("papa".replace("p", "m"));
// → mapa-
replace()方法:用於將一個字串替換為另一個字串。
- [ replace() 的第一個參數 ]
- 使用g於正規表達式中,可取代所有匹配項。
- [ replace() 的第一個參數 ]
console.log("Borobudur".replace(/[ou]/, "j"));
// → Bjrobudur
console.log("Borobudur".replace(/[ou]/g, "j"));
// → Bjrjbjdjr取代方法
console.log(
"Liskov, Barbara\nMcCarthy, John\nWadler, Philip"
.replace(/(\w+), (\w+)/g, "$2 $1"));
// → Barbara Liskov
// John McCarthy
// Philip Wadler- [ replace()的第二個參數 ]
- 使用$,可針對括號( )內的內容。
console.log(
"Liskov, Barbara\nMcCarthy, John\nWadler, Philip"
.replace(/(\w+), (\w+)/g, "$&")); // $& 指的是所有括號( )的內容
// → Liskov, Barbara
// McCarthy, John
// Wadler, Philip貪婪式比對
let html = `
<table>
<td>aaa</td>
</table>
<table>
<td>bbb</td>
</table>
`;
let reg = /<table[.\n\s\S]*<\/table>/g;
let r = html.match(reg);
console.log(r);- Greedy:使用 *、+、? 或 { } 等重複運算符,將會使之儘可能匹配最多的字元。
貪婪式比對
// let html 同上
let reg = /<table[.\n\s\S]*?<\/table>/g;
let r = html.match(reg);
console.log(r);-
Non-Greedy:使用 *?、+?、?? 或 {}? ,將會使之儘可能匹配最少的字元。
- 例如:在123abc中應用 /\d+/ 可匹配「123」,但使用 /\d+?/ 在相同字串上只能匹配「1」。
動態創建RegExp物件
使用「脫逸字元\」
// 使用 RegExp()
let pp2 = new RegExp("ab\/nc");// 使用 正斜杠 / 包覆所描述的模式
let pp1 = /ab\/nc/;欲將特殊字元,轉為一般字串
使用「脫逸字元\」
let pp1 = /ab\/nc/;
let str1 = "qaz1ab/nc";
console.log(pp1.exec(str1));let pp2 = new RegExp("ab\/nc");
let str2 = "qaz1ab/nc";
console.log(pp2.exec(str2));正規表達式固定已知!
動態創建RegExp物件
let name = "harry"; // 把 harry 當成模式
let text = "Harry is a suspicious character.";
let regexp = new RegExp("\\b(" + name + ")\\b", "gi");
// 符合模式
console.log(text.replace(regexp, "_$1_"));
// → _Harry_ is a suspicious character.正規表達式動態未知!
- 先把表示式轉換為字串,進行動態處理,再拿來建立 RegExp 物件
搜尋方法
-
indexOf() 方法
- 回傳給定元素於陣列中第一個被找到之索引,若不存在於陣列中則回傳-1。
- 不能用於正規表達
str.indexOf(/[abc]/ , i); - 優點:能從特定位置開始搜尋。
let str="Hello world!";
console.log(str.indexOf("Hello"));
console.log(str.indexOf("World"));
console.log(str.indexOf("world"));
Output:
0
-1
6搜尋方法
-
search()方法
- 可用於正規表達式。
- 回傳給定元素於陣列中第一個被找到之索引,若不存在於陣列中則回傳-1。
- 缺點:不能從特定位置才開始搜尋。
let str="Mr. Blue has a blue house";
console.log(str.search(/blue/i));console.log(" word".search(/\S/)); //012
// → 2lastIndex 屬性
-
exec()方法
- 缺點:不能從特定位置才開始搜尋。
- 正規表達式的物件,擁有以下屬性:
- source:正規表達式。
- lastIndex:用於控制,該從何處開始匹配。
lastIndex 屬性
let str = "a0bc1";
// Indexes: 01234
let rexWithout = /\d/;
//指定位子搜尋,對它沒用。從index=0開始搜尋
rexWithout.lastIndex = 2;
console.log(rexWithout.exec(str));
// → [ '0', index: 1, input: 'a0bc1', groups: undefined ]let rexWithout_g = /\d/g;
