Steganografie în fișiere cu tipuri comune
Cosmin Poieană
<cmin@ropython.org>
I. Ce este steganografia
- arta de a ascunde mesaje în mesaje
- steganografie vs. stenografie
- steganaliză
- criptografie
- ascundere fizică (tatuaj, gravură, clipire, micro puncte, vizibilitate temporară, U.V.)
- ascundere software (fișiere audio/video, imagini, documente)
I. Ce este steganografia
- încărcătură (payload)
- transport (carrier)
- pachet (package)
- dimensiuni
- compresie
I. Ce este steganografia
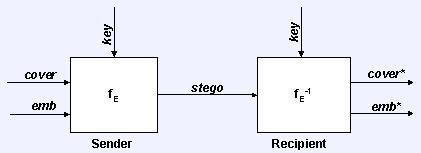
- payload: emb
- carrier: cover
- package: stego
I. Ce este steganografia
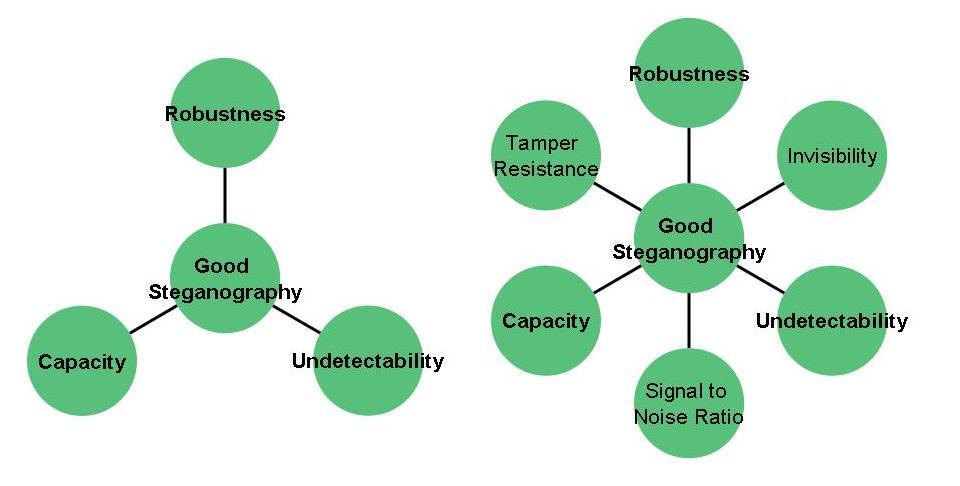
- pierderea mesajului în cazul procesărilor
II. Metode
- folosirea majusculei pentru a marca litere relevante
- scrierea împreunată a cuvintelor de interes
- greșirea în mod intenționat a unor cuvinte
- folosirea unui cifru pentru selectarea literelor/cuvintelor ce ajung să compună mesajul ascuns
II. Metode
- fișiere de interes: doc, bmp, png, pdf, wav etc.
- înțelegerea formatului
- identificarea și exploatarea secțiunilor container
- reprezentarea datelor
- compresie scăzută -> redundanță
II. Metode
II. Metode
LeastSignificantBit
- tipuri deloc/puțin compresate: bmp, png
- header, matrice pixeli
- RGB[A] 24/32bit
- MSB(payload) -> LSB(cover)
II. Metode
LeastSignificantBit
2x2 pixeli
II. Metode
LeastSignificantBit
54 octeti header și paletă + matrice pixeli
II. Metode
LeastSignificantBit
- transformare șir de caractere în șir binar
- alterarea pixelilor
- salvarea noului conținut
- citirea fiecărui LSB
- transformare șir binar în șir de caractere
- afișarea textului extras
- citirea fiecărui LSB
- transformare șir binar în șir de caractere
- afișarea textului extras
II. Metode
LeastSignificantBit
diferențe insesizabile ochiului

II. Metode
Discrete Cosine Transform
- tratamentul fișierelor media
- compresie (jpeg, mp3, mpeg)
- alterarea minoră a coeficienților
- robustețe crescută
II. Metode
Variation of Representation
- fișiere PDF
- header, obiecte, tabelă referințe, trailer
- reprezentare diversă pentru șiruri de caractere și nume de identificatori
- actualizarea tabelei de referințe cu valori de deplasament valide
II. Metode
Variation of Representation

II. Metode
Variation of Representation
PDF content example
%PDF-1.7
1 0 obj % entry point
<<
/Type /Catalog
/Pages 2 0 R
>>
endobj
2 0 obj
<<
/Type /Pages
/MediaBox [ 0 0 200 200 ]
/Count 1
/Kids [ 3 0 R ]
>>
endobj
3 0 obj
<<
/Type /Page
/Parent 2 0 R
/Resources <<
/Font <<
/F1 4 0 R
>>
>>
/Contents 5 0 R
>>
endobj
4 0 obj
<<
/Type /Font
/Subtype /Type1
/BaseFont /Times-Roman
>>
endobj
5 0 obj % page content
<<
/Length 44
>>
stream
BT
70 50 TD
/F1 12 Tf
(Hello, world!) Tj
ET
endstream
endobj
xref
0 6
0000000000 65535 f
0000000010 00000 n
0000000079 00000 n
0000000173 00000 n
0000000301 00000 n
0000000380 00000 n
trailer
<<
/Size 6
/Root 1 0 R
>>
startxref
492
%%EOF
%PDF-1.7
1 0 obj % entry point
<<
/Type /Catalog
/Pages 2 0 R
>>
endobj
2 0 obj
<<
