Graphics Programming Virtual Meetup


Discord
vk_mini_path_tracer
Chapter 1 - 3
Initialization & Memory
Link to the tutorial
https://nvpro-samples.github.io/vk_mini_path_tracer/
Source code
https://github.com/nvpro-samples/vk_mini_path_tracer
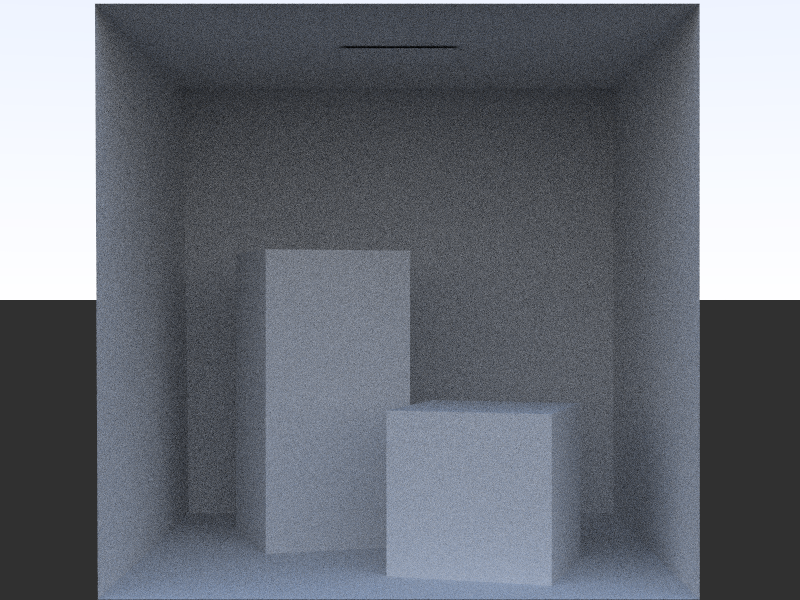
Preview of later output
Chapter 1
Hello, Vulkan!
Note on supported GPU's
- RTX GPU required to follow the tutorial exactly
- Due to using "ray queries"
- Still possible to follow along without a RTX GPU
- Some GPU's support "ray pipelines"
- Allows 1060 6gb and up to follow along
Note on debugging
- End of each chapter will have code you can run
- There are 'checkpoints' in the GitHub repo
- Useful for comparing to your implementation
Things we need:
- Required dependencies
- C++14 compiler
- Git
- CMake
- Driver which supports the ray tracing extensions
- NVIDIA's driver released December 15th, 2020
- Vulkan SDK 1.2.162
- Check the tutorial for links
Download the project
Navigate to the where the code should go
Run in a command line:
Then open the build_all folder and run either clone_all.bat (Windows) or clone_all.sh (Linux)
git clone https://github.com/nvpro-samples/build_all.gitConfigure CMake (Windows)
- Launch CMake GUI
- Make the Source and Build directories point to the project
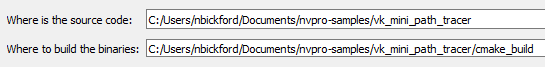
- Click "Configure"
- Set the generator. Usually the default is correct.
- Make sure to use 64 bit

- Click "Finish"
- Then when configuration finishes, click "Generate"
- Open in Visual studio
Configure Visual Studio
- The place for the code will be 'vk_mini_path_tracer_edit'
- Make it the 'startup project' by right clicking it and choosing the option
- Also make sure we are in Debug mode
- Now we are ready!
Hello Vulkan!
- Open `main.cpp` in vk_mini_path_tracer_edit
- Edit it to read the following
#include <nvvk/context_vk.hpp>
int main(int argc, const char** argv)
{
// Create the Vulkan context, consisting of an instance, device, physical device, and queues.
// One can modify this to load different extensions or pick the Vulkan core version
nvvk::ContextCreateInfo deviceInfo;
nvvk::Context context; // Encapsulates device state in a single object
context.init(deviceInfo); // Initialize the context
context.deinit(); // Don't forget to clean up at the end of the program!
