

Carlos P. Jimeno
jimenocontact@gmail.com
Jimeno0

Carlos P. Jimeno


@Jimeno0

Module 1.
Intro to backend technologies: Nodejs
@Jimeno0

What is node.js
Node.js (sometimes called just Node for short) is a JavaScript runtime developed by Ryan Dahl. Dahl created Node because of the synchronous limitations of current web frameworks.
@Jimeno0

Node is not
- It is not a framework (there are frameworks built on top of Node.js though).
- It is not a programming language (the language is still JavaScript).
@Jimeno0

- Intro & JS basics
- Objects & Arrays
- Functions
- Callbacks, Promises & async
- Node packages manager
- Testing & linting
- Express
- Restify
Topics
@Jimeno0

const, let & var
Variables
@Jimeno0

Variables
// variable declaration
let name
let name, surmane, email
// variable asignament
let name
name = 'Karl'
// or inline
let name = 'Karl'
@Jimeno0

Variables
// variable declaration
const name // throws an error
// variable declaration with asignament
const name = 'Karl'
@Jimeno0

primitives & objects
Data types
@Jimeno0

primitives
Data types
- number
- string
- boolean
- null
- undefined
@Jimeno0

Data types
- Objects
- Arrays
- Functions
Non primitives
@Jimeno0

Objects
- Key-value relationship
- Add, remove and modify keys and values in an object
- Can access values in an Object with dot and bracket notations
- List the properties of an Object
@Jimeno0

Objects
// create an object
const user = {
name: 'admin',
pasword: '12345'
}@Jimeno0

Objects
const user = {
name: 'Charlie',
pasword: '12345'
}
//add attrs
user.isAdmin = true
// modify an attr
user.name = 'Homer'@Jimeno0

Objects
const user = {
name: 'Charlie',
pasword: '12345'
}
user.isAdmin = true
// delete an attr
delete user.isAdmin@Jimeno0

Objects
const user = {
name: 'Charlie',
pasword: '12345'
}
user.isAdmin = true
delete user.isAdmin
// attrs can be acces via [ ]
console.log(user['name'])@Jimeno0

Objects
const user = {
name: 'Charlie',
pasword: '12345'
}
user.isAdmin = true
delete user.isAdmin
console.log(user['name'])
Object.keys(user)@Jimeno0

Arrays
- Basic & object lists
- Understand advanced array methods
- filter
- reduce
- map
- clone an array
@Jimeno0

Arrays
const myArray = [
'Charlie',
'Bob',
'Petter'
]
const myArrayOfUsers = [
{name: 'Charlie', age: 28},
{name: 'Bob', age: 30},
{name: 'Petter', age: 25}
]@Jimeno0

Arrays
// MAP
const array = [1, 2, 3]
// map each element to the value*2
const newArray = array.map(number => number * 2)
console.log(newArray) // <== [ 2, 4, 6 ]
.map()
@Jimeno0

Arrays
// basic sintax
array.reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue, initialValue)
const numbers = [12, 9, 1, 8]
const total = numbers.reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => {
console.log("accumulator is: ", accumulator, "and current value is: ", currentValue)
return accumulator + currentValue;
}, 0)
.reduce()
@Jimeno0

Arrays
.filter()
// FILTER
var people = [
{ name: "Candice", age: 25 },
{ name: "Tammy", age: 30 },
{ name: "Allen", age: 20 },
{ name: "Nettie", age: 21 },
{ name: "Stuart", age: 17 },
{ name: "Bill", age: 19 }
]
//get the list of pepole older than 21
const ofDrinkingAge = people.filter(person => person.age >= 21)
@Jimeno0

Arrays
arrays practice

@Jimeno0

Functions
@Jimeno0

Functions
Declaration, invocations and returning values
// Function Declaration
function sayHelloWorld() {
const whatToSay = 'Hello, World!';
console.log(whatToSay);
}
// Function Invocation
sayHelloWorld(); // => Hello, World!
function sayHello(name) {
console.log(`Hello ${name}!`);
}
// returning values
function printName(name){
return name;
}
// return
printName("Ana");
@Jimeno0

