SURVEYING - I
UNIT-1
PART-1
According to RTU syllabus

Syllabus of Unit-1
Introduction:
- Importance of surveying to Engineers,
- Plane and geodetic surveying,
- Methods of
location of points, -
Principle of surveying from whole to part, - Conventional sign.
Measurement of Distances:
- Different types of chain,
- Tapes and their uses,
- Sources of Errors and precautions,
- Correction to tape measurements,
- Field problems in distance measurement
Surveying Definition:
Surveying is an art of determining the relative positions of points on, above and below the surface of earth and presenting it graphically and numerically.
Importance of Surveying to Engineers:
- To determine relative position of points.
- To layout proposed structure on the ground.
- To measure relative quantities like area and volume.
Classification of Surveying:
Plane Surveying
Geodetic Surveying
- we neglect the effect of
curvature of Earth's surface - It is done for small area i.e.area less than 195.5 km^2
- It is done for local surveys.
- Plane
trignometry is used.
- we consider the effect of
curvature of Earth's surface. - It is done for large area i.e. area greater than 195.5 km^2
- It is done to establish control points which
serves the purpose ofreference point forlocal survey. - spherical
trignometry is used
Text
- oblate spheroid
- ellipsoid
ovaloid - new name given: GEOID
For area
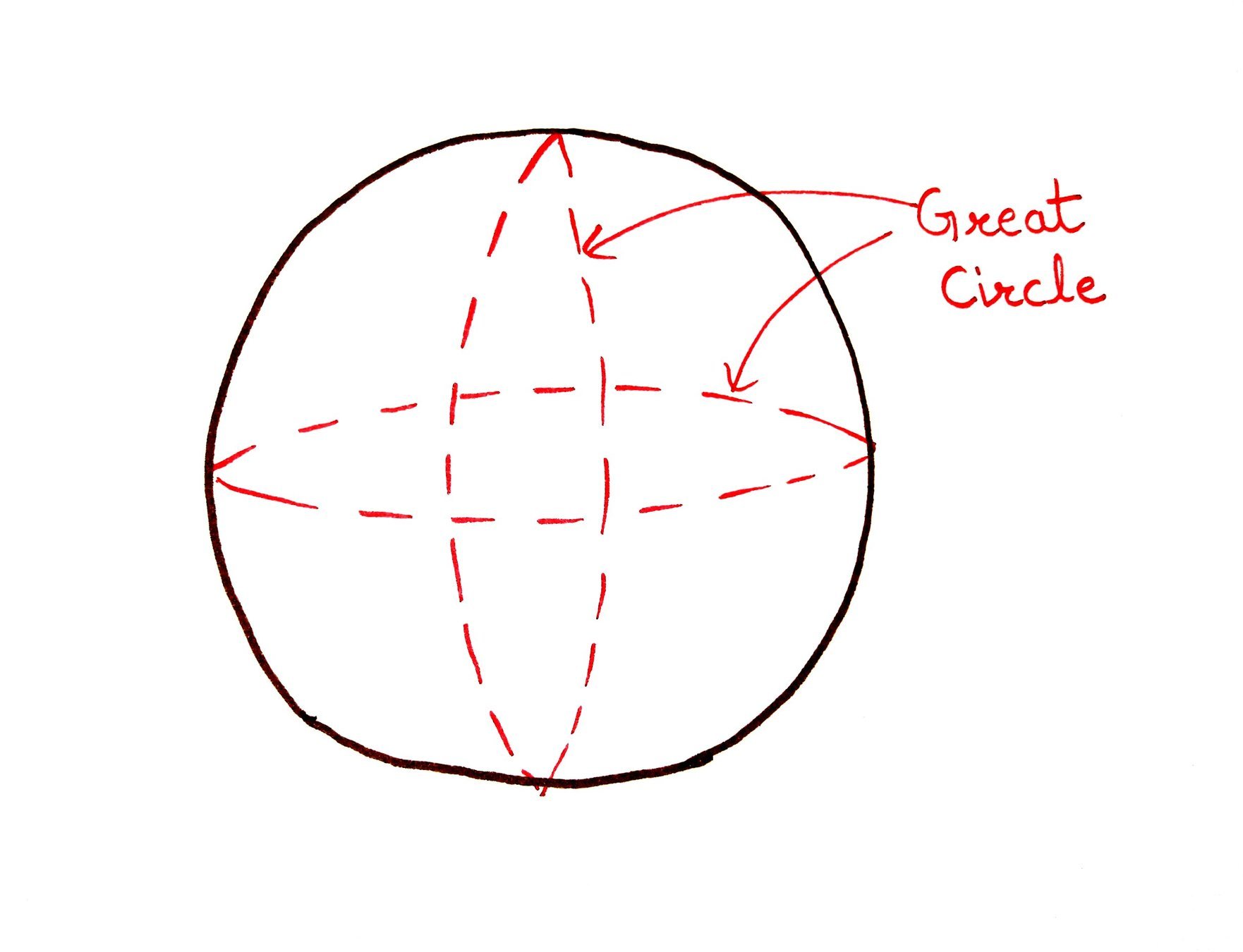
Great Circle:
- It is an imaginary circle passing through the
center of Earth. - A great circle divides the earth into two equal parts.
