Detailed table of contents 2/4
New features
Named arguments
Attributes
DOM living standards APIs
Cryptographic Message Syntax (CMS) (RFC 5652) support
Weak map
Detailed table of contents 3/4
New functions
match
str_contains
str_starts_with
str_ends_with
fdiv
get_resource_id
preg_last_error_msg
Detailed table of contents 4/4
Them Changes
Trailing comma in parameters list
Catch structure changes
Throw as an expression
array sorting functions are now stable
PhpTokenClass
Create Datetime From Interface
ext-json
Validation for abstract trait methods
PhpToken::getAll( )
2021 schedule, according to Gabriel Caruso
PHP 7.2 won't be supported anymore
Only security fixes will be applied to PHP 7.3
PHP 7.4 and PHP 8.0 will remained supported
PART III
JIT
NEW FEATURES
Release schedule
Them Changes
New functions
NEW FEATURES / ATTRIBUTES
Once called annotations, ATTRIBUTES carry metadata for classes, properties or methods.
ATTRIBUTES are usually introduced in docblocks with an @
With PHP 8.0, they are flagged with a different syntax even if their operating mode remains the same.
NEW FEATURES / ATTRIBUTES
PhpStorm 2020.3 suggests its own built-in Attributes (such as #[Deprecated, #[Pure] or #[Immutable]).
Learn more in this article.
REFLECTION API IMPROVEMENTS
NEW FEATURES / ATTRIBUTES
To access the Attributes info, a few changes have been added to the Reflection API.
For example, the function `getAttributes( )` retrieves the names and data of the Attributes associated with an object, a method, etc.
PART IV
JIT
New features
Release schedule
NEW FUNCTIONS
Them Changes
NEW FUNCTIONS / MATCH
SWITCH statements have been criticized for their tricky structure and their lack of flexibility.
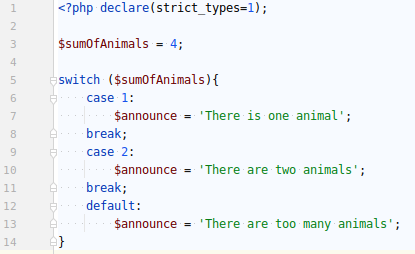
MATCH is an alternative to SWITCH (SWITCH is still available). Results can be stored in variables. "Breaks" have been removed and "cases" have been replaced with arrow operators.
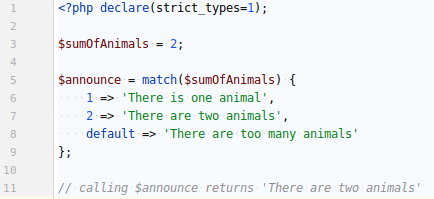
NEW FUNCTIONS / MATCH
MATCH structure is lighter and flexible. It is now possible to suggest multiple values and separate them with a comma.
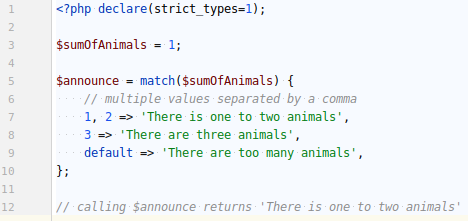
NEW FUNCTIONS / MATCH
MATCH doesn't require a default option.
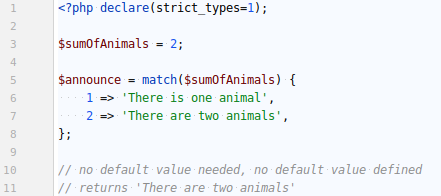
NEW FUNCTIONS / MATCH
However if the input that we seek to compare has no "match" (hehe) and the MATCH statement has no default option, it triggers an error.
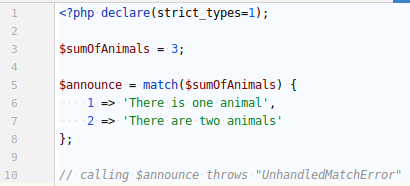
NEW FUNCTIONS / MATCH
SWITCH allows large comparisons...
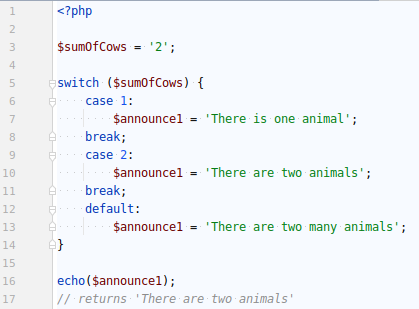
Unnecessary directive "strict-type" has been removed to avoid confusion
Switch operates a large comparison :
'2' == 2 is true.
NEW FUNCTIONS / MATCH
... whereas MATCH operates strict ones.
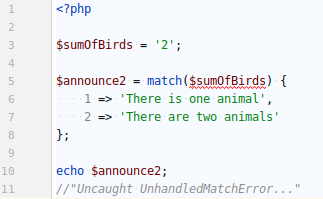
Match operates a strict comparison :
'2' === 2 is false
An UnhandledMatchError exception is thrown
NEW FUNCTIONS / MATCH
NEW FUNCTIONS / STR_CONTAINS
`STR_CONTAINS( )` checks if a string contains a given substring.
