JavaScript
Weblaunch


A dynamic , interpreted and high-level programming language.




Background-color: #E8E9ED














































Recap







Cheong Pui Yien



























📖 BSc (Hons) in Computer Science
( Year 2 )
🧩 Vice President of Sunway Tech
Club

Chai Chang Cheng


























- Software developer @ Map72
- AWS Student Ambassador
- Freelance Web/Mobile developer
- Head of Marketing of Sunway Tech Club
- A first-year student in Computer science (Technically😏)

JavaScript
Weblaunch


A dynamic , interpreted and high-level programming language.





Resources:
Help!!!





























🚩 Static vs Dynamic Language
🚩 How to write JS in HTML
🚩 Basics of JavaScript
Control Flow 🚩
🎯 Exercise
🔓 Variables
🔓 Constant
🔓 Primitive Types
🔓 Array
Conditional Statements: 🔓
If Else 🔑
Switch Case 🔑
Comparison Operators 🔓
Loops: 🔓
While 🔑
For 🔑
Object 🔓
Array🔓
Function🔓

















🚩 How to write JS in HTML
🚩 Basics of JavaScript
Control Flow 🚩
🎯 Exercise
🔓 Variables
🔓 Constant
🔓 Primitive Types
🔓 Array
🔓 Arithmetic Operators
Conditional Statements: 🔓
If Else 🔑
Switch Case 🔑
Comparison Operators 🔓
Loops: 🔓
While 🔑
For 🔑
Object 🔓
Array🔓
Function🔓
















Programming Languages
Static
Dynamic
Type of variable is set and can not be changed in the future
Type of variable can be changed at run time
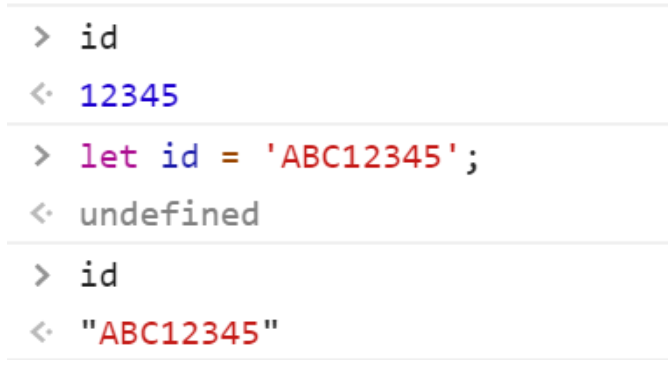
String name = 'Jeffrey';let id = 12345;
Changing the value of a variable in a DYNAMIC language






🚩 How to write JavaScript in HTML
>
















✔️ How to write JavaScript in HTML?
We need to include <script> </script> in the <body> of the HTML element.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>This is the HTML Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Let's try writing JavaScript in HTML!</p>
<p id='this'>Try This!</p>
<script>
alert('Hello World');
document.write('I love WebLaunch');
document.getElementById('this').innerHTML='Change to This!';
</script>
</body>
</html>
🚩How to write JavaScript in HTML
>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>This is the HTML Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Let's try writing JavaScript in HTML!</p>
<p id='this'>Try This!</p>
<script src="webLaunch_js.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
🚩How to write JavaScript in HTML
>

Outputs:
alert("Hello World");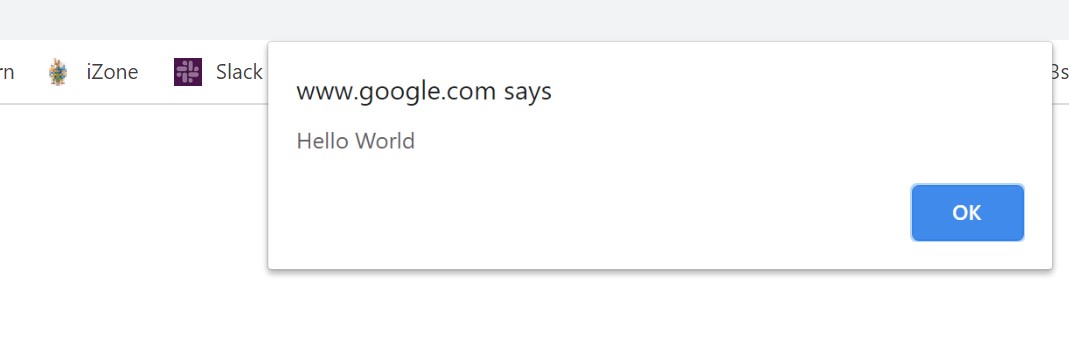
document.write('I love WebLaunch');


























