According to RTU Syllabus
SURVEYING - I
Syllabus




LINEAR AND ANGULAR MEASUREMENTS
Method of Linear Measurements
- By using Chain or Tape
- By using Tachometer
- By using EDMI Instruments
Chain
- It is used for measurement of distances where very high accuracy is not required.
- Distances are measured from outside of one handle to the outside of another handle

To enable the readings of fraction of chain length without difficulty,brass tallies and rings are attached to the chain at some fixed interval.
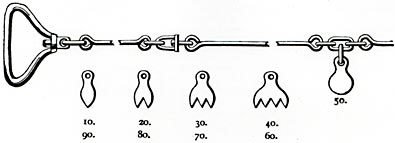
Types of chain
- Revenue chain-33 ft.long
- Gunter's chain-66 ft.long
- Engineer's chain-100 ft.long
- Metric chain-30 m(150 links) or 20 m(100 links)
Suitability of chain-
- It is suitable for rough use only.
Unsuitability of Chain-
- It sags when suspended in air.
- It is heavier.
- Length of links gets altered.
Tapes
Types of tapes-
1.Cloth or linen tape-
- It is made up of closely woven linen and is varnished to resist the moisture.
- It is available in length of 10-30m and width of 12-15 mm.
Disadvantages of cloth or linen tape-
- It is affected by moisture and gets shrunk easily.
- Its length gets changed by stretching.
- It does not remain straight in strong winds and likely to twist.

2.Metallic tape-
- It is a linen tape with brass or copper wires woven into it.
- These are available in length of 20-30m.
3.Steel tape-
- It is more accurate than metallic tape.
- They are made up of steel.


4.Invar tape-
- These are made up of an alloy of nickel(36%) and steel(64%)
- These are available in length of 30,50 and 100m and width of 6mm.
Advantages of Invar tape-
- They have a very low coefficient of thermal expansion.so they are less affected by temperature changes.
- Highly precise.
Disadvantages of Invar tape-
- It is soft hence deforms easily.
- It can not be used for ordinary works.

MISTAKES & ERRORS
Mistakes-
They are caused by carelessness or poor judgement.
ex-
- A reading of 10m is booked as 1m.
- Miscounting the no.of tape lengths. etc.
These can be revealed by taking same measurement again with same instrument.
Errors
- It does not arise due to mistake.
Errors are classified as-
- Systematic error/Cumulative error
- Random error/Accidental error/compensating error
Error = Measured value - True value
Correction = True value - Measured value
Systematic Error/Cumulative Error
- These Errors follow a definite mathematical or physical law.
- They are cumulative in nature.
e.g.-
Expansion of steel tape due to increase in temperature.
- These Errors can be checked by remeasuring the quantity by a different method using different instrument.
Random Error/Compensating Error/Accidental Error
- These are the Errors which remains after the mistakes and systematic errors are removed.
- They are random in nature.
- They are mainly caused by limitations of observer and instruments.
Aditi Sharma
Text

