建國中學
暑假地球科學讀書會
海洋和氣候
Presenter: 122527 Brine
Index
definition
What is climate?
〞
The long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years.
– Wikipedia
to be more specific
- The average and variability of variables
- temperature
- humidity
- pressure
- wind speed / direction
- precipitation
- months ~ thousands of years
Classification
How do we categorise different climates?
Bergeron classification scheme
- Simplest
- Classifies the air masses
- This was used in weather forecasting first
mPk
moisture
region
stability
List of properties
| Moisture | Region | Stability |
|---|---|---|
| continental | Equatorial | kolder |
| maritime | Tropical | warmer |
| Polar | ||
| Arctic / Antartic | ||
| Monsoon | ||
| Significant downward |
Major air masses
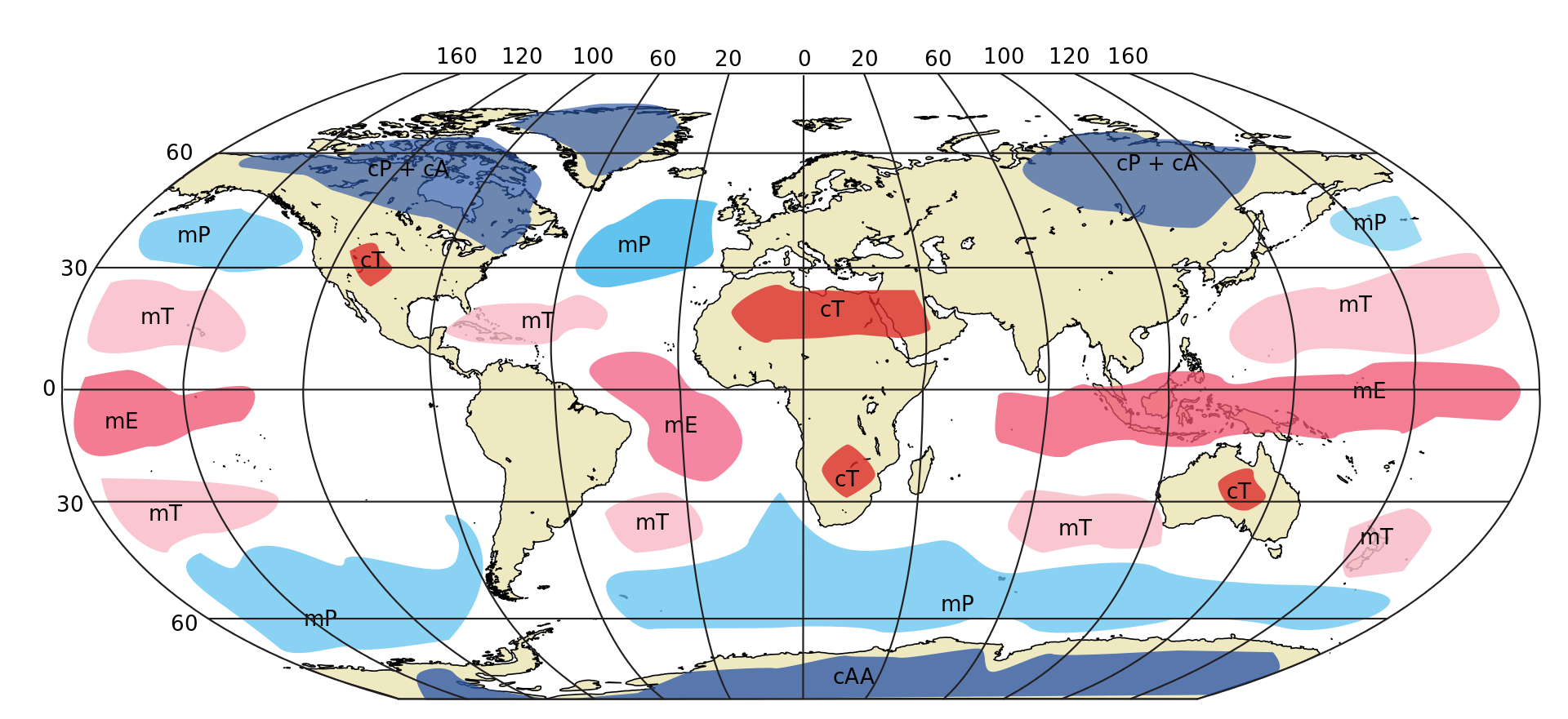
Transformation
- When the air mass move the another place
- both notations are accepeted
cA-mPk
mT/cP
Simplified
| Moisture | Region | Stability |
|---|---|---|
| continental | Equatorial | kolder |
| maritime | Tropical | warmer |
| Polar | ||
| Arctic / Antartic | ||
| Monsoon | ||
| Significant downward |
Spatial Synoptic Classification system
Simplified
| Moisture | Region |
