OWASP - ASVS
ASVS role in Security Testing?
Who am I?
* Application Security Researcher
* Ethical (White Hat) Hacker
* CEH certified
Twitter: @parag_dave
Disclosure
* The view expressed are my personal.
* My employer is not responsible for my talk.
* No offense to anyone
OWASP Top 10
The OWASP Top 10 is a standard awareness document for developers and web application security. It represents a broad consensus about the most critical security risks to web applications.
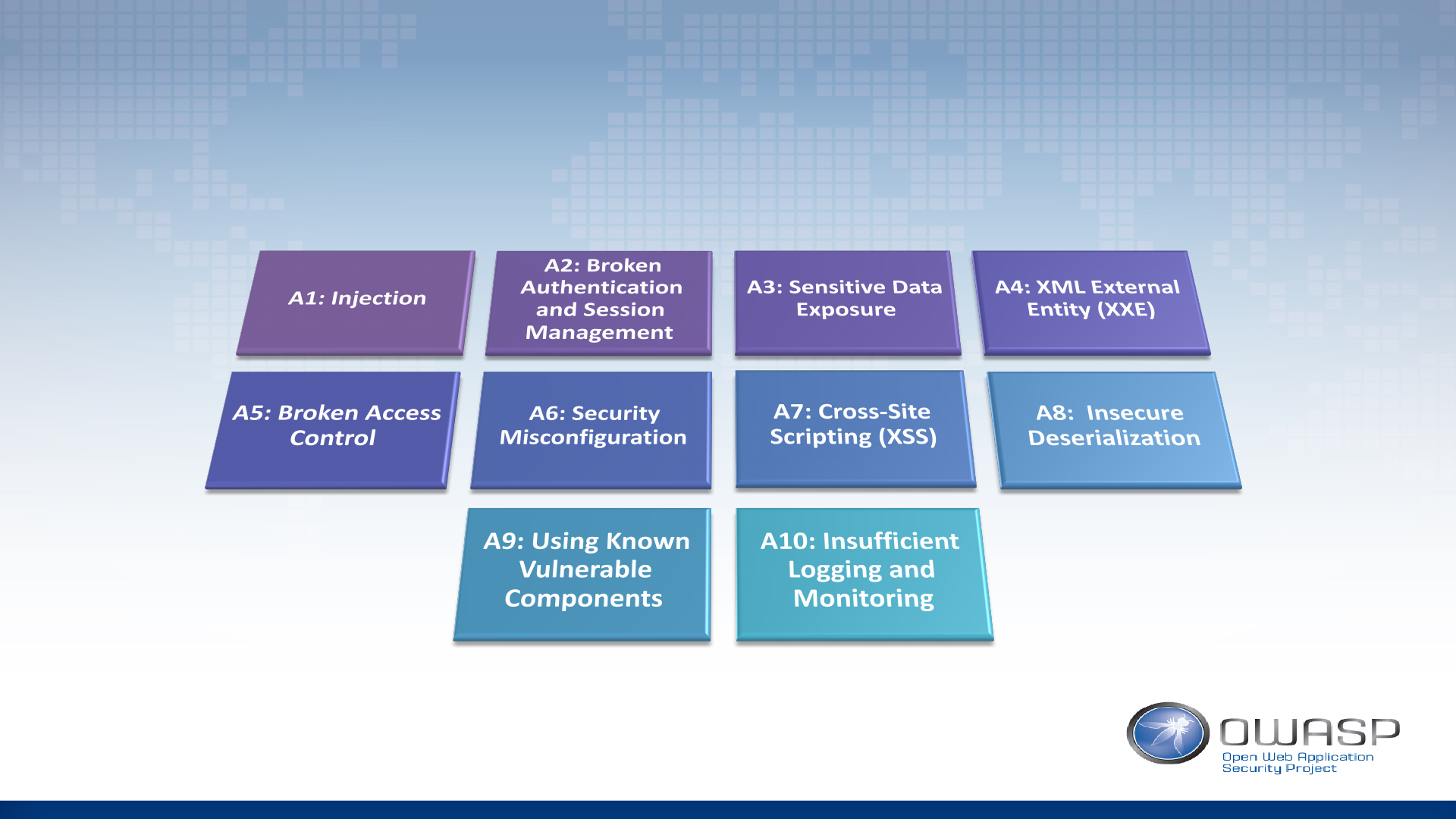
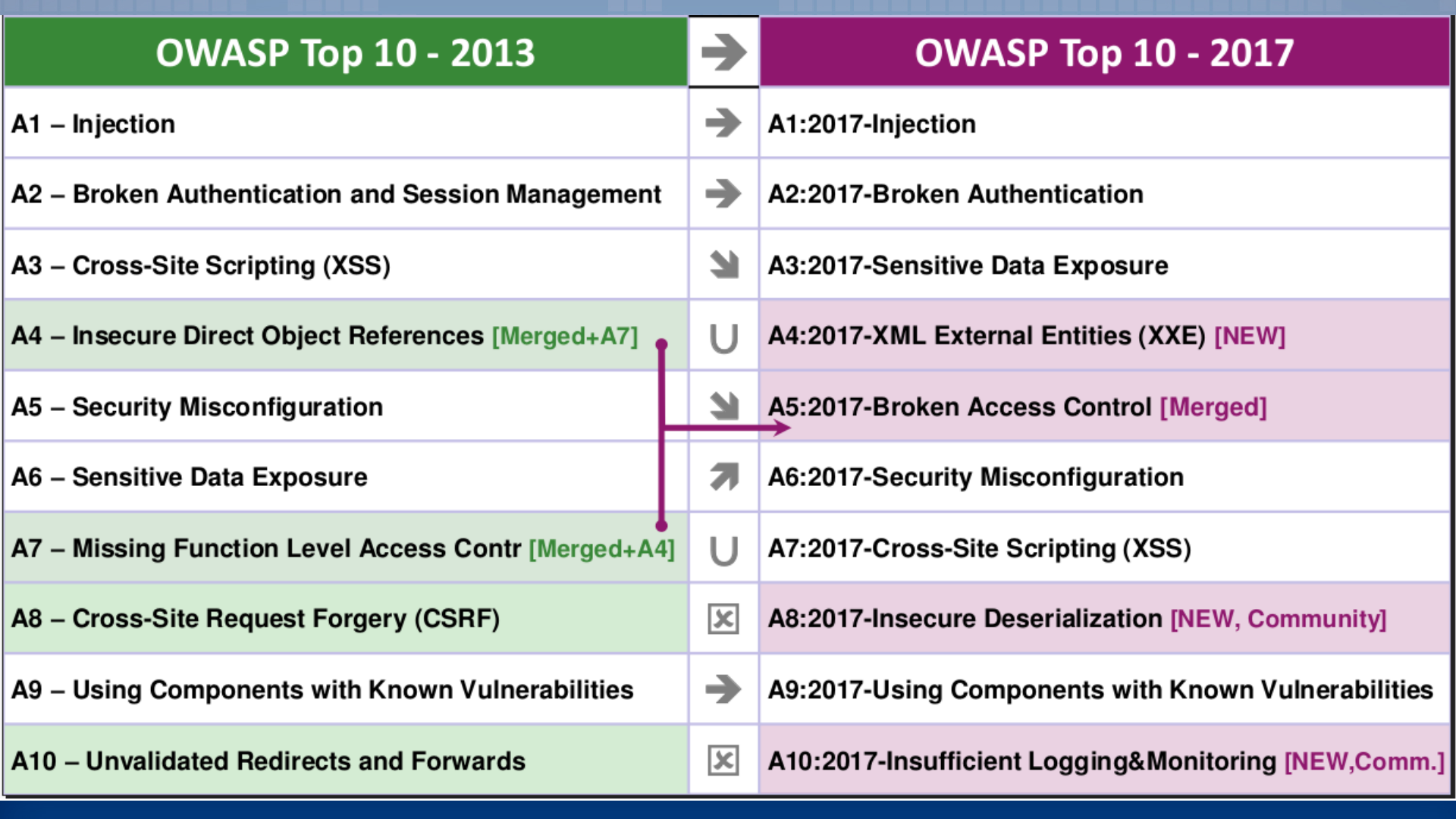
Notable Changes the OWASP Top 10
from 2013 to 2017
How to justify client about detailed testing?

Yes and even BETTER!