/Type /Pages
/MediaBox [ 0 0 200 200 ]
/Count 1
/Kids [ 3 0 R ]
>>
endobj
3 0 obj
<<
/Type /Page
/Parent 2 0 R
/Resources <<
/Font <<
/F1 4 0 R
>>
>>
/Contents 5 0 R
>>
endobj
4 0 obj
<<
/Type /Font
/Subtype /Type1
/BaseFont /Times-Roman
>>
endobj
5 0 obj % page content
<<
/Length 44
>>
stream
BT
70 50 TD
/F1 12 Tf
(Hello, world!) Tj
ET
endstream
endobj
xref
0 6
0000000000 65535 f
0000000010 00000 n
0000000079 00000 n
0000000173 00000 n
0000000301 00000 n
0000000380 00000 n
trailer
<<
/Size 6
/Root 1 0 R
>>
startxref
492
%%EOF
II. Metode
Variation of Representation
-
șiruri de caractere: (Hello, world!)
-
reprezentare octală: (He\154\154o, world!)
-
hexazecimal: <48656c6c6f2c20776f726c6421>
- existența a două tipuri de reprezentări
- număr variabil de spații
II. Metode
Variation of Representation
-
nume de identificatori: /Root
-
reprezentare hexazecimală: /Roo#74
- nu se permit alte forme sau spații
II. Metode
Variation of Representation
%PDF-1.7
1 0 obj % entry point
<<
/Type /Catalog
/Pages 2 0 R
>>
endobj
2 0 obj
<<
/Type /Pages
/MediaBox [ 0 0 200 200 ]
/Count 1
/Kids [ 3 0 R ]
>>
endobj
3 0 obj
<<
/Type /Page
/Parent 2 0 R
/Resources <<
/Font <<
/F1 4 0 R
>>
>>
/Contents 5 0 R
>>
endobj
4 0 obj
<<
/Typ#65 /Font
/Subtype /Type1
/BaseFont /Times-Roman
>>
endobj
5 0 obj % page content
<<
/L#65ngth 44
>>
stream
BT
70 50 TD
/F1 12 Tf
(Hello, world!) Tj
ET
endstream
endobj
xref
0 6
0000000000 65535 f
0000000010 00000 n
0000000079 00000 n
0000000173 00000 n
0000000301 00000 n
0000000382 00000 n
trailer
<<
/Size 6
/Root 1 0 R
>>
startxref
496
%%EOF
%PDF-1.7
1 0 obj % entry point
<<
/Type /Catalog
/Pages 2 0 R
>>
endobj
2 0 obj
<<
/Type /Pages
/MediaBox [ 0 0 200 200 ]
/Count 1
/Kids [ 3 0 R ]
>>
endobj
3 0 obj
<<
/Type /Page
/Parent 2 0 R
/Resources <<
/Font <<
/F1 4 0 R
>>
>>
/Contents 5 0 R
>>
endobj
4 0 obj
<<
/Typ#65 /Font
/Subtype /Type1
/BaseFont /Times-Roman
>>
endobj
5 0 obj % page content
<<
/L#65ngth 44
>>
stream
BT
70 50 TD
/F1 12 Tf
(Hello, world!) Tj
ET
endstream
endobj
xref
0 6
0000000000 65535 f
0000000010 00000 n
0000000079 00000 n
0000000173 00000 n
0000000301 00000 n
0000000382 00000 n
trailer
<<
/Size 6
/Root 1 0 R
>>
startxref
496
%%EOFII. Metode
- acoperirea întregului spațiu disponibil
- dispersia biților
- date aleatoare
- cheie steganografică
- generator pseudo-aleator
- încorporare pachet în alte fișiere
III. Modificare, validare și recuperare
- analiza în detaliu a structurii carrier-ului
- transformarea până la nivel de bit a datelor ce se doresc a fi ascunse
- modificarea efectivă a conținutului
- păstrarea integrității structurii
- afișarea (aproape) identică a vechiului conținut
III. Modificare, validare și recuperare
Script naiv ce aplică metoda LSB
#! /usr/bin/env python3
# 05.04.2010 <> 06.04.2010 | cmiN
# Text In Bmp (console)
import sys
from hashlib import md5
class Image:
def load(self, path):
with open(path, "rb") as file:
buffer = file.read()
self.bfType = buffer[0:2]
if self.bfType != b"BM":
raise Exception("not a bitmap")