|---|---|
| continental | Equatorial |
| maritime | Tropical |
| Polar | |
| Arctic / Antartic | |
| Monsoon | |
| Moderate |
Spatial Synoptic Classification system
Köppen climate classification
- Published by Wladimir Köppen, 1884
- Main group
- Precipitation subgroup(Not for E)
- Temperature subgroup(Not for A)
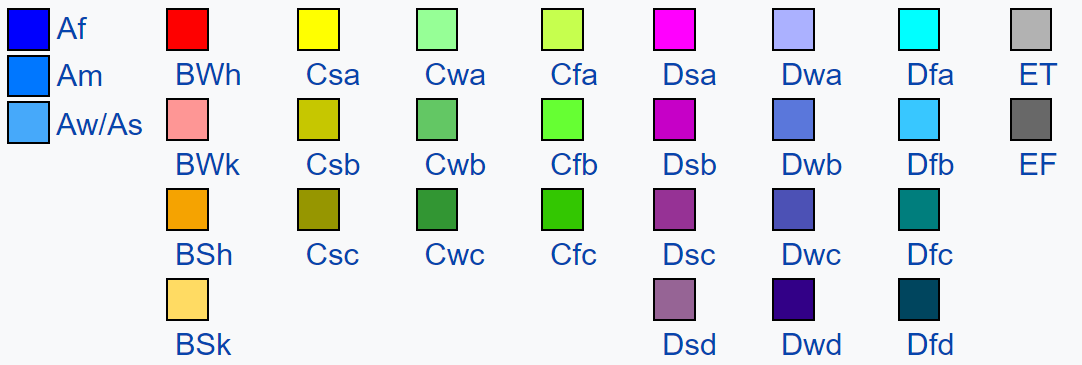
| Abbr. | Full name |
|---|---|
| Af | Tropical rainforest |
| Am | Tropical monsoon |
| Aw | Tropical dry winter savanna |
| As | Tropical dry summer savanna |
Köppen climate classification
| Code | Precipitation | Code | Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| W(B) | desert | h(B) | hot |
| S(B) | steppe | k(B) | cold |
| w | dry winter | a | hot summer |
| f | no dry season | b | warm summer |
| s | dry summer | c | cold summer |
| T(E) | Tundra | d | very cold winter |
| F(E) | eternal Front |
Köppen climate classification
| Code | Main |
|---|---|
| A | Tropical |
| B | Arid |
| C | Temperate |
| D | Continental |
| E | Polar |
Köppen climate classification
exercise!
Af
BWh
CFa
EF
DFb
What the world looks like
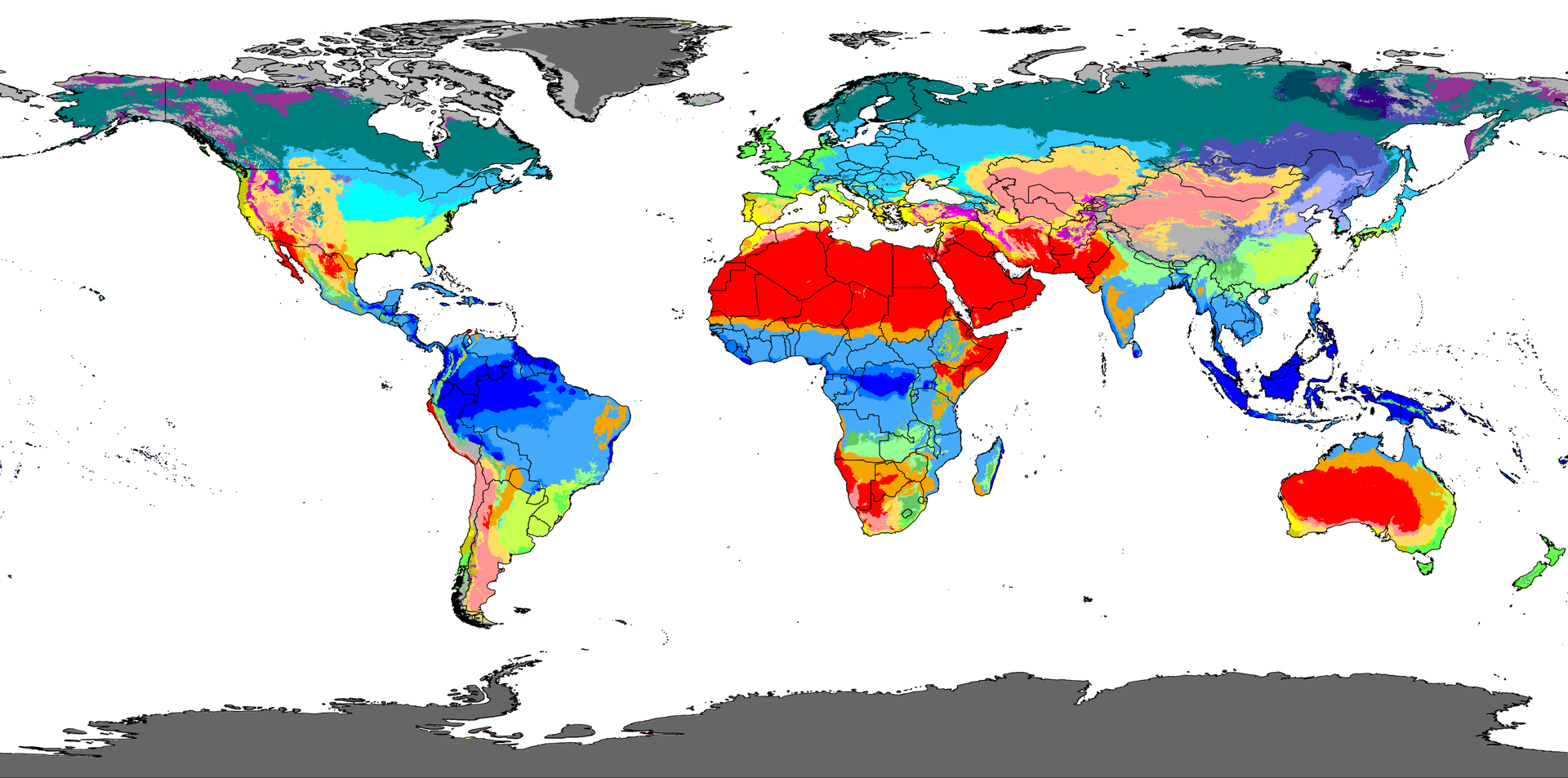
FactorS
What has an effect on climate?