Spherical Triangle:
A spherical traingle is that triangle which is formed on the surface of a sphere by intersection of three arcs of great circle.
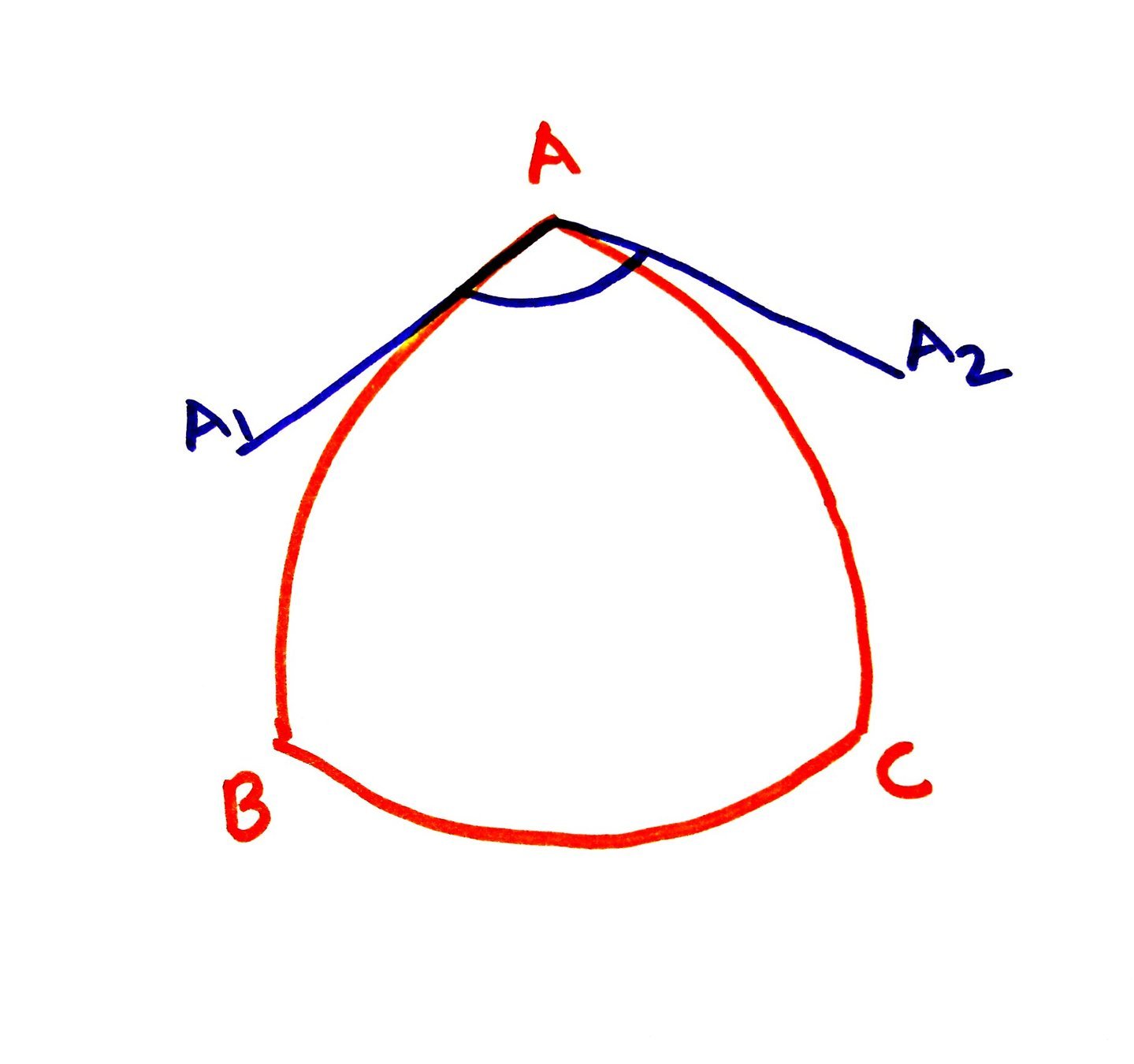
Spherical angle:
Spherical angle is defined as the angle between tangents to the great circle drawn at a point of intersection i..e. angle A1 A A2.

