COMP2511
25T3 Week 1
Slides by Christian Tolentino (z5420628)
Tuesday 10AM - 1PM (T10C)
Introduction
- My name is Christian
- 4th Year Adv. Computer Science (Honours) student
- Industry experience: Interned @ Atlassian & Mastercard & Splunk
- Email: z5420628@ad.unsw.edu.au (Please try using the forums before emailing me, unless its for a personal reason)
- Include your zID somewhere so I can easily identify you
- Prefix your email's title with 2511-[CLASSNAME] (e.g., 2511-W14A)
- Course email: cs2511@cse.unsw.edu.au
- Don't like how something is handled? You're welcome to escalate it to course admins. (Do talk to me first if possible).
Today
- General Tutorial/Lab Introduction
- Design Problem
- Java Syntax
- Object-Oriented Paradigm
- Abstraction
How will it work?
- 1 hour tutorial, 2 hour lab
- Tutorial: Tutorial questions that go over recent lecture topics
- Lab: Lab exercises & marking, assignment and general help
- Slides: Via email
- Coursework: 15% (from your Course Outline)
- Lab exercises (Must be marked within 2 weeks of it being due)
- i.e., you cannot get lab01 marked off in week 10 unless you have a valid excuse (it will incur a penalty e.g. capped at half or 0) (see course outline)
- Course revamped! Second half the course used to go over more object-oriented design patterns but will focus on software design and architecture (designing for real-life systems and applications)
- Lab exercises (Must be marked within 2 weeks of it being due)
My Suggestions
- Make sure you are keeping up with lecture content
- Read your course outline.
- Plan out your term, COMP2511 can take up a lot of time!
- Please start assignments/projects early! (Looking at assignment 1)
- Ask lots of questions
- Prepare to learn how to read documentation & google on your own
Ice Breaker
- Name (and preferred name)
- Degree
- Favourite emoji or favourite chip flavour
Solving Design Problems
- Design Problem: UNSW has decided that they want to create their own light rail, which takes students from upper campus to lower campus. Design a solution for this - how will it work? What will need to be changed about the campus layout for it to work?

Git
Git Revision
-
git add- Stage files
-
git commit- Commit the staged files as a snapshot
-
git push- Push your new commits to an online origin (GitLab, BitBucket, GitHub)
-
git status- State of current repository & branch
-
git log- History of current branch
-
git checkout
- Change to a different branch
Git Config
When you commit something, you are effectively saving the staged files as a new snapshot and signing it with your name and email.