self.bfSize = buffer[2:6]
self.bfReserved1 = buffer[6:8]
self.bfReserved2 = buffer[8:10]
self.bfOffBits = buffer[10:14]
self.biSize = buffer[14:18]
self.biWidth = buffer[18:22]
self.biHeight = buffer[22:26]
self.biPlanes = buffer[26:28]
self.biBitCount = buffer[28:30]
if baconvert(self.biBitCount) != 24:
raise Exception("not 24-bit")
self.biCompression = buffer[30:34]
self.biSizeImage = buffer[34:38]
self.biXPelsPerMeter = buffer[38:42]
self.biYPelsPerMeter = buffer[42:46]
self.biClrUsed = buffer[46:50]
self.biClrImportant = buffer[50:54]
self.bHeader = buffer[:54]
self.bMatrix = list(buffer[54:])
def create(self, path, buffer):
with open(path, "wb") as file:
file.write(buffer)
def process(digsig, mode, infile, outfile=None, string=None):
bmp = Image()
bmp.load(infile)
bmp.width = baconvert(bmp.biWidth)
bmp.height = baconvert(bmp.biHeight)
bmp.index = 0
bmp.count = 0
rem = (bmp.width * 3) % 4
if rem:
bmp.padding = 4 - rem
else:
bmp.padding = 0
if mode == "write":
bits = str()
for char in md5(bytes(digsig, "ascii")).digest():
bits += bin(char).replace("0b", "").zfill(8)
bits += bin(len(string)).replace("0b", "").zfill(16)
for char in string:
bits += bin(ord(char)).replace("0b", "").zfill(8)
if len(bits) > bmp.width * bmp.height * 3:
raise Exception("string too long")
for bit in bits:
char = bin(bmp.bMatrix[bmp.index])
char = int(char[:-1] + bit, 2)
bmp.bMatrix[bmp.index] = char
bmp.index += 1
bmp.count += 1
if bmp.count == (bmp.width * 3):
bmp.count = 0
bmp.index += bmp.padding
bmp.create(outfile, bmp.bHeader + bytes(bmp.bMatrix))
elif mode == "read":
bits = bitjoin(bmp, 128)
if bytes([int(bits[i:i + 8], 2) for i in range(0, 128, 8)]) == md5(bytes(digsig, "ascii")).digest():
nr = int(bitjoin(bmp, 16), 2) * 8
bits = bitjoin(bmp, nr)
string = "".join([chr(int(bits[i:i + 8], 2)) for i in range(0, nr, 8)])
print(string)
else:
raise Exception("invalid signature")
else:
raise Exception("invalid mode")
def bitjoin(bmp, nr):
bits = str()
for i in range(nr):
bits += bin(bmp.bMatrix[bmp.index])[-1]
bmp.index += 1
bmp.count += 1
if bmp.count == (bmp.width * 3):
bmp.count = 0
bmp.index += bmp.padding
return bits
def baconvert(buffer):
return int("".join([hex(char).replace("0x", "").zfill(2) for char in reversed(buffer)]), 16)
def main(args):
usage = """\t\t Text In Bmp 1.0
\t Usage: source.ext digsig mode infile [outfile text]
Where digsig is a digital signature string
mode can be write or read
infile is a valid 24-bit bitmap image
outfile is the output image name (used with write mode)
text is the string that will be written in image (used with write mode)
\t Example: tib.py cmiN write image1.bmp image2.bmp http://rstcenter.com
\t tib.py cmiN read image2.bmp"""
try:
print("Please wait...")
if len(args) == 4:
process(args[1], args[2], args[3])
elif len(args) == 6:
process(args[1], args[2], args[3], args[4], args[5])
else:
print(usage)
except Exception as message:
print("An error occurred: {}".format(message))
except:
print("Unknown error.")
