muppetforge
what are we talking about?
Managing Puppet modules.
the problem:
For various reasons, we use Puppet in "push" mode.
We separate the reusable declarations in modules.
How do we manage these modules?
(versioning, distribution, packaging, deps...)
what we tried:
Hg subrepos.
Parent repo with manifests for customer/environment.
Subrepos for env-independent modules.
Distribute copying on servers.
Versioning with Hg revisions.
Build a single tarball with everything inside.
Parent depends from present subrepos, at current revision.
what we hated:
It's custom stuff, non-standard and needs explaination.
Cloning a parent repo is a pain.
Merging hell.
Hand-handled dependencies.
Easy to mismatch subrepo version when editing a single module.
Mantain ad-hoc custom scripts.
what does puppet gives us?
(2.7 +)
puppet module tool:
Modules built to tarballs with standard metadata.
Semantic versioning.
Distributed via specific repo.
Automatic dependency resolution.
and the repository?

Problems?
Yes, it's public, controlled by Puppetlabs and is not distributed for private instances.
what we tried:
Replicates the Puppet Forge API.
Python + Django
what we hated:
Python (requires 2.7 -> 2.6 on RHEL...).
Deploying modules was terribad.
Customizing the authentication looked hard (LDAP).
so?
In the same week, we wanted to try some Erlang.
Erlang is a programming language used to build massively scalable soft real-time systems with requirements on high availability.
Some of its uses are in telecoms, banking, e-commerce, computer telephony and instant messaging.
Erlang's runtime system has built-in support for concurrency, distribution and fault tolerance.
(from the official page)
what we did:
Looked at django-forge and discovered it only had 3 endpoints.
Decided to implement the toy in Erlang and add to it some awesomeness.
muppetforge:
What's new?
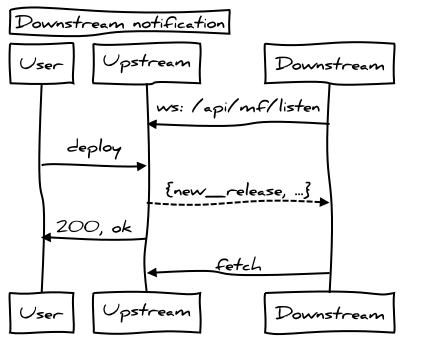
Deploy endpoint on the API.
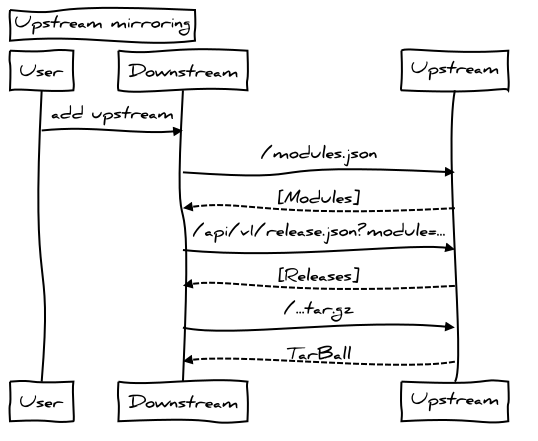
Easy mirroring of other forges (upstream/downstream).
Distributable in a self-contained tarball.
upstream mirroring
downstream notification
and on the client side?
How should I use modules?
muppetforge/integration
Like java libraries (Modulefile instead of pom.xml)
modulefile
name 'fmeden/sample'
version '1.1.0'
source '?'
author 'fmeden'
license 'BSD3'
summary 'A sample module'
description 'A sample module'
project_page 'http://example.com'
dependency 'another/module', '>= 1.2.0'puppet module install
fmeden@Eve:~/projects/fmeden-sample$ puppet module install muppetforge/integration
Notice: Preparing to install into /home/fmeden/.puppet/modules ...
Notice: Downloading from http://localhost:8080/mf ...
Notice: Installing -- do not interrupt ...
/home/fmeden/.puppet/modules
└── muppetforge-integration (v0.0.1)
puppet module build
fmeden@Eve:~/projects/fmeden-sample$ puppet module build
Notice: Building /home/fmeden/projects/fmeden-sample for release
Module built: /home/fmeden/projects/fmeden-sample/pkg/fmeden-sample-1.1.0.tar.gzpuppet module deploy
fmeden@Eve:~/projects/fmeden-sample$ puppet module deploy pkg/fmeden-sample-1.1.0.tar.gz
Notice: Preparing to deploy pkg/fmeden-sample-1.1.0.tar.gz into http://localhost:8080/mf ...
Module succesfully deployed.
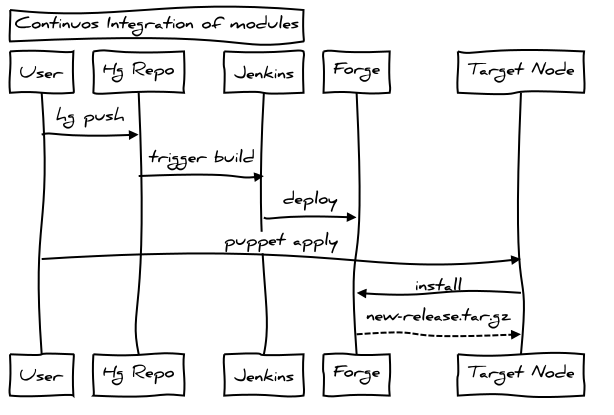
and when applying?
Have to puppet module install by hand on every node?
muppetforge/integration
require_module("fmeden", "sample", ">= 1.0.0")
import dev.pp
import [...]Just use it on top of site.pp
enable ci
what we learned (erlang):
Small, coherent language.
Stdlib/OTP contains stuff that really matters.
Abstraction to swap between sync/async easily.
Contracts via pattern matching.
Let It Fail.
what we learned (puppet):
The tool has much more to offer, we need to dig deeper!
Extendible: Facts, Functions, Faces (and more...).
Public documentation sucks, but the rdoc on the sources is good.
Codebase has coherent abstractions.
A Ruby debugger is still a life-saver (caches, DSLs).
puppet help
Available subcommands:
agent The puppet agent daemon
apply Apply Puppet manifests locally
ca Local Puppet Certificate Authority management.
catalog Compile, save, view, and convert catalogs.
cert Manage certificates and requests
certificate Provide access to the CA for certificate management.
certificate_request Manage certificate requests.
certificate_revocation_list Manage the list of revoked certificates.
config Interact with Puppet's configuration options.
describe Display help about resource types
device Manage remote network devices
doc Generate Puppet documentation and references
facts Retrieve and store facts.
file Retrieve and store files in a filebucket
filebucket Store and retrieve files in a filebucket
help Display Puppet help.
inspect Send an inspection report
instrumentation_data Manage instrumentation listener accumulated data.
instrumentation_listener Manage instrumentation listeners.
instrumentation_probe Manage instrumentation probes.
key Create, save, and remove certificate keys.
kick Remotely control puppet agent
man Display Puppet manual pages.
master The puppet master daemon
module Creates, installs and searches for modules on the Puppet Forge.
node View and manage node definitions.
parser Interact directly with the parser.
plugin Interact with the Puppet plugin system.
queue Queuing daemon for asynchronous storeconfigs
report Create, display, and submit reports.
resource The resource abstraction layer shell
resource_type View classes, defined resource types, and nodes from all manifests.
secret_agent Mimics puppet agent.
status View puppet server status.
