暑假資讀[0]
負責人介紹
- 22719 張庭瑋
- 建中資訊社 學術
- alvingogo
- DC : Alvin Chang#6995
- FB : Alvin Chang
講師介紹
- 22724 陳泓宇
- 建中資訊社 副社兼學術
兼披薩長 - chenhowie
- DC : chenhowie#1138
- FB : Howie
資讀簡介
資訊讀書會
- FB : No Code No Life 從零開始的資訊讀書會
- DC : 從零開始的資訊讀書會
暑假資讀
- C++ 基本語法
- 日期 : 7/4、7/19、8/9、8/23、8/24
- 時間 : 下午 2:00 ~ 5:00
暑假資讀
| 日期 | 講師 | 內容 |
|---|---|---|
| 7/4 | 227 陳泓宇 | 資讀介紹 C++ 編輯器安裝 C++ 語法 (輸入輸出 變數 運算子) |
| 7/19 | 225 陳澔樂 | 競賽介紹 OJ 介紹 語法 (條件 迴圈 陣列 時間複雜度) |
| 8/09 | 227 張秉中 | 函數 struct & object 運算子重載 指標 參考 |
| 8/23 | 227 張庭瑋 | stack queue heap STL |
| 8/24 | 227 陳柏凱 | 基本演算法介紹 ( 排序 枚舉 greedy 二分搜 ) |
開學後資讀
- C++
- 跟暑假資讀差不多
- 時間 : 每周二晚上 6:00 ~ 9:00
程式語言簡介
什麼是程式語言
- 使用者用來與電腦溝通之文字記號所形成的集合
常見程式語言
- Python
- C++
- JavaScript
- Java
- C#
- Node.js
- PHP
低階語言
執行速度快,編寫程式較困難且程式碼不易理解。
高階語言
接近人類日常生活用語,簡單易懂,在高階語言中,一個命令就可以代表數個組合語言中的命令。
低階語言
- 組合語言必須先被翻譯成機器語言後才能被電腦接受,擔任這個翻譯工作的程式叫做組譯器 (assembler)
高階語言
- 電腦不能直接接受以高階語言所寫成的程式,必須先轉換成機器語言後才能執行,而依轉換工具不同可分為直譯器 (interpreter) 及編譯器 (compiler) 二種,
直譯器
- 將高階語言逐行翻譯成機器語言後直接執行
- 每次執行時都必須執行翻譯的動作
- 效率較差
- ex. Python, JavaScript, Ruby, PHP
編譯器
- 將高階語言所寫的原始程式整個轉成 (object code)
- 只需將程式編譯過一次,以後便可以直接拿目的碼使用
- 執行速度較快
- ex. C++, C#
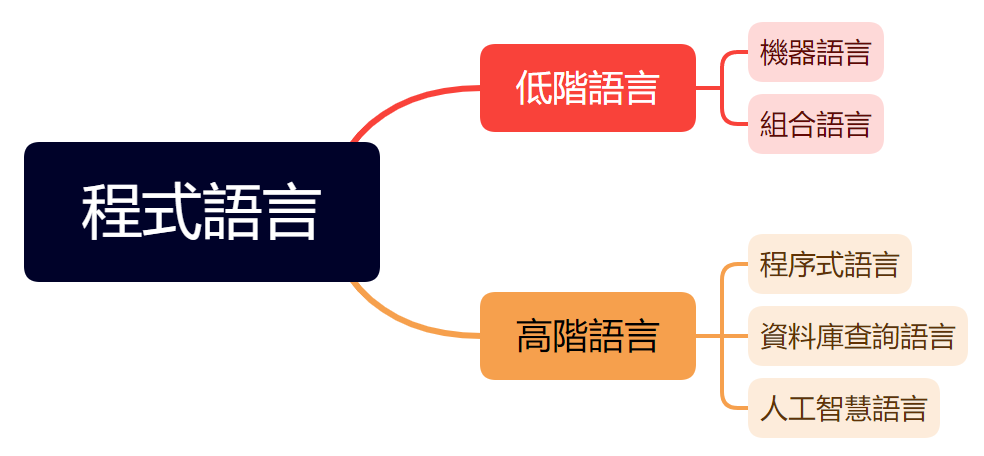
機器語言
- 機器語言 (machine language) 是電腦所能處理最直接
的語言 - 所有的程式在執行前都必須被轉換成機器語言
組合語言
- 使用英文簡寫來代表各種基本運算的語言
- ex. 以 ADD 代表「加」,以 SUB 代表「減」
程序式語言
- 語法接近人類日常生活用語
- 一個命令就可代表數個組合語言中的命令
- 以程式的「過程」為程式設計的重心
資料庫查詢語言
- 以程式的「目的」為程式設計的重心
- 缺少了控制性及設計彈性
- 速度較慢
人工智慧語言
- 利用人工智慧技術
- 接近人類使用的自然語言
- 能容忍少量的拼字及語法錯誤
C++簡介
C++
- 1979年 Bjarne Stroustrup 發明
- 從C改良而來
C++
- 編譯式語言
- 執行速度快
C++編譯環境安裝
常用C++編輯器
- code::blocks
- Eclipse
- dev C++
- visual studio code
- Vim
- sublime
Visual studio code
需要下載的東西
- MinGW : https://sourceforge.net/projects/mingw/files/latest/download
- visual studio code : https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/?dv=win
MinGW
設定環境變數
切記一定要按確定而不是直接關掉
visual studio code
code runner
一鍵編譯&執行C++
在extensions安裝輔助插件
實用型
- Bracket Pair Colorizer 2 (已成為vscode的內建功能)
- Better Comments
- Indenticator
- Chinese (Traditional) Language Pack for Visual Studio Code
- Discord Presence
無用型
- background-cover
- Power Mode
- vscode-icons
- SynthWave '84
- Atom One Dark Theme
以上三個都裝不了的話
Hello World
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout << "Hello World";
return 0;
}變數
什麼是變數
- 記憶體裡存在值且被命名的儲存空間
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a; //定義變數名稱為a 型別為int
a = 5; //把a的值變成5
}變數種類
- 整數
- 浮點數
- 布林值
- 字元
- 字串
整數
| 名稱 | 使用空間 bytes |
值域 |
|---|---|---|
| short | 2 | -32768~32767 |
| int | 4 | -2147483648~2147483647 |
| unsigned int | 4 | 0~4294967295 |
| long long | 8 | -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 ~ 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
| unsigned long long | 8 | 0~18,446,744,073,709,551,615 |
浮點數
| 名稱 | 使用空間 bytes |
值域 | 有效位數 |
|---|---|---|---|
| float | 4 | ±3.4× \(10^{-38}\) ~ ±3.4× \(10^{38}\) |
7 |
| double | 8 | ±1.7× \(10^{-308}\) ~ ±1.7× \(10^{308}\) |
15 |
| long double | 8 | ±1.7× \(10^{-308}\) ~ ±1.7× \(10^{308}\) |
15 |
布林值
- bool
- true/false
- 佔用空間為1byte
- 值域 : 0 ~ 1
字元
- char
- 可以存一個字元(ASCII code裡的字元)
- 值域 : -128 ~ 127
字串
- string
- 字元的陣列
宣告變數&賦值
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
n = 99;
string s;
s = "Hello World";
char c;
c = 'h';
float f;
