According to RTU Syllabus
SURVEYING-I
UNIT-2
PART-1

Measurement of Angles and direction
- Different types of direction measuring instruments and their uses.
- Reference Meridians.
- Bearings and Azimuths.
- Magnetic Declination and its Variation.
- Use and adjustment of Surveyors and Prismatic Compass.
- Vernier and MIcro-optic Theodolite
- Temporary and Permanent adjustment of Vernier Theodolite.
- Measurement of the Horizontal and Vertical angle by different methods.
- Application of Theodolite in field Problems.
Syllabus of Unit-2
Different types of direction Measuring instruments and their uses.
Compass - used for horizontal angle measurements
Theodolite - used for horizontal and vertical angle measurements
Reference Meridians
A direction of survey line can be defined in two ways-
1. Relative to each other
2. Relative to some fixed reference direction
In surveying, this fixed reference direction is called as Meridian
Types of Meridian-
There are 4 types of meridians used in surveying-
- True Meridian
- Magnetic Meridian
- Grid Meridian
- Arbitrary Meridian
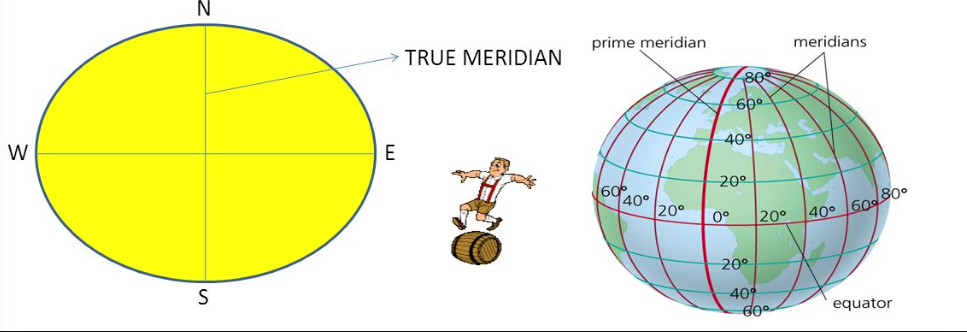
TRUE MERIDIAN
True meridian is a line which passes through a given point and the geographical north and south poles.
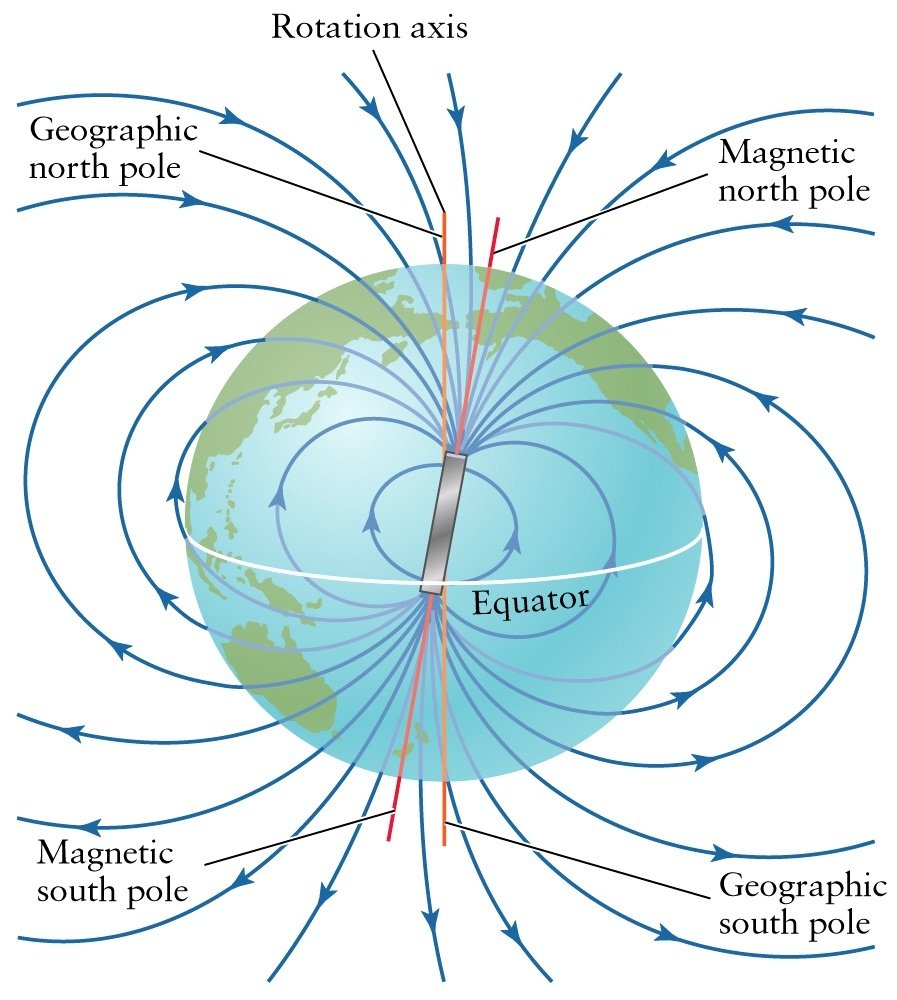
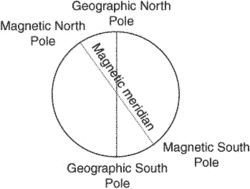
MAGNETIC MERIDIAN
Magnetic Meridian at a point
GRID MERIDIAN
For the survey of a country, the true meridian passing through the central place is called as Grid meridian.
