初探機器學習
Machine Learning Intro

決策樹
Decision Tree
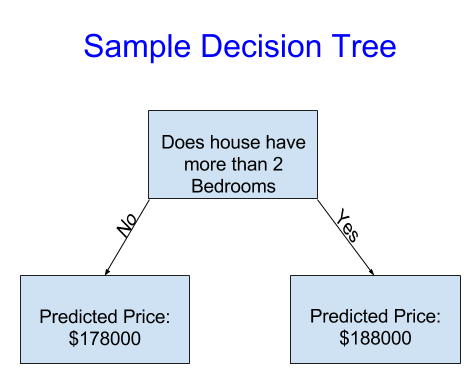
利用歷史資料來決定樹要怎麼分組和每組的值,這步驟稱為擬合(fitting)或訓練(training)模型
而其中用來訓練模型的歷史資料稱為
訓練資料(training data)
增進決策樹
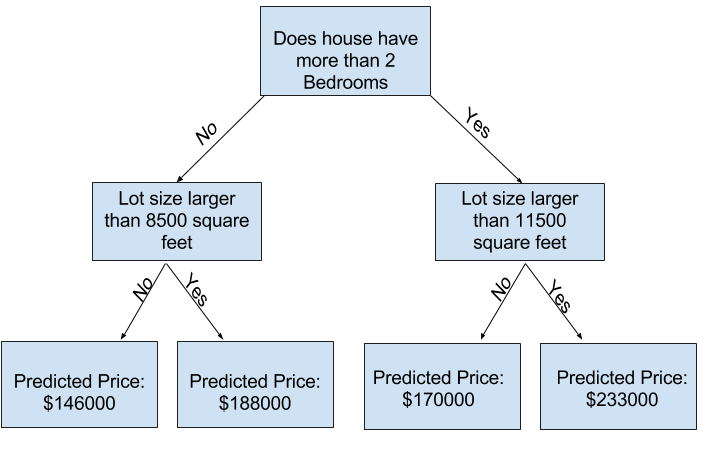
使用更多的變因,來讓決策樹有更多分支,也可以稱為更深的決策樹
樹葉
預測數值的地方
數據處理
Data Processing

下載pandas套件
在cmd打上 pip install pandas
怎麼使用?
import pandas
melbourne_data = pandas.read_csv("melb_data.csv")
print(melbourne_data.describe())output
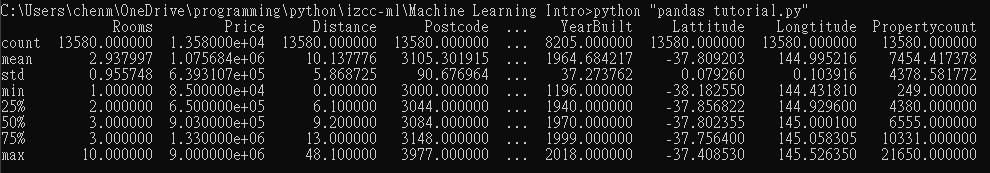
| count | 有幾行值 |
| mean | 平均 |
| std | 標準差 |
| min | 最小值 |
| 25% | PR25 |
| 50% | PR50 |
| 75% | PR75 |
| max | 最大值 |
資料概述
第一個機器學習模型
First Machine Learning Model

