專案建置[4]
C++ Struct
各位,從今天開始,要進入我們物件導向的範圍了
也就是說,我們要開始嘗試建立一個專案了!
好誒!所以我們要做什麼專案呢?
我們這學期的目標是,所有同學可以建立一個屬於自己的 Linked List 模板!
另外,在學期最後一天,我們會有一個成發的時間,到時候我們會請大家向同學簡單介紹一下自己的專案,會有獎品喔~
- 成發規則如下:
- 你可以建立任何一個C++的專案函式庫,並且用到我們上課教的東西
- 例如:加密解密函式庫、logger、json讀取函式庫之類的
- 或是你可以幫我們上課教的linked list加上一個新的功能
- 並且在最後一堂課之前,把自己的專案放到github上面
Struct
什麼是struct呢?
假設我今天要建立乘一的資料
我可能會要記錄他的身高、體重等等
像是這樣:
int height = 150;
int weight = 90;
int IQ = 10;
int EQ = 15;
long long girlfriend;可是假設我今天要記錄很多個人呢
假設我要記錄乘一、阿蘇、和田鼠的資料
int times1_height = 150;
int times1_weight = 90;
int times1_IQ = 10;
int times1_EQ = 15;
int ivanlo_height = 200;
int ivanlo_weight =60;
int ivanlo_IQ = 180;
int ivanlo_EQ = 180;
int Repkironca_height = 170;
int Repkironca_weight = 70;
int Repkironca_IQ = 180;
int Repkironca_EQ = -200;要記錄這麼多東西就太亂了
所以這時候struct就發明了
struct的中文稱為結構,可以讓你定義一種新型態的變數,其中包含多項資料
struct 從C語言裡面就有,但是有點難用
C++出現之後,除了誕生了下禮拜要教的class以外,也把這個跟他很像東西做了優化
struct people {
int height;
int weight;
int IQ;
int EQ;
};
int main() {
people times1;
times1.IQ = 10;
cout << times1.IQ << endl;
}有了struct,你就可以把好幾個變數包成同一個
現在就來詳細的講到底struct要怎麼用吧
- 定義
- 在使用struct時,一開始要先定義這一個struct
- 要注意的是,這個定義要寫在 main函數外面
- 宣告方式(記得加分號!):
struct 結構名字 { // 沒有小括號!加了小括號就變成函數了
// 裡面等著放東西
}; // 要注意這裡有一個分號
// example
struct people {
}; 2. 宣告變數
- 當我定義完一個struct之後(舉例:people)
- 我就可以宣告一個屬於此結構的變數了
- 宣告時,直接把我的結構名當作int之類的東西使用
- 例如:
struct people {
};
int main() {
people AaW;
}看到這邊,你可能還是不理解struct的到底可以幹嘛,因此我們要繼續往下介紹
Member
成員變數
struct people {
int height;
int weight;
int IQ;
int EQ;
};
int main() {
people times1;
times1.IQ = 10;
cout << times1.IQ << endl;
}回到一開始那一段程式碼
可以看到在struct的定義裡面,我們還放了一些變數
這些在struct內的變數我們就稱為成員變數
所以成員變數的作用是什麼?
- 剛剛一開始有說,struct的用途就是把多個變數包成一個
- 也就是說,每一個類別為people的變數,都包含了 height、weight、IQ、EQ這四個變數!
struct people {
int height;
int weight;
int IQ;
int EQ;
};
int main() {
people times1;
times1.IQ = 10;
cout << times1.IQ << endl;
}要怎麼使用成員變數呢?