Functions
anonymous
// anonymous function
setTimeout(function(){
console.log("This is just an example of anonymous")
}, 1000);
// naming it...
function someFunctionName(){
console.log("This is just an example of not anonymous")
}
setTimeout(someFunctionName, 1000);
@Jimeno0

Functions
Arrow functions
let greeting = function(name) {
console.log(`Hello, ${name}`);
}
// arrow function:
let greeting = name => {
return name;
}
@Jimeno0

Functions
Global vs local scope
// local scope
function sayHello() {
let firstName = "Ana"; // <== local variable
console.log(`Hello ${firstName}!`);
}
sayHello(); // <== Hello Ana!
console.log(firstName); // <== ReferenceError: firstName is not defined
// global scope
const firstName = "Ana"; // <== global variable
function sayHello() {
console.log(`Hello ${firstName}!`);
}
sayHello(); // <== Hello Ana!
console.log(firstName); // <== Ana
@Jimeno0

Functions
Global vs local scope
let firstName = "Ana"; // <== global variable
function sayHello() {
let firstName = "Martina"; // <== local variable with the same name as the global one
console.log(`Hello ${firstName}!`);
}
console.log(`Before the function executes the first name is ${firstName}.`); // <=
sayHello(); // <=
console.log(`After the function executes the first name is ${firstName}.`); // <=
@Jimeno0

Functions
Global vs local scope
let firstName = "Ana"; // <== global variable
function sayHello() {
let firstName = "Martina"; // <== local variable with the same name as the global one
console.log(`Hello ${firstName}!`);
}
console.log(`Before the function executes the first name is ${firstName}.`); // <= Ana
sayHello(); // <= Martina
console.log(`After the function executes the first name is ${firstName}.`); // <= Ana
@Jimeno0

Greatest movies exercise

@Jimeno0

Asyncronous
in JS
"JavaScript is not asynchronous language, but synchronous one with some asynchronous behaviors"
@Jimeno0

Why async
single-threaded
only one block of code is executed at the time
@Jimeno0

Why async
synchronous - the code gets executed line by line, from top to bottom, in the order in which they are put in
@Jimeno0

Why async
🤔
@Jimeno0

Why async
// hypothetical example
function readFile (file) {
// read the file
// veeeeeeeeeeeeeery large file
return contentFile.length;
}
const textSize = readFile("odyssey.txt");
console.log(textSize); // => undefined@Jimeno0

Callbacks
Promises
Async & await
How async
@Jimeno0

Callbacks
function someCallbackFunction(){
console.log("Hey there, crew!!");
}
const timeoutId = setTimeout(someCallbackFunction, 1000);@Jimeno0

Promises
const myPromise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
if (/* condition */) {
resolve(/* value */); // fulfilled successfully
}
else {
reject(/* reason */); // error, rejected
}
});
myPromise.then((val) => console.log(val));@Jimeno0

Promises
const p1 = Promise.resolve(3);
const p2 = 1337;
const p3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(resolve, 100, 'foo');
});
Promise.all([p1, p2, p3]).then(values => {
console.log(values); // [3, 1337, "foo"]
});.all()
@Jimeno0

Async await
async function f() {
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve("done!"), 1000)
});
let result = await promise; // wait till the promise resolves (*)
console.log(result); // "done!"
}
f();@Jimeno0

Async practice

@Jimeno0

Data types
@Jimeno0

primitives
Data types
- number
- string
- boolean
- null
- undefined
@Jimeno0

Data types
- Objects
- Arrays
- Functions
Non primitives
@Jimeno0

Objects & functions
Data types
// Obects
let myCar = {
make: 'Honda',
model: 'Accord',
year: 1998
}
// arrays
let cars = [
'honda',
'ford',
'fiat'
]
// functions
funtion getCar(){
return 'Honda'
}@Jimeno0

Data types
Objects & functions
- value vs reference
- clone (spread)
- compare (JSON.stringify)
@Jimeno0