else:
print("Ready!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(sys.argv)
#! /usr/bin/env python3
# 05.04.2010 <> 06.04.2010 | cmiN
# Text In Bmp (console)
import sys
from hashlib import md5
class Image:
def load(self, path):
with open(path, "rb") as file:
buffer = file.read()
self.bfType = buffer[0:2]
if self.bfType != b"BM":
raise Exception("not a bitmap")
self.bfSize = buffer[2:6]
self.bfReserved1 = buffer[6:8]
self.bfReserved2 = buffer[8:10]
self.bfOffBits = buffer[10:14]
self.biSize = buffer[14:18]
self.biWidth = buffer[18:22]
self.biHeight = buffer[22:26]
self.biPlanes = buffer[26:28]
self.biBitCount = buffer[28:30]
if baconvert(self.biBitCount) != 24:
raise Exception("not 24-bit")
self.biCompression = buffer[30:34]
self.biSizeImage = buffer[34:38]
self.biXPelsPerMeter = buffer[38:42]
self.biYPelsPerMeter = buffer[42:46]
self.biClrUsed = buffer[46:50]
self.biClrImportant = buffer[50:54]
self.bHeader = buffer[:54]
self.bMatrix = list(buffer[54:])
def create(self, path, buffer):
with open(path, "wb") as file:
file.write(buffer)
def process(digsig, mode, infile, outfile=None, string=None):
bmp = Image()
bmp.load(infile)
bmp.width = baconvert(bmp.biWidth)
bmp.height = baconvert(bmp.biHeight)
bmp.index = 0
bmp.count = 0
rem = (bmp.width * 3) % 4
if rem:
bmp.padding = 4 - rem
else:
bmp.padding = 0
if mode == "write":
bits = str()
for char in md5(bytes(digsig, "ascii")).digest():
bits += bin(char).replace("0b", "").zfill(8)
bits += bin(len(string)).replace("0b", "").zfill(16)
for char in string:
bits += bin(ord(char)).replace("0b", "").zfill(8)
if len(bits) > bmp.width * bmp.height * 3:
raise Exception("string too long")
for bit in bits:
char = bin(bmp.bMatrix[bmp.index])
char = int(char[:-1] + bit, 2)
bmp.bMatrix[bmp.index] = char
bmp.index += 1
bmp.count += 1
if bmp.count == (bmp.width * 3):
bmp.count = 0
bmp.index += bmp.padding
bmp.create(outfile, bmp.bHeader + bytes(bmp.bMatrix))
elif mode == "read":
bits = bitjoin(bmp, 128)
if bytes([int(bits[i:i + 8], 2) for i in range(0, 128, 8)]) == md5(bytes(digsig, "ascii")).digest():
nr = int(bitjoin(bmp, 16), 2) * 8
bits = bitjoin(bmp, nr)
string = "".join([chr(int(bits[i:i + 8], 2)) for i in range(0, nr, 8)])
print(string)
else:
raise Exception("invalid signature")
else:
raise Exception("invalid mode")
def bitjoin(bmp, nr):
bits = str()
for i in range(nr):
bits += bin(bmp.bMatrix[bmp.index])[-1]
bmp.index += 1
bmp.count += 1
if bmp.count == (bmp.width * 3):
bmp.count = 0
bmp.index += bmp.padding
return bits
def baconvert(buffer):
return int("".join([hex(char).replace("0x", "").zfill(2) for char in reversed(buffer)]), 16)
def main(args):
usage = """\t\t Text In Bmp 1.0
\t Usage: source.ext digsig mode infile [outfile text]
Where digsig is a digital signature string
mode can be write or read
infile is a valid 24-bit bitmap image
outfile is the output image name (used with write mode)
text is the string that will be written in image (used with write mode)
\t Example: tib.py cmiN write image1.bmp image2.bmp http://rstcenter.com
\t tib.py cmiN read image2.bmp"""
try:
print("Please wait...")
if len(args) == 4:
process(args[1], args[2], args[3])
elif len(args) == 6:
process(args[1], args[2], args[3], args[4], args[5])
else:
print(usage)
except Exception as message:
print("An error occurred: {}".format(message))
except:
print("Unknown error.")
else:
print("Ready!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(sys.argv)III. Modificare, validare și recuperare
Rularea comenzilor de scriere și respectiv citire
$ ./tib.py sparks2014 write pylogo.bmp out.bmp "Hello, world!"
Please wait...
Ready!
$ ./tib.py sparks2014 read out.bmp
Please wait...
Hello, world!
Ready!
$ ./tib.py sparks2013 read out.bmp
Please wait...