>

Outputs:
document.getElementById('this').innerHTML='Change to This!';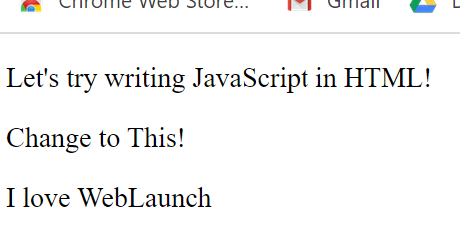

















alert()alert('Hello World');For example:
Output:
✔️ How to write a message in JavaScript
















>
🚩How to write JavaScript in HTML
document.write()document.write("Hello World");For example:
Output:
>



























🚩How to write JavaScript in HTML

innerHTML<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>InnerHTML</title>
</head>
<body>
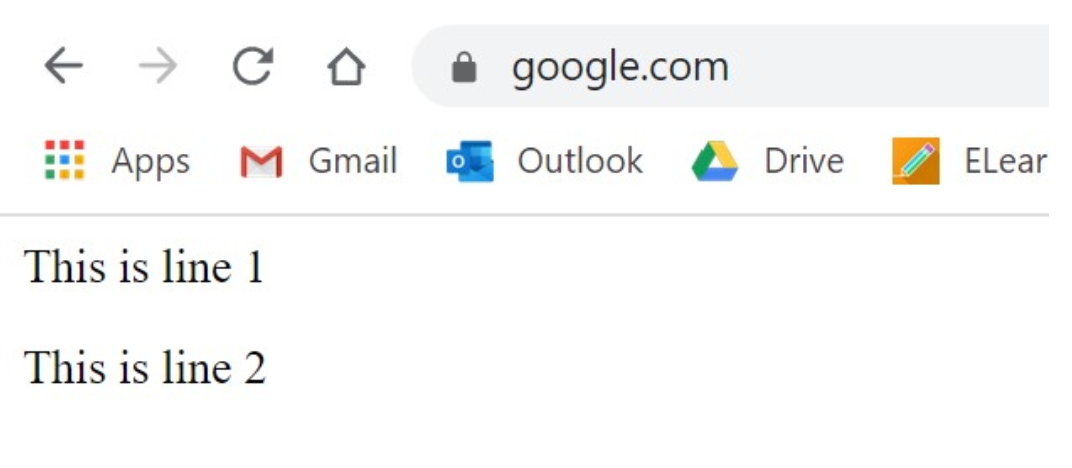
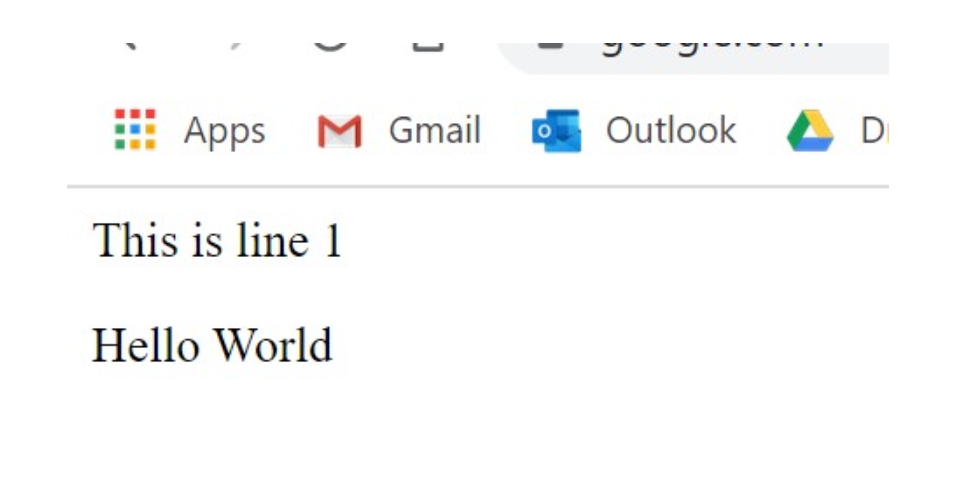
<p>This is line 1</p>
<p id='change'>This is line 2</p>
<script>
document.getElementById('change').innerHTML = 'Hello World';
</script>
</body>
</html>innerHTML has to be tagged along with the element that you want to change using a query selector i.e. getElementById()
For example:
