On a macroscopic scale
- Where we are
A bit smaller
- How fast we are spinning
\vec \Omega
\vec V
Atmosphere
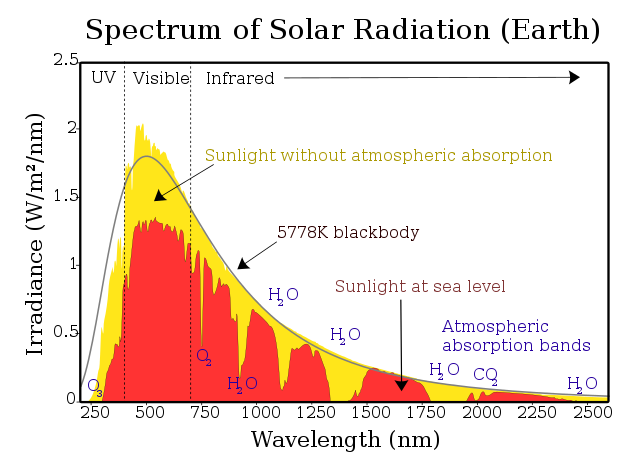
Atmosphere
Ground



OCEAN
Hold on, there is too much!

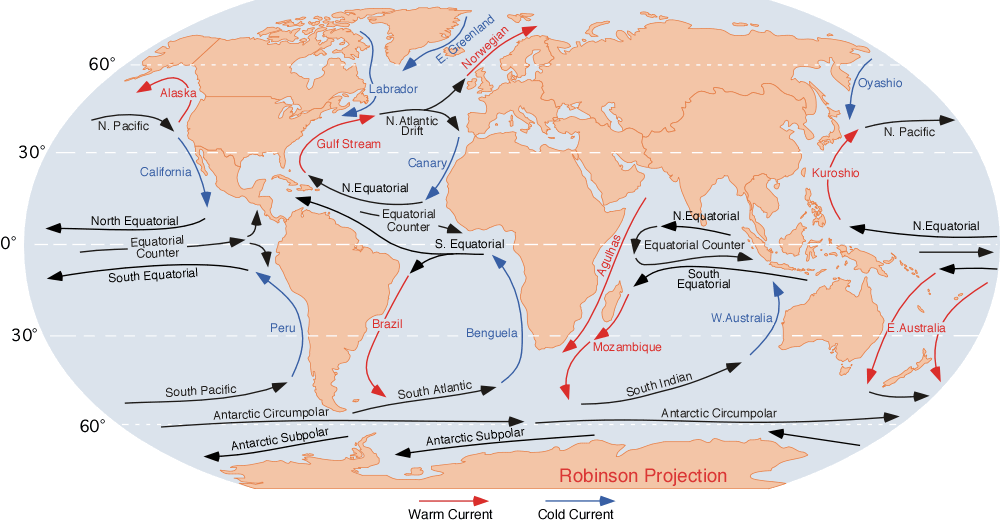
Ocean Current
It does a lot, apparently.