You have to configure your git identity if you haven't done it before.
git config --global user.name "Your Name Here"
git config --global user.email "z555555@unsw.edu.au"You then can add whatever email you have set in user.email on GitLab, so that it recognises all the commits that have been pushed to GitLab.
Please do this, its important Git etiquette.
It also allows your tutor to track the work you have done in your pair assignment.
Differences between Java, C, Python, JS/TS
- Syntax
- C, Java, JS/TS use
{and}to describe code blocks (also scopes) - Python uses whitespaces (tabs/indentations)
- C, Java, JS/TS use
- Classes:
- Java, Python, JS/TS support Object Oriented programming (OOP)
- Supports classes and inheritance
- C does not support classes. Closest things are pure 'data classes' called structs
- All code within Java needs to exist within a class
- JS/TS and Python can have runnable code outside classes
- Java, Python, JS/TS support Object Oriented programming (OOP)
Differences between Java, C, Python
- Types:
- Java, C and TypeScript are statically typed
- Python and JavaScript are dynamically typed
- Memory:
- C allows you to manually allocate memory
- Java, Python, JS/TS have automatic memory management
- Compilation vs Interpretation
- C compiles into machine code
- Python compiles into byte code, which is interpreted
- TypeScript transpiles to JavaScript which is then interpreted
- Java both compiles into byte code and is interpreted (on a VM)
VSCode Config Tips
Ensure that you open the correct folder
example: cs2511-project
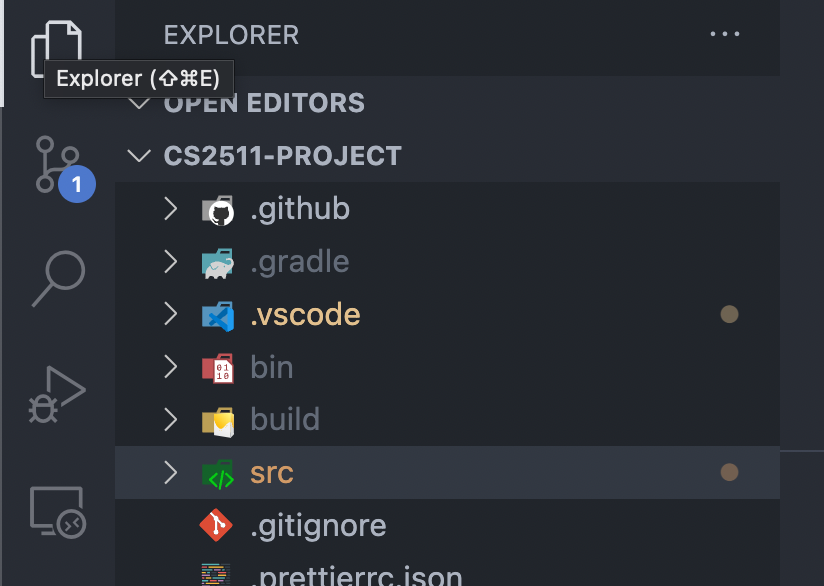
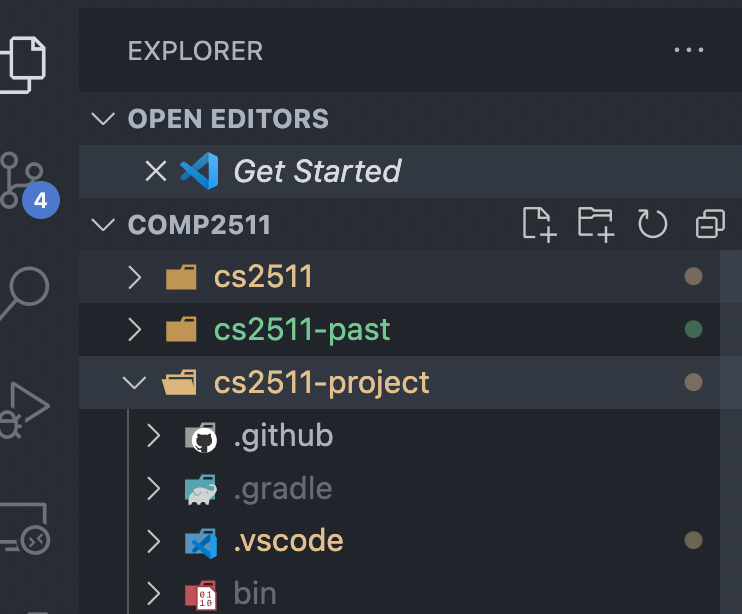
Good
Bad
Name of folder open
The folder I want to actually open
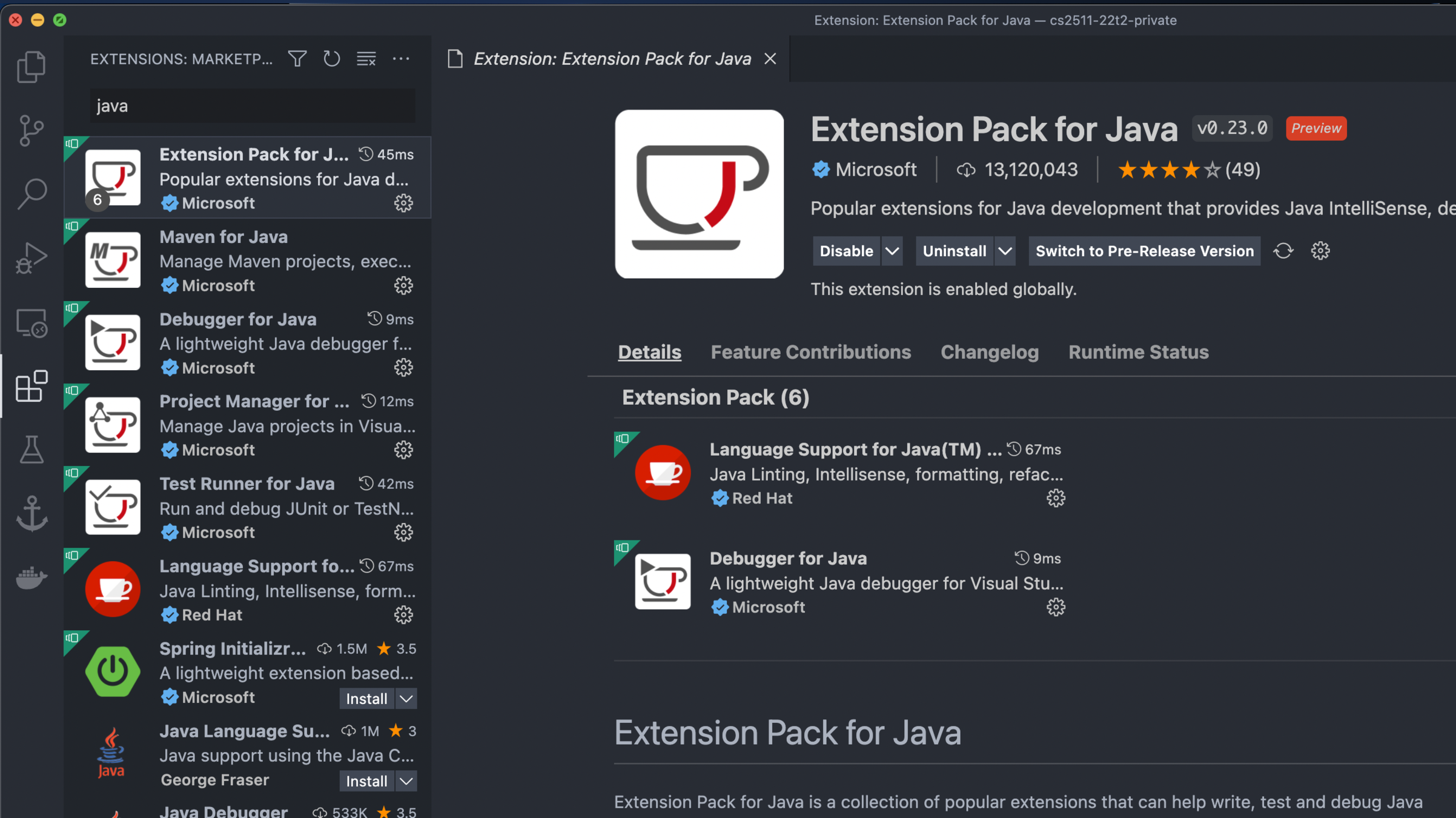
VSCode Config Tips
Ensure you have the correct Java extension installed
VSCode Config Tips
Ensure that you are running code using the "Run" button
Always use this to run code in this course
Code Demo
HelloWorld.java
Code Demo
Make a simple Java program that prints "Hello World" in the HelloWorld class.
Code Demo
package example;
/**
* Prints "Hello World" to the console.
*/
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Does it need a \n?
// No, .println appends a \n to your string when it prints
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
Code Demo
Sum.java
Code Demo
Inside a new file called Sum.java, write a program that uses the Scanner class which reads in a line of numbers separated by spaces, and sums them.
package example;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* Write a program that uses the `Scanner` class