🚩How to write JavaScript in HTML

🚩 Basics of JavaScript
Control Flow 🚩
🎯 Exercise
🔓 Variables
🔓 Constant
🔓 Primitive Types
🔓 Array
🔓 Arithmetic Operators
Conditional Statements: 🔓
If Else 🔑
Switch Case 🔑
Comparison Operators 🔓
Loops: 🔓
While 🔑
For 🔑
Object 🔓
Array🔓
Function🔓
















🚩 How to write JS in HTML
Basics of JavaScript
🚩


















Programming is all about processing the data

🔓 Variables
( Give a name to your data! )
🚩Basics of JavaScript
















>

🚩Basics of JavaScript 🔓 Variables
var surname = 'Cheong';
let name = 'Yien';
let birthDate = 10;
console.log(surname);
console.log(name);
console.log(birthDate);To print to variables that you have keyed in to the console you can use console.log()
For Example:
console.log(surname);
















String name = 'Jeffrey';This method is also called static typing and is not the best practise as the type of variable is set and cannot be changed in the future.
Thus, let or var is more widely use in declaring a variable as we can change the type of value stored in the variable. This is also called dynamic typing.
What about using this?





🔓 Constant
( You can't change me! )
🚩Basics of JavaScript 🔓 Constant
















>

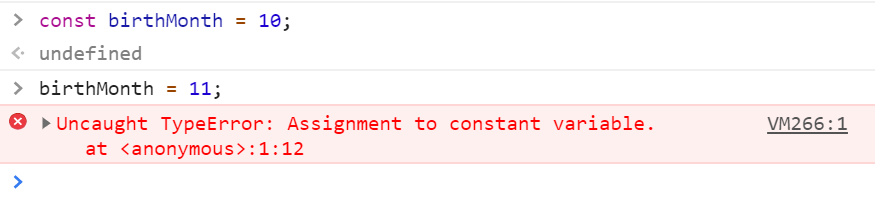
To fix the value of a variable or disable change
const birthMonth = 10;
console.log(birthMonth);















🚩Basics of JavaScript 🔓 Constant

















Data types
( Different type of data! )
🔓 Primitive Types
🚩Basics of JavaScript 🔓 Primitive Types
>

-
String
-
Number
-
Boolean
-
Undefined
-
Null
let name = "My Name";
let age = 18;
let choice = true;
let lastName = undefined;
let firstName = null;

Check the type of the data using typeof in the console:



























-
String
-
Number
-
Boolean
-
Undefined
-
Null


























>
🚩Basics of JavaScript 🔓 Primitive Types
🔓 Primitive Types

-
String
let name = 'My Name';

Check the type of the data using typeof in the console:


























🚩Basics of JavaScript 🔓 Primitive Types
>

-
Number
let age = 18;

Check the type of the data using typeof in the console:


























>
🚩Basics of JavaScript 🔓 Primitive Types

-
Boolean
let choice = true; 
Check the type of the data using typeof in the console:


