An error occurred: invalid signature
III. Modificare, validare și recuperare
Diferența între original și package


III. Modificare, validare și recuperare
Diferența între original și package
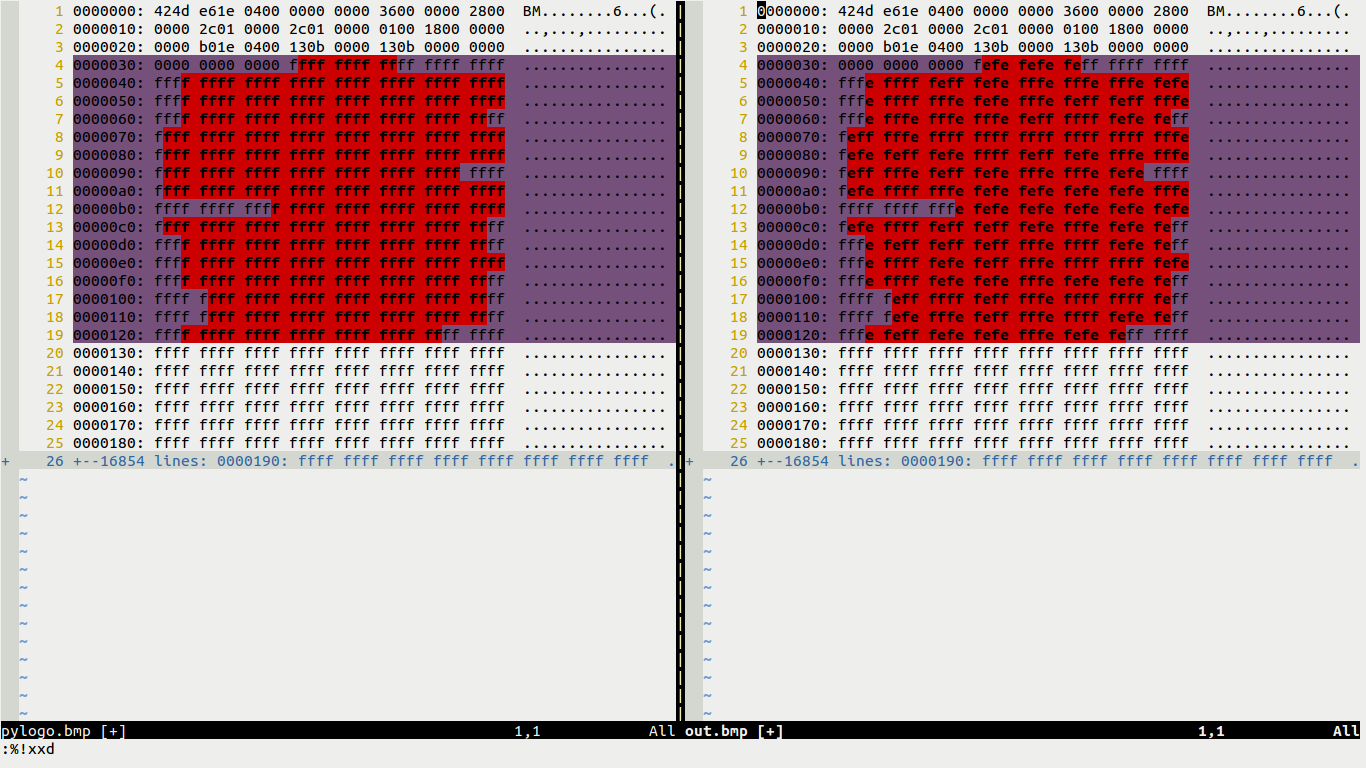
III. Modificare, validare și recuperare
Diferența între original și package

III. Modificare, validare și recuperare
Un exemplu mai complex
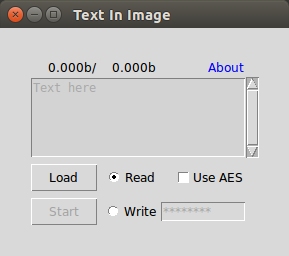

III. Modificare, validare și recuperare
Un exemplu mai complex
#! /usr/bin/env python
# Text In Image
# 02.01.2012 cmiN
#
# This is a simple GUI script which can hide text in pictures
# using least significant bit method.
# Also the input text can be encrypted and the output can be decrypted too
# with a symmetric key using AES.
# Writing is done directly on input image so be careful with certain extensions
# because the output will always have the BMP format.
#
# Contact: cmin764@yahoo/gmail.com
import os
from Tkinter import * # widgets's classes
from tkFileDialog import askopenfilename # get file name
from tkMessageBox import showerror, showinfo # user dialog
from PIL import Image # image converting
from Crypto.Cipher import AES # text cipher
class Engine:
"""
Code for processing the image.
Separated from GUI.