What is the cause
- surface wind
- density
8\%
400\ m
\rho
P,\ T,\ S
surface currents
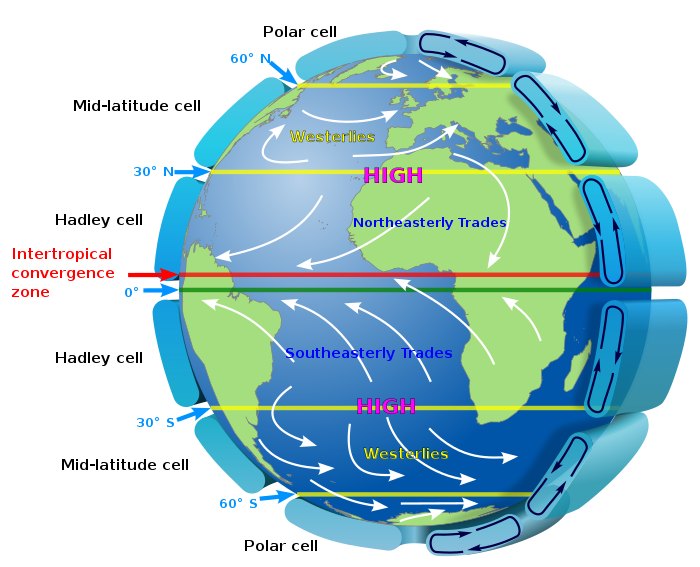
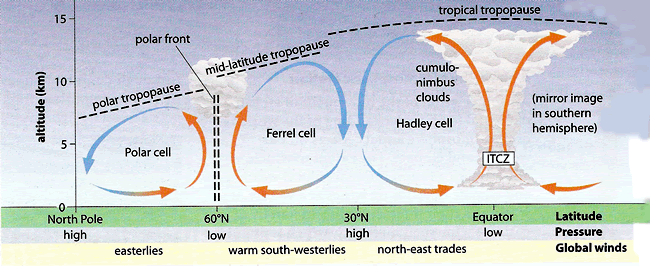
Tri-cellular circulation
Prevailing winds
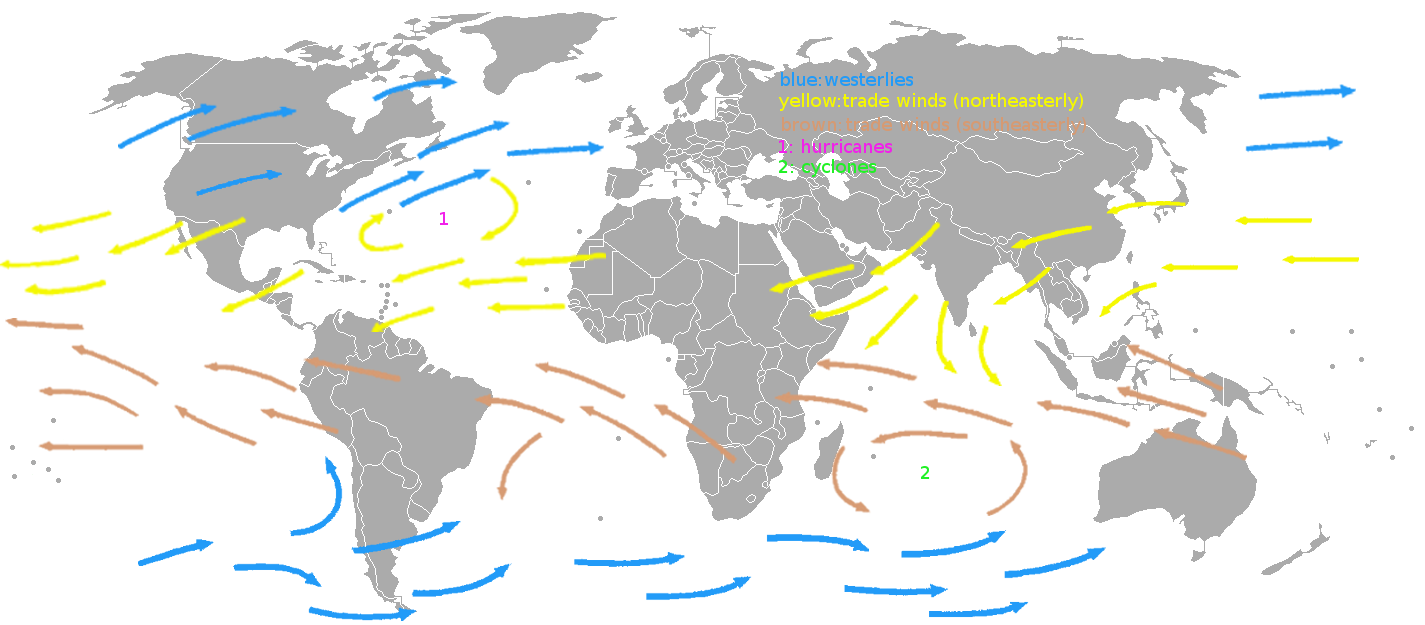
- also the sea / land breeze cycle
