Elemente de Soft Computing
Fuzzy Evolutionary Algorithms
Ciprian Chichirita grupa 507 (I.A.)
Cuprins
-
Why
-
Fuzzy logic
-
Evolutionary algorithms (EA)
-
Fuzzy Evolutionary Algorithms
-
Fuzzy knowledge base (fuzzy government)
-
Embed fuzziness into the evolutionary algorithm
- Bibliography
Why (parameter setting)
- Evolutionary algorithms
- exploitation versus exploration
- parameter setting, big impact on performance
- Poor settings
- slow-down of the search process
- premature convergence
- When to stop
- trade-off - solution quality, time limit & other human intervention
- Solution
- Human supervisor (tailors the parameters)
- Alternative
- Adaptive evolutionary algorithm
Why (parameter setting)
-
Evolutionary algorithms parameters
- parameters are not well chosen initially for a given task
- parameters do not change through a run, even though evolutionary conditions may vary
- interactions between distinct parameters is complex and difficult to undestand
Fuzzy Logic
Fuzzy logic is a form of many-valued logic in which the truth values of variables may be any real number between 0(false) and 1(true).
Example:
True
Maybe
False
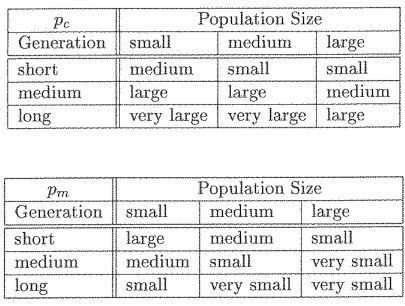
Evolutionary algorithms (EA)
In artificial intelligence, an evolutionary algorithm (EA) is a subset of evolutionary computation, a generic population-based metaheuristic optimization algorithm. An EA uses mechanisms inspired by biological evolution, such as reproduction, mutation, recombination, and selection.
Example
Step One: Generate the initial population of individuals randomly. (First generation)
Step Two: Evaluate the fitness of each individual in that population (time limit, sufficient fitness achieved, etc.)
Step Three: Repeat the following regenerational steps until termination:
Select the best-fit individuals for reproduction. (Parents)
Breed new individuals through crossover and mutation operations to give birth to offspring.
Evaluate the individual fitness of new individuals.
Replace least-fit population with new individuals.
Fuzzy[Adaptive] Evolutionary Algorithms
-
Fuzzy knowledge base (fuzzy government)
-
Embed fuzziness into the evolutionary algorithm
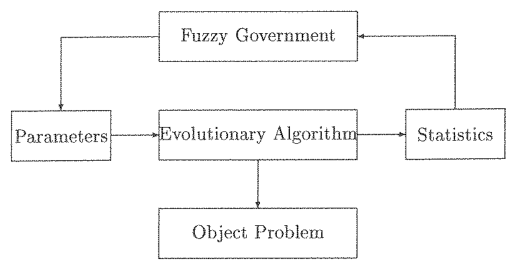
Fuzzy knowledge base (fuzzy government)
-
fuzzy knowledge base (fuzzy government) - detect the emergence of a solution, dynamically tune algorithm parameters and monitor the evolutionary process to avoid undesired behaviors such as premature convergence.
Embed fuzziness into the evolutionary algorithm
-
Embed fuzziness into the evolutionary algorithm itself. For instance, some precision in the calculation of fitness could be sacrificed to save computational resources by defining a fuzzy fitness, or even fuzzy alleles for genes, thus fuzzifying also genetic operators.
Fuzzy[Adaptive] Evolutionary Algorithms

Fuzzy Goverment - collection of fuzzy rules and routines in charge of controlling the evolution of a population, detecting the emergence of a solution, tuning algorithm parameters "on flight" and avoiding undesirable behaviors such as premature convergence
Fuzzy[Adaptive] Evolutionary Algorithms

Statistics - can be divided into two classes: genotypic statistics, which summarize aspects related to the genotypes of individuals in a population, regardless of their meaning when decoded, and phenotypic statistics, which concern properties of individual performance for the problem at hand, or fitness.
Fuzzy[Adaptive] Evolutionary Algorithms

Parameters (C.P.) - outputs of the fuzzy government may be directly control parameter values or changes in these parameters. C.P. may be the usual parameters of an evolutionary algorithm (population size, mutations and crossover rate, selection pressure).
Fuzzy[Adaptive] Evolutionary Algorithms
- Automatic learning
- A genetic algorithm runs on top of the evolutionary algorithm to be controlled, whose individuals encode possible fuzzy governments for the object evolutionary algorithm
- Co-evolution with a Fuzzy Government
- An alternative approach to writing a fuzzy government or learning it once and for all using a set of test problems as a benchmark for evolutionary algorithm performance is to have the fuzzy government co-evolve along with the solution to the object problem
Fuzzy[Adaptive] Evolutionary Algorithms
- Fuzzy Fitness (Embed fuzziness)
- In some applications, it is hard to asses the quality of candidate solutions with precision (ex: a solution is tested against an infinite number of cases and fitness is the function of the scores obtained in each test).
- Recombination Operators Based on Fuzzy Connectives
Multumesc!
Bibliografie
- Wikipedia
- Soft Computing (Andreea Tettamanzi, Marco Tomassini)