//指定位子搜尋,對它有用。從index=2開始搜尋,會繼續往後搜尋
rexWithout_g.lastIndex = 2;
console.log(rexWithout_g.exec(str));
// → [ '1', index: 4, input: 'a0bc1', groups: undefined ]lastIndex 屬性
let str = "a0bc1";
// Indexes: 01234
let rexWith_y = /\d/y;
rexWith_y.lastIndex = 2;
//指定位子搜尋,對它有用。只搜尋index=2,"不會"繼續往後搜尋
console.log(rexWith_y.exec(str));
// → nulllet str = "a0bc1";
// Indexes: 01234
let rexWith_y = /\d/y;
rexWith_y.lastIndex = 1;
console.log(rexWith_y.exec(str));
rexWith_y.lastIndex = 4;
console.log(rexWith_y.exec(str));lastIndex 屬性
console.log("Banana".match(/an/g));
// → ["an", "an"]-
match()方法 + g (global option)
- match()方法會在字串中找到該模式的所有匹配項,並回傳包含匹配字串的陣列。
解析一個INI文件
searchengine=https://duckduckgo.com/?q=$1
spitefulness=9.7
; comments are preceded by a semicolon...
; each section concerns an individual enemy
[larry]
fullname=Larry Doe
type=kindergarten bully
website=http://www.geocities.com/CapeCanaveral/11451
[davaeorn]
fullname=Davaeorn
type=evil wizard
outputdir=/home/marijn/enemies/davaeorn解析一個INI文件
| \r | 返回符號(返回同一行的開頭,不前進到下一行) |
|---|---|
| \n | 換行符號 |
| /\r?\n/ | 允許行與行之間為\n或\r\n的拆分方式。 |
function parseINI(string) {
let result = {};
let section = result;
string.split(/\r?\n/).forEach(line => {
let match;
if (match = line.match(/^(\w+)=(.*)$/)) {
//是屬性
section[match[1]] = match[2];
} else if (match = line.match(/^\[(.*)\]$/)) {
//是節標題
section = result[match[1]] = {};
} else if (!/^\s*(;.*)?$/.test(line)) {
//不是節標題或屬性
// 檢查它是註釋還是空行 // (;.*) 匹配註釋 ? 匹配空格
throw new Error("Line '" + line + "' is not valid.");
// 與任何形式都不匹配時,引發異常。
}
});
return result;
}
console.log(parseINI(`
name=Vasilis
[address]
city=Tessaloniki`));
// → {name: "Vasilis", address: {city: "Tessaloniki"}}國際字符
- JavaScript的word character只包含26個大小寫的英文字母、十進位數字、底線。
- 而像是é、β等字符,將不被匹配\w(文字字符),但可匹配\W(非文字字符)。
- \s (空白),可匹配Unicode標準認為的所有字符,包括不間斷空格和蒙古元音分隔符之類的東西。
國際字符
- JavaScript預設:
- 處理正規表達式的單個程式碼字元,而不是處理實際的單個字符。
console.log(/🍎{3}/.test("🍎🍎🍎"));
// → false
console.log(/<.>/.test("<🌹>"));
// → false
console.log(/<.>/u.test("<🌹>"));
// 必須在正則表達式中添加`u`,以Unicode使其正確處理此類字符。
// → true國際字符
- u 意味以Unicode處理此類字符。
- \p是 Unicode 屬性轉義,它賦予了我們根據 Unicode 字符的屬性數據構造表達式的能力。
/* \p{Property=Value} */
console.log(/\p{Script=Greek}/u.test("α"));
// → true
console.log(/\p{Script=Arabic}/u.test("α"));
// → false/* \p{Name} */
console.log(/\p{Alphabetic}/u.test("α"));
// → true
console.log(/\p{Alphabetic}/u.test("!"));
// → false