0 to Production!
Workshop
Requirements
- github account
- heroku account
- JS basic knowledge
- computer with node.js (>=10)
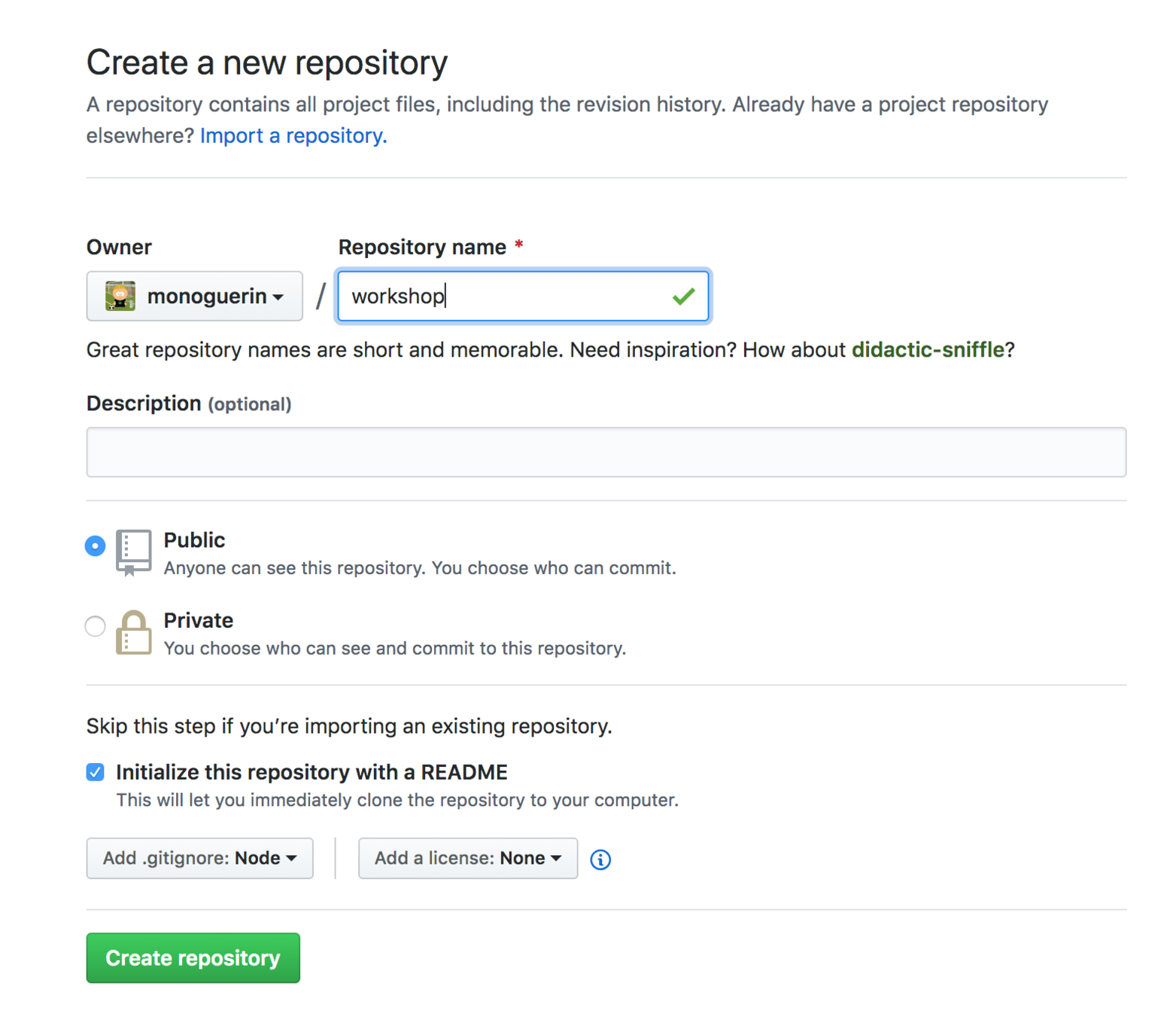
Let's create the repo
- Go to github.com
- Click the New button
- Fill the information needed
- Initialize with a README file
- Add .gitignore node
Create a new github repo
Now clone the repo
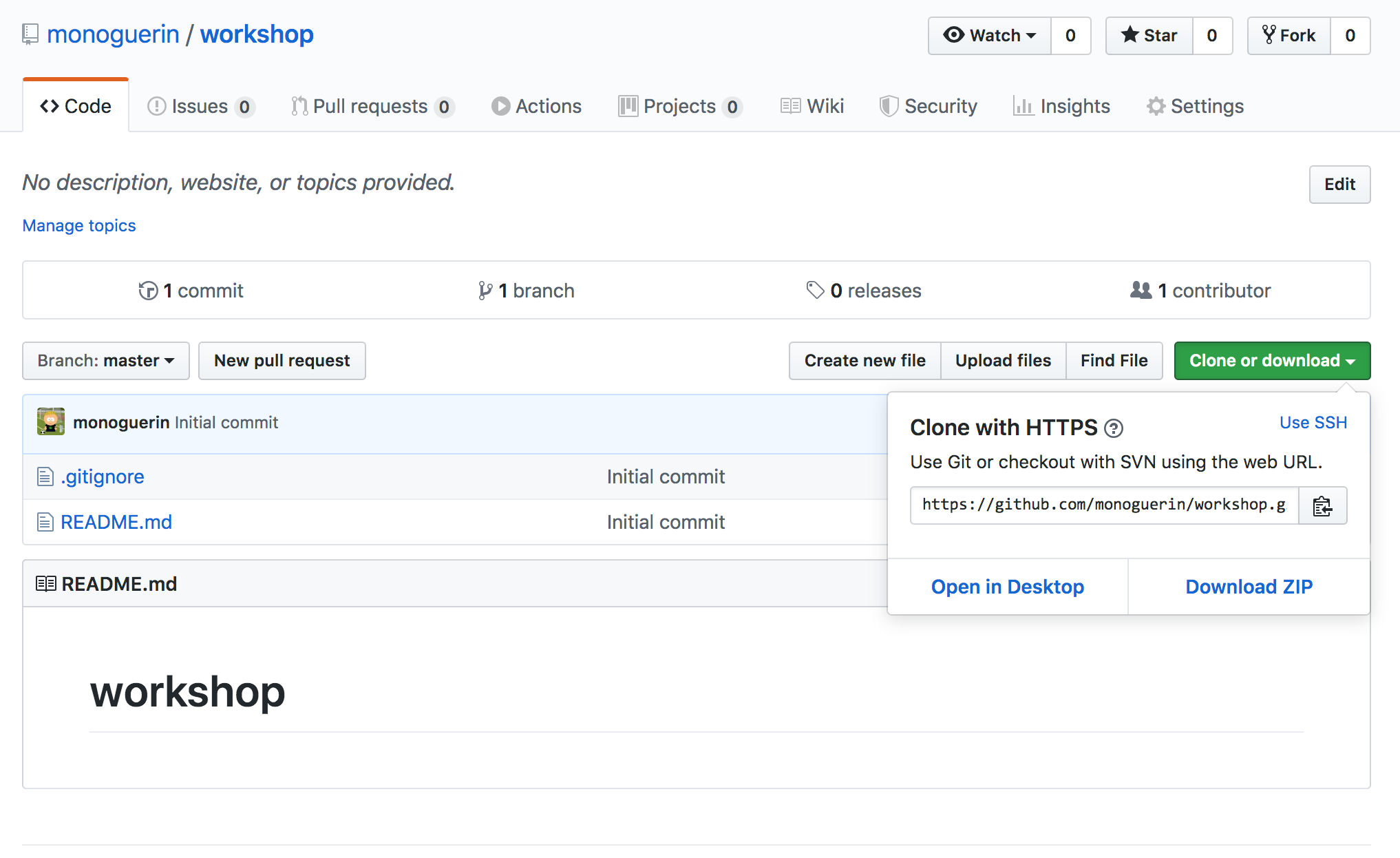
git clone https://github.com/monoguerin/workshop.git
cd workshopInit Node
npm initThis will create a package.json file where the project information is stored including dependencies and running scripts
Install Next.js
npm install --save next react react-dom
Modify the scripts in the package.json
{
"scripts": {
"dev": "next",
"build": "next build",