>
🚩Basics of JavaScript 🔓 Primitive Types

-
Undefined
let lastName = undefined;Check the type of the data using typeof in the console:


























>

🚩Basics of JavaScript 🔓 Primitive Types

-
Null
let firstName = null;
Check the type of the data using typeof in the console:



























🚩Basics of JavaScript 🔓 Primitive Types

















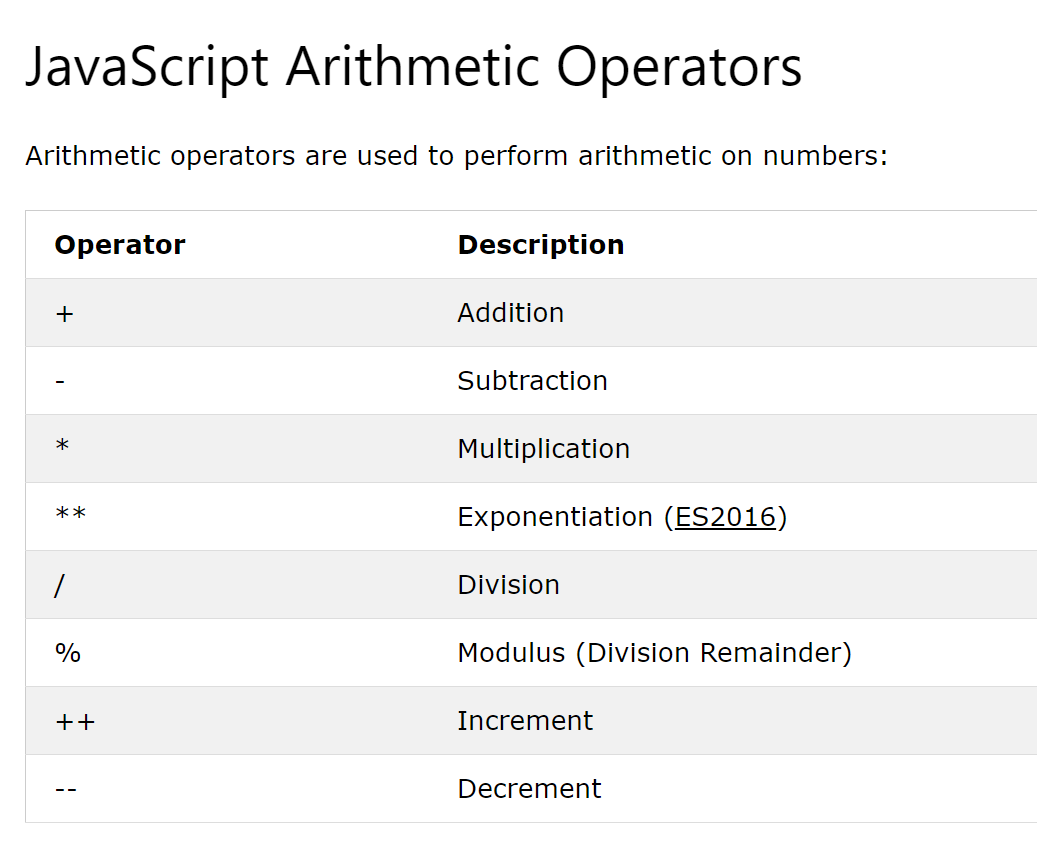
🔓 Arithmetic Operators
🚩Basics of JavaScript 🔓 Arithmetic Operators

📃 Collection of data
( Basically grouping them )


























🔓 Array
🚩Basics of JavaScript 🔓 Array
>

To store list of items.
Let's try making a list of colour using array !
let colours = [];let colours = ['red','orange','yellow','green','violet'];
console.log(colours);console.log(colours[4]);colours[5]='blue';

