}- Compile and run it, it should print some useful info about your GPU and system
Vulkan is a CPU API for the GPU
- You run code on the CPU which directs what the GPU should do
- But Vulkan is an API, not an implementation
- We need drivers to make do anything with a GPU
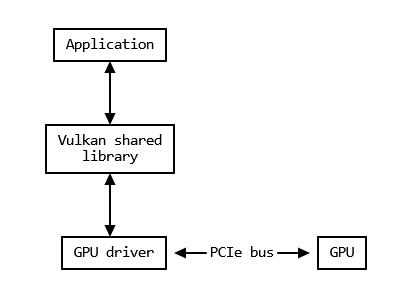
nvvk::Context: The Vulkan Instance
- This is the 'context' which is necessary to access Vulkan
- We use this abstraction to handle setup and creation
- Contains the VkInstance, VkPhyiscalDevice, VkDevice, and VkQueue
- Simplifies a large portion of setup into a single function
-
context.init(deviceInfo);
-
VkInstance
- The context for the "Vulkan Shared Library"
- Handles initializing internal components, like drivers
- Customized with:
- Layers - mainly for debugging
- Instance extensions - extend what Vulkan can do
Vulkan Layers
- Mechanism which allows runtime interception of vulkan function calls
- Major use case is validation & debugging
- `VK_LAYER_KHRONOS_VALIDATION`
- This layer catches many many mistakes
- Automatically enabled in ContextCreateInfo
- Other uses are: Overlay, capture/replay, and logging
ContextCreateInfo(bool bUseValidation = true);Example BUG Validation catches
nvvk::ContextCreateInfo deviceInfo;
nvvk::Context context;
context.init(deviceInfo);
// Invalid call!
vkAllocateCommandBuffers(context, nullptr, nullptr);ERROR: VUID-vkAllocateCommandBuffers-pAllocateInfo-parameter
--> Validation Error: [ VUID-vkAllocateCommandBuffers-pAllocateInfo-parameter ]
Object 0: handle = 0x158dfd26f68, type = VK_OBJECT_TYPE_DEVICE; |
MessageID = 0x72e32441 | vkAllocateCommandBuffers: required parameter
pAllocateInfo specified as NULL The Vulkan spec states: pAllocateInfo must be a
valid pointer to a valid VkCommandBufferAllocateInfo structure
(https://www.khronos.org/registry/vulkan/specs/1.2-extensions/html/
vkspec.html#VUID-vkAllocateCommandBuffers-pAllocateInfo-parameter)What validation reports
Vulkan Instance Extensions
- Extend the VkInstance with additional functionality
- Windowing Functions: like VK_KHR_win32_surface
- Debug callback: VK_EXT_debug_utils
- Multi-GPU support
- And more!
- Not to be confused with the list of Device extensions
- Raytracing extensions are Device extensions
VkPhysicalDevice
- A handle for a "Physical GPU"
- Used to query information about the GPU
- Possible to have 1 driver that supports 2 physical devices
- We create a `VkDevice` from this
Chapter 2
Device Extensions and Vulkan Objects
More setup!
- We need to use Vulkan version 1.2
- Request it through the nvvk::ContextCreateInfo
Add these additional includes to the code
#include <cassert>
#include <nvvk/context_vk.hpp>
#include <nvvk/structs_vk.hpp> // For nvvk::makedeviceInfo.apiMajor = 1; // Specify the version of Vulkan we'll use
deviceInfo.apiMinor = 2;Output should be now have something like
_______________
Vulkan Version:
- available: 1.2.154
- requesting: 1.2.0Vulkan Struct Initialization
Many Vulkan structures have `sType` as the first member
This is for the driver & layer to know the 'type'
Multiple methods to set it
Manual:
nvvk::make
auto + nvvk::make
use vulkan.hpp
VkPhysicalDeviceRayQueryFeaturesKHR rtFeatures =
{VK_STRUCTURE_TYPE_PHYSICAL_DEVICE_RAY_QUERY_FEATURES_KHR};VkPhysicalDeviceRayQueryFeaturesKHR rtFeatures =
nvvk::make<VkPhysicalDeviceRayQueryFeaturesKHR>();auto rtFeatures = nvvk::make<VkPhysicalDeviceRayQueryFeaturesKHR>();Requesting Device Extensions
- Three Vulkan KHR ray tracing extensions
- VK_KHR_acceleration_structure
- VK_KHR_ray_query
- VK_KHR_ray_tracing_pipeline
- We will mainly use VK_KHR_ray_query
-
But looking at the docs, VK_KHR_ray_query requires VK_KHR_acceleration_structure
- Which in turn requires VK_KHR_deferred_host_operations!
