International Relations of the Middle East
15 February 2017
Reading Quiz #1
1. What was the purpose of the 'Jordan is Palestine' campaign in 1981-82?
2. Name at least two reasons why the situation in Israel-Palestine can be regarded as 'Apartheid'
3. What role did the Irgun play in creating a Jewish state?
4.What was Plan D?
5. What is the meaning of Al-Nakba?
Conceptualizing Home
A future Home
- early impetus: Zionism and Nationalism
- Theodore Herzl
- Leo Pinsker
- Religious considerations, although important were secondary

Theodore Herzl
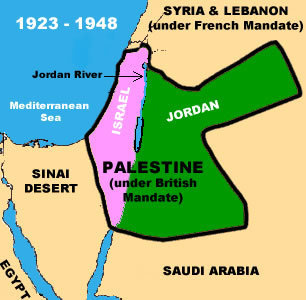
Israel and Palestine
Map 1:
Map 2:
Map 3:

Al-Nakba

Since 1948
- There does NOT exist two states. There is Israel and there territories of the West Bank and Gaza.
- 1.4 Million Palestinians live inside Israel
- Currently 5 Million refugees eligible for services from the United Nations Relief and works agency
Some rebuttals
- Palestine did not exist prior to 1948.
- The area was majority Arab and it was a part of the Ottoman Empire, linked with Greater Syria.
- Arabs rejected previous deals.
- Who would agree to being moved and displaced from ancestral land?
- Jordan and Egypt had administration over land left to the palestinians, not Israel.
- Before the Oslo peace accords Israel has been able to control the movements of legal punishment of Palestinians

The years from 48'-87'
- Large waves of European migration to Israel (Ashkenazi)
- Large waves of Middle Eastern migration to Israel (Sephardic)
- Palestinians actively discriminated against
- id cards required
- land expropriation
- employment discrimination
Diverse Jewish communities of the Middle East dwindled or disappeared entirely.
- Yemen
- Eritrea
- Egypt
- Iraq
- Saudi Arabia
The June War 1967
the 6-day war
- Israel successfully destroys most of Egypt, Syria and Jordan's air forces
- Jordan loses administrative control of East Jerusalem and West Bank
- Syrians lose the Golan heights

Resolution 242
- A violation to take territory through war
- Israeli withdrawal from seized lands
- a "just settlement of the refugee problem"
The years from 48'-87'
West Bank and Gaza
- refugee camps became less temporary
- Construction of Israeli settlements in the West Bank and Gaza Strip
- Formation of the Palestinian Liberation Organization
- prevented from securing an independent economy
- Large pool of west bank palestinians that relied on work in Israel
- tariffs imposed on goods sent into Israel from West Bank

The West Bank and Gaza are on 6,020 sq.km. In that area 4,654,421 palestinians live.
West Bank: 5,655 sq. km
Gaza: 365 sq. km
West Bank: 2,785,366
Gaza: 1,869,055
Break down of area and population:
Israel: 20,770 sq.km (commonly compared to the size of New Jersey)
Population: 7,817,174 within 1948 borders
(An additional 232,140 settlers reside in occupied East Jerusalem and Golan Heights.)
Palestinian Refugees
United Nations Relief Works Agency: " Nearly one-third of the registered Palestine refugees, more than 1.5 million individuals, live in 58 recognized Palestine refugee camps in Jordan, Lebanon, the Syrian Arab Republic, the Gaza Strip and the West Bank, including East Jerusalem."
"The remaining two thirds of registered Palestine refugees live in and around the cities and towns of the host countries, and in the West Bank and the Gaza Strip, often in the environs of official camps. "
Palestinian Economy
"Efforts by the Government of Israel can mitigate the stress of economic stagnation. Israeli restrictions remain the main constraint to Palestinian economic competitiveness and have pushed private investment levels to amongst the lowest in the world, particularly the ones on Area C (agricultural areas) which could increase Palestinian GDP by 35 percent and lead to a similar increase in employment. GDP losses in Gaza since the blockade of 2007 are above 50 percent."- World Bank
Israeli Economy
"Israel consistently ranks high among the world’s economies in terms of its technological readiness, venture capital availability, and the quality of its research organizations. The country ranks 1st in availability of scientists and engineers, number of start-ups per capita, and venture capital investments per capita."
Israeli Society
Society:
- Jewish 74.8%
- Muslim 17.6%
- Christian 2%
- Druze 1.6%
- 4% other
Economy:
GDP per capita 34, 800
Internet usage 70.8%
***
Services: 69% of GDP
Industry: 27.3%
First Intifada (1987)
- Began in Gaza
- goals:
- stop settlements
- stop unfair taxation
- Israeli boycott
- wanes in the mid 1990s