Data types
let book1 = 'Harry Potter'
let book2 = book1
book1 = 'The power of now'
console.log(book1); // <== The power of now
console.log(book2); // <== Harry Potter
@Jimeno0

Data types
const book1 = {
author: "Charlotte Bronte"
}
const book2 = book1; // <== copy the book1 into the new object - book2
console.log(book1); // <== { author: 'Charlotte Bronte' }
console.log(book2); // <== { author: 'Charlotte Bronte' }
// CHANGE THE VALUE OF AUTHOR PROPERTY IN BOOK1:
book1.author = "Jane Austen";
// BOTH ARE CHANGED
console.log(book1); // <== { author: 'Jane Austen' }
console.log(book2); // <== { author: 'Jane Austen' }
// CHANGE THE VALUE OF AUTHOR PROPERTY IN BOOK2:
book2.author = "Edith Wharton";
// BOTH ARE CHANGED
console.log(book1); // <== { author: 'Edith Wharton' }
console.log(book2); // <== { author: 'Edith Wharton' }
@Jimeno0

Data types
// object:
const book1 = {
author: "Charlotte Bronte"
}
const book2 = book1; // <== copy the book1 into the new object - book2
console.log(book1 === book2); // <== true
// array:
const students = ['Ana', 'John', 'Fabio'];
const attending = students;
console.log(students === attending); // <== true
Compare by reference
@Jimeno0

Data types
Copy in objects & arrays
const book1 = {
author: "Charlotte Bronte"
}
const book2 = Object.assign({}, book1);
console.log(book2); // <== { author: "Charlotte Bronte" }
console.log(book1 === book2); // <== false
const students = ['Ana', 'John', 'Fabio'];
const attending = [...students];
students.push("Sandra");
console.log(students); // <== [ 'Ana', 'John', 'Fabio', 'Sandra' ]
console.log(attending); // <== [ 'Ana', 'John', 'Fabio' ]
@Jimeno0

Node packages manager
npm
@Jimeno0

npm is a package manager for Node
share your JavaScript code easily, using a command line tool.
Get track of the package versions
@Jimeno0

npm --version
$ mkdir myNpm
$ cd myNpm
$ npm init
Create our fist project
@Jimeno0

Lets try it!

@Jimeno0

Our first package
reload automatically
@Jimeno0

Our first package
1. Add nodemon
2. Add start script
@Jimeno0

linting
@Jimeno0

linting engines
@Jimeno0

$ sudo npm i --global eslint
$ eslint --init
Add code extension

@Jimeno0

Practice: create our fist linted project

@Jimeno0

testing

@Jimeno0


Our first testing enviroment
$ npm i jasmine --save-dev
$ sudo npm i --global jasmine
$ node node_modules/jasmine/bin/jasmine init
Initialize global
Initialize local
$ jasmine init
@Jimeno0


Playing around with examples
$ jasmine examples
Config file
/spec/support/jasmine.json
@Jimeno0


Config file
{
// Spec directory path relative to the current working dir when jasmine is executed.
"spec_dir": "spec",
// Array of filepaths (and globs) relative to spec_dir to include and exclude
"spec_files": [
"**/*[sS]pec.js",
"!**/*nospec.js"
],
// Array of filepaths (and globs) relative to spec_dir to include before jasmine specs
"helpers": [
"helpers/**/*.js"
],
// Stop execution of a spec after the first expectation failure in it
"stopSpecOnExpectationFailure": false,
// Run specs in semi-random order
"random": false
}@Jimeno0