"""
def __init__(self):
""" Initialize parameters. """
self.ext = "bmp" # save format
self.name = None # save name
self.path = None # save path
self.im = None # image object, read and write
self.generator = None # get locations to write/read bits
self.useAES = None # use it or not
self.aes = None # AES object
self.data = None # data to be written to image
self.width = None # image width
self.height = None # image height
self.tmp = None # last string, used when key changes
def binary(self, nr, size):
""" Get 1&0 representation. """
return bin(nr).replace("0b", "").zfill(size * 8)
def path_name(self, path):
""" Split a file path in path and name. """
ind = path.rfind("/") + 1
return (path[:ind], path[ind:])
def set_generator(self):
""" Useful for resetting. """
self.generator = ((wp, hp, ch) for wp in xrange(self.width) # WxHxC
for hp in xrange(self.height)
for ch in xrange(3))
def load(self, path):
""" Load image. """
self.im = Image.open(path)
(self.width, self.height) = self.im.size
(self.path, self.name) = self.path_name(path)
return self.width * self.height * 3 # total useful bytes
def parse_key(self, key):
""" If key exists make an AES object from it. """
if not key:
self.aes = None # empty key == no encryption
return self.parse_string(self.tmp) # must return size (see the next return)
key.decode() # test availability
size = len(key)
for padding in (16, 24, 32): # fixed key size
if size <= padding:
break
key += chr(0) * (padding - size)
self.aes = AES.new(key)
return self.parse_string(self.tmp) # if key changes you must update string
def parse_string(self, string):
""" Convert to bitstring. """
if not string: # without string can't start the process
self.tmp = None
self.data = None
return 0
string.decode() # test availability
self.tmp = string
if self.useAES and self.aes: # encrypt it
string += chr(0) * ((16 - len(string) % 16) % 16) # multiple of 16 string
string = self.aes.encrypt(string)
string = str().join([self.binary(ord(x), 1) for x in string]) # convert every char in a set of 8 bits
size = self.binary(len(string), 4) # get binary representation of string's length in 4 bytes
self.data = size + string
return len(self.data)
def write(self):
""" Write using LSB. """
self.set_generator() # rearm
for bit in self.data:
(wp, hp, ch) = self.generator.next() # get next position
values = list(self.im.getpixel((wp, hp))) # retrieve its values
tmp = self.binary(values[ch], 1) # convert one of them
values[ch] = int(tmp[:7] + bit, 2) # alter that channel
self.im.putpixel((wp, hp), tuple(values)) # put it back
self.im.save(self.path + self.name, format=self.ext) # save the new output
def read(self):
""" Read from every LSB. """
self.set_generator() # rearm
total = self.width * self.height * 3
if total < 32:
raise Exception("Text not found.")
size = chunk = string = str()
i = 0 # for(i=0; true; ++i)
while True:
(wp, hp, ch) = self.generator.next() # i byte
values = self.im.getpixel((wp, hp))
tmp = self.binary(values[ch], 1)
if i < 32: # it's lame but I prefer string/bitset
size += tmp[7]
if i == 31:
size = int(size, 2)
if size < 1 or (size + 32) > total:
raise Exception("Text not found.")
elif i < size + 32:
chunk += tmp[7]
if len(chunk) == 8:
string += chr(int(chunk, 2))
chunk = str()
else:
break
i += 1
if self.useAES and self.aes:
if len(string) % 16 != 0:
raise Exception("Text not encrypted.")
string = self.aes.decrypt(string).rstrip(chr(0))
string.decode() # rise an exception if invalid
return string
class GUI(Frame):
"""
Main window, inherited from Frame.
Here we put our widgets and set their behavior.
"""
def __init__(self, master=None, margin=30):
""" Same as Frame's constructor. """
Frame.__init__(self, master, padx=margin, pady=margin)
self.grid()
self.widgets()
self.behavior()
def widgets(self):
""" Build and grid widgets. """
# ---- create variables ----
self.totalBytes = IntVar() # depends on image size
self.usedBytes = IntVar() # how many of them are used
self.textStatus = StringVar() # used per total bytes
self.useEncryption = IntVar() # 0-plain 1-AES
self.mode = IntVar() # 0-read 1-write
self.textOpt = dict() # text last config
self.keyOpt = dict() # key last config
self.loaded = False # image loaded or not
# ---- create widgets ----
self.label = Label(self, textvariable=self.textStatus)
self.about = Label(self, text="About", fg="blue")
self.text = Text(self, width=30, height=5, fg="grey")
self.scrollbar = Scrollbar(self, orient="vertical", command=self.text.yview)
self.loadButton = Button(self, text="Load", width=5, command=lambda: self.action("load"))
self.readRadio = Radiobutton(self, text="Read", variable=self.mode, value=0, command=self.set_state)
self.checkButton = Checkbutton(self, text="Use AES", variable=self.useEncryption, onvalue=1, offvalue=0, command=self.set_state)
