Scope
What Is it Good For?
What We'll Cover
- What is Scope
- Global Scope
- Functional/Local Scope
- Scope in ES6
- Hoisting
What is scope?



Scope:
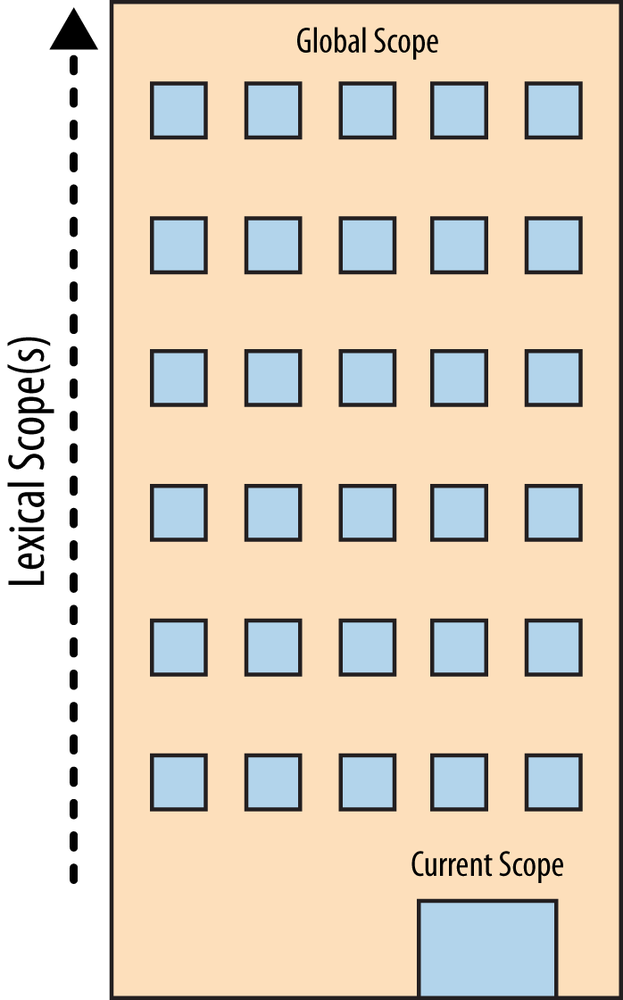
In JavaScript, scope refers to the visibility of variables
The set of rules for storing variables, and for finding those variables at a later time
local
- Variables which are defined outside of a function
- Visible to whole program
- Variables declared inside the function
- Function parameters
- Only visible inside function
Global
VS
local
Global
VS
var number = 100; // Global variable
function changeNumber() {
var number = 200; // Local variable
number += 100;
return number;
}
console.log(changeNumber()); // 300
console.log(number); // 100 This was not changedLHS
Tries to find the variable. Checks to see if variable exists
RHS
Looks up the value of a variable
var x = 'Goodbye';
var y = ' Alvaro';
console.log(x + y);
LHS
Tries to find the variable. Checks to see if variable exists
RHS
Looks up the value of a variable
var x = 'Goodbye';
var y = ' Alvaro';
console.log(x + y);
x = 'Good Riddance';It's a conversation
- Engine
- Compiler
- Scope
Engine
Responsible for start-to-finish compilation and execution of our JavaScript program

Compiler
Handles parsing and code-generation

Basically it makes the code executable
Scope
Collects and maintains list of variables

Enforces rules how these variables are accessible to code
Conversation
function foo(a) {
console.log( a ); // 2
}
foo( 2 );Nested scope
function foo(a) {
console.log( a + b );
}
var b = 2;
foo( 2 ); // 4Nested scope
SCope in es6
var VS let
var numArray = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
numArray.push(i);
}
console.log(numArray); // returns [0, 1, 2]
console.log(i); // returns 3var numArray = [];
var i;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
numArray.push(i);
}
console.log(numArray); // returns [0, 1, 2]
console.log(i); // returns 3
SCope in es6
var VS let
var printNumTwo;
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if(i === 2){
printNumTwo = function() {
return i;
};
}
}
console.log(printNumTwo()); // returns 3SCope in es6
var VS let
let printNumTwo;
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (i === 2) {
printNumTwo = function() {
return i;
};
}
}
console.log(printNumTwo()); // returns 2
console.log(i); // returns "i is not defined"SCope in es6
var VS let
Hoisting
a = 2;
var a;
console.log( a );var a;
a = 2;
//var a; This code gets moved up essentially
console.log( a );Hoisting
console.log( a );
var a = 2;var a;
console.log( a );
a = 2; // 'a' was declared but was not defined