Oslo I(1993)
- recognition of the right of Israel to exist
- 5-year program for Palestinian administration in West Bank and Gaza
- not a peace settlement
Oslo II(1995)
- Divides West Bank into zones of administration, Israel controls bulk of the areas.
The Oslo Accords
Yitzak Rabin, Yassir Arafat, Clinton Administration


Israeli Settlements
Israeli Settlements

- Woven throughout the west bank and serviced by special roads that provide settlers with easy access to mainland Israel.
- Settlements are concentrated in Area C. This area has the majority of Palestinian agricultural land and mineral resources. This area is in the full control of the Israelis
The second Intifada
- Ariel Sharon visit Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem
- not centrally organized
- Israel reoccupies territories and halts commerce
- More deadly conflict, leaves the Oslo process in shambles

Mohammad Durrah
Internationally:

- There exists recognition for Palestine as a state. However, this recognition has very little power with Western Europe and the United States (particularly) withholding recognition. Israel has been accused of war crimes, breaking international law and Human rights abuses but it has gone largely without punishment.
The United States and Israel
With the promises of President Harry Truman to Help a Jewish state develop, the U.S. and Israel has maintained a strong bilateral relationship
- Over 233.7 billion dollars in aid
- President Obama just approved 38 billion in military assistance for the next 10 years
- The U.S. is Israel's largest trading partner with a 1985 trade agreement easing barriers and promoting free trade.
- The United States traditionally pushed a two-state solution. The Trump administration is poised to suspend that policy.
Israel, Palestine and the world
Middle East: Palestine occupies a high position socially with the people of the MENA.
Representative of:
- European colonization
- American policy
Yet, politically, Palestine has been neglected as a major issue.
Record! I am an Arab
Mahmood Darwish
What does the word 'home' mean to you?
Do you have a place you would consider your homeland?
You've read Michel Aflaq and his ideas for the Arab nation. Have you ever felt so strongly about your home/homeland?
Is the concept of a nation outdated?
Aftermath of World War II
Nationalism and the inter-war period
- In Eastern European Baltic states, self-determination proved difficult to maintain
- Arabs desired a state, but are revoked by European powers
- Jews in Europe lived lives regularly under threat throughout Europe. Anti-semitism and violence, particularly in Eastern Europe and Germany increased.
Arab Resistance
Largely resisted attempts by British Mandate government for compromise:
- Refusal to participate in council for the development of a national constitution.
- Refusal to vote
- refusal to sit on advisory council.

Hajj Amin al-Husayni
Before the violence of partition and displacement was the violence of British Colonialism
Unfortunately It Was Paradise
British control 1917-1948
exile and killing of Palestinian leadership
Promise of the British to Jewish Zionists
Military expertise of Jewish soldiers vs. Arabs
Factors that led to the creation of Israel:
1948
- Jewish military Training from World War II
- U.S. Support
- Displacement of 400,000 Arabs
- Massacres, starvation and death
- Led to 48' Arab-Israeli War
- negation of UN plan for partition
- embarrassment for Arab world
- enlargement and legitimization for Israel
- Plan D
Palestinian Strike
1936-1939
- a response to the perceived bias of the mandatory government, zionism, and class divisions, weak Arab leadership and increasing waves of Jewish migration
- Destroyed infrastructure, killed British officers and Jewish settlers
- disintegration of Arab leadership
- British particularly brutal in retaliation against Arabs
Israel-Palestine today
- population of Israel consists of settlers from the Jewish Diaspora
- from 1948-1992 all leaders ,except Rabin, born in Poland or Russia
- Parliamentary Democracy
- 5.9 million jewish residents and 1.4 million Palestinians (Arabs) under direct Israeli control.
- Israeli society largely secular
Palestine over time