"start": "next start"
}
}Create your first page
Create a folder called "pages" and a new file called "index.js" with the next content
import React from 'react';
function Home() {
return <div>Welcome to Next.js!</div>;
}
export default Home;Test it by running the next command
npm run devTry building and running locally too as a production build
npm run build
npm startLet's configure eslint
npm install --save-dev eslint
// Config is broken so we need this
npm install inquirer@6.3
npx eslint --init"rules": {
"react/jsx-filename-extension": [
1,
{
"extensions": [".js", ".jsx"]
}
]
}Add this rule to enable JSX in JS files
Ex. Create 2 more pages one "posts" and another called "account"
Push to master
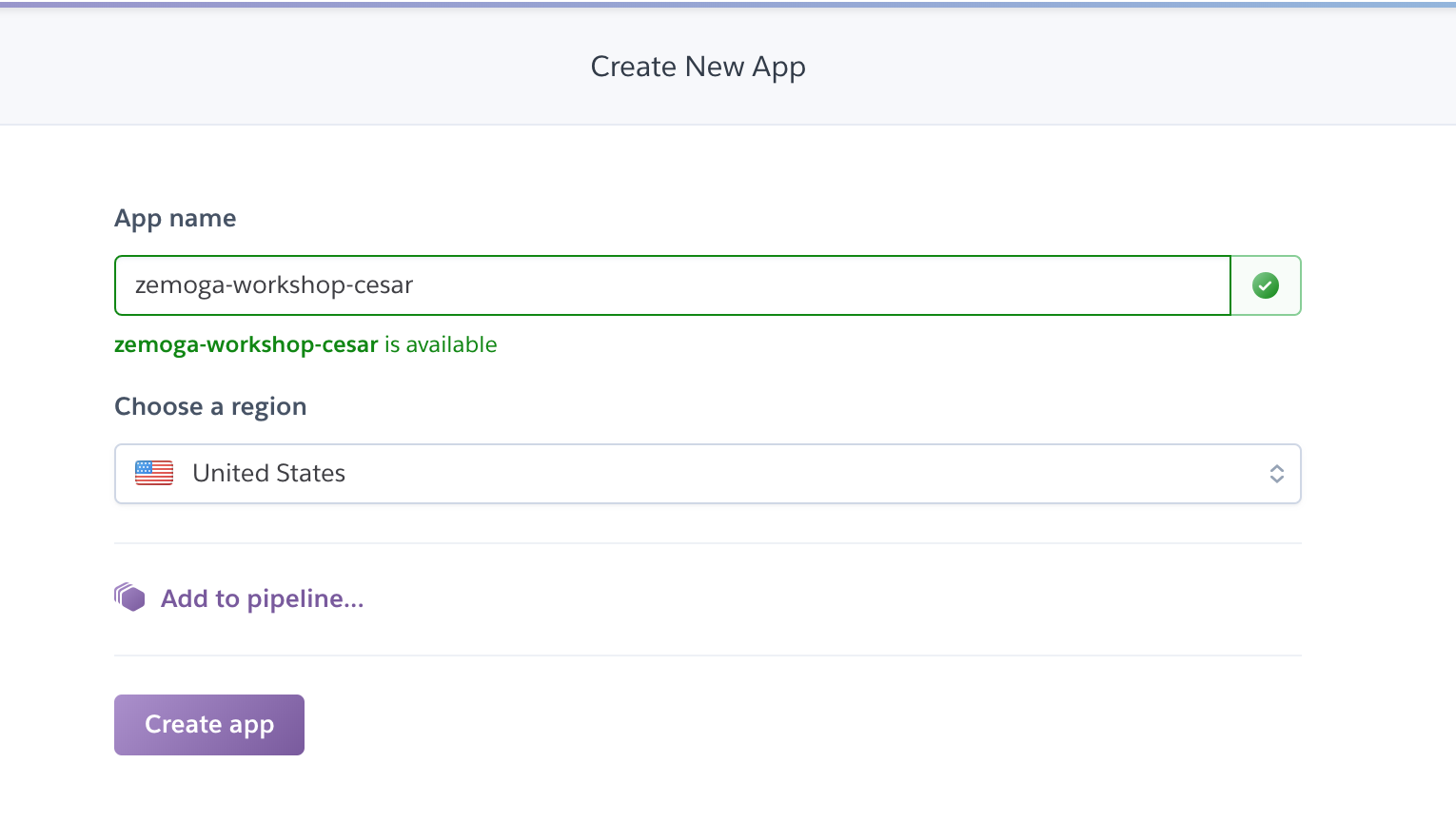