🚩Basics of JavaScript 🔓 Array

🚩 Basics of JavaScript
Control Flow 🚩
🎯 Exercise
🔓 Variables
🔓 Constant
🔓 Primitive Types
🔓 Array
🔓 Arithmetic Operators
Conditional Statements: 🔓
If Else 🔑
Switch Case 🔑
Comparison Operators 🔓
Loops: 🔓
While 🔑
For 🔑
Object 🔓
Array🔓
Function🔓
















🚩 How to write JS in HTML
Control Flow
🚩


















Handling of data


























🔓 Conditional Statements
🚩Control Flow

🔑 If and Else (if....else)
















>
🔑 Switch and Case
🚩Control Flow 🔓 Conditional Statements

- If and Else
if (condition){
action
}else (condition){
action
}else{
action
}; - Switch and Case
switch (input){
case input1
action
break;
case input2
action
break;
case input3
action
break;
default:
action
}















🚩Control Flow 🔓 Conditional Statements

🎯 Try This!
🔑 If and Else (if....else)
Create a simple if and else statement that checks the score.
If the score is more than or equal 80, let's print 'Congratulations!' . Else, print 'It's ok, try harder next round.'
❗ Initialise the score first!
let score = 40;
if (score >= 80){
console.log("Congratulations!!!");
}
else
console.log("It's ok, try harder next round.");















>
🚩Control Flow 🔓 Conditional Statements

🎯 Exercise
If i'm hungry, I want the application to print " I'm hungry!!!Feed me now!!!! ". If i'm not, i want it to print " I'm not hungry ".
let hungry = false;
if (hungry){ //hungry === true
console.log("I'm hungry!!!Feed me now!!!!");
}
else
console.log("I'm not hungry");















>
🚩Control Flow 🔓 Conditional Statements 🔑 If and Else

🎯 Try this!
🔑 Switch and Case
Print out the choice that you / the user input using a switch case.
let choice;switch (choice){ case 'A':
console.log('I chose A');
break;
case 'B':
console.log('I chose B');
break;
case 'C':
console.log('I chose C');
break;
default:
console.log('Please make a choice');
}















🚩Control Flow 🔓 Conditional Statements

I have strawberries, mango, durian. I want the application to print out "I Love Strawberries!" if I choose A , and mango if i choose B, vice versa.
🎯 Exercise
let choice;
switch (choice){
case 'A'
console.log("I LOVE Strawberries!");
break;
case 'B'
console.log("I LOVE Mango!");
break;
case 'C'
console.log("I LOVE Durian!");
break;
default:
console.log("Please make a choice.");
}
















🚩Control Flow 🔓 Conditional Statements
if (choice === 'A'){
console.log('I chose A');
}
else if (choice === 'B'){
console.log('I chose B');
}
else (choice === 'C'){
console.log('I chose C');
}
else{
console.log('Please make a choice');
If and else vs Switch and Case
let choice;
switch (choice){
case 'A':
console.log('I chose A');
break;
case 'B':
console.log('I chose B');
break;
case 'C':
console.log('I chose C');
break;
default:
console.log('Please make a choice');
}if (choice === 'A'){
console.log('I chose A');
}
else if (choice === 'B'){
console.log('I chose B');
}
else (choice === 'C'){
console.log('I chose C');
}
else{
console.log('Please make a choice');
