sklearn下載
在cmd打上 pip install scikit-learn
1
選擇訓練模型的資料
2
選擇要用的特徵
3
選擇要用的模型
5
用訓練好的模型來預測結果
4
用訓練資料來訓練模型
6
為結果評分
選擇訓練模型的資料
前面pandas用到的檔案
import pandas
melbourne_data = pandas.read_csv("melb_data.csv")去除沒有用的資料
import pandas
melbourne_data = pandas.read_csv("melb_data.csv")
melbourne_data = melbourne_data.dropna(axis=0)選定預測的目標
import pandas
melbourne_data = pandas.read_csv("melb_data.csv")
melbourne_data = melbourne_data.dropna(axis=0)
y = melbourne_data.Price選擇要用的特徵
import pandas
melbourne_data = pandas.read_csv("melb_data.csv")
melbourne_data = melbourne_data.dropna(axis=0)
y = melbourne_data.Price
melbourne_features = ['Rooms', 'Bathroom', 'Landsize', 'Lattitude', 'Longtitude']
X = melbourne_data[melbourne_features]選擇要用的模型
import pandas
melbourne_data = pandas.read_csv("melb_data.csv")
melbourne_data = melbourne_data.dropna(axis=0)
y = melbourne_data.Price
melbourne_features = ['Rooms', 'Bathroom', 'Landsize', 'Lattitude', 'Longtitude']
X = melbourne_data[melbourne_features]
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
melbourne_model = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=1)利用訓練資料訓練模型
import pandas
melbourne_data = pandas.read_csv("melb_data.csv")
melbourne_data = melbourne_data.dropna(axis=0)
y = melbourne_data.Price
melbourne_features = ['Rooms', 'Bathroom', 'Landsize', 'Lattitude', 'Longtitude']
X = melbourne_data[melbourne_features]
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
melbourne_model = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=1)
melbourne_model.fit(X, y)預測結果
import pandas
melbourne_data = pandas.read_csv("melb_data.csv")
melbourne_data = melbourne_data.dropna(axis=0)
y = melbourne_data.Price
melbourne_features = ['Rooms', 'Bathroom', 'Landsize', 'Lattitude', 'Longtitude']
X = melbourne_data[melbourne_features]
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
melbourne_model = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=1)
melbourne_model.fit(X, y)
predict = melbourne_model.predict(X.head())加上結果輸出
import pandas
melbourne_data = pandas.read_csv("melb_data.csv")
#print(melbourne_data.columns)
melbourne_data = melbourne_data.dropna(axis=0)
y = melbourne_data.Price
melbourne_features = ['Rooms', 'Bathroom', 'Landsize', 'Lattitude', 'Longtitude']
X = melbourne_data[melbourne_features]
#print(X.describe())
#print(X.head())
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
melbourne_model = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=1)
melbourne_model.fit(X, y)
predict = melbourne_model.predict(X.head())
print(predict)驗證模型
Model Validation
簡單來說就是模型預測的正確程度
平均絕對誤差
錯誤 = |實際值 - 預測值|
實作
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
predicted_home_prices = melbourne_model.predict(X)
mean_absolute_error(y, predicted_home_prices)前面是不是哪裡怪怪的
使用樣本內的資料來測預測誤差
就等於你用作業裡的題目來出段考題目
將資料分為測試資料和驗證資料
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_X, val_X, train_y, val_y = train_test_split(X, y, random_state = 0)過適&乏適
Overfitting&Underfitting
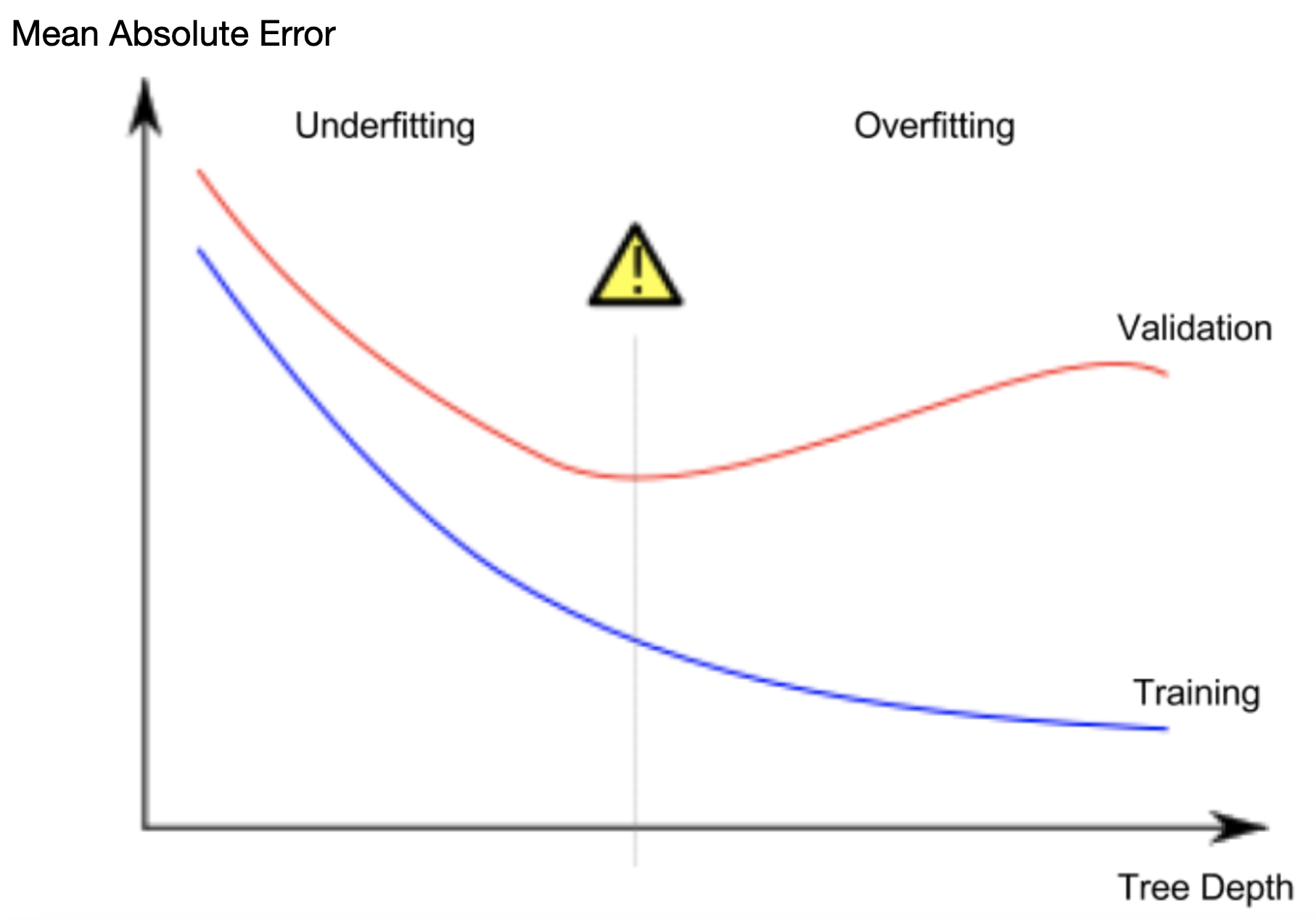
樹有很多層,導致每層只有少量的房子,因此無法準確預測價格
過適
樹只有一層,完全沒辦法把房子分類來預測價格
乏適
過適vs乏適



解決辦法
DecisionTreeRegressor(max_leaf_nodes=counts, random_state=0)實作練習
測試要用哪種最大樹葉深度才會有最好的結果
隨機森林
Random Forests
生成很多棵樹,最後對每個樹的預測結果取平均
使用方法
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
forest_model = RandomForestRegressor(random_state=1)