JS koans
The Koans are a series of assertions you must solve to understand how a programming language works
- You get an assertion that is not passing a test.
- You need to change/add code to make the test pass.
@Jimeno0

http
@Jimeno0

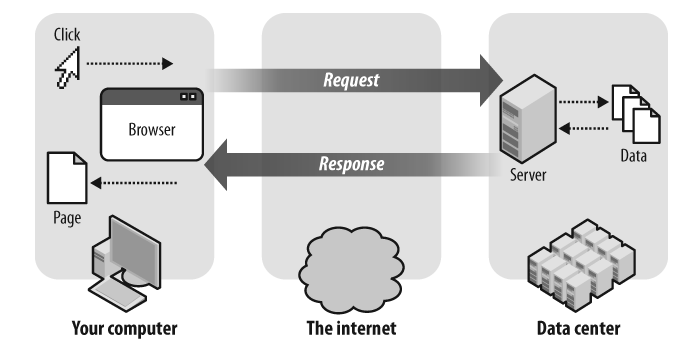
The request-response cycle
@Jimeno0

Always check the console
@Jimeno0

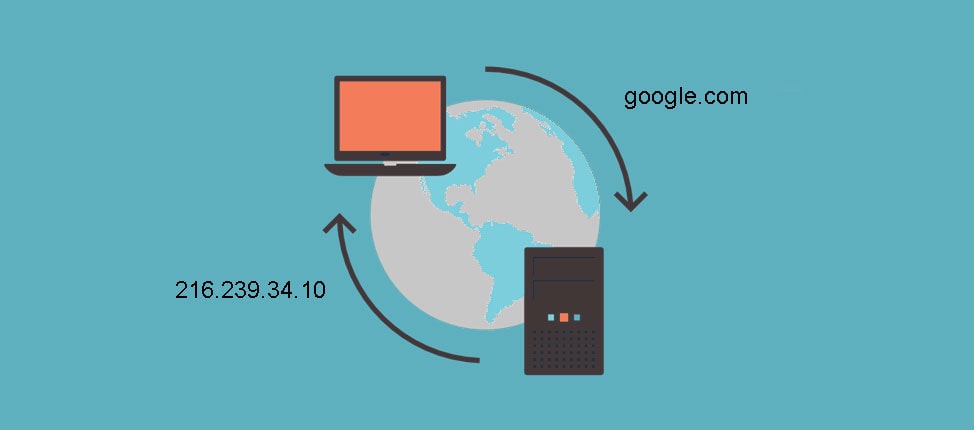
DNS
@Jimeno0

HTTP
HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol.
Network protocol used to deliver all files and data on the World Wide Web
A protocol is simply a set of rules for communication, here between client and server
Clients use the rules of HTTP to send its requests to servers and servers respond using those rules as well
@Jimeno0

HTTP verbs
GET / POST / DELETE ...
@Jimeno0

Backend in JS

@Jimeno0

Express hello world
$ mkdir express-hello-world
$ cd express-hello-world
$ npm init
$ npm install express --save
$ touch app.js
@Jimeno0

Express hello world
edit our app.js
const express = require('express');
// We create our own server named app
// Express server handling requests and responses
const app = express();@Jimeno0

Express hello world
setup a route
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
// our first Route
app.get('/', (request, response, next) => {
console.log(request)
response.send('<h1>Welcome fellas</h1>')
})@Jimeno0

Express hello world
start the server
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
// our first Route
app.get('/', (request, response, next) => {
console.log(request);
response.send('<h1>Welcome fellas</h1>');
});
// Server Started
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('My first app listening on port 3000!')
});@Jimeno0

Express hello world
$ node app.js
👉 visit localhost:3000
@Jimeno0

Express hello world
Add nodemon
create our "start" script in out package.json
"start: : "nodemon app.js"
@Jimeno0

Serving statics
Create a images folders and serve it
@Jimeno0

Serving statics
$ mkdir public
$ mkdir public/images
$ curl -o public/images/cool-cat.jpg https://wallpapercave.com/wp/X7VjxFk.jpg
@Jimeno0

Serving statics
// ...
const app = express();
// Make everything inside of public/ available
app.use(express.static('public'));
// our first Route:
app.get('/', (request, response, next) => {
// ...@Jimeno0

Practice
Create a project with at least 3 pages
&
serve 4 pictures
@Jimeno0

Express
Get methods
Route Params & Query string
@Jimeno0

Express
Route params
app.get('/users/:username', (req, res, next) => {
res.send(req.params);
})Navigate to http://localhost:3000/users/devAcademy
{"username" : "devAcademy"}
@Jimeno0