- 一樣以剛剛的people為例
- 首先,一樣都是people建立出來的多個變數,彼此的成員變數是不同的變數,可以有獨立的值
- 簡單來說,雖然都是人,但
AaW的身高怎麼會和乘一一樣矮
- 簡單來說,雖然都是人,但
- 因此,取用成員變數時,作法為:
例如:
struct people {
int height, weight, IQ, EQ;
// 和宣告一般變數一樣,也可以這樣寫
};
people times1;
cout << times1.IQ << endl;cout << people.IQ << endl;
// 錯誤!電腦哪知道你要輸出誰的IQX
變數名.成員變數名
更多關於struct的語法補充
- 自定義型別也可以有指標變數
- 指標不熟的可以回去看鹽亞倫的大社簡報,之後會常常用到,要記熟用法喔
struct people{
int IQ, EQ;
int burned_chicken[100];
}
people AaW;
people* idiot = &AaW;
// 完全合法
- 成員變數型態不能和struct一樣,但是可以是指標
- 你沒辦法在一個people裡面再塞一個people,會無限輪迴啦
struct people{
people girlfriend; // 不合法
people* boyfriend; // 合法
// 變數名稱請忽略www
}
- 成員變數也可以是陣列、或甚至STL
更多關於struct的語法補充
-> 運算子
假設你有一個指標times1,你想要輸出他的IQ
你應該會這樣寫
cout << (*times1).IQ << endl;但是這樣有點麻煩,因此有了以下的用法,和上面完全一樣
cout << times1->IQ << endl;struct people {
double height;
double weight;
};
double BMI(people a) {
return a.weight / (a.height * a.height);
}
int main() {
people times1;
times1.height = 1.5;
times1.weight = 90;
cout << BMI(times1) << endl;
people AaW;
AaW.height = 1.8;
AaW.weight = 60;
cout << BMI(AaW) << endl;
}以下就是一個利用struct求BMI的實例
不過你會發現,像BMI這種函數,完全和people相關,有沒有辦法像成員變數一樣宣告/使用他呢?
像是 AaW.BMI()這樣?
Method
方法
方法
想要把函式寫在struct裡面? 可以!
在struct裡面的函式,我們就稱之為「member function」或「method」
透過method,
可以讓code變得更加精簡。
那method究竟要如何使用呢?
//函式寫在struct內部
struct people {
double height;
double weight;
double BMI() { //不用把自己當參數傳入
return this->weight / (this->height * this->height);
// 預設會有一個指標this指向"自己"
}
};
int main() {
people times1;
times1.height = 1.5;
times1.weight = 90;
cout << times1.BMI() << endl; //記得呼叫時前面要加名稱
}範例
可以看到第六行中,在方法函數內部,可以使用this取得自己的成員變數
但...this是甚麼?_?
剛剛在BMI的程式當中,我們希望取得這個人“自己”的身高及體重等資料
這時候C++預設有一個指標this,
會指向呼叫此方法的物件本身。
如果times1.BMI()在執行時this就會指向times1
this
但C++預設使用方法時,本來就有辦法取得自己的成員變數
所以在這裡this其實可以省略
也就是說...
範例
//函式寫在struct內部
struct people {
double height;
double weight;
double BMI() { //不用把自己當參數傳進去
return weight / (height * height); //可以省略this
}
};
int main() {
people times1;
times1.height = 1.5;
times1.weight = 90;
cout << times1.BMI() << endl; //記得呼叫時前面要加名稱
}可以看到第六行中,在方法函數內部,預設就會有辦法取得自己的成員變數
範例
//函式寫在struct外部
struct people {
double height;
double weight;
double BMI(); //要寫在外面要先宣告!
};
double people::BMI() { //一樣不用把自己當參數傳進去
return weight / (height * height);
}
int main() {
people times1;
times1.height = 1.5;
times1.weight = 90;
cout << times1.BMI() << endl; //記得呼叫時前面要加名稱
}方法函數也可以寫在外面~
這樣在寫多檔案時比較方便
但這又是之後的事了
我想傳參數...
//函式寫在struct內部
struct people {
void say(string content){ //宣告時裡面加參數
cout<<"say"<<content<<'\n';
}
};
int main() {
people times1;
times1.say("hello!"); //記得傳參數進去!
}
//say hello!
我想傳參數...
//函式寫在struct外部
struct people {
void say(string content); //宣告時裡面加參數
};
void people::say(string content) { //一樣要加參數
cout<<"say"<<content<<'\n';
}
int main() {
people times1;
times1.say("hello!"); //記得傳參數進去!
}
//say hello!
是不是很簡單啊
:: 範圍解析運算子
如果有認真上課
那你可能會想問 :: 到底是做甚麼用的?
答案是...
::可以讓電腦知道你要用的函式
是這個struct裡的這個函式
不過這個雙冒號
只有在struct、class、namespace中適用
至於這些是甚麼,歡迎參加下一堂小社課!