- terrain
how we determine
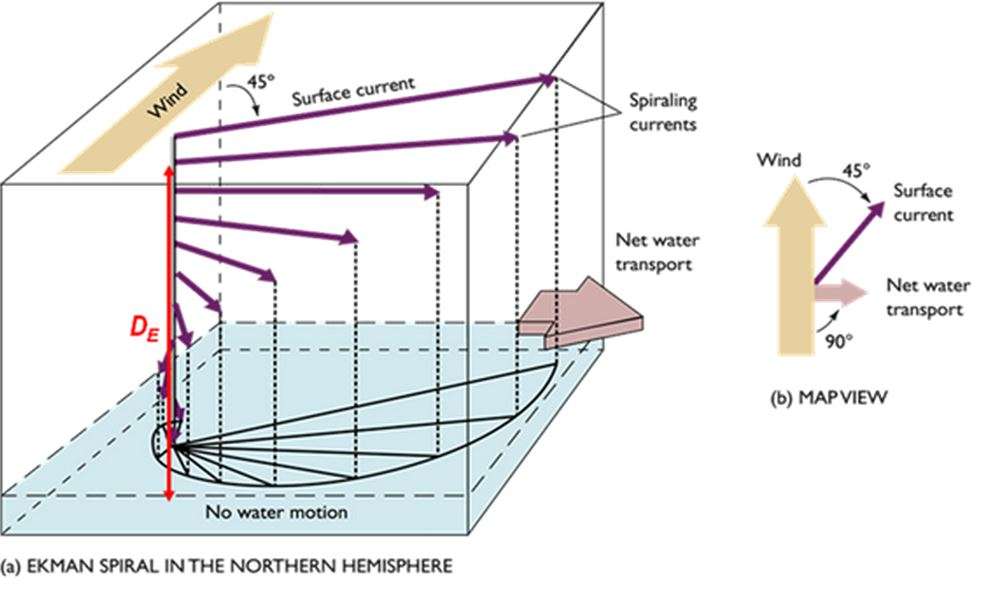
Ekman spiral
Thermohaline circulation
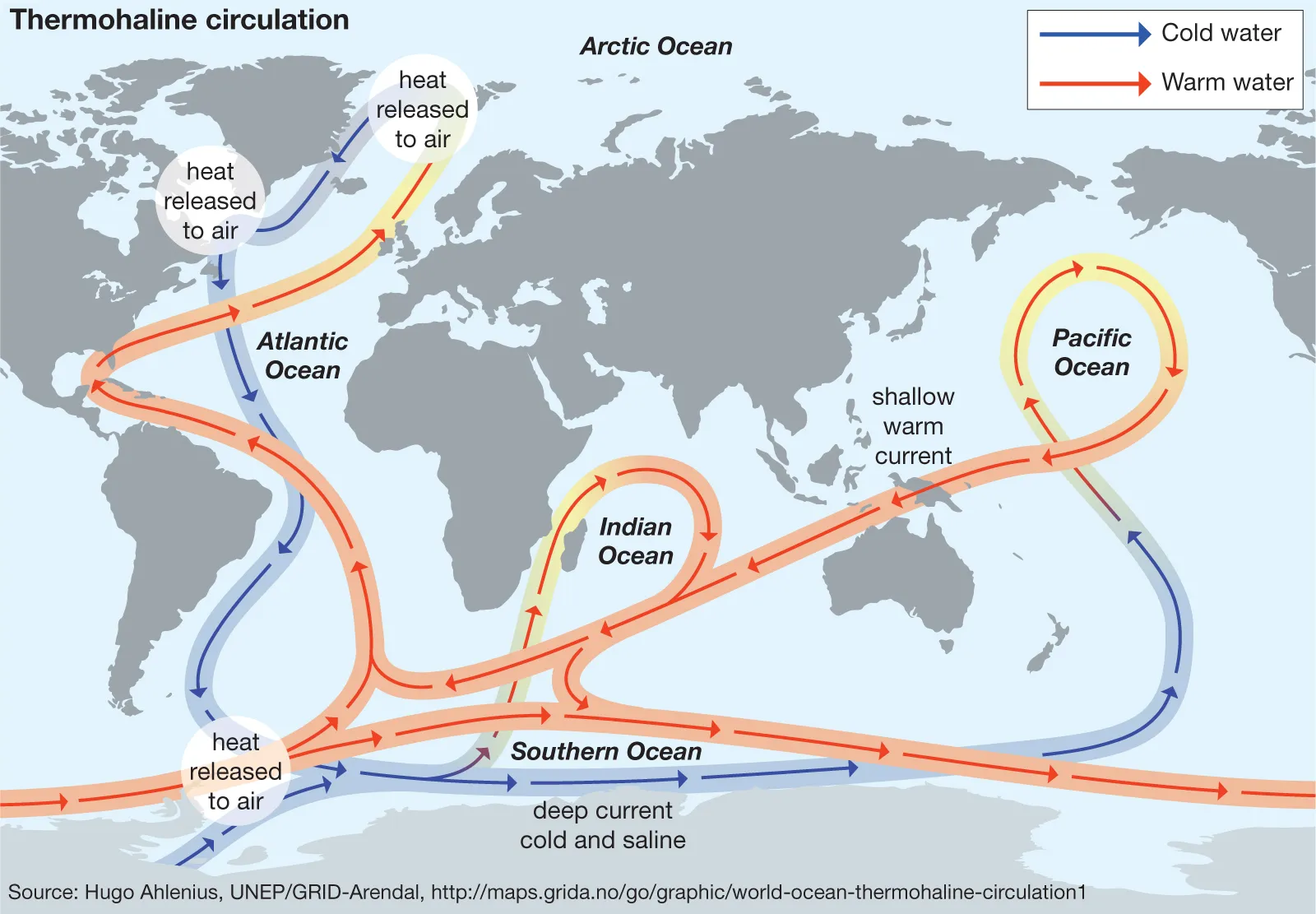
"the ocean's conveyor belt"
How important is it
$$"possibly"$$
Water MASS
A lot of water together, basically.