ARBITRARY MERIDIAN
It is the meridian which is taken in any convenient arbitrary direction.
Ex-top of the chimney, church spire or the first traverse line etc.
BEARING OR AZIMUTH
It is the horizontal angle which it makes with reference line i.e. Meridian
Types of Bearings-
- True Bearing
- Magnetic Bearing
- Grid Bearing
- Arbitrary Bearing
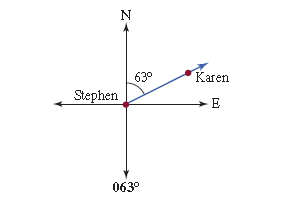
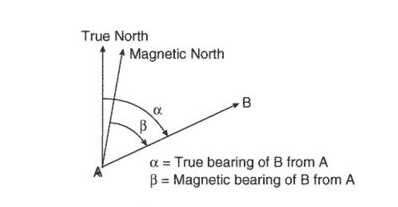
True Bearing
It is the horizontal angle between the true meridian and the line.
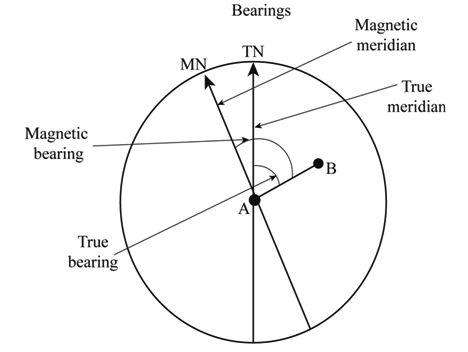
Magnetic Bearing
It is the horizontal angle between the magnetic meridian and the line.
Grid Bearing
- It is the horizontal angle between the grid meridian and the line.
Arbitrary Bearing
- It is the horizontal angle between the arbitrary meridian and the line.
ADITI SHARMA
Traversing
Different Methods of Traversing :
Chain Traverse
Chain and Compass Traverse
Transit tape Traverse
Methods of Computation and Adjustment of Traverse :
Transit Rule
Bowditch Rule
Graphical Method
Axis Method
Gales Traverse Table
Levelling
Definition of Various Terms in Levelling
Different types of Levelling
Sources of Errors in levelling
Curvature and Refraction Corrections
Temporary and Permanent Adjustment of Dumpy and Tilting Levels
Computation and adjustment of Levels
Profile
Plane Table Surveying
Elements of Plane Table Survey Working Operations
Methods of Plane Table Survey :
Intersection
Traversing
Resection
Two
Contouring
Characteristics of Contours
Contour Interval
Contour Gradient
Methods of Locating Contours
Uses of
Methods of
Axis Signal Corrections
Determination of Difference in Elevations of Points.
Curve Surveying
Elements of Circular(Simple
Transition Curves
Degree of Curves
Methods of setting out circular and transition curves
Triangulation
Merits and Demerits of Traversing
Triangulation and Trilateration
Grades of Triangulation
Strength of Figure
Field Procedure of Triangulation
Reconnaissance and Selection of Triangulation Stations
Intervisibility of Stations and calculation of the height of towers.
Equipment Needed for base line measurement
Corrections to
Satellite Station and
Errors in Surveying
Classification of Errors in Surveying
Probability curve
Its equation and properties
Theory of Least Squares
Weight
Most Probable value
Probable Errors
Standard Errors
Normal Equation Correlates
Adjustment of Triangulation Figures:
Adjustment of levels
Adjustment of Triangulation Figures
Braced Quadrilateral triangle with
Approximate and Method Of least squares for figure Adjustment
Trilateration
Field Astronomy
Definition of
Co-ordinate Systems
Relationships between different Co-ordinate Systems.
Astronomical Triangle
Napier's Rule
Different Methods of Determination of Azimuth
Electronic Distance measurement and use of Total Station