Go to Heroku and create a new app
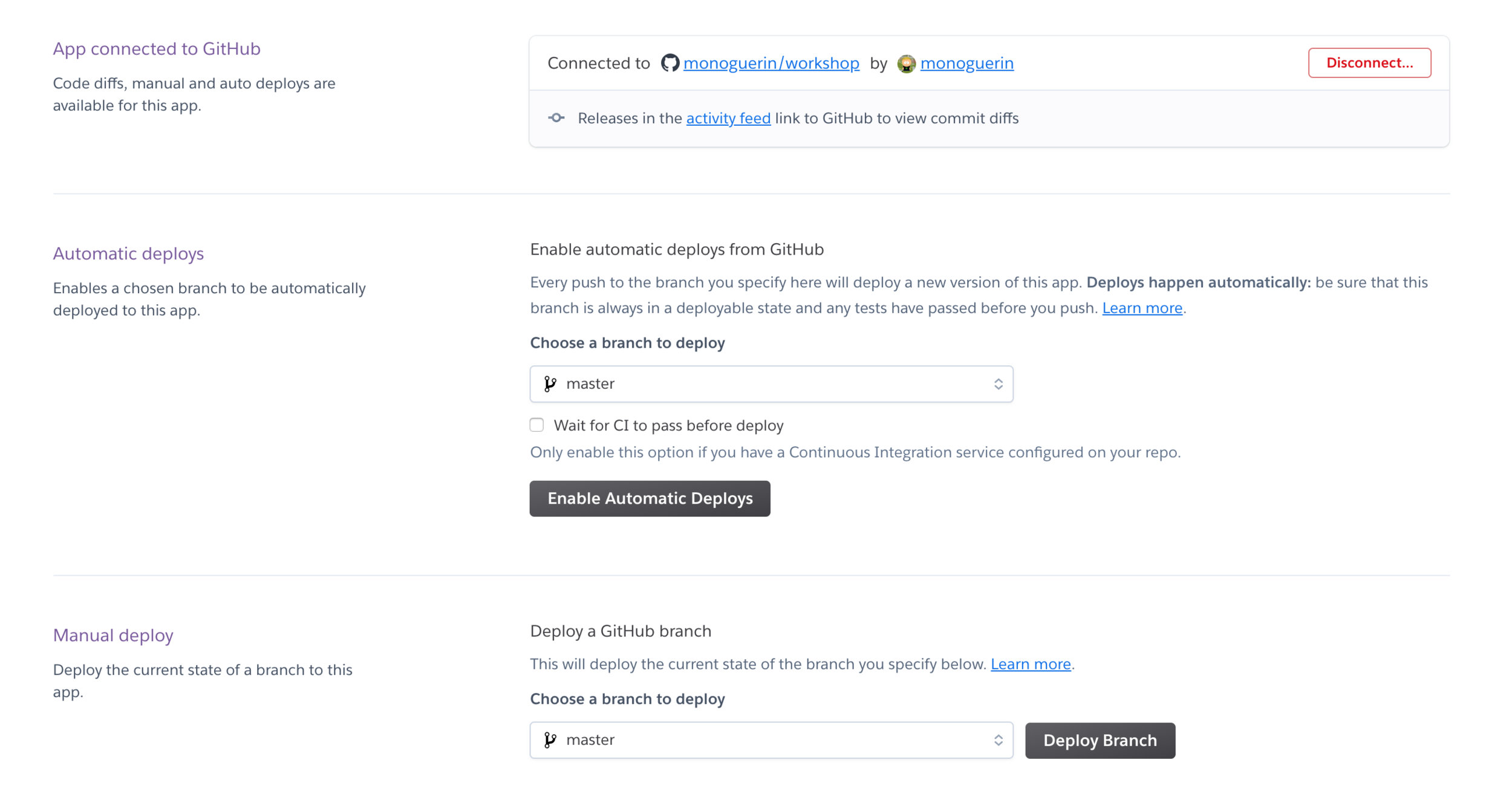
Adjust scripts to be run in Heroku
"scripts": {
"dev": "next",
"build": "next build",
"heroku-postbuild": "npm run build",
"start": "next start -p $PORT"
},Push again 🔥
Install Material Library
Modify _document.js
Add a couple components to the page
Push to master
Push again 🔥🔥
Let's create our custom express server
npm install --save expressCreate a folder called "server" and an "index.js" file inside it
const express = require('express');
const next = require('next');
const dev = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production';
const app = next({ dev });
const handle = app.getRequestHandler();
app.prepare()
.then(() => {
const server = express();
server.get('*', (req, res) => handle(req, res));
server.listen(3000, (err) => {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
console.log('> Ready on http://localhost:3000');
});
})
.catch((ex) => {
console.error(ex.stack);
process.exit(1);
});
Adjust scripts to use our new express server
"scripts": {
"dev": "node server",
"build": "next build",
"start": "NODE_ENV=production node server",
"heroku-postbuild":"npm run build"
},Ex. Create 2 GET routes one /test and another /posts
Push to master
Let's add our API
npm install --save express-graphql graphql-toolsCreate a basic Schema
const { makeExecutableSchema } = require('graphql-tools');
const schema = makeExecutableSchema({
typeDefs: `
type Post {
id: Int!