-
But looking at the docs, VK_KHR_ray_query requires VK_KHR_acceleration_structure
- Thus we need to enable all three for VK_KHR_ray_query to work
Requesting Device Extensions
Done through ContextCreateInfo
// Required by VK_KHR_ray_query; allows work to be offloaded
// onto background threads and parallelized
deviceInfo.addDeviceExtension(VK_KHR_DEFERRED_HOST_OPERATIONS_EXTENSION_NAME);Some extensions have 'Features' that aren't guaranteed
We can query them by giving the context a`Features` struct by pointer that the driver fills in.
auto asFeatures = nvvk::make<VkPhysicalDeviceAccelerationStructureFeaturesKHR>();
deviceInfo.addDeviceExtension(VK_KHR_ACCELERATION_STRUCTURE_EXTENSION_NAME, false, &asFeatures);
auto rayQueryFeatures = nvvk::make<VkPhysicalDeviceRayQueryFeaturesKHR>();
deviceInfo.addDeviceExtension(VK_KHR_RAY_QUERY_EXTENSION_NAME, false, &rayQueryFeatures);
// Device must support acceleration structures and ray queries:
assert(asFeatures.accelerationStructure == VK_TRUE && rayQueryFeatures.rayQuery == VK_TRUE);'false' indicates the extension is 'required' and should abort if not available
Chapter 3
Memory
Data transfer Overview
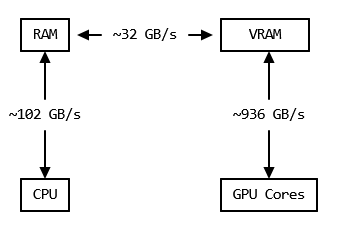
- GPU's have their own memory, VRAM, which is very fast
- Getting data in RAM to and from VRAM however is much slower
- Therefore we need to minimize transfers
In general, this means we try to do what we need on the CPU, upload the data all at once, then let the GPU work on it as much as possible before sending it back.
Memory in Vulkan
- Vulkan makes memory (VRAM) allocation explicit
- Its up to the application to acquire and release `VkDeviceMemory`s as necessary
- Compared to C/C++ (malloc and new), Vulkan is lower level
- Allows applications to use VRAM in an optimal manner, instead of relying on a driver to do so
- But: Vulkan only requires 4096 distinct VkDeviceMemory handles
- `nvvk::AllocatorDma`makes each allocation, eg buffer or image, get its own VkDeviceMemory
- `nvvk::AllocatorVma`will collate multiple buffers and images into a few VkDeviceMemory objects
NVVK Memory Allocator
We need to include it first
#define NVVK_ALLOC_DEDICATED
#include <nvvk/allocator_vk.hpp> // For NVVK memory allocatorsThen we create and initialize it
// Create the allocator
nvvk::AllocatorDedicated allocator;
allocator.init(context, context.m_physicalDevice);After we are done, we need to destroy it
allocator.deinit();Helpful wrapper to handle memory allocation
Vulkan Buffers
- A VkBuffer is like a pointer to an array of bytes
- Unlike in C, it also contains the size of the array' as well as usage information
- Just like in C, a pointer initially points to nothing. Thus we must get memory for it then bind it.
- Fortunately, the allocator we just made will do it for us
// Create a buffer
VkDeviceSize bufferSizeBytes =
pushConstants.render_width * pushConstants.render_height * 3 * sizeof(float);
VkBufferCreateInfo bufferCreateInfo = nvvk::make<VkBufferCreateInfo>();
bufferCreateInfo.size = bufferSizeBytes;
bufferCreateInfo.usage = VK_BUFFER_USAGE_STORAGE_BUFFER_BIT | VK_BUFFER_USAGE_TRANSFER_DST_BIT;
// VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_VISIBLE_BIT means that the CPU can read this buffer's memory.
// VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_CACHED_BIT means that the CPU caches this memory.
// VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_COHERENT_BIT means that the CPU side of cache management
// is handled automatically, with potentially slower reads/writes.
nvvk::BufferDedicated buffer = allocator.createBuffer(bufferCreateInfo,
VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_VISIBLE_BIT
| VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_CACHED_BIT
| VK_MEMORY_PROPERTY_HOST_COHERENT_BIT);Using a Buffer for an Image?
- You may have noticed the 'size' of the buffer, we are in fact making it big enough to hold an image!
- VkImage and VkBuffer both do the same thing, reference GPU memory
- VkImage has a bunch of extra information and capabilities
- VkBuffer doesn't, but none of the missing functionality is needed in this tutorial
- So we choose the simpler option for now
Getting the data out of the buffer
- We have a buffer, but no way to see whats in it
- Currently it is blank, but future chapters will fill it in on the GPU
- So lets copy it from VRAM to the CPU's RAM
- Mapping a buffer allows a CPU to read VRAM as if it was regular memory
void* data = allocator.map(buffer);
float* fltData = reinterpret_cast<float*>(data);
printf("First four elements: %f, %f, %f, %f\n", fltData[0], fltData[1], fltData[2], fltData[3]);
allocator.unmap(buffer);First four elements: 0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 0.000
Run the program...