Constructor
and
Destructor
看看這個 struct
struct Person {
double height;
double weight;
double bmi;
int iq;
int eq;
};
int main() {
Person p;
// 初始化各屬性的值
p.height = 160.5;
p.weight = 55.2;
p.bmi = p.weight / ((p.height/100)*(p.height/100))
p.iq = 130;
p.eq = 100;
// 終於…設定完了…
return 0;
}有沒有更快的作法?
每宣告一個新的物件
都要手動設定屬性值!
建構式:一開始要做的事
struct Person {
double height;
double weight;
double bmi;
int iq;
int eq;
Person(double height, double weight) {
this->height = height;
this->weight = weight;
this->bmi = weight / ((height/100) * (height/100));
this->iq = 120;
this->eq = 100;
}
};跟 struct 同名的成員函式
沒有回傳型別
建構式,這樣用才方便
int main() {
Person p(160.5, 55.2);
cout << p.height << '\n'; // 160.5
cout << p.bmi << '\n'; // 21.4284
cout << p.iq << '\n'; // 120
return 0;
}現在一行就設定完了
蛤,寫建構式你也嫌麻煩?
更精簡的建構式
struct Person {
double height;
double weight;
double bmi;
int iq;
int eq;
Person(double height, double weight) : height(height), weight(weight), iq(120), eq(100) {
this->bmi = weight / ((height/100) * (height/100));
}
};在小括號後面放冒號
用「屬性(值)」快速設定屬性的值
解構式:資源回收守則
struct Person {
// ...
~Person() {
cout << "This person is deleted.\n";
}
};物件被刪掉、其記憶體被回收時做的事
以這個範例來說,沒什麼要做的
因為解構式通常跟「動態配置的記憶體」有關
動態配置記憶體
一般來說,程式會用到多少記憶體
(幾個變數、陣列多大)
都是事先就決定好的
這也是為什麼宣告陣列時要指定長度
如果需要額外的記憶體(如不定長度陣列)
就需要特別「申請」
new & delete
int main() {
int *p = new int(42);
cout << *p << '\n' // 42;
delete p;
return 0;
}可用 new 配置記憶體
並得到指向這塊記憶體的指標
使用 new 配置的記憶體最後要 delete
範例:不定長度陣列
int main() {
int *p = new int[1000];
// ...
delete [] p;
return 0;
}注意到 delete 後面多了一對方括號
這是為了要讓電腦知道
要解放的是一整個陣列的空間
struct 當然也可以這樣用!
int main() {
Person *p = new Person(160.5, 55.2);
cout << p->bmi << '\n' // 21.4284
delete p; // This person is deleted.
return 0;
}什麼樣的時機會這樣寫呢?
你待會就知道了
實作時間!!!
先做一點小補充
struct 裡面也可以再宣告一個struct
struct people{
struct head{
int hair_amount;
};
int body;
head myhead;
};
int main() {
// 宣告一個人,裡面就會有一個myhead
people times1;
// 要怎麼單獨宣告一個head的物件呢?
people::head single_head;
}先幫大家複習一下linked list是什麼
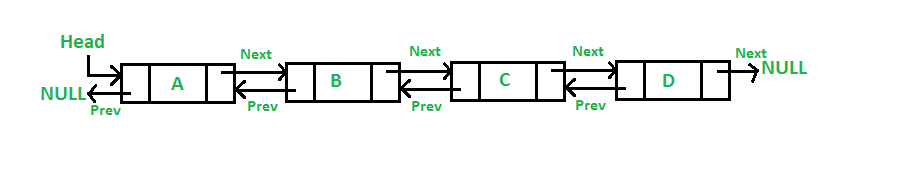
所以一個linked list要有哪些東西?
頭的虛節點
尾巴的虛節點
struct node
int val
next & prev
struct LinkedList
各種method:
begin() end() size() empty()
insert() erase()
看起來好複雜?
學長,我不會寫怎麼辦!?
沒關係,我們已經幫你把架構寫好了!
你只要填空就好!
注意!
填空在2022-11-16-practice分支裡面
答案在2022-11-16-answer分支裡面
不會用github的人可以看main branch裡面的readme.md教學(連結一進去那個頁面就是了)
或是上週小社簡報
把它git clone到你的電腦吧
下課啦~
下週繼續來喔~

別忘記我們的寒訓ㄛ!!!
報名會在二段後開始,敬請期待