self.startButton = Button(self, text="Start", width=5, state="disabled", command=lambda: self.action("start"))
self.writeRadio = Radiobutton(self, text="Write", variable=self.mode, value=1, command=self.set_state)
self.keyEntry = Entry(self, width=10, fg="grey", show="*")
# ---- show widgets ----
self.label.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=2, sticky="w")
self.about.grid(row=0, column=2, sticky="e")
self.text.grid(row=1, column=0, rowspan=3, columnspan=3)
self.scrollbar.grid(row=1, column=3, rowspan=3, sticky="ns")
self.loadButton.grid(row=4, column=0, sticky="w", pady=5)
self.readRadio.grid(row=4, column=1)
self.checkButton.grid(row=4, column=2, sticky="e")
self.startButton.grid(row=5, column=0, sticky="w")
self.writeRadio.grid(row=5, column=1)
self.keyEntry.grid(row=5, column=2, sticky="e")
def behavior(self):
""" Customize widgets. """
self.text.config(yscrollcommand=self.scrollbar.set)
self.text.insert(0.0, "Text here")
self.keyEntry.insert(0, "Key here")
self.text.bind("<Button>", self.handle_event)
self.text.bind("<KeyRelease>", self.handle_event)
self.keyEntry.bind("<Button>", self.handle_event)
self.keyEntry.bind("<KeyRelease>", self.handle_event)
self.textOpt = self.get_opt(self.text)
self.keyOpt = self.get_opt(self.keyEntry)
self.about.bind("<Button>", self.handle_event)
self.set_state()
def action(self, arg):
""" What every button triggers. """
if arg == "load":
fileTypes = [("BMP", "*.bmp"), ("JPEG", ("*.jpeg", "*.jpg")), ("PNG", "*.png"), ("All Files", "*.*")]
path = askopenfilename(parent=self, title="Open image", filetypes=fileTypes)
if path != "":
try:
self.totalBytes.set(app.load(path))
except IOError as msg:
showerror("Error", str(msg).capitalize().strip(".") + ".") # some formatting
else:
self.loaded = True
self.set_state()
self.master.title("Text In Image - %s" % app.name) # update name in title
elif arg == "start":
if self.mode.get():
try:
app.write()
except Exception as msg:
showerror("Error", str(msg).capitalize().strip(".") + ".")
else:
showinfo("Info", "Done.")
else:
try:
string = app.read()
except UnicodeError:
showerror("Error", "Text not found or wrong key.")
except Exception as msg:
showerror("Error", str(msg).capitalize().strip(".") + ".")
else:
self.text.config(state="normal")
self.textOpt["fg"] = "black" # touched
self.text.delete(0.0, END)
self.text.insert(0.0, string)
self.text.config(state="disabled")
self.usedBytes.set(app.parse_string(string))
self.set_status()
showinfo("Info", "Done.")
def set_status(self):
""" Get used per total bytes. """
string = "%9.3f%s/%9.3f%s"
unit1 = unit2 = "b"
used = self.usedBytes.get()
total = self.totalBytes.get()
if used > total:
self.label.config(fg="red")
else:
self.label.config(fg="black")
if used > 999999:
unit1 = "Mb"
used /= 1000000.0
elif used > 999:
unit1 = "Kb"
used /= 1000.0
if total > 999999:
unit2 = "Mb"
total /= 1000000.0
elif total > 999:
unit2 = "Kb"
total /= 1000.0
self.textStatus.set(string % (used, unit1, total, unit2))
def get_opt(self, widget):
""" Get some options from a widget then pack them. """
opt = dict()
opt["state"] = widget["state"]
opt["fg"] = widget["fg"]
opt["bg"] = widget["bg"]
return opt
def set_state(self):
""" Enable or disable a widget according to option selected. """
if self.mode.get(): # write
self.text.config(**self.textOpt)
else:
self.text.config(state="disabled", bg="lightgrey", fg="darkgrey")
if self.useEncryption.get(): # use AES
self.keyEntry.config(**self.keyOpt)
app.useAES = True
else:
self.keyEntry.config(state="disabled")
app.useAES = False
length = app.parse_string(app.tmp)
self.usedBytes.set(length)
self.set_status()
if self.loaded: # a file is loaded
if self.mode.get() == 0: # read mode
ok = True
elif app.data != None and self.usedBytes.get() <= self.totalBytes.get():
ok = True
else:
ok = False
else:
ok = False # no file loaded
if ok:
self.startButton.config(state="normal")
else:
self.startButton.config(state="disabled")
def handle_event(self, event):
""" Handle events for specific widgets. """
if event.widget is self.text and self.text["state"] == "normal":
if self.text["fg"] == "grey":
self.text.delete(0.0, END)
self.textOpt["fg"] = self.text["fg"] = "black"
string = self.text.get(0.0, END).strip()
try:
length = app.parse_string(string)
except UnicodeError:
showerror("Error", "Invalid text.")
else:
self.usedBytes.set(length)
self.set_state()
elif event.widget is self.keyEntry and self.keyEntry["state"] == "normal":
if self.keyEntry["fg"] == "grey":
self.keyEntry.delete(0, END)
self.keyOpt["fg"] = self.keyEntry["fg"] = "black"
key = self.keyEntry.get()[:32] # first 32 (max size is 32)
try:
length = app.parse_key(key)
except UnicodeError:
showerror("Error", "Invalid key.")