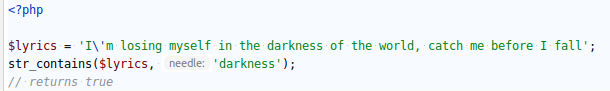
The comparison is case-sensitive.
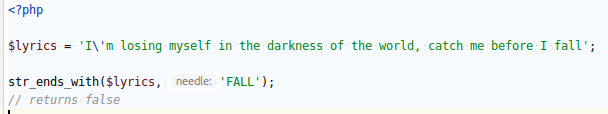
NEW FUNCTIONS /STR_STARTS_WITH
`STR_STARTS_WITH( )` checks if a string starts with a given substring.
The comparison is case-sensitive.
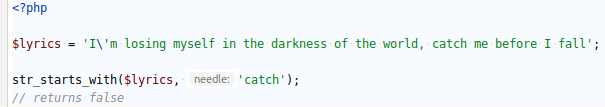
NEW FUNCTIONS / STR_ENDS_WITH
`STR_ENDS_WITH( )` checks if a string ends with a given substring.
The comparison is case-sensitive.
NEW FUNCTIONS / FDIV
Dividing any int or float by zero used to be forbidden. It'd throw a `DivisionByZeroError`, whether we use `/`, `%`, `intdiv( )` or ` fmod( )`.
The new `FDIV( )` function works as the division operator.
But its advantage is that it allows the division of any int or float by zero. It doesn't throw an error. It returns `INF`, `- INF` or `NAN` instead.
These output are more informative and useful for debugging.
NEW FUNCTIONS / FDIV
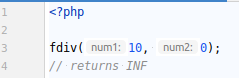
In this example, the dividend is positive, so the output is INF
When a positive number is divided by zero, the output is `INF`.
NEW FUNCTIONS / FDIV
In this example, the dividend is negative, so the output is -INF

When a negative number is divided by zero, the output is `-INF`.
NEW FUNCTIONS / FDIV
In this example, the dividend is zero, so the output is NAN.
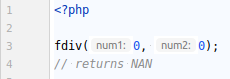
When the dividend and the divisor are zeroes, the output is `NAN`.
NEW FUNCTIONS / GET_RESOURCE_ID
RESOURCE is a PHP special type (like NULL). It designates data that are external to PHP.
There is a list of internal functions which create, use, handle or destroy resources.
For instance, the now deprecated `mysql_connect( )` function used to create a mysql link resource and open a connection to a MySQL database, whereas `mysql_close( )` (also deprecated) used to destroy the formerly created mysql link.
For more on this, see : https://www.php.net/manual/fr/resource.php
NEW FUNCTIONS / GET_RESOURCE_ID
The `get_resource_type` function, which has first been introduced with PHP 4, allows to determine a resource type.
We've also been able to retrieve the id of a given resource by casting it to an integer.
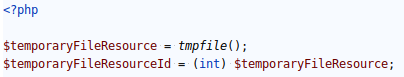
After creating a temporary file resource, we cast it to an integer to force the retrieval of its id (here, it's 4). It is not safe.
NEW FUNCTIONS / GET_RESOURCE_ID
PHP 8 introduces the `get_resource_id` function, which makes the retrieval of a resource id easier.
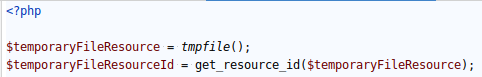
After creating a temporary file resource, we call `get_resource_id( )` in order to retrieve its id (here, it's 4... again).
NEW FUNCTIONS / PREG_LAST_ERROR_MESSAGE
There are several PCRE functions. They use regex and find occurrences within strings. They start with prefix`preg_`, like `preg_match( )`.
PCRE means Perl Compatible Regular Expression. It designates what we usually call regex, or regular expressions.
While running theses functions, errors can be spotted in the structure of regex. A list of constants and their respective codes are designed to inform on the origin of theses errors.
NEW FUNCTIONS / PREG_LAST_ERROR_MESSAGE
PHP 8 introduces `preg_last_error_message( )`, which retrieves the error message (stored in a constant such as `PREG_BACKTRACK_LIMIT`).
We can read the error code thanks to `preg_last_error( )`.
For more on this, see :
PART V
JIT
New features
Release schedule
THEM CHANGES
New functions
THEM CHANGES / THROW AS AN EXPRESSION
THROW can be used as a statement
AND as an expression.
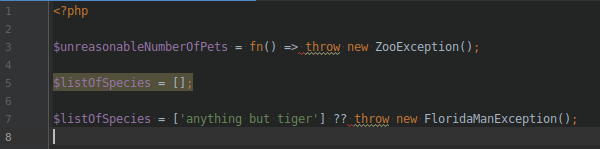
THEM CHANGES / THROW AS AN EXPRESSION
By the way, THROW can be used in MATCH statements.