title: String
}
type Query {
posts: [Post]
}
`,
resolvers: {
Query: {
posts: () => [{
id: 1,
title: 'Mi titulo',
}],
},
},
});
module.exports = schema;
Add middleware
const graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql');
const schema = require('./api');
server.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({
schema,
graphiql: true,
}));Test locally and push
Let's start using PM2 for server changes
npm install pm2Change package.json scripts
{
"dev": "pm2 start server --watch",
}Let's configure apollo client
npm install apollo-boost react-apollo graphql
Install dependencies
import ApolloClient from 'apollo-boost';
const client = new ApolloClient();
export default client;
Create a folder called "apollo" and a file inside called "client.js"
Let's test our client
import { gql } from "apollo-boost";
client
.query({
query: gql`
{
users {
id
name
email
}
}
`
})
.then(result => console.log(result));Is it working?
Let's fix Server Side calls
Install isomorphic-fetch
npm install isomorphic-fetch es6-promise
Add polyfill to _app.js
import { polyfill } from 'es6-promise';
// ES6 Promise for using isomorphic fetch
polyfill();Add fetch to client
import ApolloClient from 'apollo-boost';
import fetch from 'isomorphic-fetch';
const client = new ApolloClient({
fetch,
});
export default client;Test again
Let's fix the host and uri problem
const HOST = process.env.HOST || 'http://localhost:3000';
const client = new ApolloClient({
uri: `${HOST}/graphql`,
fetch,
});Create a file called "appConfig.js" in the root folder
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000;
module.exports = {
PORT,
HOST: process.env.HOST || `http://localhost:${PORT}`,
};
appConfig.js
Fix paths and test again
Push to master 🔥
Let's create a Posts.js Component
{
title: 'Post title 1',
description: 'Lorem ipsum...',
favorite: false
}Create an Array of at least 6 posts with this Object structure
Let's create a Post component
Title
Description....
Delete
Post.js
Stateful vs Stateless
Change "Posts.js" to be a stateful component
Create a "removePost" method and attach it to the delete button in the Post component
class Posts extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
posts: POSTS,
};
}
removePost(index) {
const {
posts,
} = this.state;
const newPosts = [
...posts,
];
newPosts.splice(index, 1);
this.setState({
posts: [
...newPosts,
],
});
}
render() {
const {
posts,
} = this.state;
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
{posts.map(post => ({
...post,
onClick: this.removePost.bind(this),
})).map(Post)}
</div>
);
}
}Make it simpler with Hooks
UseState
UseCallback
const Posts = () => {
const [posts, setPosts] = useState(POSTS);
const removePost = useCallback((index) => {
const newPosts = [
...posts,
];
newPosts.splice(index, 1);
setPosts(newPosts);
}, [posts]);
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
{posts.map(post => ({
...post,
onClick: removePost,
})).map(Post)}
</div>
);
};Create a custom hook with the hooks used before
const usePosts = (initialPosts) => {
const [posts, setPosts] = useState(initialPosts);
const removePost = useCallback((index) => {
const newPosts = [
...posts,
];
newPosts.splice(index, 1);
setPosts(newPosts);
}, [posts]);
return {
posts,
removePost,
};
};