Definition
- an identifiable body of water with a common formation history
- physical properties distinct from surrounding water
- temperature
- salinity
- isotopic ratio
- oxygen and other soluble gas
Example
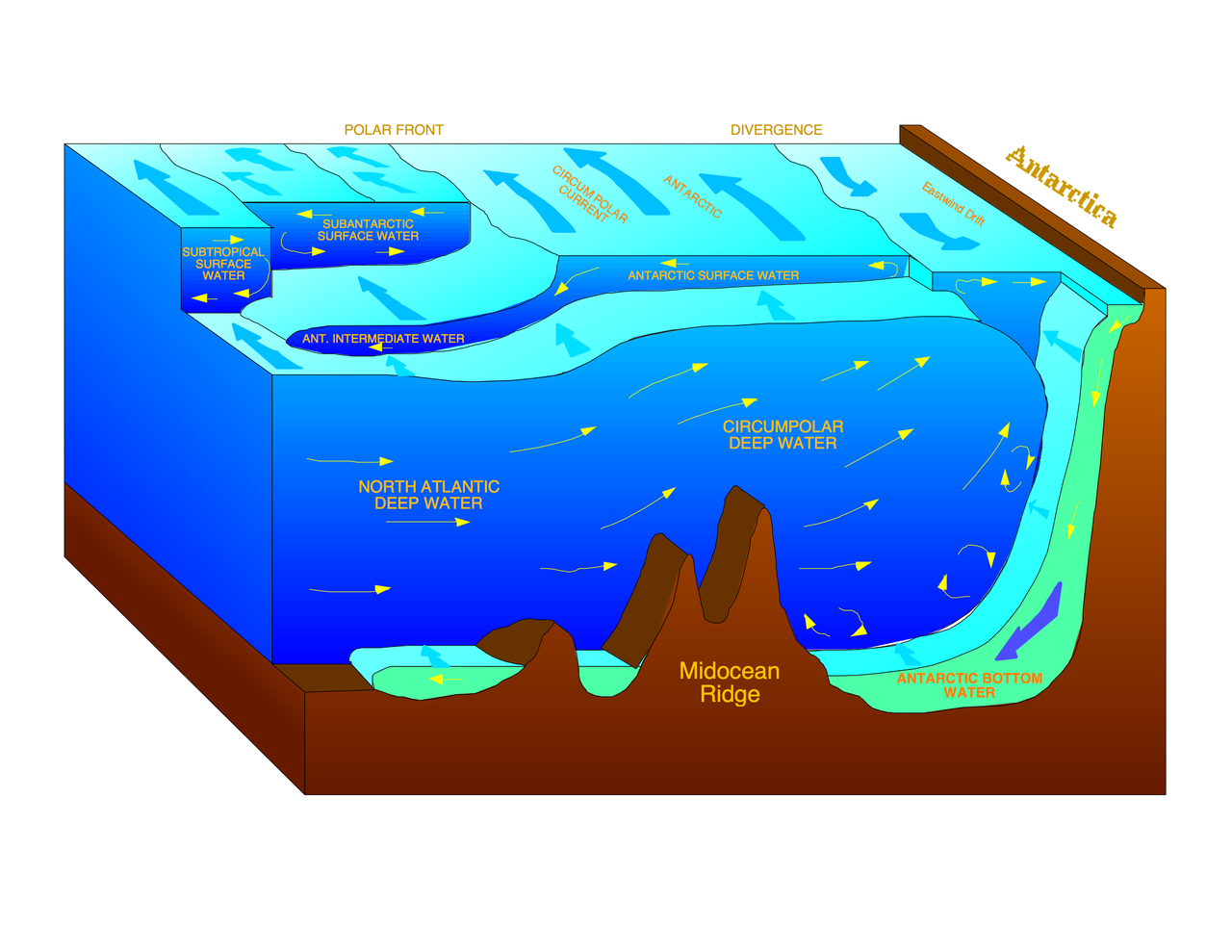
Important Water masses
- AntArctic Bottom Water
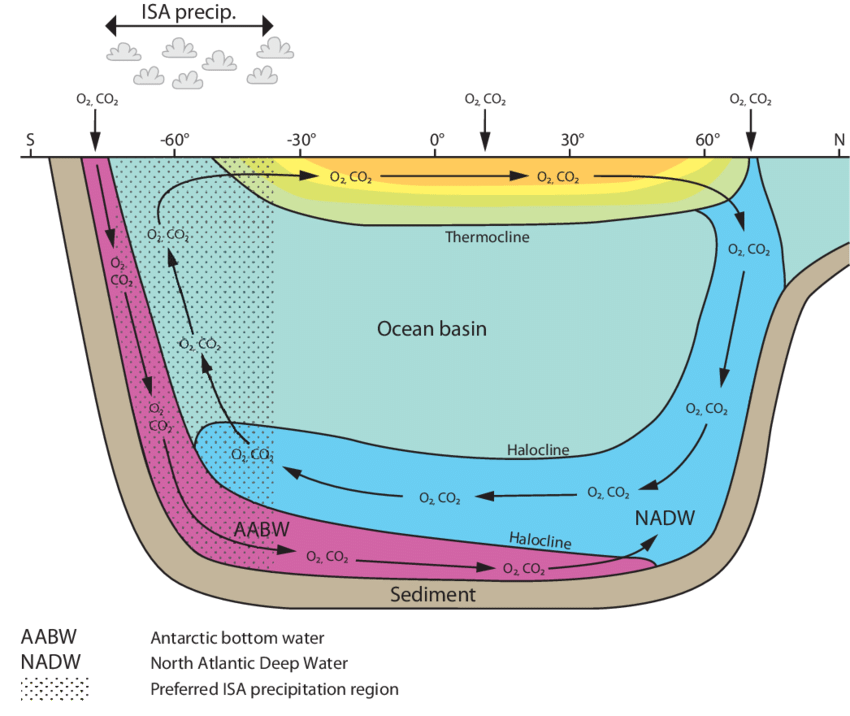
Important Water masses
- North Atlantic Deep Water
ENSO
EL NIÑO-SOUTHERN OSCILLATION
Origin
- Sir Gilbert Walker
- Weather prediction in India