🚩Control Flow
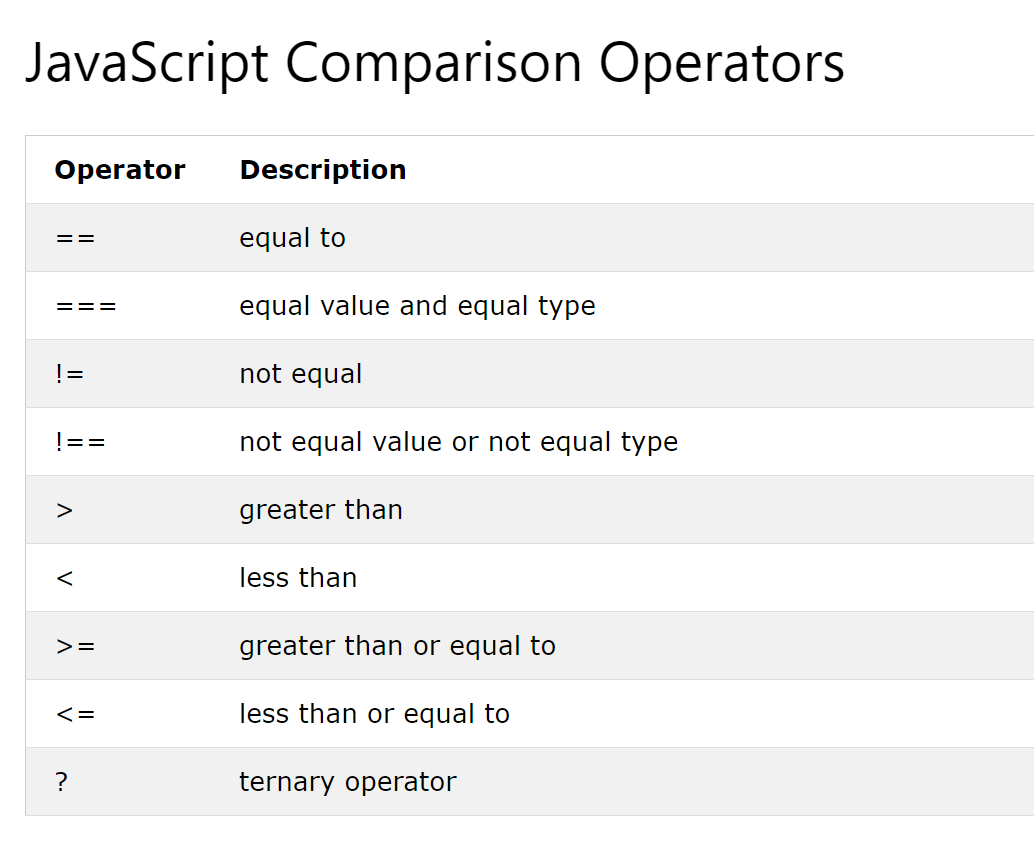
🔓 Comparison Operators

















🚩Control Flow
🔓 Loops

🔑 While Loop
















>
🔑 For Loop
🚩Control Flow 🔓 Conditional Statements

To repeat the action stated in the { }
- While
- For
Example:
Example:
while (condition) {
// code block to be executed
}let counter = 0
while(counter < 5){
console.log('Hi');
counter ++;
}for (statement 1; statement 2; statement 3) {
// code block to be executed
}for ( let counter = 0; counter <=5; counter ++ ){
console.log('HI');
}



>
🚩Control Flow 🔓 Loops

To simplify my work
🔑While Loop
let count = 1;
while(count <=100){
console.log("I Love WebLaunch!");
count ++;
}















>
🚩Control Flow 🔓 Loops

🔑For Loop
for (let count = 1; count <=100; count ++){
console.log('I love WebLaunch!');
}















🚩Control Flow 🔓 Loops

















🚩Control Flow
🔓 Object
Has characteristics and behaviour

A person has :
let name = 'Cheong';
let age = 18;
let dob = '01/01/2002';✔️ Create an Object
let person = {
name: 'Cheong',
age: 18,
dob: '01/01/2002'
};



>
🚩Control Flow 🔓 Object
✔️ To print properties and values of an object
✔️ To print the properties of an object
for (let properties in person ){
console.log(properties);
}for (let properties in person ){
console.log(properties,person[properties]);
}
















🚩Control Flow 🔓 Object

















🚩Control Flow
🔓 Array ( Continue )

Print the items in the array using for loop:
const colours = ['red','orange','yellow','green','blue','indigo','purple'];for (let count = 0; count < colours.length; count ++){
console.log(colours[count]);
}



🚩Control Flow 🔓 Array ( continue )

Handling of data (2)
(In a cooler way!)





