Express
Query string
app.get('/search', (req, res, next) => {
res.send(req.query)
})http://localhost:3000/search?city=Barcelona
{"city" : "Barcelona"}
http://localhost:3000/search?city=Barcelona&month=may
....
@Jimeno0

Express
Post method
app.post('/login', (req, res) => {
res.send('You\'ve logged in!');
});@Jimeno0

Express
Access to body data needs a parser
// ...
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
// ...
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }));$ npm i --save body-parser
@Jimeno0

Express
The body parser
// ...
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
// ...
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }));$ npm i --save body-parser
Then we can access the request body
@Jimeno0

Express
The body parser
app.post('/login', (req, res) => {
res.send(req.body);
});app.post('/login', (req, res) => {
let email = req.body.email;
let password = req.body.password;
res.send(`Email: ${email}, Password: ${password}`);
});@Jimeno0

Postman
APIs development tool
@Jimeno0

Practice
app.post('/login', (req, res) => {
// get aun user & password
const users = [
{
username: 'admin',
password: 'admin'
},
{
username: 'admin2',
password: 'admin2'
}
]
if (/* fill in this condition to be in users*/){
// send an okay message
} else {
// send an invalid user or pass message
}
})@Jimeno0

Express middlewares
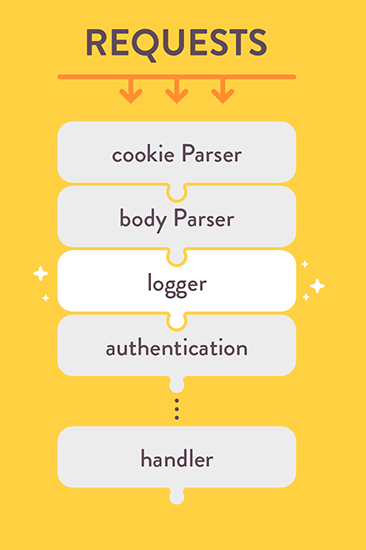
@Jimeno0

Express middlewares
// ...
app.use(myFakeMiddleware)
// ...
function myFakeMiddleware(){
console.log("myFakeMiddleware was called!")
}@Jimeno0

Express middlewares
function myFakeMiddleware(_, _, next){
console.log("myFakeMiddleware was called!");
next();
}@Jimeno0

Express middlewares
function myFakeMiddleware(_, _, next){
console.log("myFakeMiddleware was called!");
next();
}@Jimeno0

Express middlewares
function myFakeMiddleware(req, _, next){
console.log("myFakeMiddleware was called!")
req.secretValue = "swordfish"
next()
}
app.get('/test', (req, res) => {
let mySecret = req.secretValue
res.send(mySecret)
})@Jimeno0

Middleware Practice
Taking the login exercise
log something if the username is admin
@Jimeno0

Express API practice
moviesAPI
Bonus: create an endpoint that takes email, subject and message and send an email to it
@Jimeno0

Nodemailer
let transporter = nodemailer.createTransport({
service: 'Gmail',
auth: {
user: 'your email address',
pass: 'your email password'
}
});
transporter.sendMail({
from: '"My Awesome Project 👻" <myawesome@project.com>',
to: email,
subject: subject,
text: message,
//you can add any custom template
//html: `<b>${message}</b>`
})
@Jimeno0

Nodemailer
If not working with gmail try:
https://www.google.com/settings/security/lesssecureapps
Set the Access for less secure apps setting to Enable
tip:
@Jimeno0

The restify project

@Jimeno0


const restify = require('restify')
const server = restify.createServer()
const port = 3000
server.get('/hello/:name', (req, res, next) => {
res.send('hello ' + req.params.name)
next()
})
server.listen(port, function () {
console.log(`App listening at: ${port}`)
})
Hello world
@Jimeno0


server.use([
function(req, res, next) {
if (someCondition) {
res.send('done!');
return next(false);
}
return next();
},
function(req, res, next) {
// if someCondition is true, this handler is never executed
}
])middleware examples
@Jimeno0

Restify practice
moviesAPI
@Jimeno0