- Pressure variation
- Indian ocean, west and east Pacific
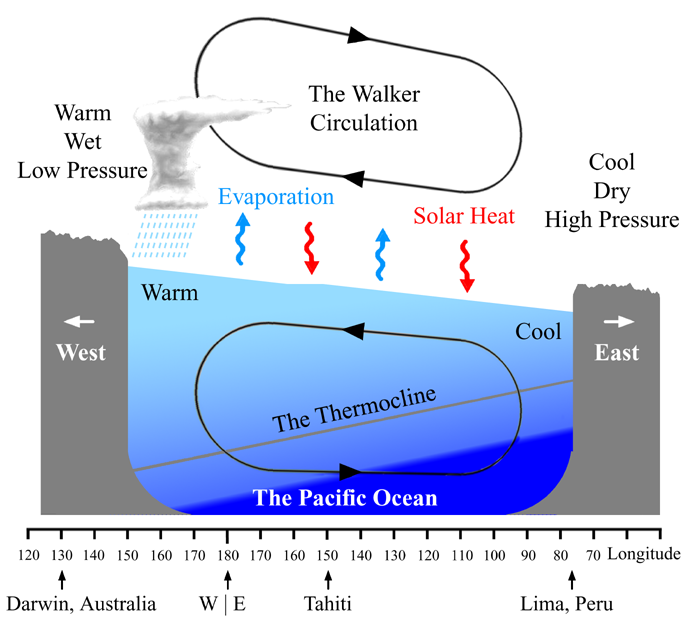
The walker circulation
- caused by differences in heat distribution
- part of Hadley cell
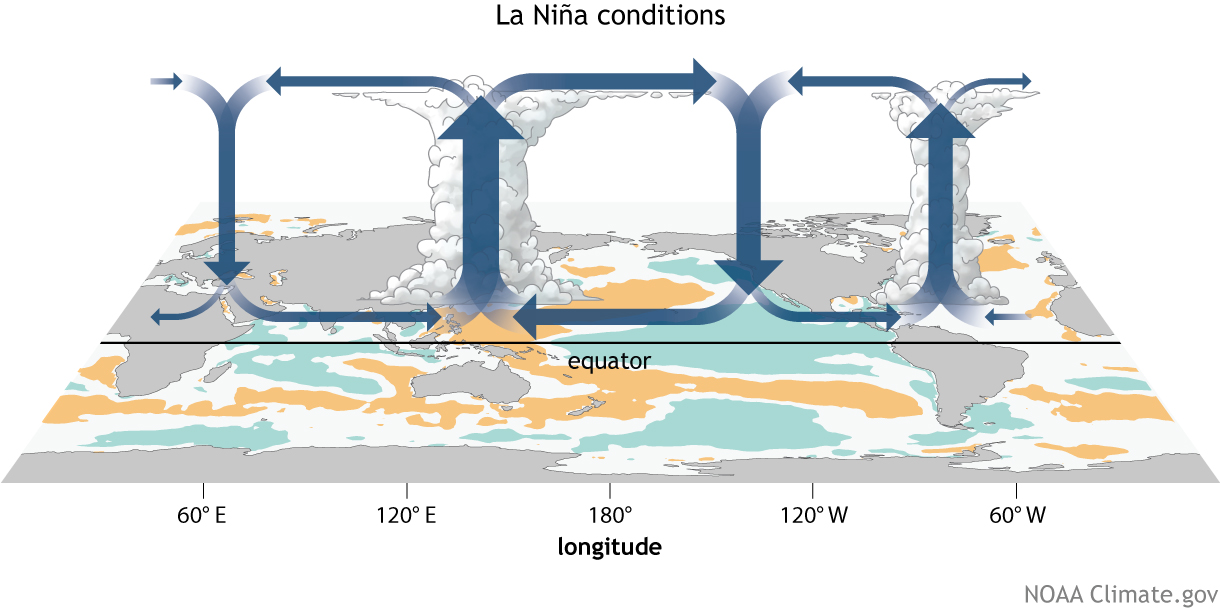
What causes it
- The energy needs to be balanced
- Winds change
- Currents change
What does it Alter
- Pressure
- Wind speed or even direction
- Precipitation
- Position of mixing layer
- Currents, especially upwelling ones
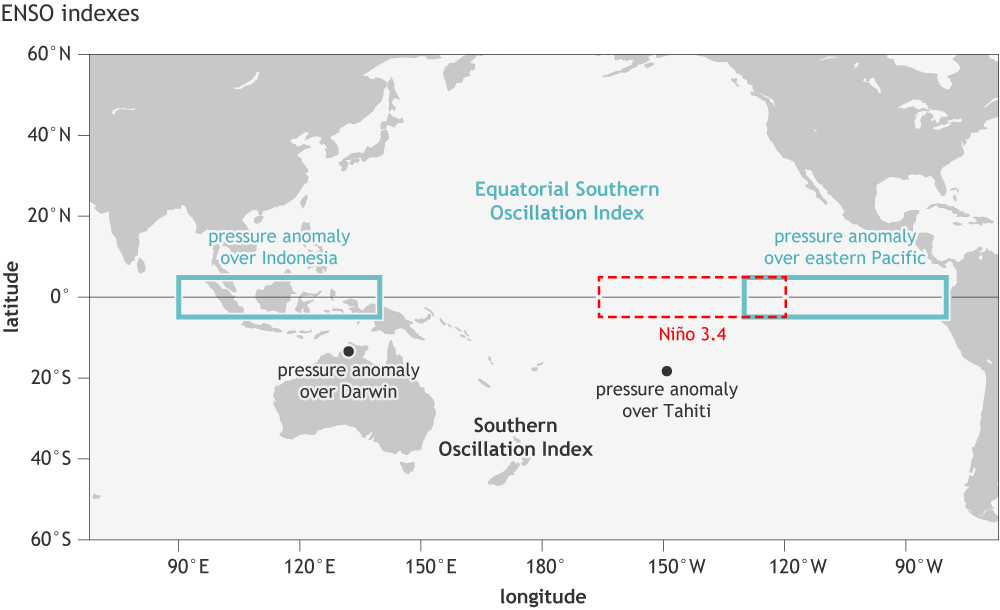
measuring