🚩Control Flow
🔓 Function
Me doing lazy work hehe 🤭

A block of code designed to perform a particular task.
function name_of_function (parameters){
//code to be executed
}function greet (name){
alert("Hi, " + name);
}















🚩Control Flow 🔓 Function

❗ Document Object Model
( The reason why we learn JavaScript )

Select the "Object" in the document
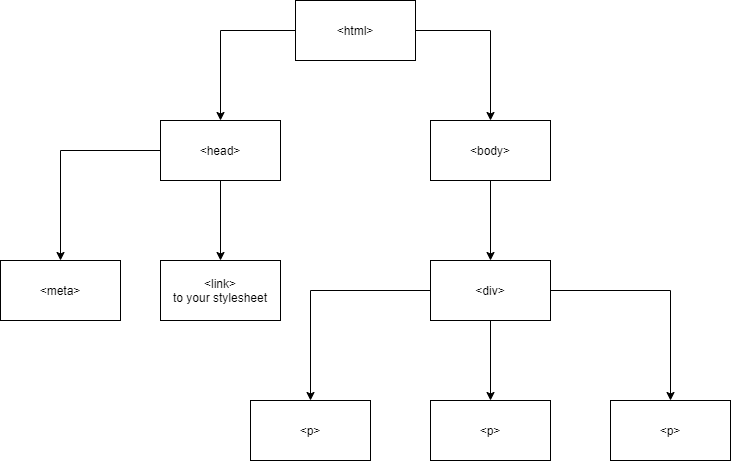
















>

Types of operation
CRUD:
- Create
- Read
- Update
- Delete

















Read ( or get ) the HTML Element
















>

Ways we can do
document.getElementById
document.getElementsByTagName
document.getElementsByClassName
































>

Ways we can do (Better!)
🌟document.querySelector🌟

















Create new HTML Element!
document.createElement

















Update HTML Element!
<element>.style.width = "500px";

















Delete HTML Element!
document.removeChild

















🚩 Basics of JavaScript
Control Flow 🚩
🎯 Exercise
🔓 Variables 🔓 Constant 🔓 Primitive Types 🔓 Array 🔓 Arithmetic Operator
Conditional Statements: 🔓
If Else 🔑
Switch Case 🔑
Comparison Operators 🔓
Loops: 🔓
While 🔑
For 🔑
Object 🔓
Array🔓
Function🔓
















🚩 How to write JS in HTML

🎯 Exercise

















Create a function named sum, that will return the total,that was calculated by adding the numbers within the range of the value stated, that are divisible by either 3 or 5.
🎯 Exercise 1
For instance:
sum(5)
Output:
8
Output = 3 + 5
within 0 to 5 only 3 and 5 are divisible by 3 or 5



>
Create a function named sum, that will return the total,that was calculated by adding the numbers within the range of the value stated, that are divisible by either 3 or 5.
🎯 Exercise 1 ( Answer )
function sum (num){
let total = 0;
for (let count = 0; count <= num; count++)
if (count%3===0 ||count%5===0)
total += count;
return total;
}

















Create a button that will add a new text node when it is clicked.
🎯 Exercise 2





🎯 Exercise 2 ( Answer )




<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="favicon.png" />
<title>WebLaunch 2020 : JavaScript</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>
Welcome to Sunway Tech Club WebLaunch 2020 JavaScript Workshop
</h1>
<div id="content">
<p>This is the first line.</p> <br />
<p>This is the second line.</p> <br />
</div>
<p id="change">Change me to something else please /.\</p>
<script>
function add(){
let new_text_node = document.createTextNode("I am new text node");
document.querySelector("#content").appendChild(new_text_node);
}
<script/>
<button onclick="add();">Don't Click Me</button>
</body>
</html>
🎌🏁 Completed 🏁🎌
🎉Congratulations 🎊
You have
the basics of JavaScript!


















Next Proceed to :
JavaScript Hands on
Link :

