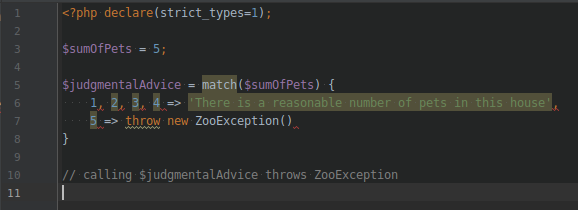
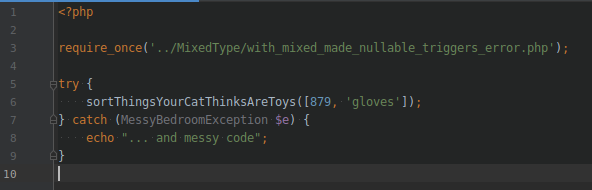
THEM CHANGES / CATCH
We used to catch errors
by storing them in an exception.
THEM CHANGES / CATCH
Now we only need to specify the type of Exception.
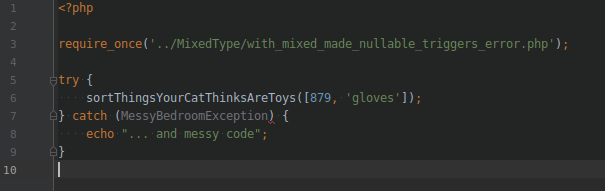
Though, if we want to catch all errors, we can use THROWABLE as the Exception type.
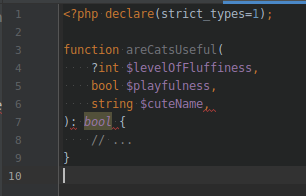
THEM CHANGES / TRAILING COMMAS IN PARAMETERS LIST
THEM CHANGES / TRAILING COMMAS IN PARAMETERS LIST
There are also supported in USE list of closures.
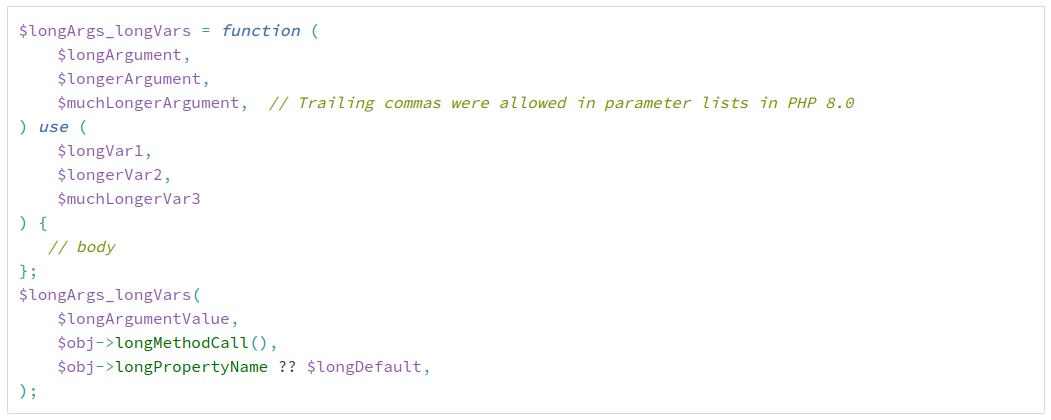
Can be added here
THEM CHANGES / CREATE DATETIME OBJECTS FROM INTERFACE
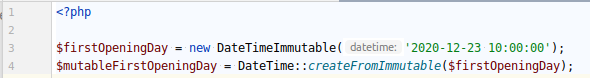
DateTime and DateTimeImmutable objects are instances of DateTimeInterface. DateTime objects are mutable, whereas DateTimeImmutable objects return a new object when a modifier is applied on them.
We can create a DateTime object from a DateTimeImmutable object.
But creating a DateTimeImmutable object from a DateTime object is complicated.
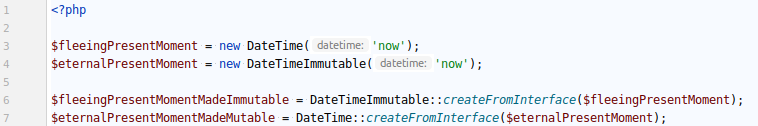
THEM CHANGES / CREATE DATETIME OBJECTS FROM INTERFACE
This is why we can know turn a Datetime object into a DatetimeImmutable object, and vice versa by implementing new static method `createFromInterface`
THEM CHANGES / EXT-JSON
In previous versions of PHP, the `ext-json` extension was optional.
But as the community use JSON format a lot, it's appeared natural to include the extension in PHP.
Starting with PHP 8, the `ext-json` extension is always available. We can disable it if needed.
THEM CHANGES / ARRAY SORTING METHODS ARE NOW STABLE
For more on this, see RFC : https://wiki.php.net/rfc/stable_sorting
THEM CHANGES / PHPTOKEN CLASS
THEM CHANGES / VALIDATION OF ABSTRACT TRAITS METHODS
THEM CHANGES / DOM LIVING STANDARD API
For more on this, see RFC : https://wiki.php.net/rfc/dom_living_standard_api