Properties of Spherical Triangle:
- Each angle of a spherical triangle should be less
then 180°. - Sum of spherical angles should be in
range of 180°-540°.
Spherical Excess:
Amount by which the sum of the angles of a spherical triangle exceed by 180 degree is called as spherical Excess.
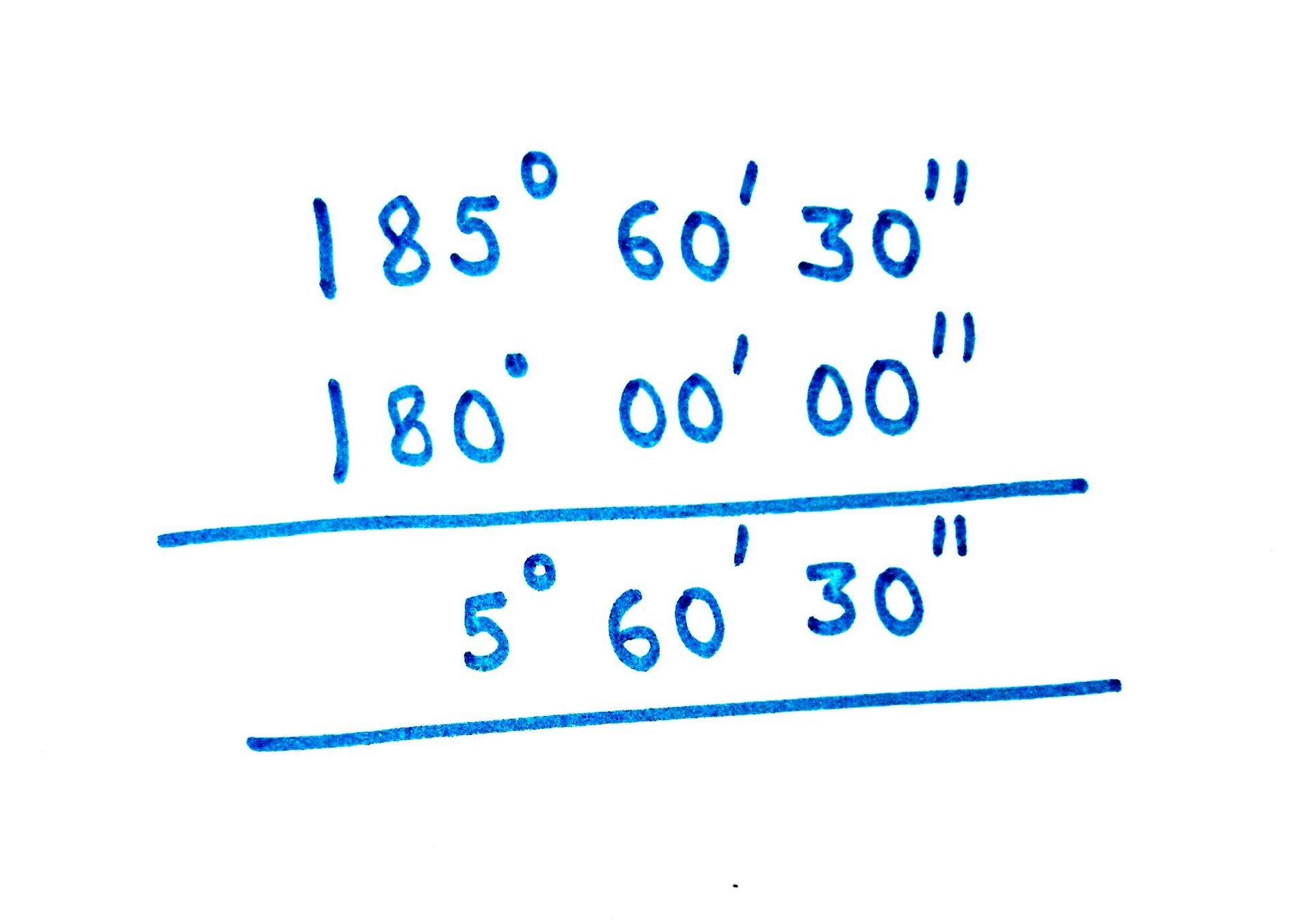
ADITI SHARMA

