Title Text

SQL.
It's so last century, amirite?



'NoSQL'
Web-trending since ~2009

'SQL alternative'
Book-trending since ~1984

Why NoSQL?
The reasons are legion...


Impedance Mismatch
UI
DB
Object Hierarchies
Table Relationships
Differing data representations
on client and server


Clustering
Does this really scale?

Alternative Approaches
Key/Value Pair
Column Family
Document
Graph
Cassandra
Apache HBASE
Oracle Berkley DB
Redis
CouchDB
MongoDB
Firebase
Riak KV
Neo4J
Sqrrl
GraphDB
ScyllaDB
Key/Value Pair
Oracle Berkley DB
Redis
Riak KV

- Value could be any type (string, number, blob, etc.)
- Some support ordering of keys
- Many are in-memory implementations for speed
- Takes up less memory than most other types since relationships are simplest
- More implementations than any other NoSQL approach
Document
CouchDB
MongoDB
Firebase
- Values are either lists of key/value pairs or 'documents'

- Similar to KVP databases
- Documents can be modified whole or in part
- Some implementations support secondary indexing
- Most commonly JSON, eliminating impedance mismatch
Column Family
Cassandra
Apache HBASE
ScyllaDB

- Similar to SQL in use of 'rows'
- Similar to Document DB in that sections can be addressed
- As with most other NoSQL approaches, notion of schema is flexible / dynamic
Graph
Neo4J
Sqrrl
GraphDB
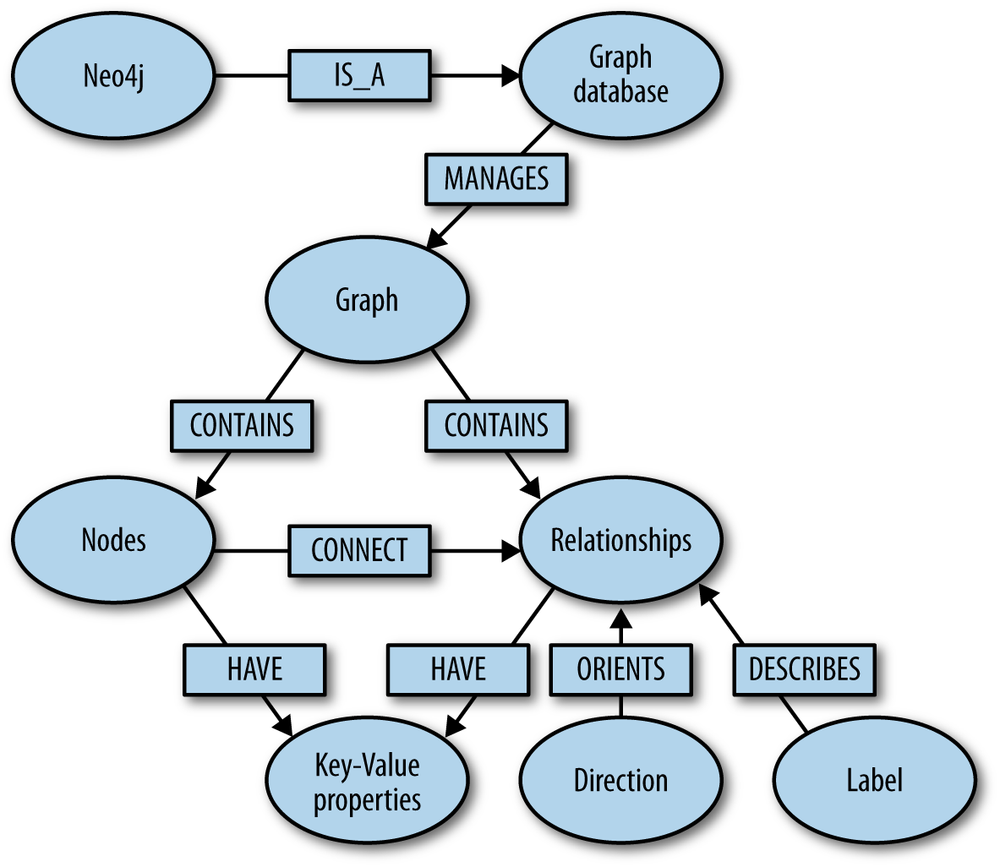
- Radically different from other NoSQL approaches
- Data model is based on nodes and edges rather than aggregation
- While both are 'relational', graph databases are more optimized than SQL for navigating and retrieving data by relationship
ACID
BASE
Atomicity (of updates), Consistency (of state), Isolation (of users from in-progress updates), Durability (of transactions across system failures)
Characteristics of SQL vs NoSQL Systems
Basically Available (data is never 'locked'), Soft state (system can change over time even without input, because of...), Eventually consistent (once input stops)
CAP Theorem
Availability
Consistency
Partition Tolerance
Clients can always read & write
Clients always see same view of data
Clients never affected by partitioning faults / delays
Choose
any
2
SQL / RDBMS
Disk-based KVP DBs
Some Document DBs
In-memory KVP DBs
Some Column DBs
Some Column DBs
Some Document DBs
Some Column DBs
Resources
This Presentation:
http://slides.com/cliffordhall/nosql
Introduction to NoSQL (Martin Fowler)
https://youtu.be/qI_g07C_Q5I
What is a Column Store Database?
http://database.guide/what-is-a-column-store-database/
What is a Graph Database?
https://neo4j.com/developer/graph-database/
What is a Key-Value Store?
https://www.aerospike.com/what-is-a-key-value-store/
What is a Document Database?
https://aws.amazon.com/nosql/document/