else:
self.usedBytes.set(length)
self.set_state()
elif event.widget is self.about:
showinfo("About", "Hide text, which can be encrypted with AES, in pictures (bitmaps). Coded by cmiN. Visit rstforums.com.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = Engine() # core
root = Tk() # toplevel
root.title("Text In Image")
root.maxsize(350, 250)
icon = "tii.ico"
if os.path.isfile(icon):
root.iconbitmap(icon)
GUI(root)
root.mainloop()III. Modificare, validare și recuperare
Un exemplu mai complex
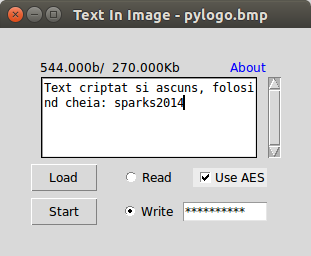

III. Modificare, validare și recuperare
Un exemplu mai complex
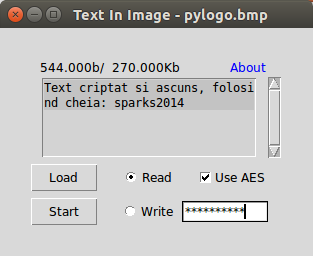

III. Modificare, validare și recuperare
- "steganoception"
- LSB2 (tradițional LSB1)
- creare obiecte dezactivate
IV. Criptare și eclipsare
- extra, dar combinație bună
- tehnica chaffing and winnowing
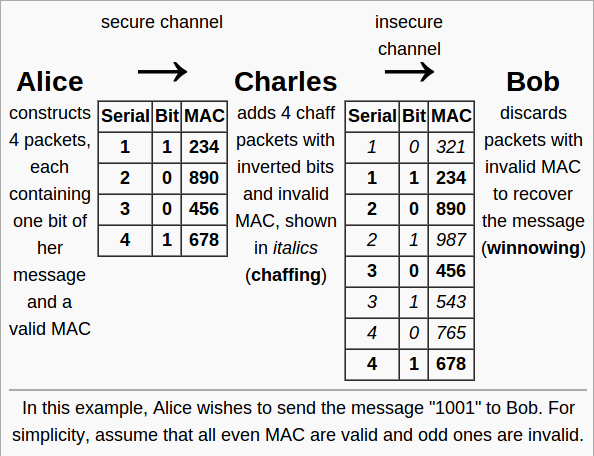
V. Steganaliză
- comparația cu originalul
- indetificarea datelor "straine" sau redundante
- examinarea paletelor de culori
- distingerea anomaliilor
- distrugerea mesajului
VI. Steganografia în practică
- comunicare
- watermarking
- scopuri (i)legale
- cicada 3301
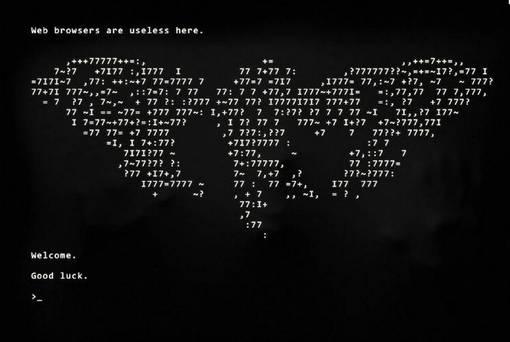
VI. Steganografia în practică
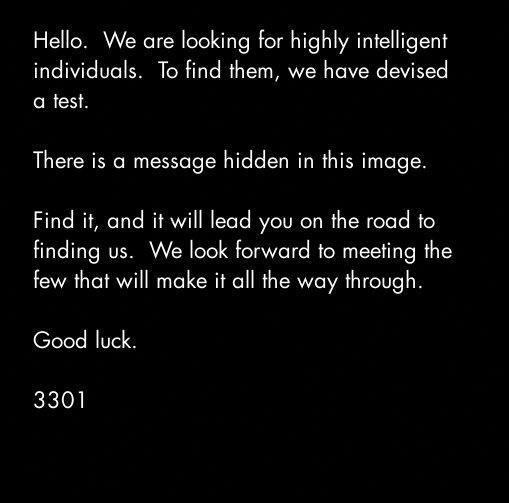
VI. Steganografia în practică

Bibliografie
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steganography
- http://arxiv.org/pdf/0912.2319.pdf
- http://arxiv.org/pdf/1111.3758.pdf
- http://www.cse.wustl.edu/~jain/cse571-09/ftp/stegano/
- http://www.gnupdf.org/Introduction_to_PDF
- http://blog.didierstevens.com/2008/04/29/pdf-let-me-count-the-ways/
Întrebări?
http://ropython.org