f = 1.65464;
bool b;
b = true;
}變數命名規則
- 命名可以包含英文字母、底線、數字
- 不能以數字開始
- 大小寫敏感
- 不能用保留字 (C++ 原有的東西 ex.int, string, max)
- 盡量用有意義的字命名
好的命名方式
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int age;
int years;
string name;
string school;
bool gender;
}建議不要的命名方式
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
int nn;
int nnn;
string s;
string ss;
string sss;
bool b;
bool bb;
}輸入輸出
輸入
- cin
- cin.get()
- cin.getline()
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string a;
cin >> a; //讀到空白或換行
char b;
cin.get(b); //一次讀一個字元
string c;
cin.getline(c); //讀到換行
}輸出
- cout
- endl
- '\n'
- cout.flush
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout << "Hello World"; //輸出 Hello World
cout << endl; //換行
cout << '\n'; //換行
cout.flush(); //清空緩衝區
}小數輸出
- #include <iomanip>
- cout << fixed << setprecision()
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main(){
float f;
f = 1.666523;
cout << fixed << setprecision(5) << f; //1.66652
}運算子
指定運算子
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a;
a = 3; //把a的值設為3
string s;
s = "abcd"; //把s的值設為abcd
}算術運算子
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a = 5;
a = a + 2; //把a設為a+2
cout << a; //7
int b = 5;
b = b - 2;
cout << b; //3
int c = 5;
c = c * 2;
cout << c; //10
int d = 5;
d = d / 2;
cout << d; //2
int e = 5;
e = e % 2; //e除以二的餘數
cout << e; //1
}算術指定運算子
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a = 5;
a += 2; //把a設為a+2
cout << a; //7
int b = 5;
b -= 2;
cout << b; //3
int c = 5;
c *= 2;
cout << c; //10
int d = 5;
d /= 2;
cout << d; //2
int e = 5;
e %= 2;
cout << e; //1
}遞增遞減運算子
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a = 5;
a++; //a變成a+1
cout << a; //6
int b=5;
b--;
cout << b; //4
}關係運算子
- >
- <
- >=
- <=
- ==
- !=
關係運算子
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
bool a;
a = (5 > 3);
cout << a; //true
bool b;
b = (5 == 3);
cout << b; //false
bool c;
c = (5 != 3);
cout << c; //true
}邏輯運算子
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
bool a;
a = (true && true);
cout << a; //true
bool b;
b = (false || true);
cout << b; //true
bool c;
c = (! false);
cout << c; //true
}位元運算子
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a = 1; //00000000000000000000000000000001
a = a << 2; //00000000000000000000000000000100
cout << a; //4
int b = 7; //00000000000000000000000000000111
b >> 2; //00000000000000000000000000000001
cout << b; //1
int c = 3; //00000000000000000000000000000011
int d = 6; //00000000000000000000000000000110
int e = c&d; //00000000000000000000000000000010
int f = 3; //00000000000000000000000000000011
int g = 6; //00000000000000000000000000000110
int h = f|g; //00000000000000000000000000000111
int i = 3; //00000000000000000000000000000011
int j = 6; //00000000000000000000000000000110
int k = i^j; //00000000000000000000000000000101
int l = 3; //00000000000000000000000000000011
int m = ~l; //11111111111111111111111111111100
cout << m; //-4
}運算子符號太難記?
| Primary | Alternative |
|---|---|
| && | and |
| &= | and_eq |
| & | bitand |
| | | bitor |
| ~ | compl |
| ! | not |
| != | not_eq |
| || | or |
| |= | or_eq |
| ^ | xor |
- 括號>乘除>加減>位元>關係>邏輯>算術指定
太難記了所以不知道的就用括號刮起來
下次讀書會時間
- 日期 : 7/19
- 時間 : 2:00 ~ 5:00
- 地點 : 電腦教室四
- 講師 : 225 陳澔樂
-
內容 : 競賽介紹 OJ 介紹
語法 (條件 迴圈 陣列 時間複雜度)