Data Structures
Wang Chien-Chieh - @jf423

Components
Graph
Sort
Queue
Tree
Hash
Set
Linked List
Stack
Reference
Stack
Last-In-First-Out
Push & Pop
Top & IsEmpty & getSize
Ex: Call Stack, Undo & Redo, Parsing
Push
Pop
Example: Call Stack
Ref:
* The JS Call Stack Explained In 9 Minutes (Video)
* Pointers and dynamic memory - stack vs heap (Video)
* Learn event loop, stack, queue, and concurrency mode of JavaScript in depth (Article)
Implementation
class ArrayStack {
constructor() {
this.data = new Array(20);
this.size = 0;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size === 0;
}
getSize() {
return this.size;
}
push(value) {
if (this.size === this.data.length) {
this.double()
}
this.data[this.size] = value;
this.size++;
}
pop() {
const result = this.data[this.size - 1];
this.data[this.size - 1] = null;
this.size--;
return result;
}
top() {
return this.data[this.size - 1];
}
double() {
let data = new Array(this.data.length * 2)
for (let i = 0; i < this.data.length; i++) {
data[i] = this.data[i]
}
this.data = data
}
}Stack with Array
Push & Pop (JS Native)
Implementation
Stack with Linked List
class LinkedStack {
constructor() {
this.top = null;
this.size = 0;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.top === null;
}
getSize() {
return this.size;
}
push(value) {
const node = new StackNode(value, this.top);
this.top = node;
this.size++;
}
pop() {
const result = this.top;
this.top = this.top.next;
this.size--;
return result.data;
}
top() {
return this.top.data;
}
}class StackNode {
constructor(data, next) {
this.data = data
this.next = next
}
}Q: Min Stack
Design a stack that supports push, pop, top, and retrieving the minimum element in constant time.
- push(x) -- Push element x onto stack.
- pop() -- Removes the element on top of the stack.
- top() -- Get the top element.
- getMin() -- Retrieve the minimum element in the stack.
Given a string containing only three types of characters: '(', ')' and '*', write a function to check whether this string is valid. We define the validity of a string by these rules:
- Any left parenthesis '(' must have a corresponding right parenthesis ')'.
- Any right parenthesis ')' must have a corresponding left parenthesis '('.
- Left parenthesis '(' must go before the corresponding right parenthesis ')'.
- ' * ' could be treated as a single right parenthesis ')' or a single left parenthesis '(' or an empty string.
- An empty string is also valid.
Given a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes' values
Input: [1,null,2,3]
1
\
2
/
3
Output: [3,2,1]Example:
Queue
First-In-First-Out
Enqueue & Dequeue
IsEmpty & getSize
Ex: Scheduling, Request
Push
Pop
Example: Scheduling Queues
Ref:
* Process Scheduling (Video)
* Scheduling Queues (Video)
* Operating System - Process Scheduling (Article)
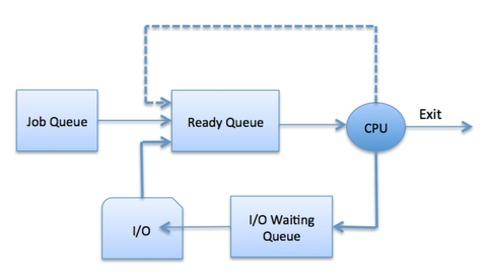
Implementation
class ArrayQueue {
constructor() {
this.queue = new Array(5)
this.capacity = 5;
this.front = -1;
this.back = -1;
}
double() {
this.capacity = this.capacity * 2;
const newQueue = new Array(this.capacity);
let j = -1;
for (let i = this.front + 1; i <= this.back; i++) {
j++;
newQueue[j] = queue[i];
}
this.front = -1;
this.back = j;
this.queue = newQueue;
}
getSize() {
return (this.back - this.front);
}
isEmpty() {
return (this.front === this.back);
}
enqueue(value) {
if (this.back + 1 === this.capacity) {
this.double();
}
this.back++;
this.queue[this.back] = value;
return value;
}
dequeue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
this.front++;
return this.queue[this.front];
}
}Queue with Array
Push & Shift (JS Native)
Implementation
class QueueNode {
constructor(data, next) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
this.size = 0;
}
}
class LinkedQueue {
constructor() {
this.front = null;
this.tail = null;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.front === null;
}
getSize() {
return this.size;
}
enqueue(value) {
const node = new QueueNode(value);
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this.front = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = node;
}
this.size++;
}
dequeue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
const result = this.front.data;
if (this.front === this.tail) {
this.front = null;
this.tail = null;
} else {
this.front = this.front.next;
}
this.size--;
return result;
}
}Queue with Linked List
Design your implementation of the circular queue. The circular queue is a linear data structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First Out) principle and the last position is connected back to the first position to make a circle. It is also called "Ring Buffer".
- MyCircularQueue(k): Constructor, set the size of the queue to be k.
- Front: Get the front item from the queue. If the queue is empty, return -1.
- Rear: Get the last item from the queue. If the queue is empty, return -1.
- enQueue(value): Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful.
- deQueue(): Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful.
- isEmpty(): Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not.
- isFull(): Checks whether the circular queue is full or not.
Given a positive integer n, find the least number of perfect square numbers (for example, 1, 4, 9, 16, ...) which sum to n
Example 1:
Input: n = 12
Output: 3
Explanation: 12 = 4 + 4 + 4.Input: n = 13
Output: 2
Explanation: 13 = 4 + 9.Example 2:
There are N rooms and you start in room 0. Each room has a distinct number in 0, 1, 2, ..., N-1, and each room may have some keys to access the next room.
Formally, each room i has a list of keys rooms[i], and each key rooms[i][j] is an integer in [0, 1, ..., N-1] where N = rooms.length. A key rooms[i][j] = v opens the room with number v.
Example :
Input: [[1],[2],[3],[]]
Output: true
Explanation:
We start in room 0, and pick up key 1.
We then go to room 1, and pick up key 2.
We then go to room 2, and pick up key 3.
We then go to room 3. Since we were able to go to every room, we return true.Initially, all the rooms start locked (except for room 0).
You can walk back and forth between rooms freely.
Return true if and only if you can enter every room.
# Event Loop
Loop
Web API
Task Queue
Call Stack