OWASP - ASVS
Application Security Verification Standard
The primary aim of the OWASP Application Security Verification Standard (ASVS) Project is to normalize the range in the coverage and level of rigor available in the market when it comes to performing Web application security verification using a commercially-workable open standard.
Use as a metric - Provide application developers and application owners with a yardstick with which to assess the degree of trust that can be placed in their Web applications.
Use as guidance - Provide guidance to security control developers as to what to build into security controls in order to satisfy application security requirements, and
Use during procurement - Provide a basis for specifying application security verification requirements in contracts
How to use ASVS during App testing?
The Application Security Verification Standard defines three security verification levels, with each level increasing in depth.

Level 1 It is for all apps
How to choose ASVS level for app testing?
Level 2 It is recommended for applications that contain sensitive data, which required protection. An application achieves ASVS Level 2 if it adequately defends against most of the risks associated with software today. Threats to Level 2 applications will typically be skilled and motivated attackers focusing on specific targets using tools and techniques that are highly practiced and effective at discovering and exploiting weaknesses within applications.
Level 3 It is suggested for applications that require significant levels of security verification, where failure could significantly impact the organization’s operations, and even its survivability. An application achieves this level if it is adequately defended against all advanced security vulnerabilities, and it also demonstrates principles of good security design. Vulnerabilities at this level would most likely be exploited by determined attackers.
Example requirements
Text
V10: Communications security verification requirements
V11: HTTP security configuration verification requirements
V13: Malicious controls verification requirements
V15: Business logic verification requirements
V16: Files and resources verification requirements
V17: Mobile verification requirements
V18: Web services verification requirements
V19. Configuration
V1. Architecture, design and threat modelling
V2: Authentication Verification Requirements
V3: Session Management Verification Requirements
V4: Access Control Verification Requirements
V5: Malicious input handling verification requirements
V7: Cryptography at rest verification requirements
V8: Error handling and logging verification requirements
V9: Data protection verification requirements
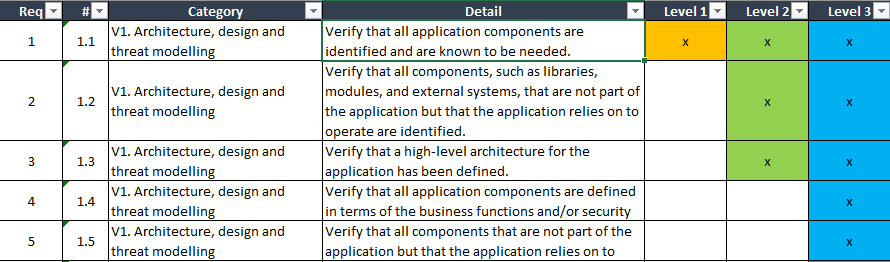
Example requirements
Every chapter has control objective, reqs and references
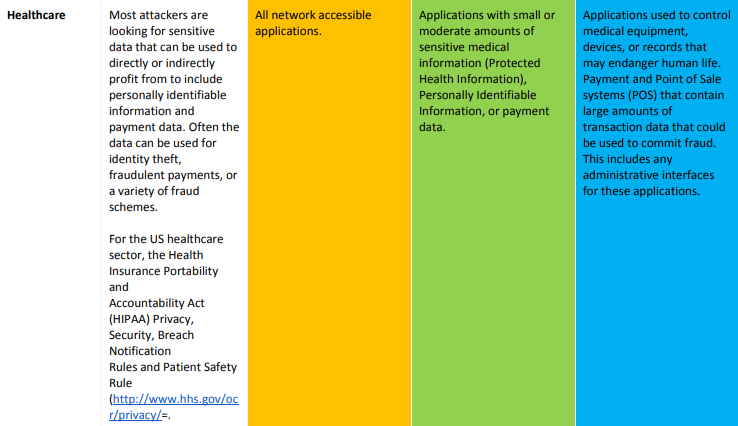
Threat Profile by Industry
Different threats have different motivations. Some industries have unique information and technology assets and domain specific regulatory compliance requirements
Benefits
- Helps to develop and maintain secure applications
- Contains clear and ready-to-use high level checklists and use cases
- Allows you as well as security services, vendors, and consumers to align requirements and offerings
Demo
The end goal is to make App secure,
So ultimately users happy.