* which reads in a line of numbers separated by spaces,
* and sums them.
*/
public class Sum {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* new - Creates a new Scanner object. (Think of it like C Malloc, but Java's
* garbage collection frees it)
* Scanner is an object that allows us to specify an input
* System.in == stdin in C
*/
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
/**
* Keeps reading input until it sees a \n
*
* Splits each string into an array of strings
*/
String[] numbers = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
int sum = 0;
for (String number : numbers) {
sum += Integer.parseInt(number);
}
System.out.println("The sum is " + sum);
// Advanced
// Using streams
int streamSum = Arrays.asList(numbers).stream().mapToInt(x -> Integer.parseInt(x)).sum();
System.out.println(String.format("The sum is %d", streamSum));
/**
* Frees I/O resources
* Java's garbage collector only manages memory, not other resources
*/
scanner.close();
}
}
Why Classes?
Why do we use classes?
Ignoring OOP, Inheritance, Polymorphism, classes are useful for:
- Grouping "global variables" together
- Group relevant functions together
- Scoping of variables/functions
- Data hiding
Code Demo
Shouter.java
Code Demo
Inside a new file Shouter.java, Write a program that stores a message and has methods for getting the message, updating the message and printing it out in all caps. Write a main() method for testing this class.
package example;
public class Shouter {
private String message;
public Shouter(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String getMessage() {
// NOTE: You don't have to use the keyword `this`
// But I use it because of clarity
return this.message;
}
public void setMessage(String newMessage) {
this.message = newMessage;
}
public String toString() {
return String.format("Shouter message = %s", this.message);
}
public void printMe() {
System.out.println(this.message);
}
public void shout() {
System.out.println(this.message.toUpperCase());
}
public void printAndShout() {
// NOTE: You don't have to use the keyword `this`
// But I use it because of clarity
this.printMe();
this.shout();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shouter s = new Shouter("This is my message");
s.printMe();
s.shout();
// When printing objects, Java will try and stringify
// In this case, it calls the .toString() method
System.out.println(s);
}
}
Abstraction
- The process of hiding certain characteristics of things to draw attention to more important things
- Examples of abstraction:
- Don't need to know how a car works to drive one.
- Name some more!