- Pressure difference
- Dahiti
- Darwin, Australia
- low = El Niño
SOI
- 3-month temperature
- Niño-3.4
- low = La Niña
- NOAA
ONI
SOI = \frac{sP_T - sP_D}{\sigma}
ONI = T_{3 m} - \overline{T}_{3 m}
measuring
- Darwin, Australia
SOI
- Niño-3.4
ONI
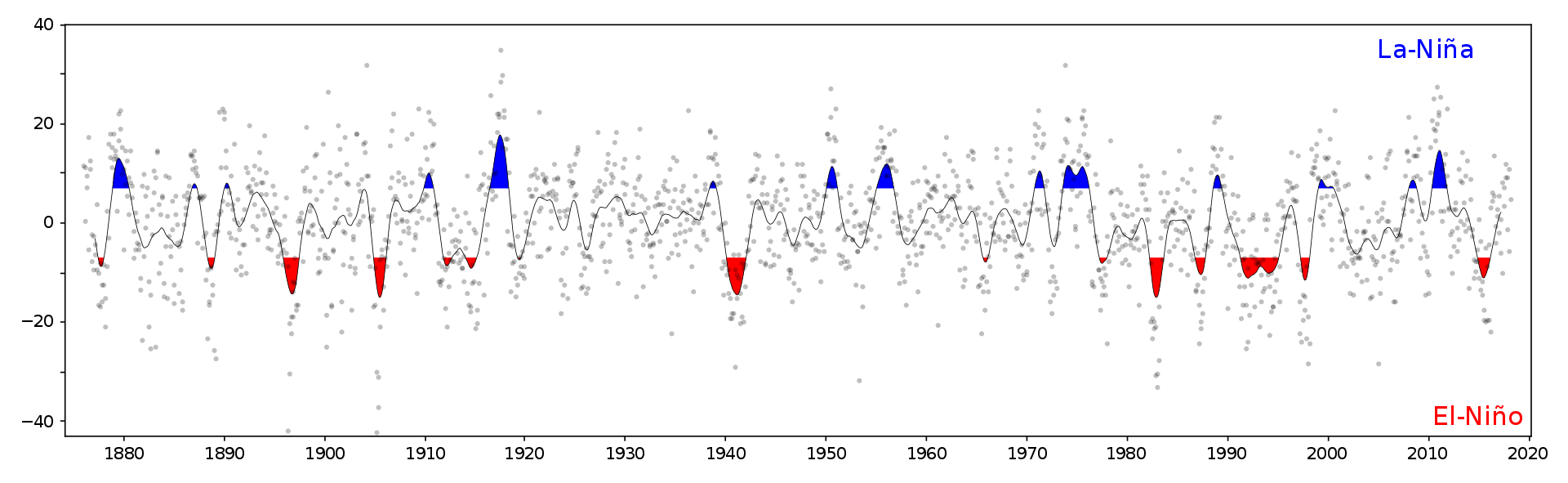
Climate Change
- Walker circulation slowed down
- Since the 19th century
- Could global warming be the reason?
- There are controversies
That's it
I don't know what I was talking, sorry for listening.